The therapeutic mechanism of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide on T2DM rats based on the Nrf2 signaling pathway
Shu-Fang Zhang,Shu-Quan Lv,Hui Zhang,Han-Zhou Li
1Community Health Center,Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Affiliated to Hebei University of Chinese Medicine,Cangzhou 061000,China.2Endocrinology Department,Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Affiliated to Hebei University of Chinese Medicine,Cangzhou 061000,China.
Abstract
Keywords:Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide;type 2 diabetes mellitus;nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling pathway;oxidative stress
Introduction
The global prevalence of diabetes mellitus(DM)has been increasing annually.According to the IDF survey,the number of humans with DM will achieve 783 million by 2045[1].Type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM)could be a common form of DM that has exhibited a worldwide public health challenge,critically threatening each human health and social development.This type of DM is predominantly associated with insulin resistance or hyperinsulinemia.The pathogenic mechanisms of T2DM are yet unclear,although they might be associated with genetic mutations,obesity,and environmental factors[2–4].According to the 2022 American Diabetes Association guidelines,the first line of treatment for T2DM is the use of metformin and lifestyle interventions,followed by the application of GLP-1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors as novel medications to decrease the odds of cardiovascular disease in patients while lowering the blood glucose level.Although these drugs have improved clinical outcomes,they pose several side effects,such as those of gastrointestinal associated with GLP-1 agonists.Moreover,it is still uncertain whether these drugs increase the risk of pancreatitis[5].Therefore,it is of urgent clinical interest to develop drugs that can effectively mitigate T2DM.
Polygonatum sibiricumpolysaccharide(PSP)is the principal phytochemical of the traditional Chinese medicinePolygonatum sibiricum.Pharmacological studies have shown that PSP effectively regulates blood glucose and lipid levels,exhibits antioxidant effects,and can improve myocardial damage[6].Furthermore,PSP has been found to improve glucose metabolism disorders and blood glucose levels by alleviating oxidative stress[7].Additionally,clinical studies have shown that phytochemical extracts fromPolygonatum sibiricumcan effectively improve blood glucose and lipid indicators in T2DM patients with qi and yin deficiency[8].Consequently,a T2DM rat model was established in the present study by subjecting the rat specimen to a high-fat diet in conjunction with streptozotocin(STZ)administration.The therapeutic effects of PSP were determined via gavage.Finally,the effects of PSP on the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2(Nrf2)signaling pathway in T2DM rat models were investigated,and it was preliminarily investigated whether PSP is effective in treating T2DM by regulation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Material and methods
Experimental animals
30 male SD rats(200±20 g)were purchased from Beijing Huafukang Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.(animal license no.:SCXK(Beijing)2021-0031).The feeding conditions are 25 °C temperature,50%humidity,12 hours of light and dark cycle,and adequate water and food.This research was authorized by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine-Western Medicine of Hebei(CZX2022-KY-008).
Reagents
High-sugar,high-fat chow(40% fat,17.7% sucrose,17.7% fructose,and 9.4% protein)and regular chow(59.4% total sugar,20% protein,and 4.8% fat)were purchased from Beijing Huafukang Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.PSP(70% purity,lot no.:S27804)was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.Total cholesterol(TC,A111-1-1),triglycerides(TG,A110-1-1),aspartate transaminase(AST,C010-2-1),alanine transaminase(ALT,C009-2-1),glutathione peroxidase(GSH-Px,lot no.:A005-1-2),total superoxide dismutase(SOD,lot no.:A001-3-2),and malondialdehyde(MDA,lot no.:C003-1-2)assay kits were purchased from Nanjing Jiansheng Bioengineering Institute.Nrf2(lot no.:ab62353),HO-1(lot no.:ab305290),glutamate-cysteine ligase chemical(GCLC)(lot no.:ab207777),NQO1(lot no.:ab80588),and β-actin(lot no.:ab179467)primary antibodies and corresponding secondary antibodies were purchased from Abcam.Experimental equipment is as thus:blood sugar analyzer(Bionime,Shenzhen,China);microplate reader(iMark680,Bio-Rad,USA);optical microscope(Olympus CKX41,Leica,Germany).And chemiluminescence imaging system(SH-523,Shenhua Science Technology Co.,Hangzhou,China).
Groups and treatment method
Following a week adaptation period,10 rats were randomly selected and fed with a regular diet as a normal group.In contrast,the rest were subjected to high-sugar,high-fat chow(40% fat,17.7% sucrose,17.7% fructose,and 9.4% protein)for 8 weeks.Rats in each group were then fasted for 12 h and injected intraperitoneally with STZ 30 mg/kg(dissolved in 0.1 mol/L citrate buffer,pH=4.5).Notably,we need to inject the same volume of citrate buffer into the rats in the normal group.The blood sample was accrued from the tail vein of rats approximately 72 h following STZ injection for a random blood glucose test,and a blood glucose concentration>16.7 mmol/L is the standard for the successful replication of a T2DM model.Consequently,a random number table was applied to evenly distribute the T2DM and PSP groups into ten.The normal and T2DM groups were each inoculated with 2 mL of normal saline via gavage.The PSP group was given 800 mg/kg PSP via gavage based on human-rat body surface area conversion(1:6.25).The Fiber Bragg Grating of the rats in each group was measured weekly for 4 weeks.
Observational indicators and assays
Oral glucose tolerance test(OGTT).After four weeks of PSP intervention,all the rats were starved while not watering for 12 h.Blood samples were obtained by tail clipping,and blood sugar levels were measured with blood sugar check paper;that was served because the blood sugar was at zero min.Later,OGTT was performed by administering five hundredth aldohexose resolution(2 g/kg)via feeding,and blood sugar values were measured at fifteen,30,60,and 120 min,severally,the next feeding.The area under the curve(AUC)for the OGTT was calculated.
Biochemical indicators.After four weeks of PSP intervention,all rats were starved for 8 h,and 50 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium was injected into the abdominal cavity of rats to anesthetize them rats.The blood sample was collected from the abdominal aorta and centrifuged at 3000 r·min-1for 15 min to obtain serum.The serum levels of the lipid-related indicators TG and TC,liver function-related indicators ALT and AST,and oxidative stress-related indicators SOD,GSH-Px,and MDA were measured in each group of rats.
ELISA.Following four weeks of PSP intervention,insulin levels were measured using the serum obtained from the blood samples of rats in each group via ELISA per the kit manufacturer’s instructions.HOMA-IR was calculated as:HOMA-IR=(fasting blood glucose×fasting insulin)/22.5.
Pathological staining of liver tissue.Four weeks following PSP intervention,rat liver tissue was isolated,fixed in formalin,embedded in paraffin,processed into 3-μm sections,and finally stained with HE.Histopathological changes were observed via light microscopy.
Assays of key Nrf2 signaling pathway proteins.Rat liver tissues were collected,and 150 μL of RIPA lysis buffer was added.The tissue was homogenized and centrifuged,and the protein supernatant was obtained.Once the total protein concentration was decided by using a BCA protein assay kit,the sample protein concentration was homogenized.
Subsequently,20 μg of protein were gathered from every pattern and separated employing 8–12% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis,and the segregates were transferred to PVDF membranes.The membranes were blocked with 5%skim milk powder for 2 h at room temperature,after which rabbit anti-rat primary antibodies against Nrf2,HO-1,GCLC,or NQO1(dilution ratios 1:600,1:800,1:5000,1:1000,respectively)were added and incubated overnight at 4°C.After washing the membranes,secondary antibodies were added and incubated for 2 h at room temperature.After that,the membranes were washed,followed by the addition of an ECL chemiluminescence reagent,and we used Image Pro Plus 6.0 software to quantify and analyze the grayscale values of the bands.
Statistics.The experimental results were analyzed by SPSS 22.0 statistical software.Experimental results were expressed as¯x±s.All data were tested for normality and homoscedasticity,applying the Student’s t-test if both tests satisfy and non-parametric tests if otherwise.P<0.05 wasconsidered statistically significant.
Results
Changes in fasting blood glucose,OGTT,FINS,and HOMA-IR
The results showed that the blood glucose in the T2DM group was significantly higher than that in the normal group(P<0.01).Compared with the T2DM group,the Fiber Bragg Grating of the PSP group was significantly lower(P<0.01).FINS and HOMA-IR were significantly higher in the T2DM group than in the normal group(P<0.01).PSP intervention significantly reduced FINS and HOMA-IR levels compared to the corresponding values in the T2DM group(P<0.01)(Table 1).
The results of OGTT-AUC showed that the T2DM group was significantly higher than the normal group(P<0.01).Compared with the T2DM group,PSP intervention could significantly reduce the OGTT-AUC of rats(P<0.01)(Table 2).
Comparison of blood lipid and liver function indicators in each group of rats
The results of blood lipid-related indicator tests revealed that serum TC and TG expression levels were significantly higher in the T2DM group than in the standard group(P<0.01)and significantly higher in the PSP group than those in the T2DM group(P<0.01)(Table 3).Liver function tests showed that serum ALT and AST levels were significantly higher in the T2DM group than those in the normal group(P<0.01)and significantly lower in the PSP group than in the T2DM group(P<0.01)(Table 4).

Table 1 PSP treatment improve the levels of blood sugar,FINS,and HOMA-IR
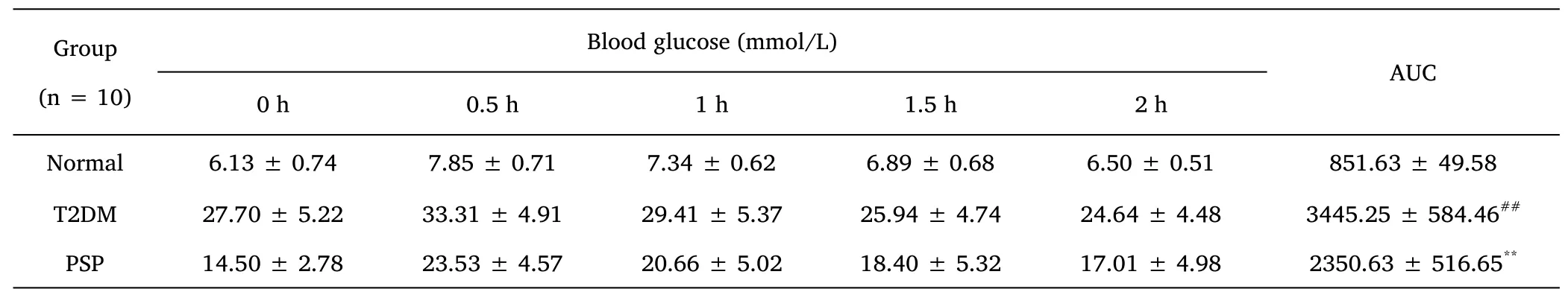
Table 2 Comparison of OGTT and AUC at different timings in each group of rats
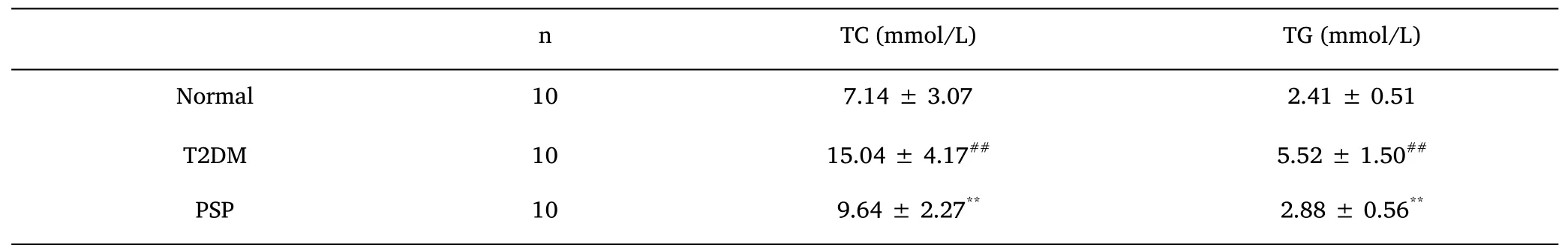
Table 3 PSP treatment improve the levels of blood lipid-related indicator

Table 4 PSP treatment improve the levels of liver function
Changes in liver tissue histopathology in each group of rats
HE staining of liver tissues revealed the presence of hepatic steatosis as well as several striations,necrosis,inflammatory cell infiltration,and vacuolar changes in the liver tissues of T2DM rat models.Further,PSP intervention significantly improved the histopathological changes in the liver tissues of T2DM rat models(Figure 1).
Changes of PSP on oxidative stress
Following model establishment,serum SOD and GSH-Px activity were appreciably decreased in the T2DM group(P<0.01)and MDA levels were increased(P<0.01)compared to the levels in the normal group.Notably,PSP intervention significantly increased serum SOD and GSH-Px activity and decreased MDA levels(P<0.01)(Table 5).
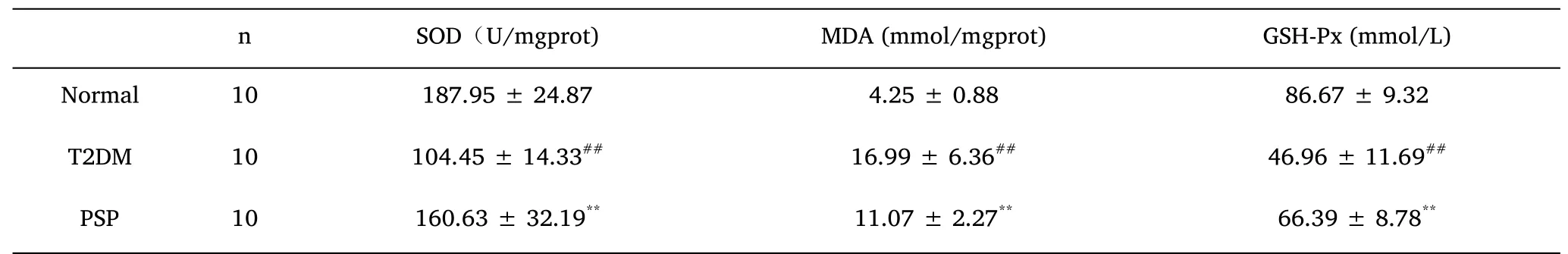
Table 5 PSP treatment improve the levels of oxidative stress in T2DM rat models
Changes of PSP on the key Nrf2 signaling pathway proteins Nrf2,HO-1,GCLC,and NQO1 in T2DM rat models
Western blot results showed that Nrf2,HO-1,GCLC,and NQO1 were considerably lower within the T2DM group than in the standard group(allP<0.01).Compared with the T2DM group,the levels of Nrf2,HO-1,GCLC,and NQO1 were considerably magnified once treated with PSP(P<0.01)(Figure 2a and Figure 2b).

Figure 1 Rat liver HE staining(×100).T2DM,type 2 diabetes mellitus;PSP,Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide.
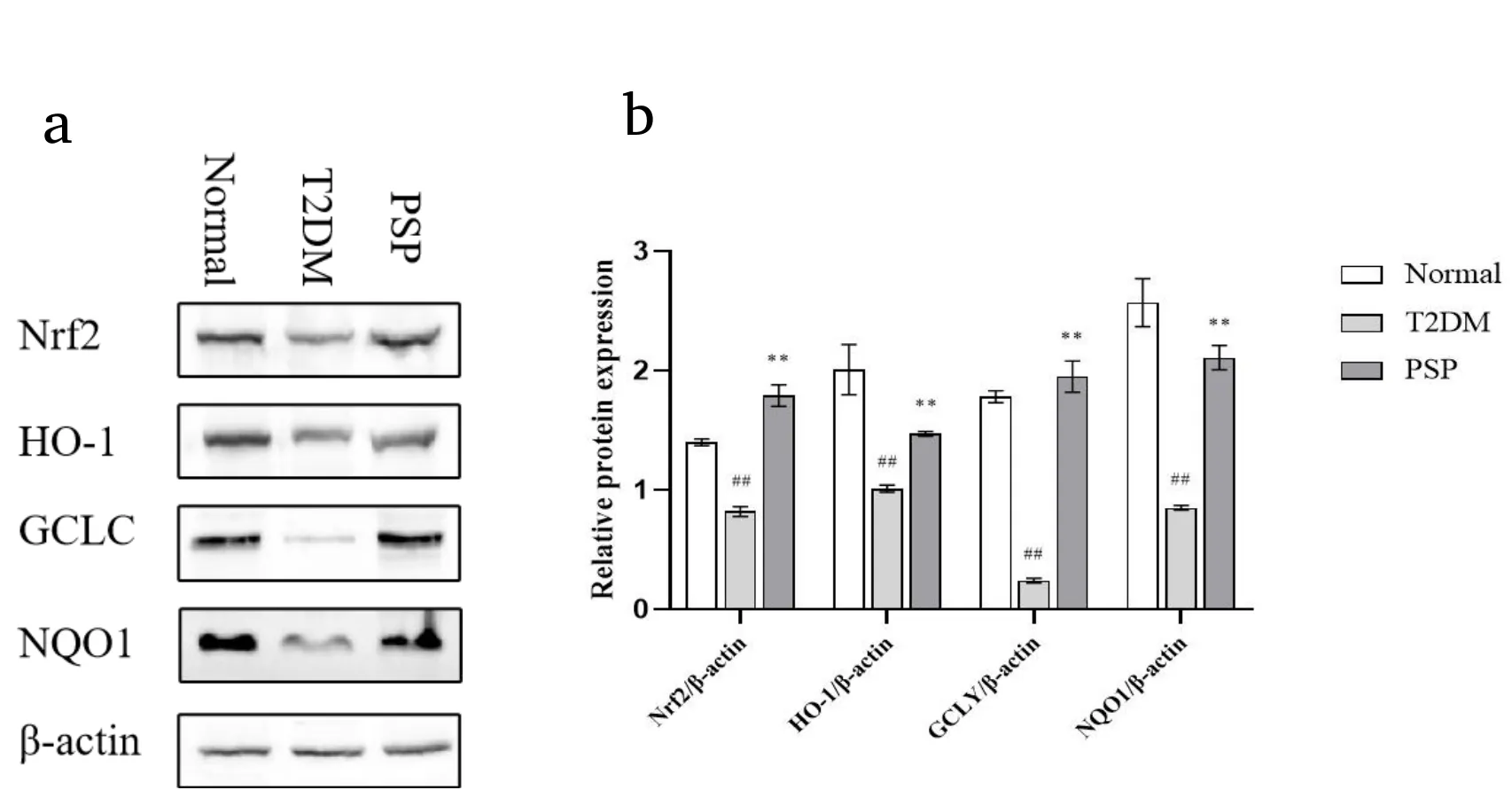
Figure 2 Changes of PSP on Nrf2,HO-1,GCLC,and NQO1 protein expressions in liver tissues of T2DM rat models.(a)The Western blot results of Nrf2,HO-1,GCLC,and NQO1.(b)The quantified gray value analysis results of Nrf2,HO-1,GCLC,and NQO1 Western blot.##,P<0.01 compared to normal group;**,P<0.01 compared to T2DM group.PSP,Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide;Nrf2,nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2;GCLC,glutamate-cysteine ligase chemical;T2DM,type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Discussion
Our results demonstrated that blood glucose level was notably higher in T2DM rat models than in the standard group.Moreover,TC and TG results suggest that T2DM rat models exhibit hyperlipoproteinemia.Elevated ALT and AST results suggest that T2DM rat models exhibit liver dysfunction.In addition,the AUC of OGTT is elevated in T2DM rat models,indicating that the rats exhibit insulin resistance,which is one of the indications of T2DM.Pathological results indicate that the structure of liver tissue in T2DM rat models is more disarrayed than that of the normal group,with diffuse edema of hepatocytes,evident steatosis,lipid deposition in the cytoplasm,and vacuolar changes.Importantly,SOD,MDA,and GSH-Px are major indicators reflecting the degree of cellular oxidative damage in organisms.Our results showed that PSP intervention considerably multiplied bodily fluid SOD and GSH-Px activity and ablated MDA levels in T2DM rats.In addition,PSP intervention ablated glucose levels and improved dyslipidemia,oxidative stress,and pathological changes within the liver tissue in T2DM rat models,suggesting that PSP mitigates T2DM.
Persistent hyperglycemia will cause ROS buildup,leading to associate oxidative stress response,then cause a series of metabolic disorders[9].As an associate in nursing result of lipid peroxidation,MDA indirectly reflects the degree of cellular harm and correlates with oxidative stress[10].Notably,SOD and GSH-Px are ubiquitous antioxidant enzymes that play crucial roles in alleviating oxidative stress-related conditions[11].Our results showed that PSP significantly increases SOD and GSH-Px activity,whereas decreasing MDA levels in the liver tissues of T2DM rat models,confirming that PSP is crucial in alleviating oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress is critical in the pathogenesis of T2DM.Among various endogenous antioxidant systems,Nrf2 is the principal signaling molecule known to mitigate T2DM by alleviating oxidative stress[12,13].Under physiological conditions,Nrf2 is transcribed at low levels and its activity depends on Keap1 regulation[14].In pathological states,Nrf2 is translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus wherever it exhibits inhibitor effects by controlling the expression of inhibitor response component(ARE)-mediated inhibitor proteins and clinical trial detoxifying enzymes,like HO-1,GCLC,and NQO1[15,16].Briefly,HO-1 catalyzes the degradation of heme to generate biliverdin,which has vigorous antioxidant activity;GCLC enhances ROS scavenging by promoting the synthesis of GSH,and NQO1 is a reductase of coenzyme Q(ubiquinone)and vitamin E that confers resistance to oxidative stress damage by maintaining the reduced state of coenzyme Q and vitamin E[17,18].Our results suggest that PSP intervention upregulates the protein expression levels of Nrf2,HO-1,GCLC,and NQO1 and thus confirms the anti-oxidative stress effects of PSP.
Conclusively,this study unconcealed the therapeutic effects of PSP on T2DM rat models.It is incontestible that its mechanism of action is also related to regulating the Nrf2 signal pathway in cells and improving oxidative stress within the body.
 Precision Medicine Research2022年4期
Precision Medicine Research2022年4期
- Precision Medicine Research的其它文章
- Combining PD1 inhibitor,PARP inhibitor and antiangiogenic medication for lung squamous cell carcinoma with liver metastasis:a case report
- Regulatory effects of evodiamine on glucose metabolism-related factors in CT26 colorectal carcinoma-bearing mice
- Network pharmacology study of drug pair Tubeimu-Zhebeimu in the treatment of breast cancer
