Taper-wedge stem suitable for anterior approach total hip arthroplasty: Adequate biomechanical reconstruction parameters and excellent clinical outcome at mid-term follow-up
Carlo Trevisan,Antonino Salvatore Lombardo, Gianluca Gallinari, Marco Zeppieri,Raymond Klumpp
Abstract
Key Words: Total hip arthroplasty; Orthopedics; Direct anterior approach; Orthopedic surgery; Stem implantation; Accolade II stem
lNTRODUCTlON
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is one of the surgical procedures with the highest levels of safety, efficacy, and clinical satisfaction[1]. In the last decade, there have been numerous improvements in techniques and technologies, which have given rise to better clinical outcomes and less need for early surgical THA revisions[2,3]. New technology, methods and implants, however, need to be carefully tested and assessed in long term studies on large cohorts to determine the clinical usefulness and safety before widespread use.
The direct anterior approach (DAA) for THA has been a debatable issue in current literature. Several studies supporting this surgical technique have reported that this less invasive and muscle-sparing approach can improve early functional and patient-reported outcomes. Others studies, however, have reported the limitations of using this approach, which include high complication and revision rates, usually dependent on long and difficult surgeon learning curves[4,5]. The technical difficulties in the DAA have been reported to be linked with the implantation of undersized stems[6] and early femoral failure[7].
The design of the femoral stem used in surgery can be an additional contributing factor in postoperative early aseptic loosening. Lindgrenet al[8] found that stems with an "anatomic" design were more likely to loosen when implanted through an anterolateral approach. Janssenet al[9] reported that cementless femoral stems with a proximal shoulder tend to be associated with early aseptic loosening when inserted through an anterior or anterolateral approach, while an anatomically shaped stem may be preferred with these approaches.
The choice of a suitable stem to be used in an anterior approach should preferably consider a reduction in possible complications rates related to the difficulties of femoral exposure. A new secondgeneration cementless stem (Accolade II) with its short length and smooth tapered tip could be considered a good candidate when using the DAA for THA. This new stem was created to better adapt to the anatomy of the femoral canal thanks to a more anthropomorphic dimension ratio between its proximal and distal portions and to the variation, size to size, of the radius of curvature of its medial side[10].
The aim of our study was to evaluate the feasibility, utility and safety of this second-generation cementless stem (Accolade II) for the DAA. The assessment in our study was based on data regarding complications, survival of the implanted prostheses, biomechanical hip reconstructions, radiographic evolutions, functional results, and patient-related outcomes.
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Study design
This retrospective observational study analyzed consecutive patients that underwent THA with DAA using the Accolade II stem (Stryker Orthopedics) in the Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics at a public Italian hospital located in Seriate, Bergamo between November 2013 and March 2019. The analysis was based on data obtained from outpatient reports, medical records, and radiographs. The investigation was performed in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and informed consent was obtained from all participants before surgery. The study was in compliance with Institutional Review Boards and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act requirements of the hospital. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Bergamo (n. 144/19, August 5, 2019).
Hip-fractured patients and patients with a final follow-up of less than 12 mo were excluded. All the surgical procedures were performedviaa mini-invasive DAA without a traction table. A preoperative radiological 2D plan, using TraumaCad® software, and intraoperative fluoroscopy evaluation of trials for stem positioning were performed for each patient. The stems were used in combination with an uncemented Trident HA-coated cup (Stryker orthopedics). In all cases, a highly cross-linked polyethylene on Biolox Delta femoral head bearing was used.
One hundred forty-eight subjects (161 hips) were treated in the time interval considered. Seventeen patients were lost to follow-up. At the last outpatient follow-up visit, these patients were stable from a clinical and radiographic point of view. Four patients died for reasons unrelated to their hip surgery. Thirteen patients, contacted by phone, refused to come to the follow-up visit for logistical or work reasons. They all reported that no other surgical revisions were performed on the operated hip.
Data collection
Body mass index (BMI), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Score, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI)[11], and Charnley classification were calculated for each patient[12]. The postoperative outcome assessments included data based on complications, implant survival, and clinical and radiological outcomes. Complications and adverse events were coded according to the Hip Society THA Complications workgroup[13]. Clinical outcomes were obtained at the last follow-up visit. Functional results were evaluated by the Harris Hip Score (HHS)[14]. Patient-related outcomes were assessed by the Hip disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score Italian version LK 2.0 (HOOS)[15].
Standardized pre- and post-operative anteroposterior radiographs of the pelvis and the lateral view of the operated hip were used for the radiological assessment. Occurrence of radiolucent lines, osteolytic changes, or cortical hypertrophy were recorded using Gruen's zones for the stem and the DeLee Charnley zones for the cup[16,17]. Stem subsidence was calculated using the method reported by Grantet al[18]. Femoral component fixation and stability were assessed by the Engh score[19]. Adequate radiographs to measure the biomechanical parameters for hip reconstruction as described by Asayamaet al[20] and Schmidutzet al[21] were available in 104 hips. Acetabular cup positioning was evaluated by referring to the safe zones defined by Lewinneket al[22].
Statistical analysis
Data regarding quantitative variables included mean, standard deviation, range and/or median, and qualitative variables as a percentage. The studentt-test for independent samples was used to compare continuous variables in normally distributed data among groups. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for data not normally distributed. The implant survival probabilities were computed using Kaplan-Meier analysis (revision of any component for any reason as the terminating event or at the end of the follow-up period). The statistical analysis was performed using the STATA11 software package (Statistic Data Analysis, StataCorp, College Station, TX).Pvalues lower than 0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
One hundred and thirty patients were included in the study. Surgery was carried out bilaterally in 14 cases for a total of 144 hips that underwent DAA for THA. One hundred and twenty cases were performed by a senior experienced surgeon; twenty-four cases by two other surgeons in their learning curve.
The demographic and clinical data of the patients are shown in Table 1.
Complications
Complications were recorded in 6 procedures (4.2%). Analytical data are reported in Table 2.
No significant differences in terms of complications were observed between the senior surgeon and the training surgeons (5 complications out of 120 proceduresvs1 complication in 24 procedures - not significant, Fisher exact test).

Table 1 Demographic and clinical data of the 144 hips included in the study

Table 2 Data of the six patients with complications
No intra-operative complications and no dislocations were reported.
Survivorship
At 69 mo, the cumulative survival of the stem and cup (that did not require surgical revisions) was 98.6% (95%CI: 90.7-99.8). Only one implant was revised due to deep infection (0.7%). No failures were observed for aseptic loosening.
Component positioning
Stem alignment averaged -0.3° ± 1.9°; 97 out of 104 stems (93.3%) were within 3° of varus/valgus. The mean cup inclination was 38° ± 5.7° and the mean anteversion was 15° ± 5.2°. Eighty-eight out of 104 cups (84.6%) were within the Lewinnek safe zone.
No significant differences were seen between the senior surgeon and the training surgeons regarding stem alignment and cup position.
Hip center of rotation, femoral offset and abduction lever arm reconstruction and leg length
When compared to the contralateral side, hip center of rotation (CoR) was postoperatively elevated by 3.7 mm ± 4.3 mm and medialized by 3.4 mm ± 4.5 mm on average. Femoral offset (FO), abduction lever arm (ALA), and leg length (LL) after surgery are shown in Figure 1. FO increased in 83 out of 104 cases (79.8%); when compared to the contralateral side, only 8 out of 104 cases (7.7%) showed a decrease of FO greater than 15%. Compared to the contralateral side, the leg length of the operated hip was longer by 2 mm ± 6.1 mm on average. In 56.7% of cases, leg length discrepancy was within ± 5 mm.
Radiographic outcomes
No lines of radiolucency or lysis were observed around any of the implanted acetabular components. One stem showed an area of lysis in Gruen zone 1 and radiolucencies in zones 3, 4, and 5 at 24 mo. This patient was asymptomatic with an Engh score of 15.
No stem showed any subsidence greater than 2 mm. The Engh score provided results between 15 and 26 suggesting osseointegration of all implanted stems. Distal femoral cortical hypertrophy (DFCH) was observed around 32 femoral stems (22.2%) (Figure 2). Gruen zone 3 was the most affected (28 cases), followed by zones 2 and 5 (respectively 13 and 11 cases). None of the patients involved were symptomatic nor showed any functional impairment. HHS and HOOS total scores were not significantly different between those with DFCH and those without it (respectively 95.8 ± 9.6vs97.4 ± 2.9 and 86.9 ± 16.6vs89.5 ± 9.9, Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
Functional outcomes and patient-related outcome
The HHS median at final follow-up was 96.2 points (range 44-100 points). The score was excellent in 119 patients (91.5%), good in 5 (3.8%), fair in 3 (2.3%) and poor in 3 (2.3%).
The patients with poor HHS included 3 Charnley class C females with disabling chronic low back pain. HOOS results at final follow-up for all patients are presented in Figure 3. Median values range from 87.5 to 95.
Two multivariate analysis was performed to identify potential risk factors for a poor outcome using HHS and total HOOS at final follow-up as independent variable and age, gender, BMI, ASA, CCI and Engh Score as dependent variables. Regarding HHS, male gender was a significant positive factor whilst age, ASA and CCI were significantly inversely correlated with the score. Age and ASA were also significantly inversely correlated with final HOOS total score.
DlSCUSSlON
The results of our study showed that the Accolade stem is suitable, safe, and efficient when used in the DAA for THA. The overall complication rate was low even for surgeons during the learning curve. None of the complications were related to the difficulties of exposure of the femur during the surgical procedure, intraoperative fractures or stem subsidence. Failures due to infection was very rare, with only one of the 144 cases that showed failure for periprosthetic infection at a mean follow-up of 35 mo.
Femoral exposure and preparation through the DAA is a complex part of the operation. Meneghiniet al[7] found that the revisions due to early femoral failure were more common in patients who had undergone the DAA. In this regard, the design of the stem can play an important role during surgery, and data from the literature suggests that the shape of the stem can induce specific problems. Janssenet al[9] found that there was a stem-approach interaction, in which shoulder stems showed a greater likelihood of early aseptic loosening when the anterolateral or the anterior approach was used.
Studies have reported that longer stems or those with particular designs were associated with more perioperative complications, especially periprosthetic fractures. Dietrichet al[23] found an odds ratio of 1.98 for intraoperative fractures when a Quadra-H stem was used compared to the Fitmore and AMIStem. Tamakiet al[24] and Grecoet al[25] reported an increase in femur complication rate using the Taperloc Microplasty short stem with full profile taper concerning the standard length Taperloc. Riveraet al[6] reported that the Fitmore stem was associated with a higher probability of undersizing when implanted by DAA.
New stem designs may reveal new problems with other surgical approaches as well, as suggested by the data from Tootsiet al[26], which reported a 5% incidence of intraoperative femoral fracture in 222 THA performed using the novel SP-CL® implant. With regards to the Accolade II, the morphometric design with a size-specific medial curvature and optimized length potentially renders this stem suitable for DAA. Our radiographic results on the reconstruction of the biomechanics of the operated hip also seem to promote the design of this stem. Stem positioning and the reconstruction of FA, ALA, and LL resulted comparable to those reported by Schmidutzet al[21] This study compared a short-stem hip with a conventional stem implanted with a minimally invasive anterolateral Hardinge approach in the supine position. The achieved degree of precision of the joint reconstruction was such as not affecting patient-related outcomes[27].
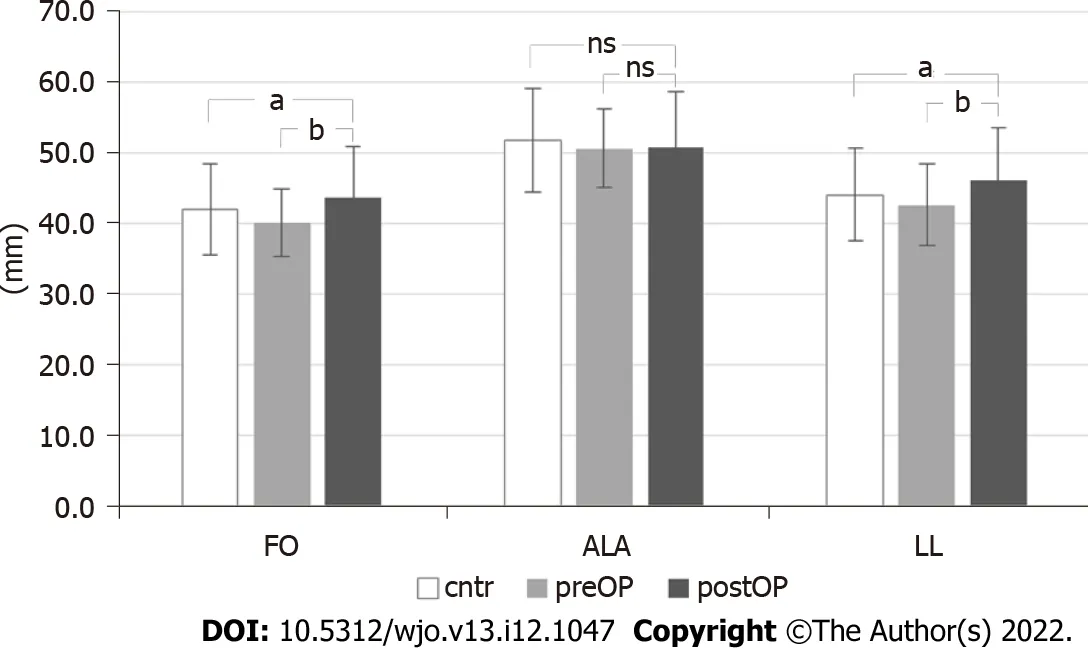
Figure 1 Comparison of postoperative femoral offset, abductors lever arm and leg length with preoperative and contralateral parameters. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01; ns: Not significant. postOP: Postoperative; FO: Femoral offset; ALA: Abductors lever arm; LL: Leg length; preOP: Preoperative; cntr: Contralateral.

Figure 3 Box plot for Hip disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome scores at final follow-up (median, 25th and 75th percentile, max and min values, outliers). HOOS: Hip disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score; ADL: Activities of daily living; QoL: Quality of life.
The performance of the Accolade II stem has also been described in other studies. Pierceet al[28] reported the results of 68 hips implanted at a high-volume institution using an anterolateral approach. No stem complications were shown, with an all-cause survivorship of 99.2% at a mean follow-up of 3.5 years. Koliseket al[29] examined 202 Accolade II femoral stems implanted in 4 different hospitals with a 2-year follow-up. They reported two surgical complications related to stem implantation, which included a posterior trochanteric avulsion and a periprosthetic fracture. Aseptic and all-cause survival rates of 100% and 99.5% were reported. Berndtet al[30] reviewed 151 THA procedures with the Accolade II/Trident implant system using DAA. With regards to complications, this study reported one intraoperative stem perforation and one aseptic stem loosening at 45 mo with a total implant survival of 96.9% at 5 years.
观赏藤本植物共89种,占总数的17.6%,以豆科、蔷薇科、葡萄科最为丰富,代表种有白花油麻藤(Mucuna birdwoodiana)、定心藤(Mappianthus iodoides)、香花崖豆藤(Millettia dielsiana)、粉叶羊蹄甲(Bauhinia glauca)、龙须藤(Bauhinia championii)、金钱豹(Campanumoea javanica)、香港双蝴蝶(Tripterospermum nienkui)、黑老虎(Kadsura coccinea)、广州槌果藤(Capparis cantoniensis)等。
Our study showed that all patients had favorable radiographic outcomes. The Engh scores suggested that all stems were well integrated and showed a low incidence of radiolucency lines (reported in 1 of the 115 hips). These results are indicative of a satisfactory fit and fill of the femoral canal and adequate adhesion of the circumferential porous coating to the surrounding bone[31].
A better "fit and fill" of the Accolade II stems when compared to the previous models has been reported in a preclinical study by Faizanet al[32], which showed a more uniform proximal-distal grip in a large sample of femoral sizes. Studies by Issaet al[10] reported a significant improvement in both proximal and distal fixation in the current version. Numerous evidences affirms that excellent "fit and fill" correlate with better clinical-functional results[33-35]. Our data confirm the excellent results in HHS and HOOS in addition to the absence of radiological subsidence in the stems.
We detected DFCH in 22% of our stems, but this did not appear to influence the implant survival and functional and subjective outcomes. Previous studies have shown that DFCH prevalence ranges from 6% to 56% in different cementless stem designs without determining any functional impairment[36,37].
Our study has several limitations. The data is based on a retrospective study in which the lack of complication related to the stem may be due to the relatively limited number in the cohort. Similar types of study in literature, however, have reported incidence rates of perioperative fractures ranging from 1 to 7 cases[23,25], which was not seen in our cohort. Moreover, our study was based on a rather short follow-up (3.5 years), thus does not provide information regarding the long-term success rates of this stem.
CONCLUSlON
The design of the stem can have an effect on the risk of adverse events in DAA for THA. Studies are needed to confirm the safety and success rates when new models are proposed for implantable stems for THA are desirable. Our preliminary data shows that the Accolade II stem tends to provide a low complication rate and satisfactory biomechanical reconstruction. The mid-term positive outcomes concerning survivorship, functional scores, and activity levels in our consecutive series of patients support the safety and suitability for DAA of this new stem design, which can be a long-term predictor of success. Further multicenter studies with longer follow-up are needed to confirm these preliminary positive results.
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS

FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Trevisan C designed the research study, performed data acquisition, and wrote the manuscript; Lombardo AS, Gallinari G, and Klumpp R designed the research study and performed data acquisition; Trevisan C, Lombardo AS, Gallinari G, Zeppieri M and Klumpp R contributed towards conception of the study and final editing; All authors revised the article critically for important intellectual content, and provided final approval for the paper to be published.
lnstitutional review board statement:The study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Bergamo, Italy (No. 144/19, August 5, 2019).
lnformed consent statement:Patients were not required to give informed consent to the study because the data was collected retrospectively and anonymized. Clinical data were obtained after each patient agreed to treatment by written consent.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All authors report no relevant conflict of interest for this article.
Data sharing statement:No additional data are available.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:Italy
ORClD number:Carlo Trevisan 0000-0002-9129-6825; Antonino Salvatore Lombardo 000-0001-7773-6567; Gianluca Gallinari 000-0001-6205-8804; Marco Zeppieri 0000-0003-0999-5545; Raymond Klumpp 0000-0002-4824-4384.
S-Editor:Zhang H
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Zhang H

