基于边界检测和骨骼提取的显著性检测网络
杨爱萍,程思萌,王金斌,宋尚阳,丁学文
基于边界检测和骨骼提取的显著性检测网络
杨爱萍1,程思萌1,王金斌1,宋尚阳1,丁学文2
(1. 天津大学电气自动化与信息工程学院,天津 300072;2. 天津职业技术师范大学电子工程学院,天津 300222)
目前一些方法通过多任务联合实现显著性检测,在一定程度上提升了检测精度,但仍存在误检和漏检问题,其原因在于各任务优化目标不同且特征域差异较大,导致网络对显著性、物体边界等特征辨识能力不足.基于此,借助边界检测和骨骼提取提出一种多任务辅助的显著性检测网络,其包括特征提取子网络、边界检测子网络、骨骼提取子网络以及显著性填充子网络.其中,特征提取子网络利用ResNet101预训练模型提取图像的多尺度特征;边界检测子网络选择前3层特征进行融合,可完整保留显著性目标的边界信息;骨骼提取子网络选择后两层特征进行融合,可准确定位显著性目标的中心位置;所提方法基于边界检测数据集和骨骼提取数据集分别对两个子网络进行训练,保留最好的边界检测模型和骨骼提取模型,作为预训练模型辅助显著性检测任务.为降低网络优化目标与特征域之间的差异,设计了显著性填充子网络将提取的边界特征和骨骼特征进行融合和非线性映射.在4种数据集上的实验结果表明,所提方法能有效恢复缺失的显著性区域,优于其他显著性目标检测方法.
边界检测;骨骼提取;多任务;显著性检测网络
显著性检测可通过计算机模拟人类视觉系统,快速分析输入图像并保留最引人注意的区域.广泛应用在图像检索[1]、目标检测[2]、行为识别[3]、图像分 割[4]和目标识别[5]等计算机视觉任务.
现有显著性检测方法主要采用“主体检测为主,边界细化为辅”的思想,通过不同任务分别检测显著性目标区域和显著性目标边界.根据边界检测方式可分为基于单数据集的多任务检测网络和基于多数据集的多任务检测网络.
基于单数据集的多任务检测网络一般设计两个并行网络分别检测显著性目标区域和显著性目标边界,两个网络均使用DUTS数据集[6]进行监督学习.Wei等[7]通过数学运算将输入图像分解为边界图和目标区域图,并设计两个子网络分别学习.Song 等[8]提出一种多层次边界细化的显著性检测网络,先获得粗糙的显著性预测图,后对显著性边界进行细化.该类方法由于利用边界检测算子在计算过程中存在误差,导致提取的边界不完整.因此,一些学者使用多个数据集对网络进行监督训练来提升显著性判别能力和边界提取能力.Wu等[9]采用边界检测和显著性检测多任务联合训练方式,提升网络的特征提取能力;然而该方法没有考虑多个检测任务之间的协作问题,导致提取的目标区域和边界特征不完整.在此基础上,Liu等[10]增加了骨架检测任务,通过对3个任务联合训练,提升网络边界检测能力和中心定位能力.该方法使用权重共享策略交换多任务信息,忽略了不同检测任务之间的差异,导致预测图不完整.
由以上分析可知,目前多任务检测方法大都通过特征堆叠或权重共享等方式交换信息,而未考虑不同任务之间特征域差异性,导致特征提取不完整.与现有方法不同,本文采用“分治”思想,提出了一种基于多数据集多任务辅助的显著性检测网络.具体地,通过对边界检测任务和骨骼提取任务独立训练,保留最优的边界检测模型和骨骼提取模型,并将它们作为预训练模型辅助显著性目标检测任务,分别提取边界特征和骨骼特征来准确定位显著性目标的边界位置和中心位置,缓解因不同任务目标之间特征域的差异性导致的特征提取不完整问题.最后,将提取的边界特征和骨骼特征进行融合和非线性映射得到完整的显著性图.
1 本文方法
本文提出了一种基于多任务辅助的显著性检测网络,其整体结构如图1所示.该网络由特征提取子网络、边界检测子网络、骨骼提取子网络和显著性填充子网络组成.其中,特征提取子网络用于提取输入图像的多尺度特征,由5个残差卷积块级联而成,可表示为RB1-RB5.边界检测子网络通过前3层卷积RB1、RB2、RB3提取显著性目标的轮廓,得到边界信息;骨骼提取子网络利用后两层卷积RB4、RB5提取显著性目标的骨骼,定位中心位置;为了提升网络的辨识能力,利用金字塔卷积模块增大特征的感受野,并设计特征增强模块对特征进行自适应加权.最后,显著性填充子网络根据显著性目标的边界信息和中心位置进行填充,得到显著性预测图.

图1 网络整体结构
1.1 特征提取子网络
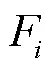
1.1.1 金字塔卷积模块
为了增强网络的全局感知能力,受金字塔网络结构[12-13]启发,本文设计了金字塔卷积模块,将多种感受野下的特征进行融合.金字塔卷积模块结构如图2所示.

图2 金字塔卷积模块结构
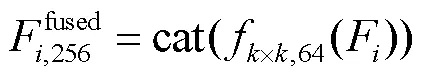
1.1.2 特征增强模块
为提升特征表达能力,筛选有用特征、抑制无用特征,设计了特征增强模块,利用通道注意力机制[14]和空间注意力机制[15],从通道维度和空间维度对特征进行筛选和增强,特征增强模块结构如图3所示.

图3 特征增强模块


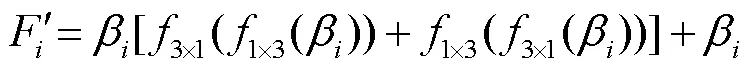
1.2 边界检测子网络


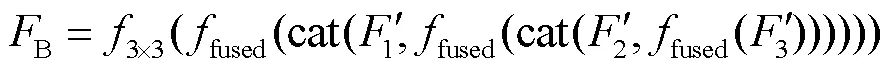
1.3 骨骼提取子网络
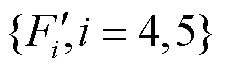

1.4 显著性填充子网络


1.5 损失函数
分阶段对不同任务进行监督学习.第1阶段为边界检测任务,选择二进制交叉熵函数[16]作为损失函数,即
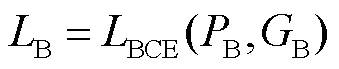
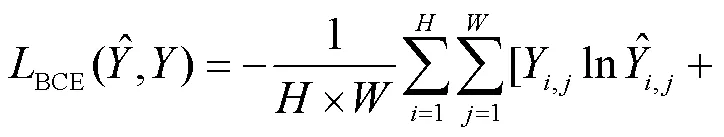

第2阶段为骨骼提取任务,其损失函数为

第3阶段为显著性目标检测任务,其损失函数为


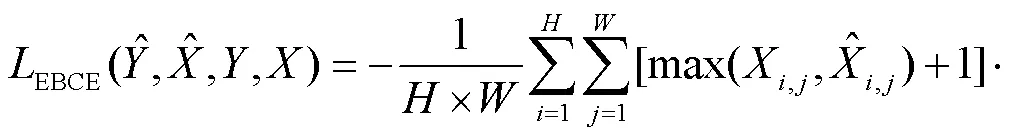

2 实验与结果分析
2.1 实验设置
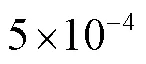
选择BSDS500[17]数据集作为边界检测任务的训练集,该数据集包含200张图像,每张图像对应3~4张真值图,随机选取一张用于网络训练;选择SK-LARGE[18]数据集为骨骼提取任务的训练集,包含746张图像;选择DUTS-TR[6]数据集为显著性检测任务的训练集,包含10553张图像;DUTS-TE[6]、ECSSD[19]、HKU-IS[20]和PASCAL-S[21]作为测试集.
2.2 对比实验
为了验证本文方法的有效性,从客观指标和主观效果两方面与现有显著性目标检测方法进行对比,对比方法包括PAGR[22]、PiCANet[23]、MLM[9]、ICNet[24]、BASNet[25]、AFNet[26]、PAGE[27]、CPD[28]、ITSD[29]、CANet[30]、CAGNet[31]、HERNet[8]、AMPNet[32].



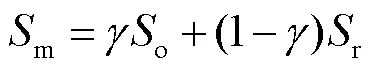

图4为主观效果对比结果.选取了一些代表性场景图像,如复杂场景的显著性目标(第1行)、前景和背景相似的显著性目标(第2行)、小型显著性目标(第3行)、规则显著性目标(第4行)、被遮挡的显著性目标(第5行)、多个显著性目标(第6行).可以看出,所提方法取得了理想的检测结果,尤其在小型显著目标图像中,大部分方法漏检了远处的鸭子(第3行);在显著目标被覆盖和复杂场景图像中,多数方法均存在误检问题,将狗上方的黄色字母(第1行)和覆盖在鸟身上的叶子(第5行)判定为显著目标;在长条状显著目标图像中,本文方法得到了更精确的显著目标边界.由图4可以看出,本文方法在多个场景下,主观效果都优于其他多任务联合方法(MLM[9]).由此可以得知,本文提出的基于边界检测和骨骼提取的多任务辅助方法能有效恢复缺失的显著性区域,解决检测结果不完整的问题.
表1 不同显著性目标检测方法的客观指标
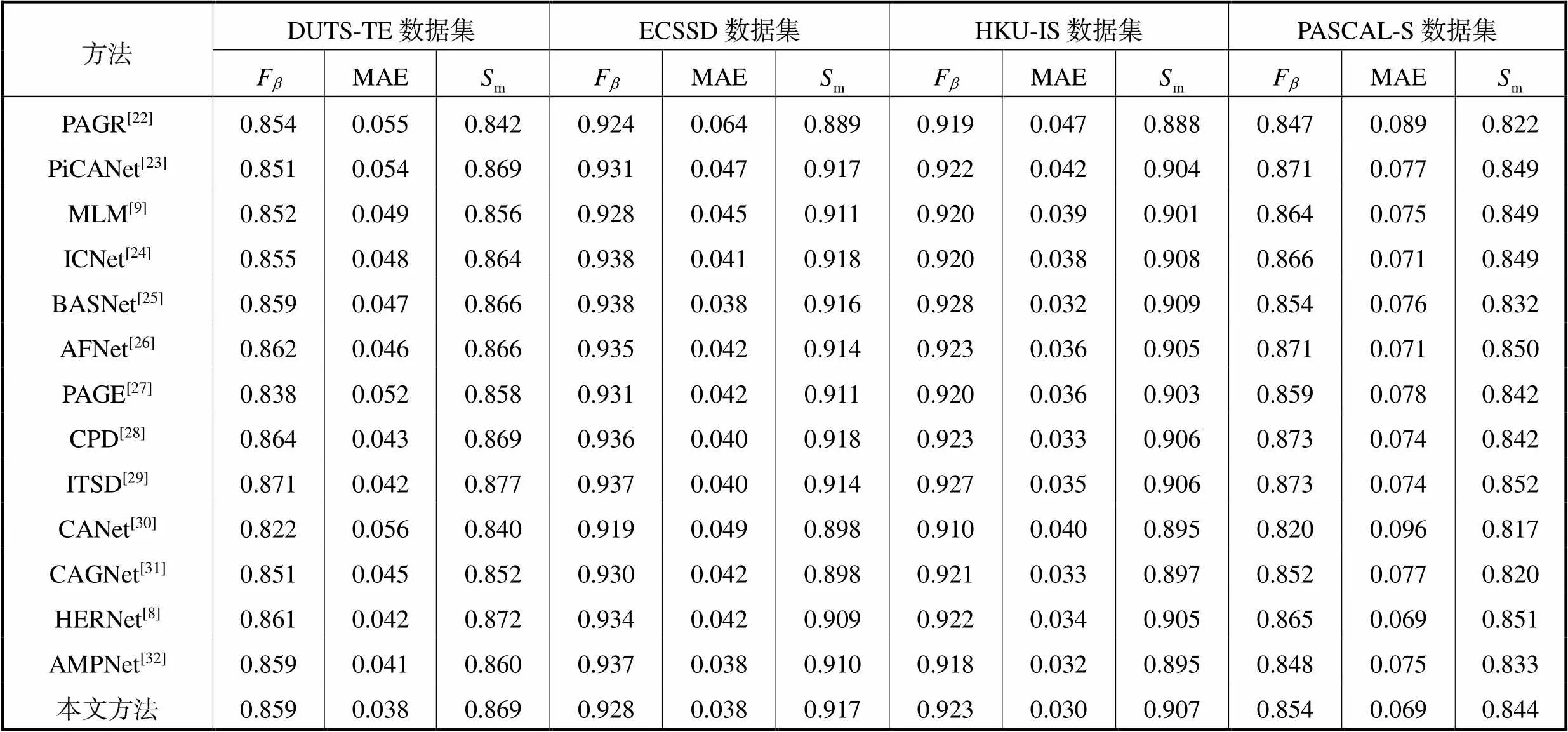
Tab.1 Objective metrics of different saliency detection methods

图4 所提方法和其他方法的主观比较
2.3 平均速度比较
表2比较了本文方法与其他方法的平均速度.可以看出,本文方法的运行速度优于大部分显著性检测方法;相比于ITSD[29]和CPD[28]两个快速显著性检测网络,本文方法也有一定竞争力.
2.4 消融实验

表2 本文所提方法与其他方法在平均速度上的比较
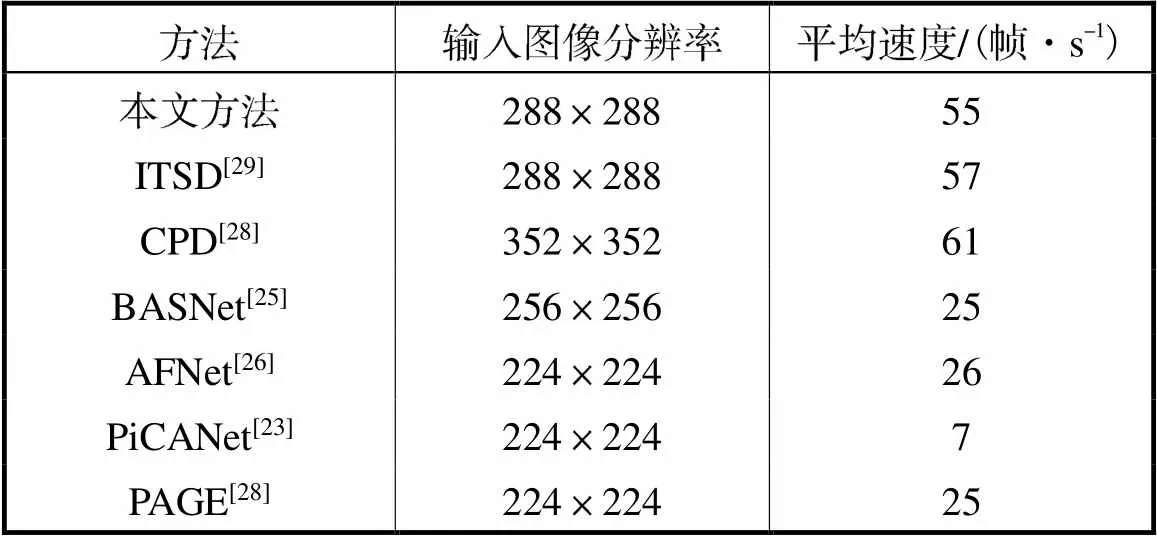
Tab.2 Comparison of the proposed method with other methods in terms of average speed
为了验证所提方法中金字塔卷积模块(PCM)的作用,进行了消融实验.共包括如4个实验:实验1为浅层特征和深层特征均不使用PCM(without PCM,WPCM);实验2为仅浅层特征使用PCM (shallow PCM,SPCM);实验3为仅深层特征用PCM(deep PCM,DPCM);实验4为浅层特征和深层特征均用PCM(both PCM,BPCM).

为了验证所提方法中特征增强模块(FEM)的有效性,在4个数据集上进行消融实验,分别为:浅层特征和深层特征均不使用FEM(without FEM,WFEM)(实验1);仅浅层特征使用FEM(shallow PCM,SFEM)(实验2);仅深层特征用FEM(deep FEM,DFEM)(实验3);浅层特征和深层特征均用FEM(both FEM,BFEM)(实验4);不同模型是否使用FEM的值和MAE的结果如表5所示.

表3 消融实验结果

Tab.3 Ablation results
表4 金字塔卷积模块的消融实验结果
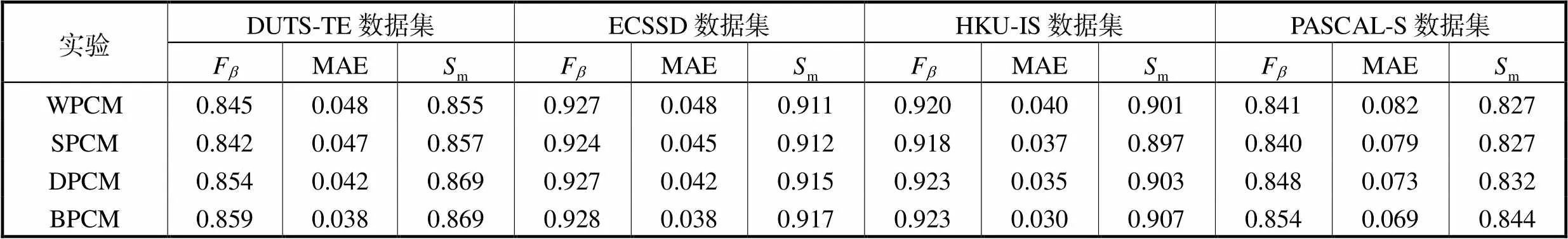
Tab.4 Ablation results on the pyramid convolutional module
表5 特征增强模块的消融实验结果
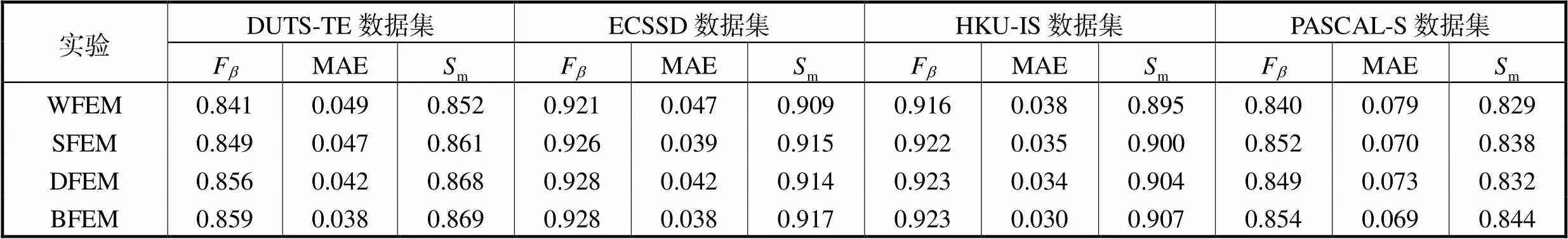
Tab.5 Ablation results on the feature enhancement module
3 结 语
本文提出了一种基于边界检测和骨骼提取的显著性检测网络,通过对两个任务分别训练,辅助显著性检测网络生成完整的显著性图,可有效解决检测结果中部分显著区域漏检和误检的问题.具体来说,本文将输入图像分解,利用边界检测子网络和骨骼提取子网络分别获得显著性目标边界特征和骨骼特征,可准确地定位显著性目标的边界位置和中心位置;为了降低多任务之间的差异,设计显著性填充子网络,以骨骼特征为中心、边界特征为边界,对显著性目标区域进行填充,获得完整的显著性图.此外,文中还设计了金字塔卷积模块和特征增强模块对边界特征和骨骼特征进行筛选和增强,提升网络表达能力.实验结果表明,本文方法能在降低特征提取难度的同时,完整且准确地检测出显著性目标.
[1] Babenko A,Lempitsky V. Aggregating local deep features for image retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago,Chile,2015:1269-1277.
[2] 庞彦伟,余 珂,孙汉卿,等. 基于逐级信息恢复网络的实时目标检测算法[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版),2022,55(5):471-479.
Pan Yanwei,Yu Ke,Sun Hanqing,et al. Hierarchical information recovery network for real-time object detection[J]. Journal of Tianjin University(Science and Technology),2022,55(5):471-479(in Chinese).
[3] Abdulmunem A,Lai Y K,Sun X. Saliency guided local and global descriptors for effective action recognition[J]. Computational Visual Media,2016,2(1):97-106.
[4] Zhou S P,Wang J J,Zhang S,et al. Active contour model based on local and global intensity information for medical image segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing,2016,186:107-118.
[5] Cao X C,Tao Z Q,Zhang B,et al. Self-adaptively weighted co-saliency detection via rank constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2014,23(9):4175-4186.
[6] Wang L J,Lu H C,Wang Y F,et al. Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,USA,2017:136-145.
[7] Wei J,Wang S H,Wu Z,et al. Label decoupling framework for salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle,USA,2020:13025-13034.
[8] Song D W,Dong Y S,Li X L. Hierarchical edge refinement network for saliency detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2021,30:7567-7577.
[9] Wu R M,Feng M Y,Guan W L,et al. A mutual learning method for salient object detection with intertwined multi-supervision[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach,USA,2019:8150-8159.
[10] Liu J J,Hou Q B,Cheng M M. Dynamic feature integration for simultaneous detection of salient object,edge,and skeleton[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2020,29:8652-8667.
[11] He K M,Zhang X Y,Ren S Q,et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas,USA,2016:770-778.
[12] Chen L C,Papandreou G,Kokkinos I,et al. Dee-plab:Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets,atrous convolution,and fully connected crfs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,40(4):834-848.
[13] He K M,Zhang X Y,Ren S Q,et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2015,37(9):1904-1916.
[14] Hu J,Shen L,Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks [C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City,USA,2018:7132-7141.
[15] Peng C,Zhang X Y,Yu G,et al. Large kernel matters—Improve semantic segmentation by global convolutional network[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu,USA,2017:4353-4361.
[16] De Boer P T,Kroese D P,Mannor S,et al. A tutorial on the cross-entropy method[J]. Annals of Operations Research,2005,134(1):19-67.
[17] Arbelaez P,Maire M,Fowlkes C,et al. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2011,33(5):898-916.
[18] Shen W,Zhao K,Jiang Y,et al. Object skeleton extraction in natural images by fusing scale-associated deep side outputs[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas,USA,2016:222-230.
[19] Yan Q,Xu L,Shi J D,et al. Hierarchical saliency detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland,USA,2013:1155-1162.
[20] Li G,Yu Y. Visual saliency based on multiscale deep features[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston,USA,2015:5455-5463.
[21] Li Y,Hou X D,Koch C,et al. The secrets of salient object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus,USA,2014:280-287.
[22] Zhang X W,Wang T T,Qi J Q,et al. Progressive attention guided recurrent network for salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City,USA,2018:714-722.
[23] Liu N,Han J W,Yang M H. Picanet:Learning pixel-wise contextual attention for saliency detection[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City,USA,2018:3089-3098.
[24] Wang W G,Shen J B,Cheng M M,et al. An iterative and cooperative top-down and bottom-up inference network for salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach,USA,2019:5968-5977.
[25] Qin X B,Zhang Z C,Huang C Y,et al. Basnet:Boundary-aware salient object detection[C]// Proceed-ings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach,USA,2019:7479-7489.
[26] Feng M Y,Lu H C,Ding E. Attentive feedback network for boundary-aware salient object detection[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach,USA,2019:1623-1632.
[27] Wang W G,Zhao S Y,Shen J B,et al. Salient object detection with pyramid attention and salient edges[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach,USA,2019:1448-1457.
[28] Wu Z,Su L,Huang Q M. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach,USA,2019:3907-3916.
[29] Zhou H J,Xie X H,Lai J H,et al. Interactive two-stream decoder for accurate and fast saliency detection[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle,USA,2020:9141-9150.
[30] Li J X,Pan Z F,Liu Q S,et al. Complementarity-aware attention network for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics,2020,52(2):873-887.
[31] Mohammadi S,Noori M,Bahri A,et al. CAGNet:Content-aware guidance for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition,2020,103:107303.
[32] Sun L N,Chen Z X,Wu Q M J,et al. AMPNet:Average- and max-pool networks for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology,2021,31(11):4321-4333.
[33] Achanta R,Hemami S,Estrada F,et al. Frequency-tuned salient region detection[C]//2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami,USA,2009:1597-1604.
[34] Fan D P,Cheng M M,Liu Y,et al. Structure-measure:A new way to evaluate foreground maps[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice,Italy,2017:4548-4557.
[35] DeepSaliency:Muilt-task deep neural network model for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2016,25(8):3919-3930.
Saliency Detection Network Based on Edge Detection and Skeleton Extraction
Yang Aiping1,ChengSimeng1,Wang Jinbin1,Song Shangyang1,Ding Xuewen2
(1. School of Electrical and Information Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China;2. School of Electronic Engineering,Tianjin University of Technology and Education,Tianjin 300222,China)
Recently,considerable progress has been made in salient object detection based on joint multitask learning. However,false detection and leak detection persist owing to differences in optimization objectives and feature domains among different tasks. Therefore,current networks are incapable of identifying features such as saliency and object boundaries. Herein,we proposed an assisted multitask saliency detection network based on edge detection and skeleton extraction,comprising a feature extraction subnetwork,edge detection subnetwork,skeleton extraction subnetwork,and saliency filling subnetwork. The feature extraction subnetwork extracts multilevel features of images using ResNet101 pretrained model. The edge detection subnetwork selects the first three layers for feature fusion to retain the salient edge completely. The skeleton extraction subnetwork selects the last two layers for feature fusion to locate the center of the salient object accurately. Unlike the current networks,we train two subnetworks on edge detection dataset and skelecton extraction dataset to preserve the best models separately,which are used as pretrained models to assist with saliency detection tasks. Furthermore,to reduce the discrepancy between optimization objects and feature domains,the saliency filling subnetwork is designed to make the fusion and non-linear mapping for extracted edge and skeletal features. Experimental results for four datasets show that the proposed method can not only restore the missing saliency regions effectively but also outperform other methods.
edge detection;skeleton extraction;multitask;saliency detection network
10.11784/tdxbz202204052
TP391
A
0493-2137(2023)08-0823-08
2022-04-29;
2022-12-16.
杨爱萍(1977— ),女,博士,副教授.Email:m_bigm@tju.edu.cn
杨爱萍,yangaiping@tju.edu.cn.
国家自然科学基金资助项目(62071323,61632018,61771329);天津市科技计划资助项目(20YDTPJC01110).
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 62071323,No. 61632018,No. 61771329),Tianjin Science and Technology Planning Project(No. 20YDTPJC01110).
(责任编辑:孙立华)

