Probable beneficial effects of black seeds (Nigella sativa) in the management of langya henipavirus infection
Naina Mohamed Pakkir Maideen
1PhD.Pharmacologist,Dubai Health Authority,Dubai,The United Arab Emirates.
Abstract Background: The patients with Langya henipavirus (LayV) infection are managed mainly with symptomatic treatment and supportive care.Objective:This review article focuses on the beneficial effects of black seeds (Nigella sativa)in the management of Langya henipavirus(LayV) infection.Methods:The literature was searched in online databases,including Medline/Pubmed/PMC,Google Scholar,Science Direct,Ebsco,Scopus,Web of Science,Embase,and reference lists,to identify published studies,which established beneficial effects of black seeds (N.sativa) related to signs and symptoms of LayV infection.Results:Black seeds (N.sativa) have shown potential antiviral,bronchodilatory,antihistaminic,antitussive,hepatoprotective,renoprotective,anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,and immunomodulatory properties in various clinical,animal,in-vitro,in-vivo,and in-silico studies,which would help the patients with LayV infection.Conclusion: N.sativa would be a potential herbal candidate in the management of LayV infection along with symptomatic treatment and supportive care,to prevent further deterioration,and hospitalization.The safety and efficacy of N.sativa in patients with LayV infection would further be established by future randomized controlled clinical trials.
Keywords: Langya henipavirus; Hendra virus;Nipa virus; Nigella sativa;black seeds;kalonji;thymoquinone
Introduction
Langya henipavirus(LayV) belongs to the familyParamyxoviridae,and the genusHenipavirusand it is closely related toHendra virusandNipah virus.LayVis named after a Chinese town calledLangya,in Shandong province,where the first case was identified in December 2018.An epidemiological study covering April 2018 to August 2021,reported that 35 patients had been identified withLayVinfection and 26 of them were infected withLayValone [1].
The patients withLayVinfection have shown respiratory symptoms such as fever,cough,and fatigue,and other symptoms including anorexia,myalgia,nausea,vomiting,and headache [1].Besides,the patients withLayVinfection were likewise seen with laboratory abnormalities including leukopenia,thrombocytopenia,lymphocytopenia,elevated liver enzymes (alanine amino-transferase(ALT),aspartate amino-transferase (AST)),and impaired kidney function (elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels)[1].
TheLayVRNA(ribonucleic acid)was detected mainly in shrews and subsequently they may be considered to be natural reservoir ofLayV.Moreover,theLayVinfection might be sporadic as the infected individuals had no close contact among themselves [1].
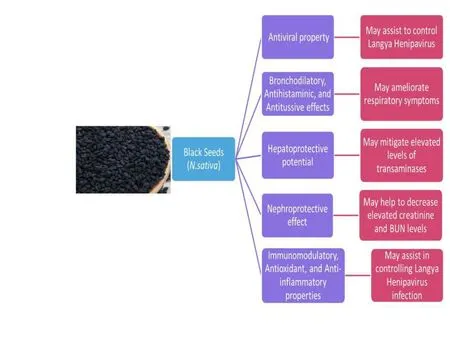
Currently,no antiviral drugs are approved for the management of patients withLayVinfection and they are treated symptomatically with supportive care.Hence,we propose the adjuvant use of black seeds (Nigella sativaorN.sativa) in the management ofLayVinfection along with the symptomatic treatment and supportive care.N.sativahas shown likely antiviral,bronchodilatory,hepatoprotective,nephroprotective,immunomodulatory,antioxidant,and anti-inflammatory properties in various clinical and preclinical studies.
Methods
The literature was searched in online databases including Medline/Pubmed/PMC,Google Scholar,Science Direct,Ebsco,Scopus,Web of Science,Embase,and reference lists,to identify published studies,which established beneficial effects of black seeds(N.sativa) related to signs and symptoms ofLayVinfection,using keywords likeLangya henipavirus,Henipaviruses,black seeds,Nigella sativa,Kalonji,and thymoquinone.
Results and Discussion
The viral loads ofLayVinfected individuals were determined to be much higher among patients with pneumonia and impaired function of liver and kidneys have been noted among the patients withLayVinfection[1].Subsequently,N.sativamay assist the patients withLayVinfection to achieve less severe symptoms and faster recovery,as various clinical,animal,in-vivo,and in-vitro studies demonstrated antiviral,bronchodilatory,hepatoprotective,nephroprotective,immunomodulatory,antioxidant,and anti-inflammatory properties ofN.sativa.
N.Sativais a medicinal plant belonging to the Ranunculaceae family.It is used in various traditional medicine systems including Unani,Ayurveda,Siddha,and others to manage patients with wide a variety of diseases [2].The presence of various bioactive phytoconstituents including thymoquinone (TQ),thymohydroquinone,thymol,α-pinene,nigellicine,nigellimine,nigellidine,gallic acid,ferulic acid,catechin,quercetin,rutin,and many others have been identified in the phytochemical analysis ofN.sativa[3].
LayVbelongs to paramyxovirus family and the antiviral efficacy ofN.sativaagainst Newcastle disease virus (NDV),a kind of paramyxovirus.It has been established in anin-ovostudy,in which the administration of ethanolic extract ofN.sativain embryonated eggs inoculated with NDV,ensued in strong immunotherapeutic effect [4].Moreover,highest antibody titers against Newcastle disease were observed in chickens fed with a diet containing 1%N.sativaseeds.In addition,the chickens,which received 1-2% ofN.sativaseeds have shown many positive effects,including improved performance,enhanced humoral immune responses,and changes in hemogram,and serum biochemical profiles [5].
Besides,antiviral efficacy against paramyxovirus (NDV),N.sativasupplementation was found to be effective against Severe Acute Respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) in several clinical as well asin-silico,and in-vitro studies.Different phytoconstituents ofN.sativasuch as thymoquinone,dithymoquinone,thymohydroquinone,thymol,nigellidine,nigellone,and α-hederin have been determined to prevent SARS-CoV-2 viral entry/fusion and/or viral replication [6,7].In addition,N.sativasupplementation led to seroreversion of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV),and elevated CD4 and CD8 counts,which were observed in different pilot studies and case reports [8].Moreover,N.sativahas established antiviral efficacy against several other viruses including hepatis C virus(HCV),H9N2 avian influenza,Murine cytomegalovirus(MCMV),herpesviruses,Epstein-Barr virus (EBV),Peste des petits ruminants(PPR)virus,broad bean mosaic virus(BBMV),Zucchini yellow mosaic virus (ZYMV),and Papaya ring spot virus [9,10].
Various clinical as well animal studies have established bronchodilatory,antihistaminic,and antitussive properties ofN.sativa,which may assist in relieving the signs and symptoms ofLayVinfection [2].In addition,N.sativasupplementation may diminish elevated levels of ALT and AST due toLayVinfection.Significant reduction of both ALT and AST levels have been observed by the supplementation ofN.sativain several randomized,placebo-controlled,clinical trials [11].Similarly,N.sativasupplementation may decrease creatinine and BUN levels enhanced byLayVinfection.Various animal,in-vitro,and in-vivo studies demonstrated the nephroprotective potential of TQ and its supplementation resulted in a significant decline in creatinine and BUN levels [12].
Moreover,N.sativasupplementation may assist in enhancing platelet levels diminished byLayVinfection.An animal study of albino rats with chloroquine phosphate-induced thrombocytopenia,determined that the administration of aqueous seed extract ofN.sativaensued in increased platelet counts along with the elevation of antioxidants (catalase,and ascorbic acid),and micronutrients (iron,nickel,and cobalt) [13].Besides antiviral and other beneficial effects,N.sativaalso has an immunomodulatory activity which could help to control theLayVinfection.Supplementation ofN.sativaensued in enhanced cellular immune responses (T lymphocyte proliferation,CD4+T cell activation),and modulation of T helper cell 1 (Th1)response (secretion of interleukin-2 (IL-2),interleukin-12 (IL-12)interferon-γ (IFN-γ),tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) as well as T helper cell 2 (Th2) response (secretion of IL-4,IL-5,IL-10,and IL-13)[14].
Conclusion
N.sativawould be a potential herbal candidate in the management ofLayVinfection along with symptomatic treatment and supportive care,to prevent further deterioration,and hospitalization.As numerous clinical,animal,in-vitro,in-vivo,andin-silicostudies have established different beneficial effects of black seeds (N.sativa) relevant to causative organism,symptoms and laboratory abnormalities ofLayVinfection.The safety and efficacy ofN.sativain patients withLayVinfection would further be established by future randomized controlled clinical trials.
- Food and Health的其它文章
- Anxiety disorder:definition,symptoms,causes,epidemiology and treatments
- A review on the recent advances in the effects of exogenous substances in food on gut microbiota
- Investigation physico-chemical characterization of jaggery from different sugarcane varieties
- Research progress of metal chelating peptides
- Comment on"The association between dairy products and the risk of COVID-19"

