Study on the correlation between Serum HDAC3, HMGB-1 and nonvalvular atrial fibrillation
Chuan-Qi Sun, Zhuo-Ya Yao, Qi Gao, Ning Xu, Pin-Fang Kang, Da-Sheng Gao
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233000, China
Keywords:Atrial fibrillation Histone Deacetylase 3 High Mobility Protein B1
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the relationship between serum histone Deacetylase 3(HDAC3), High Mobility Group B 1(HMGB-1) and the occurrence, development and structural remodeling of nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Methods: Patients admitted to non-valvular atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation AF group, n=166) were selected and divided into paroxysmal atrial fibrillation group (paroxysmal AF group, n=42), persistent atrial fibrillation group(persistent AF group, n=63), and permanent atrial fibrillation group (permanent AF group,n=61).50 cases of sinus rhythm were selected as the control group, general clinical data, heart color ultrasound, NT-proBNP, and the levels of HDAC 3 and HMGB-1 were determined by enzyme-linked adsorption immunoassay (ELISA). Results: The levels of HDAC3,HMGB-1, LAD, and LVEDD were all higher than those in the control group (P <0.05);The levels of LAD, LVEDD, HDAC3, and HMGB-1 were all higher in the permanent AF groups than in the persistent AF versus paroxysmal AF groups (P <0.05), And the persistent AF group was higher than the paroxysmal AF group (P <0.05); According to the Pearson correlation analysis, HDAC3 vs. LAD (r=0.635), P<0.01), LVEDD(r=0.651, P<0.01), HMGB-1(r=0.757, P <0.01) showed a positive correlation; HMGB-1 was compared with LAD(r=0.658), P<0.01), LVEDD(r=0.569, P <0.01) showed a positive correlation; After a binary logistic regression analysis, HDAC3(OR= 1.712, 95%CI:1.070-2.739, P<0.05), HMGB-1(OR=1.287, 95%CI:1.008-1.634, P <0.05) was associated with whether atrial fibrillation occurred. Conclusion: The levels of HDAC3 and HMGB-1 are correlated to the occurrence and development of AF and are independent risk factors for the occurrence of AF; HDAC3 and HMGB-1 levels are related to the structural remodeling of atrial fibrillation.
1. Introduction
Atrial fibrillation ( AF ) is a tachyarrhythmia characterized by disturbance of atrial electrical activity followed by atrial mechanical dysfunction , and its prevalence is increasing year by year . heart failure and thromboembolism [1] . Studies have shown that the incidence of stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation is 4-5 times that of normal people[2-4]. However, the clinical treatment of atrial fibrillation is still difficult at present. The main reason is that the mechanism of atrial fibrillation is still unclear .Therefore, finding relevant indicators that can affect the occurrence and promote the progression of atrial fibrillation can not only promote the understanding of the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation.Understanding, may also provide new ideas for future treatment.
Histone deacetylase 3 ( HDAC3 ) belongs to the class I histone deacetylase, which affects myocardial cell contraction, promotes myocardial hypertrophy, fibrosis, autophagy and apoptosis through deacetylation modification, and plays an important role in the occurrence of cardiovascu- lar diseases , fibrosis, autophagy and apoptosis. It plays an important regulatory role in the devel- opment process [ 5-11 ]. Risebro et al. [ 12-15 ] have confirmed that HDAC3 is related to the maintenance of cardiomyocyte potential stability and energy metabolism, and its abnormal expression may lead to abnormal myocardial structure and function ; High mobility protein B1 ( HMGB-1) is a a structurally non-histone chromatin-binding protein involved in the regulation of transcription, DNA replication and repair , extracellular HMGB-1 is passively released by necrotic tissue or actively secreted by stressed cells [ 16-19 ] . Studies have shown that HMGB-1 can reduce myocardial contractility, induce myocardial hypertrophy, apoptosis and promote the formation of myocardial fibrosis [20-26] . In view of the above mechanisms,we speculate that the two are related to the occurrence of atrial fibrillation and myocardial remodeling . At present, there are few reports at home and abroad. Therefore, this paper aims to investigate the correlation between serum HDAC3 and HMGB-1 and the occurrence, development and structural remodeling of non-valvular atrial fibrillation, so as to clarify the role of HDAC3 and HMGB1 in the occurrence of atrial fibrillation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Research objects and inclusion criteria
166 patients with atrial fibrillation who were admitted to the hospital from September 2019 to December 2020 and were diagnosed with atrial fibrillation by 24-hour dynamic electrocardiography were selected as the experimental group . According to the diagnostic criteria of non-valvular atrial fibrillation and its classification established by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) [ 27 ] , they were divided into paroxysmal atrial fibrillation group (paroxysmal group, n=42) , continuous Atrial fibrillation group (persistent group,n=63) , permanent atrial fibrillation group (permanent group, n=61). Fifty patients with healthy sinus rhythm during the same period in our hospital were selected as the control group.
2.2 Exclusion criteria
(1) Heart valve abnormalities (calcification, surgery, etc.) caused by congenital heart disease, rheumatic heart disease and other related causes .

2. 3 Methods
5ml of venous blood was collected from the enrolled patients,centrifuged to prepare serum, and stored in a -80℃ freezer . Purchase ELISA kits (Shanghai Yuduo), and measure the concentrations of HDAC3 and HMGB-1 according to the instructions. Other general basic information and cardiac color Doppler ultrasound were determined by the laboratory and color Doppler ultrasound room of our hospital .
2.4 Statistical processing
SPSS25.0 statistical software was used to analyze the collected data .The normal distribution of measurement data was expressed as±s , the non- normal distribution was expressed as M ( P25 , P75 ), and the count data was expressed as percentage . For comparison between groups, t test, rank sum test, and chi-square test were used;for correlation, Pearson correlation analysis was used ; multivariate binary Logistic regression was used to explore the independent risk factors affecting the occurrence of atrial fibrillation, and P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
3. Result
3.1 Comparison of clinical data between the atrial fibrillation group and the control group
No significant difference between the two groups in age, gender,hypertension, diabetes, blood routine, liver and kidney function,blood lipids, CRP, EF % , NT-proBNP , etc. ( P>0.05 ). Compared with the control group, the levels of HDAC3, HMGB-1, LAD and LV EDD in the atrial fibrillation group were significantly increased ;the difference was statistically significant ( P<0.05 ). (See Table 1)
3.2 Comparison of HDAC3, HMGB-1, LAD, LV E DD levels in patients with different types of atrial fibrillation
By comparing the levels of HDAC3, HMGB-1, LAD, and LVEDD in patients with different types of atrial fibrillation , we found that the levels of HDAC3, HMGB-1, LAD, and LVEDD in the permanent group were significantly higher than those in the persistent group and the paroxysmal group (P <0.05) , and the above indicators in the continuous group were also significantly higher than those in the paroxysmal group (P<0.05) ( see Table 2)
3.3 Correlation analysis between HDAC3, HMGB-1, LAD and LVEDD in atrial fibrillation group
Pearson correlation analysis showed that the level of HDAC3 in atrial fibrillation group was positively correlated with HMGB-1 ( r =0.757 , P = 0.001 ) ; P = 0.000 ) was positively correlated ; HMGB-1 level was also positively correlated with LAD (r=0.658, P = 0.002 )and LV EDD (r= 0.569 , P = 0.000 ) . (see Table 3 )
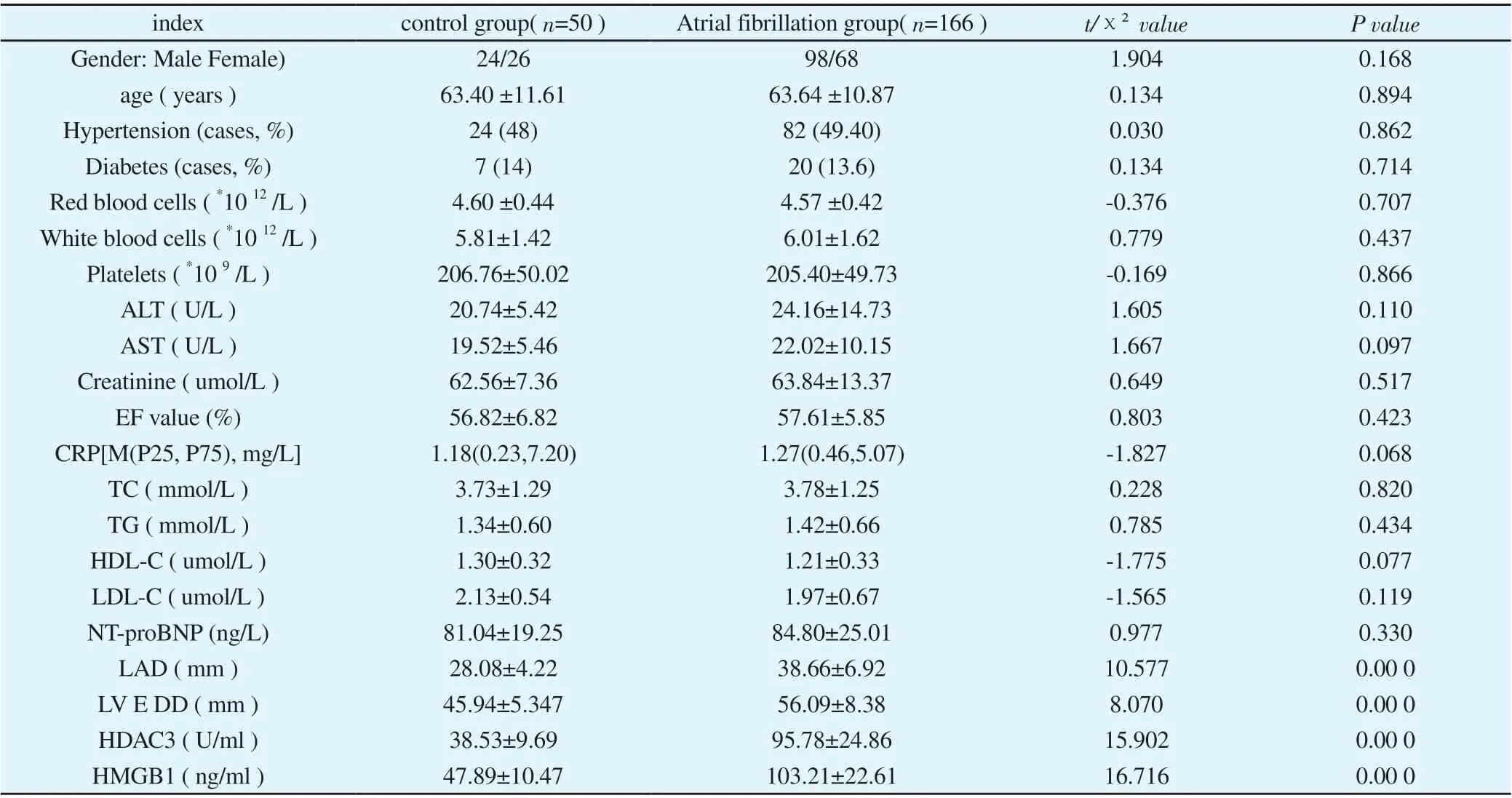
Table 1 Comparison of each clinical data between the control and AF groups

Table 2 HDAC3, HGMB-1, LAD, LV E DD comparison within the experimental group

Table 3 HDAC3, HMGB-1, LAD, LVEDD correlation analysis of the experimental groups
3.4 Binary logistic regression analysis of risk factors for atrial fibrillation
For all the enrolled patients, with the occurrence of atrial fibrillation as the dependent variable and the variables with differences in Table 1 ( HDAC3, HMGB-1, LAD, LVEDD ) as the covariates, binary Logistic regression analysis was used to show that HDAC3 ( OR=1.712, 95%CI: 1.070-2.739, P<0.05), HMGB-1 (OR=1.287, 95%CI:1.008-1.634, P<0.05), LAD (OR=1.709, 95%CI: 1.095- 2.666,P<0.05) was an independent risk factor for atrial fibrillation. (see Table 4)
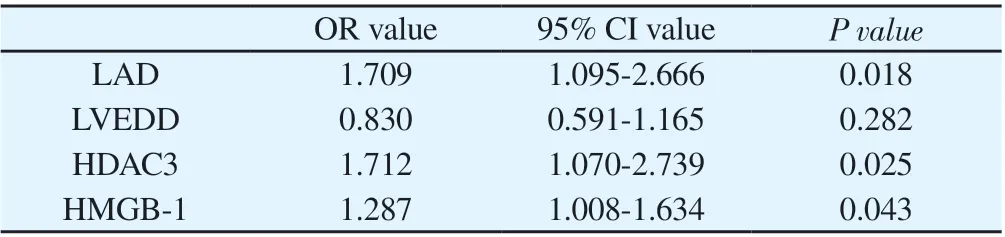
Table 4 Multivariate binary Logistic regression analysis of atrial fibrillation
4. Discussion
Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia in clinical practice, and its prevalence and incidence are increasing year by year. It can lead to ischemic stroke, systemic arterial embolism, heart failure and other hazards, seriously threatening human health [1] . In view of the unclear pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation, there are many difficulties in the clinical treatment of atrial fibrillation. Electrical remodeling and structural remodeling are currently considered to be an important pathological basis for its occurrence and development.Anything that can affect any of the above links can provide a pathological basis for the occurrence of atrial fibrillation, and the two can aggravate each other to form a vicious circle and eventually lead to the progression of the disease [28 ] . At present, early electrical remodeling can be improved by radiofrequency ablation and other methods, but there is currently no effective treatment for structural remodeling, which also brings difficulties to postoperative recurrence and treatment . Indicators of progress are particularly important.
HDAC3 belongs to the class I histone deacetylase. Recently, a large number of literatures [ 8-11 ] reported that HDAC3 is closely related to the occurrence and development of cardiovascular diseases. It affects the function of cardiomyocytes and energy metabolism through deacetylation . Important regulator of cardiovascular disease. Studies have found that both actin and fibrillin are the substrates of HDAC3-induced deacetylation. HDAC3 can regulate the deacetylation of myosin heavy chain , which can deteriorate myocardial contractility and lead to the remodeling of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy structure ; HDAC3 can directly It interacts with actinbinding protein (CapZ β1 ) and myofibrils in cardiomyocytes,directly induces cardiac hypertrophy , and is closely related to the occurrence of heart failure [ 29 ] . Risebro [ 13-15 ] et al. found that HDAC3 is involved in the regulation of sodium calcium exchanger( NCX ), which is related to maintaining the balance of Ca2+inside and outside myocardial cells and myocardial mitochondria.Overexpression of HDAC3 can increase the concentration of intramyocardial Ca2+ In addition, HDAC3 has been confirmed to be involved in the regulation of myocardial metabolic remodeling , and regulate myocardial fatty acid metabolism through the interaction with Krüppel -like factor (KLF5) . KLF5 is a transcriptional regulator of peroxidase-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α) cardiac energetics, and overexpression of HDAC 3 inhibits KLF5-dependent activation of endogenous downstream fatty acid metabolism-related genes , resulting in fatty acid uptake, fatty acid Oxidation and electron transport/oxidative phosphorylation disorders eventually lead to myocardial energy supply disorders, remodeling and fibrosis[ 30 ] . In this experiment , it was found that HDAC3 in the atrial fibrillation group was significantly higher than that in the control group, suggesting that the overexpression of HDAC3 may be related to the occurrence of atrial fibrillation; the internal reason may be that the overexpression of HDAC3 interferes with the calcium ion balance and energy metabolism in cardiomyocytes , make the electrical activity and structure of cardiomyocytes related to it abnormal, and provide the pathological basis for the occurrence of atrial fibrillation. In addition, in the comparison of different types of atrial fibrillation groups, we found that with the progression of atrial fibrillation , the levels of HDAC3, LAD, and LVEDD gradually increased, and HDAC3 was positively correlated with LAD and LV EDD , which was consistent with the results of domestic and foreign studies. These findings suggest that HDAC3 may be involved in the progression of atrial fibrillation by mediating structural remodeling in patients with atrial fibrillation. Studies have shown that HDAC3 can promote myocardial cell proliferation and hypertrophy by inhibiting cell cycle-dependent protein kinase inhibitors (Cdkn1a,Cdkn2a, Cdkn1b), leading to myocardial remodeling [31] .
HMGB-1 is a non-histone nuclear protein that exists both inside and outside cells. Extracellular HMGB-1 is mainly passively released by necrotic tissue or actively secreted by stressed cells , and has the activity of inflammatory factors , which can combine with different receptors to play a pro-inflammatory role [ 16 ] . Its main receptors include Toll-like receptors (Toll-like receptors, TLR) and receptors for advanced glycation end products ( Receptor for advanced glycation end products, RAGE ), etc. [ 17,18 ] . HMGB-1 binds to TLR-2 and activates α-smooth muscle actin (SMA), downstream mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK ), transforming growth factor (TGF-β) and collagen (type I and type III), which are involved in regulating the proliferation and activity of cardiac fibroblasts , ultimately leading to cardiomyocyte inflammation and fibrosis [ 32 ] . In addition , HMGB-1 binds to RAGE and activates the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which can lead to cardiomyocyte inflammation, fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction [33-35 ] . The binding of HMGB-1 to the receptor TLR-4 increases the expression of apoptotic proteins and caspase-3, and reduces the antifibrotic/anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-33, resulting in the formation of cardiomyocyte apoptosis and fibrosis [20] . In this study , the level of HMGB-1 in patients with atrial fibrillation was significantly higher than that in the control group , indicating that there may be a certain correlation between the elevated level of HMGB-1 and the occurrence of atrial fibrillation ; Its levels increased sequentially ,suggesting that HMGB-1 may be associated with the development of atrial fibrillation. And HMGB-1 is positively correlated with LAD and LVEDD , suggesting that HMGB1 may be related to myocardial structural remodeling in atrial fibrillation , which is consistent with the research results at home and abroad. The binding of receptors such as TLR and RAGA induces myocardial inflammation,promotes myocardial fibrosis, and induces myocardial apoptosis,etc., and finally causes the abnormality of myocardial cells in terms of tissue structure and ultra-microscopic structure, and then causes myocardial cell electrical remodeling or structural remodeling. ,provides a pathological basis for the occurrence and progression of atrial fibrillation. In addition , this experiment found that there is a positive correlation between the serum concentrations of HDAC3 and HMGB - 1, indicating that the two have a synergistic effect in the occurrence and development of atrial fibrillation, which may be related to the regulation of apoptosis by the two. The release of HMGB - 1 inhibits apoptosis-related pathways [ 36 ] . Finally, binary logistic regression analysis showed that HDAC3, HMGB-1, and LAD were independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation, and could be used as influencing factors for predicting atrial fibrillation .
In conclusion , the detection of HDAC3 and HMGB-1 is very helpful for exploring the pathogenesis and disease progression of atrial fibrillation, and may provide a new direction for the clinical treatment and prognosis improvement of atrial fibrillation in the future . In addition, in addition to the above research results, this experiment has the following shortcomings and considerations.The number of case samples collected in this study is limited, and a sufficient number of samples are still needed for verification ; this study is a retrospective study and cannot be carried out on the same individual. The values of HDAC3 and HMGB-1 in each stage of the disease process node are continuously detected, so it is necessary to further improve the prospective clinical trial research.
Author's contribution
Gao Dasheng and Kang Pinfang are responsible for proposing research topics, designing research plans, providing research funding, and guiding support; Sun Chuan, Xu Ning, and Gao Qi are responsible for implementing the research process, collecting and arranging data; Sun Chuan is responsible for arranging literature,designing Thesis framework, drafting thesis; Gao Dasheng, Kang Pinfang, Sun Chuanqi, Yao Zhuoya revised thesis and final review.
Conflict of interest statement There is no conflict of interest for investigators, ethics committee members, subject guardians, and disclosure of research results in this study.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年13期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年13期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Study on key genes and pathways of myocardial fibrosis and prediction of effective traditional Chinese medicine
- Study on the clinical correlation between serum total IgE level and peripheral blood eosinophil count in patients with eczema
- Effect of Qingguangan Ⅱ on Rho/ROCK associated factors in the retina of DBA/2J mice
- Clinical effect of governor meridian moxibustion on treatment of lumbar disc protrusion: A meta analysis
- Effect of HK3 on immune invasion, proliferation and invasion of colon cancer cells
- Canagliflozin attenuates hypertension induced myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis via RAS and TGF-β1/Smad pathway
