Keto-form directed hierarchical chiral self-assembly of Schiff base derivatives with amplified circularly polarized luminescence
Yimeng Sun ,Yuqin Jing ,Jin Jing,∗ ,Tiesheng Li,∗ ,Minghu Liu,c,d,∗
a Green Catalysis Center,and College of Chemistry,Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450001,China
b Key Laboratory of Nanosystem and Hierarchical Fabrication,CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience,National Center for Nanoscience and Technology,Beijing 100190,China
c National Laboratory for Molecular Science (BNLMS),CAS Laboratory of Colloid,Interface and Chemical Thermodynamics,Institute of Chemistry,Chinese Academy of Science,Beijing 100190,China
d University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190,China
Keywords:Enol-keto tautomerism Chiral self-assembly Schiff base Circularly polarized luminescence Nanofiber bundle
ABSTRACT While enol-keto tautomerism has attracted great interest in Schiff bases and related compounds in solution and crystal states,the self-assembly of energy-unfavored keto form were scarcely investigated.Here,we report a keto-form directed self-assembly of a naphthalene-attached enantiomeric Nsalicylideneanil analog L/DGG-Nap accompanied with a significantly amplified circularly polarized luminescence (CPL).It was found that LGG-Nap exists as a mixture of enol and keto form in monomer at a diluted toluene solution.The increment of the concentrations leads to the formation of predominated keto form,which subsequently triggers the self-assembly.Cryo-transmission electron microscopy (Cryo-TEM)revealed that a hierarchical assembly process happened upon increasing the concentration of LGG-Nap in toluene.Individual nanofibers formed at 1×10−4 mol/L and transferred into helical nanofiber bundles in 5×10−3 mol/L.Interestingly,while these is nearly no circular dichroism (CD) or CPL in the monomeric solution,the assembly showed strong CD and CPL.Remarkably,the dissymmetry factor (glum) was significantly amplified from zero in solution through the 0.005 in individual nanofiber to 0.1 in nanofiber bundles.This work demonstrates that the enol-keto tautomerism can be broken and trigger the selfassembly upon increasing the concentration,which can subsequently direct the chiral self-assembly and significantly amplify the dissymmetry factor of assembled CPL materials.
Self-assembly plays an essential role in nature,in which various components are well assembledviaprecise control of thermodynamic and kinetic equilibrium and achieve diverse physiological functions [1–6].Inspired by nature,the artificial supramolecular assemblies have been extensively studied and extended into many research fields including luminescence,energy,environment and biomimic fields [7–12].During the self-assembly,the control of thermodynamic and kinetic equilibrium has also been paid great attentions [13–15].For instance,energy-unfavored molecular conformation in a monomer could be stabilized in an aggregate with the help of multiple intermolecular non-covalent interactions,and become thermodynamically favored molecular conformation in the resulted supramolecular polymer [16–19].Therefore,in-depth study of the self-assembly process is not only meaningful for understanding the complex and delicate assembly behavior,but also helpful to construct unprecedented supramolecular functional materials.N-Salicylideneanil and its analogues have attracted particular interest in chemistry and materials due to their well-known keto-enol tautomerism [20–25].The enol form is thermodynamically more stable than the keto form,which is the dominant molecular conformation for monomers in dilute solution.However,Ogawaetal.observed that the enol form ofN-salicylideneanil was tautomerized into keto form efficiently due to the formation of aggregates under 77 K [26].Besides,it was discovered that enol and keto forms coexisted inN-salicylideneanil crystal,because intermolecular hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions could lower the energy of keto tautomer and increase its Boltzmann distribution [27–29].In recent years,some researchers have reported that keto-enol tautomerism can be regulated in theN-salicylideneanil analogs-based supramolecular gels,and found that keto forms could be partially stabilized in the gel phase [30,31].However,in all these cases,the enol forms are still more thermodynamic and kinetic stable in the aggregates.It remains a challenge to make the keto form dominant and lead to new functions.Here,we developed a chiral long alkyl chain attached Schiff base and found that keto-form could direct the selfassembly hierarchical to a higher order helical nanofiber and significantly amplify the circularly polarized luminescence (CPL).
CPL has attracted much more attention due to its unique property of excited states of chiral system and the potential application in 3D display,chiral sensors,photoelectric devices and so on [32–36].So far,CPL from chiral luminescent molecules[37–43],supramolecular chiral assemblies [44–48],chiral liquid crystals [49–51],helical polymers [52–54] and chiral cluster[55–57] have made notable success.Previously,CPL has been achieved inN-salicylideneanil and its analogues coordinated metal complex [58].However,CPL from pureN-salicylideneanil and its analogue is little success due to the excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) effect weakening the fluorescence emission[59,60].Here,by stabilizing the keto form in self-assemblyviaconcentration control,we obtained the assemblies with the dissymmetry factor (glum) of 0.1,a higher value for CPL material.
We designed the enantiomericN-salicylideneanil derivativeLGG-Napas shown in Fig.1.The compounds were obtained by the reaction of 2-hydroxynaphthalene formaldehyde withN,N'-bis(octadecyl)-L-Glu-Gly.It should be noted that the Schiff base unit was not directly linked to the dialkyl glutamide 17 but through a glycine spacer,which is very important to realize ketoform directed self-assembly.We found that the enol and keto forms co-existed forLGG-Napin monomer at diluted toluene(1×10−5mol/L).The assembly was triggered by increasing the concentration,where aggregation occurred.To our delight,the keto form became dominant and promote the hierarchical selfassembly.Theoretical calculations demonstrated that the keto form was a little less stable than the enol form forLGG-Napin monomer,so both forms could coexist in dilute toluene.However,during the self-assembly process,keto-form aggregated and induced the stronger intermolecularly interacted packing structure,resulting in lower system energy in comparison with enol-form aggregation.Therefore,a stable keto formLGG-Napsupramolecular polymer was produced,as illustrated in Fig.1.
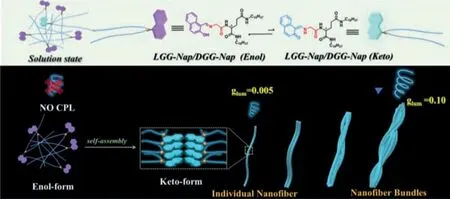
Fig.1. Upper photograph: The molecular structures of enol and keto forms of LGG-Nap,where the enol part is displayed as a purple cartoon molecular mode,and the keto part is displayed in pale blue.Down photograph: The equilibrium in supramolecular polymers tends to be keto mode.The dissymmetry factor (glum) was significantly amplified from zero in solution through the 0.005 in individual nanofiber to 0.1 in nanofiber bundles.
More interestingly,a hierarchical self-assembly process was observed by Cryo-transmission electron microscopy (Cryo-TEM).LGG-Napmainly existed as individual nanofibers at the concentration range from 1×10−4mol/L to 2×10−4mol/L,while they turned into nanofiber bundles as the concentration increased to 5×10−3mol/L gradually.Both circular dichroism (CD) and CPL were detectable for the resulted supramolecular assemblies.We found that CPL signal is significantly enhanced upon hierarchical self-assembly.While theglumis undetectable in solution of 1×10−5mol/L,it is about 0.005 for individual nanofibers and reached 0.1 for nanofiber bundles (Fig.1).It is speculated that the more tight packing ofLGG-Napmolecules in nanofiber bundles could further restrict the free motion of the chromophore and reducing non-radiative transitions,thus strengthened exciton delocalization and resulting in a higher dissymmetry factor [61].This study demonstrates that the concentration can shift the equilibrium from enol to keto and triggered the self-assembly,which subsequently direct the equilibrium towards the energy-unfavored keto form to be predominant and realize the chiral nanofiber bundles with stronger CPL.
LGG-Napwas synthesized referring to a reported method.The intermediateN,N'-bis(octadecyl)-L-Glu (LGAm) was first obtained,which was converted toN,N'-bis(octadecyl)-L-Glu-Glyafter condensed withN-Boc-Gly,and further reacted with 2-hydroxynaphthalene formaldehyde to obtain naphthalene-basedNsalicylideneanil analogLGG-Nap,the detailed synthesis process was shown in supporting information.
The photophysical property ofLGG-Napmonomer was first investigated.The ultraviolet visible absorption (UV–vis) ofLGG-Napin diluted toluene solution (1×10−5mol/L) is presented in Fig.2a(red line),where the absorption band around 309 nm can be assigned to theπ-π∗transitions of the naphthalene moieties,the broad band in the range of 325–375 nm can be assigned to the adsorption of enol-form,and the bands appearing at 402 nm and 423 nm suggesting the existence of the keto-form tautomer.Depended on time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) calculations,the ensemble averaged UV–vis absorption at room temperature forLGG-Napin toluene was also simulated and presented in Fig.2a (black dotted line),which showed good agreement with the experimental spectrum.
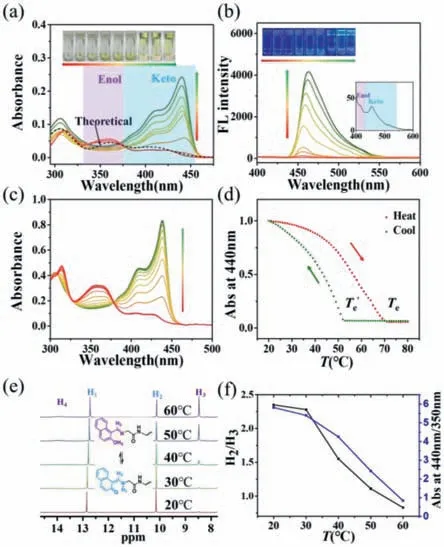
Fig.2. (a) UV–vis absorption spectra and (b) fluorescence spectra of LGG-Nap in toluene,where the concentrations change from 1×10−5 mol/L to 5×10−3 mol/L.(as the direction of the arrow increases,excitation wavelength: 365 nm).(c)Temperature-dependent UV–vis spectra of LGG-Nap in toluene upon a cooling process at a rate of 1 °C/min,c=2×10−4 mol/L,80–20 °C.(d) Variation of polymerization (Abs=440 nm) versus temperature curve for LGG-Nap in toluene upon the cooling and heating process respectively,which be fitted well with a cooperation polymerization mode,c=2×10−4 mol/L.(e) Temperature-dependent partial 1H NMR spectra of LGG-Nap in toluene/CDCl3 (1:1) at 2×10−4 mol/L.(f) H2/H3 in 1H NMR and UV absorption at 440 nm/350 nm in different temperatures.
The fluorescence spectrum ofLGG-Napin diluted toluene solution is shown in Fig.2b (inserted photo images),where the peaks at 415 nm and 456 nm are ascribed to emission radiative decays of enol and keto form respectively.Both UV–vis and fluorescent spectra as well as theoretical analyses indicate that enol and keto forms co-exist forLGG-Napmonomer in diluted toluene.
The concentration-dependent self-assembly behavior ofLGGNapin toluene was further studied.With increasing the concentration,the solution changed into gel gradually (Figs.2a and b,inserted photo images).The UV–vis spectra revealed that the absorption of enol form decreased,while the absorption of keto form increased gradually with the increase of concentration from 1×10−5mol/L to 5×10−3mol/L,and keto form became the major existing molecular conformation above 1×10−4mol/L (Fig.2a).In addition,an obvious bathochromic shift on the absorption band of keto form (from 423 nm shifted toca.440 nm) was observed,indicating the formation of J-type keto aggregates.The emission spectra ofLGG-Napexhibited a similar concentration-dependent enol-keto tautomerism behavior.The emissive band of keto form at around 455 nm increased dramatically with the concentration ofLGG-Napin toluene,while almost no enol form emission could be detected (Fig.2b).The redshift in emission was also observed upon increasing the concentration,indicating that the intermolecular interaction of excited state became stronger as the aggregation increasing.These results demonstrated that keto forms could be stabilized and became the main component in the supramolecular assemblies,and the possible excited-state intramolecular photon transfer effect (ESIPT) noradiative decay pathway from excited keto tautomer was efficiently inhibited.
The temperature effect on UV–vis absorption and nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectral (1H NMR) have also been explored for a deep understanding of the supramolecular polymerization process,where 2×10−4mol/L was chosen as the represented concentration.Dramatic changes in absorption happened during a cooling process,where the band of enol form reduced while the band of keto form raised gradually,and the enol form absorption almost disappeared when the temperature was below 30 °C (Fig.2c).These results again proved that the keto form ofLGG-Napwas efficiently stabilized upon supramolecular polymerization and became predominant.To elucidate the mechanism of supramolecular polymerization,the variation of polymerization,represented by the normalized absorption coefficient at 440 nm,(Abs=440 nm)versustemperature,was analyzed,as shown in Fig.2d,which was fitted well with a cooperation polymerizetion model [62].Furthermore,a thermal hysteresis was observed between heating (Te=70 °C) and cooling (Te=52 °C) curves withΔTeequal to 28 °C,indicating that the presence of inactive enol-keto clusters upon cooling at a temperature range of 52–70 °C,which retarded the nucleation growth process.
Fig.2e revealed the temperature-dependent equilibrium between enol-form (OH group) and keto-form (NH group) by1H NMR spectroscopy.The population of the OH peak was higher than NH at high temperatures 60 °C,while the relative intensity NH peak increased gradually as decreasing the temperature.The NH peak became the dominant tautomer after further decreasing to 20 °C.In addition,the population of protons belonging to enamine (enol-form) and imine (keto-form) presented a similar temperature-dependent changing behavior.
These results once again demonstrated that keto form was efficiently stabilized in supramolecular polymer upon cooling down.Through the ratio of H2and H3in1H NMR at different temperatures and the ratio of UV absorption at 440 nm to 350 nm,it can be found that the dynamic equilibrium of Keto Enol mode of variation with temperature is consistent (Fig.2f).It is confirmed that self-assembly can stabilize the Keto mode as the temperature decreases.
The morphology ofLGG-Napin toluene was investigated by Cryo-TEM.No obvious aggregation structure was observed for the samples at a concentration range from 1×10−5mol/L to 5×10−5mol/L (Fig.S1 in Supporting information),while nanofibers with diameter of around 6–8 nm and length of about dozens of micrometers were observed for 1×10−4mol/L and 2×10−4mol/L ofLGG-Napin toluene (Fig.3a and Fig.S1).
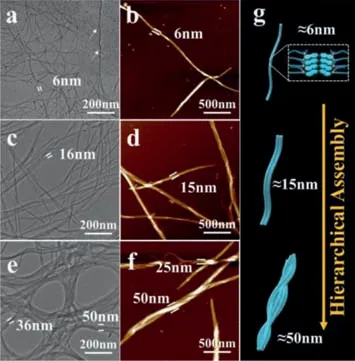
Fig.3. Cryo-TEM images of LGG-Nap based supramolecular polymer under different concentrations: (a) 2×10−4 mol/L,(c) 5×10−4 mol/L,and (e) 5×10−3 mol/L,the dimension is the width of nanofiber and nanofiber bundles.AFM images of LGG-Nap based supramolecular polymer under different concentrations: (b)2×10−4 mol/L,(d) 5×10−4 mol/L and (f) 5×10−3 mol/L,the dimensioning is the height of nanofiber and nanofiber bundles.(g) The LGG-Nap assembly simulation diagram.
These results demonstrated that supramolecular polymerization has markedly happened with the concentration exceeding 1×10−4mol/L.Interestingly,nanofiber bundles (14–16 nm in width) emerged gradually as the concentration increased to 5×10−4mol/L (Fig.3c),and nanofiber bundles became the dominant architectures by further increasing the concentration bundles,nitrogen freezing process,thus the images represented.It should be noted that these Cryo-TEM samples were obtained from a liquid actual morphology of the supramolecular polymer.Therefore,the increase of original polymerization concentration can facilitate hierarchical assembly to form nanofiber bundles instead of individual nanofibers.In addition,the atomic force microscopy (AFM) images also supported a hierarchical assembly process that happened from individual nanofibers to nanofiber bundles (Figs.3b–f).
Since theLGG-Napmolecule contains the chiral center at the alkyl chains,the chiroptical properties ofLGG-Napwere investigated.It was found that no CD signal could be detected forLGG-Napin dilute toluene solution (below 1×10−4mol/L,Fig.S3 in Supporting information),while an obvious positive CD signal with a peak around 440 nm emerged at the concentration above 1×10−4mol/L,and a near mirror-imaged CD was observed forDGG-Napsystem (Fig.4a,2×10−4mol/L).It is noted that the CD spectrum coincided with the UV–vis absorption of keto-form,indicating that ground-stated keto-form ofLGG-Nap/DGG-Napwas chirally arranged in the supramolecular polymer.Moreover,the chiroptial intensity of gabs was almost unchanged as the concentration further increased to 5×10−3mol/L gradually (Fig.4b),suggesting that the ground state chirality of keto form aggregates was independent ofLGG-Naporigin concentration in toluene.
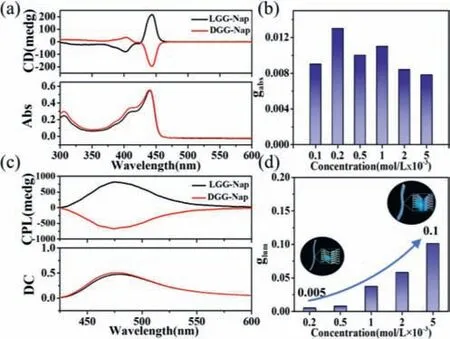
Fig.4. (a) CD spectra of LGG-Nap and DGG-Nap based supramolecular polymers in toluene,c=2×10−4 mol/L;(b) gabs of LGG-Nap based supramolecular polymer in toluene under different concentrations;(c) CPL spectra of LGG-Nap and DGG-Nap based supramolecular polymer in toluene,c=5×10−3 mol/L.Direct current (DC),0.5 V.(d) glum of LGG-Nap based supramolecular polymer in toluene under different concentrations.Excitation wavelength: 365 nm.
The CPL spectra were measured using the solution or toluene gel with the excitation at 365 nm.CPL signal was observed forLGG-Napin toluene with concentrations above 2×10−4mol/L,a positive peak at 475 nm belonged toLGG-Napassemblies,and a near mirror-imaged CPL was obtained forDGG-Napassemblies(Fig.4c).It should be noted that the CPL spectrum coincided with the fluorescence emission of keto-form,indicating that the excited keto-form ofLGG-Nap/DGG-Napwas also chiral arrangement in the supramolecular assemblies.
Theglumis about 0.005 forLGG-Nappolymer at 2×10−4mol/L.To our surprise,glumis significantly enhanced upon increasing the original concentration ofLGG-Napin toluene and reached 0.1 at 5×10−3mol/L,which is nearly 20 folds amplified (Fig.4d).Theglumwas no longer increasing as further increase the concentration (Fig.S4 in Supporting information).
We then tried to work out the keto-enol tautomerism mechanism ofLGG-Napbased supramolecular polymer by plotting out the potential energy surface.To deeply understand the absorption property,a theoretical conformational search based on Molclus [63],xtb [64] and Gaussian 16 [65] programs was performed highly accurate energy calculation results illustrated that keto-form tautomer did coexist with enol-form in toluene at room temperature.Nevertheless,the most stable and contributed conformation was still enol-form.AsLGG-Napsingle molecular state in dilute toluene solution,the optimized enol and keto molecular structures all contained three intramolecular hydrogen bonds as shown in Fig.5a.Thus,we considered that the self-assembling process should undergo two steps,one is the breaking of intramolecular hydrogen bond and the other is forming of intermolecular hydrogen bonds.We built up the aggregates of enol and keto respectively(decamer) to do Fig.5b.The potential energy surface ofLGG-Napsingle molecules and decamers has been marked with blue dashed lines in Fig.5b.The total system energy of keto form decamer is about 13.00 kcal/mol lower than enol form decamer,indicating keto form aggregates are more stable in the supramolecular polymer.By combining “gentor” implemented in Molclus program and the semi-empirical GNF2-xTB method [66],the optimized enol and ketoLGG-Napdecamer structures were obtained.For computing the binding energy of enol/keto aggregate,one molecule of the decamer was extracted to optimize alone which was treated as the transient state of self-assembling process.
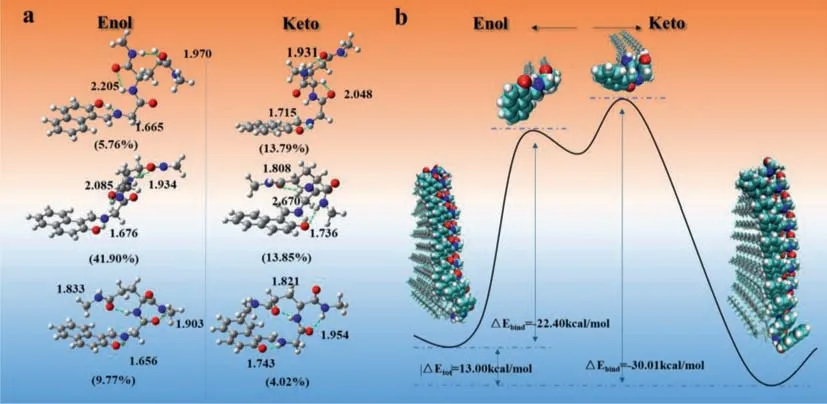
Fig.5. (a) Selected low-energy optimized structures of LGG-Nap in the S0.Numbers listed below each structure are the corresponding Boltzmann populations (in parentheses).The N···HO/O···HN distances,in ˚A,are also given.(b) The potential energy surface of LGG-Nap single molecules and decamers.The total system energy of keto form decamer is about 13.00 kcal/mol lower than enol form decamer,indicating keto form aggregates are more stable in the supramolecular polymer.
Calculation results showed that the binding energy of keto decamer was much larger than that of enol decamer,therefore,it is considered that the intermolecular hydrogen bonding andπ-πinterplay can stabilize the ketoLGG-Napaggregates during the selfassembling process.Finally,stable ketoLGG-Napsupramolecular nanofiber can be formed under dynamic and thermodynamic driving forces.
Based on the above spectral data and Cryo-TEM images,it is possible to provide an explanation for hierarchical assembly enhanced CPL behavior.The individual nanofibers are converted into nanofiber bundles as the original concentration ofLGG-Napin toluene increases,and more long-range ordered packing structures form upon the hierarchical assembling process [67].Such ordered aggregates can increase the exciton coherence effect,namely,one exciton in nanofiber bundles can coherently delocalized over more molecules than individual nanofiber (Fig.4d,inserted diagrams),thus resulting in redshifted emission as well as a stronger CPL signal.However,the hierarchical self-assembly process has little effect on UV–vis absorption,so the CD signal ofLGG-Nappolymer has almost no concentration-dependent effect.
In conclusion,we designed enantiomeric naphthalene-basedNsalicylideneanil derivativesL/DGG-Nap,which could self-assemble into nanofibers and nanofiber bundlesviaa cooperation polymerization.It revealed that the coexisted enol and keto in monomeric dilute solution can shift to keto-form dominant in concentrated solution and triggered self-assembly.Theoretical calculations revealed that the energy of keto-forming aggregates was lower than that of enol-forming aggregates,thereby keto aggregation is an energy favourable pathway for supramolecular self-assembly.A hierarchical assembly enhanced CPL was observed with the increase of the polymerization concentration,the |glum| value reached 0.1 at a concentration of 5×10−3mol/L,which was almost 20 times amplified than that at 2×10−4mol/L.It was speculated that a more regular and tight packing structure of keto aggregation was formed in nanofiber bundles which could strengthen the exciton coherence and delocalization,and then improved the excited chirality performance.We believed that combining the exquisite design of molecules and well control of the self-assembly process will be an efficient method for constructing functional nanomaterials.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Natural Science foundation of China (Nos.21861132002,21773043,21973020 and 21890734).
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108409.
 Chinese Chemical Letters2023年12期
Chinese Chemical Letters2023年12期
- Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Spin switching in corrole radical complex
- Benzothiadiazole-based materials for organic solar cells
- Mono-functionalized pillar[n]arenes: Syntheses,host–guest properties and applications✰
- Recent advances in two-step energy transfer light-harvesting systems driven by non-covalent self-assembly✩
- From oxygenated monomers to well-defined low-carbon polymers
- Doping-induced charge transfer in conductive polymers
