The mechanism behind activation of the Nod-like receptor family protein 3 inflammasome in Parkinson’s disease
Jing Wang ,Xiao-Na Zhang ,Jin-Ni Fang ,Fei-Fei Hua ,Jing-Yang Han,Zeng-Qiang Yuan,An-Mu Xie,
Abstract Previous studies have shown that the ATP-P2X4 receptor signaling pathway mediates the activation of the Nod-like receptor family protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome.The NLRP3 inflammasome may promote renal interstitial inflammation in diabetic nephropathy.As inflammation also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease,we hypothesized that the ATP-P2X4 receptor signaling pathway may activate the NLRP3 inflammasome in Parkinson’s disease.A male rat model of Parkinson’s disease was induced by stereotactic injection of 6-hydroxydopamine into the pars compacta of the substantia nigra.The P2X4 receptor and the NLRP3 inflammasome (interleukin-1β and interleukin-18) were activated.Intracerebroventricular injection of the selective P2X4 receptor antagonist 5-(3-bromophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzofuro[3,2-e]-1,4-diazepin-2-one (5-BDBD) or knockdown of P2X4 receptor expression by siRNA inhibited the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and alleviated dopaminergic neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation.Our results suggest that the ATP-P2X4 receptor signaling pathway mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation,dopaminergic neurodegeneration,and dopamine levels.These findings reveal a novel role of the ATP-P2X4 axis in the molecular mechanisms underlying Parkinson’s disease,thus providing a new target for treatment.This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Qingdao University,China,on March 5,2015 (approval No.QYFYWZLL 26119).
Key Words:ATP;neurodegenerative disorder;neuroinflammation;neuroinflammatory response;NLRP3;P2X4;Parkinson’s disease
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second-most-common progressive neurodegenerative disorder (Moon and Paek,2015).Although the exact mechanisms underlying PD remain unknown,inflammatory factors are critical determinants of PD onset (Forloni et al.,2021;Martin-Bastida et al.,2021).Accordingly,the role of inflammatory signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of PD has become a focus of recent research.Secretion of inflammatory molecules and degeneration of dopaminergic neurons are regulated by inflammatory pathways and may influence the development of PD (Lee et al.,2021).Therefore,a better understanding of the pathways underlying PD pathogenesis will facilitate the development of novel neuroprotective strategies.
The P2X4 receptor (P2X4R),a ligand-gated ion channel that is part of the ionotropic purinergic P2X receptor (P2XR) family,is sensitive to ATP and functions as a nonselective cation channel to permit Na+,K+,and Ca2+fluxes (Burnstock,2015;Zhang et al.,2020).Extracellular ATP is widely recognized as an exclusive neurotransmitter or an important coneurotransmitter in most nerve types.P2X4R was the first P2X receptor identified in the central nervous system (CNS)(Antonioli et al.,2019).Along with P2X1R and P2X6R,it is among the most widely expressed ATP-gated purinergic receptor in most neurons and glial cells (Burnstock et al.,2011).P2X4 regulates microglial cell activation and migration at a site of injury (Trang et al.,2020).Microglia regulate cytokine production and inflammatory processes in the brain(Duveau et al.,2020).Elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines typically define a state of neuroinflammation(González et al.,2014).Some neurodegenerative diseases are associated with neuroinflammation,in which microglia play a central role (Mehrabadi and Sadr,2020;Rivers-Auty et al.,2021).In patients with PD,P2X4R may exacerbate inflammation in the CNS by regulating microglial pathways(Liu et al.,2013).The ATP-P2X4R signaling axis mediates activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.Extracellular ATP mediates the inflammatory responses and activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via P2X7R and P2X4R (Chen et al.,2018).
The NLRP3 inflammasome is composed of NLRP3,procaspase-1,and apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain-containing protein(Malhotra et al.,2020;Wani et al.,2021).It senses danger signals including lipopolysaccharides and high glucose levels and then triggers the inflammatory cascade,resulting in the cleavage of procaspase-1 and the activation of interleukin (IL)-1β,IL-18,and IL-33 (Piccini et al.,2008;Jiang et al.,2021).
The NLRP3 inflammasome plays an important role in the molecular mechanisms underlying many inflammatory diseases,including diabetes,Alzheimer’s disease,arteriosclerosis,and gout (Tan et al.,2013;Holbrook et al.,2021).The inflammasome may also contribute to renal interstitial inflammation in diabetic nephropathy (Chen et al.,2013).Dopamine may exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting NLRP3 (Yan et al.,2015).Because inflammatory factors play a crucial role in the onset of PD,NLRP3 activation is very likely to participate in PD pathogenesis (Mao et al.,2017).Therefore,we hypothesized that the ATP-P2X4R axis mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in PD.The present study was performed to verify this hypothesis.
Materials and Methods
Experimental animals
Two hundred and forty adult male Wistar rats of 40–50 days of age (specific-pathogen-free,weighing 180–200 g) were obtained from the Qingdao Experimental Animal Center,Qingdao,China (license No.SCXK (Lu) 2014-0001).This study adhered to the principles of the Basel Declaration and to the recommendations of the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals(NIH publication No.8023).The protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Qingdao University,China(approval No.QYFYWZLL 26119) on March 5,2015.Isoflurane(MilliporeSigma,St.Louis,MO,USA) was used to anesthetize animals via inhalation.
Experimental design and procedures
Experiment I
Rats were divided randomly into four treatment groups (n=20 in each group;Figure 1).Control group:after 1 week of pretreatment with 0.9% physiological saline,we injected 0.02% ascorbic acid into the substantia nigra pars compacta(SNpc) stereotactically;6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) group:after 1 week of pretreatment with 0.9% physiological saline,we injected 6-OHDA into the SNpc stereotactically to establish PD;5-(3-bromophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzofuro[3,2-e]-1,4-diazepin-2-one (5-BDBD) group:after 1 week of pretreatment with 5-BDBD (a selective P2X4R antagonist),we injected ascorbic acid into the SNpc stereotactically;and 5-BDBD +6-OHDA group:after 1 week of pretreatment with 5-BDBD,we injected 6-OHDA into the SNpc stereotactically.
Experiment II
Rats were divided randomly into eight treatment groups (n=20 in each group;Figure 1).Control group:after 1 week of pretreatment with 0.9% physiological saline,we injected 0.02%ascorbic acid into the SNpc stereotactically;6-OHDA group:after 1 week of pretreatment with 0.9% physiological saline,we injected 6-OHDA into the SNpc stereotactically to establish PD;P2X4R-NC group:after 1 week of pretreatment with a negative control lentivirus (NC),we injected 0.02% ascorbic acid into the SNpc stereotactically;P2X4R-NC+6-OHDA group:after 1 week of pretreatment with the negative control lentivirus,we injected 6-OHDA into the SNpc stereotactically;P2X4R-RNA group:after 1 week of pretreatment with a lentivirus carrying P2X4R,we injected 0.02% ascorbic acid into the SNpc stereotactically;P2X4R-RNA+6-OHDA group:after 1 week of pretreatment with a lentivirus carrying P2X4R,we injected 6-OHDA into the SNpc stereotactically;P2X4R-siRNA group:after 1 week of pretreatment with a lentivirus carrying small-interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting P2X4R,we injected 0.02% ascorbic acid into the SNpc stereotactically;P2X4RsiRNA+6-OHDA group:after 1 week of pretreatment with the lentivirus carrying siRNA targeting P2X4R,we injected 6-OHDA into the SNpc stereotactically.
Intracerebroventricular injection of 5-BDBD
Each rat was slowly injected,over 4 minutes,with 10µg of 5-BDBD (MilliporeSigma) dissolved in 2 µL of 0.9%physiological saline into the left lateral ventricle,determined according to the stereotactic coordinates calculated using the rat brain atlas,The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates,7thedition (Paxinos and Watson,2013):posterior of anterior fontanel,–0.9 mm;mediolateral,–1.5 mm;dorsoventral,3.5 mm.After daily injections for 1 week,the animals were injected every other day for 2 weeks.Rats in the control and 6-OHDA groups in Experiment I were stereotactically injected with 2 µL of 0.9% physiological saline.
Pretreatment with lentiviral vectors carrying P2X4R or siRNA targeting P2X4R
Rats received injections (2 µL) of a lentivirus carrying P2X4R,lentivirus carrying siRNA targeting P2X4R,or a negative control (Shanghai GeneChem Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai,China) into the SNpc according to the following stereotactic coordinates:posterior of anterior fontanel,–5 mm;dorsoventral,7.7 mm;mediolateral,–2.1 mm.Rats in the control and 6-OHDA groups in Experiment II were stereotactically injected with 2 µL of 0.9%physiological saline.
6-OHDA lesions
One week after lentivirus pretreatment,8 µg of 6-OHDA(MilliporeSigma) dissolved in 2 µL of 0.02% ascorbic acid(MilliporeSigma) was injected into the SNpc stereotactically to establish PD (Bigham et al.,2021).Rats in the control,5-BDBD,and P2X4R-NC groups were injected with the same volume (2µL) of 0.02% ascorbic acid.
Behavioral test
PD model rats were injected with apomorphine(MilliporeSigma;0.5 mg/kg,intraperitoneally) on day 14 after surgery and placed in stainless steel bowls.The number of rotation cycles in 30 minutes was recorded.The rate for PD rats should be >7 rotations/min (Liu et al.,2018) (Results are shown inAdditional Table 1).
Immunofluorescence staining
Four weeks after surgery,five rats in each group were deeply anesthetized intraperitoneally with ethyl carbamate(Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co.Ltd.,Shanghai,China) and perfused transcardially with 4% paraformaldehyde.Each rat’s brain was removed and post-fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 hours.Next,we dehydrated the brain tissue with a sucrose gradient at 4°C.We created continuous coronal sections(20 µm) through the SNpc using a freezing cryostat (Leica Biosystems,Nussloch,Germany).The sections were kept freefloating in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).We incubated the sections with an anti-tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) antibody(rabbit,1:2000,Cat # 58844S;Cell Signaling Technology,Danvers,MA,USA).The sections were shaken at 4°C overnight and then washed with 0.05% Tween-20 in PBS thrice.The sections were incubated with a secondary antibody (rabbit,1:1000,Cat # 4413;Cell Signaling Technology),shaken at room temperature for 2 hours,and washed thrice with 0.05%Tween-20 in PBS.The sections were placed on glass slides,sealed with 70 g/L glycerophosphate buffer,and rinsed with distilled water.We analyzed every sixth section for a total of 20 sections.We counted the TH-positive neurons in the SNpc of these slices under a fluorescence microscope (Axio Imager,LSM 800;Carl Zeiss Meditec AG,Jena,Germany).
Western blot assay
Four weeks after surgery,eight rats in each group were deeply intraperitoneally anesthetized with ethyl carbamate,and the SNpc of the left brain was separated.Tissues were homogenized in 200 µL of lysis buffer containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Roche,Basel,Switzerland).The homogenates were centrifuged at 13,000 ×gat 4°C for 5 minutes.A bicinchoninic acid colorimetric protein assay kit(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA) was used to analyze protein concentrations in the supernatants.Protein samples were homogenized with 20% 5× loading buffer,boiled for 10 minutes,and stored at–80°C.
Total protein (20 µg) was separated on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels and transferred electrophoretically to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Roche).The membranes were blocked in 5% non-fat dried milk at room temperature for 1 hour and incubated with primary antibodies against P2X4R (rabbit,1:400,Cat# APR-002;Alomone Labs,Jerusalem,Israel),NLRP3 (rabbit,1:1000,Cat# 13158;Cell Signaling Technology),caspase-1 (rabbit,1:500,Cat# 3866;Cell Signaling Technology),IL-1β (rabbit,1:2000,Cat# 12703;Cell Signaling Technology),IL-18 (rabbit,1:1000,Cat# 54943;Cell Signaling Technology),and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH;rabbit,1:1000,Cat# 5174;Cell Signaling Technology) at 4°C overnight.The membranes were washed with 0.05% Tween-20 in PBS and incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated IgG (rabbit,1:2000,Cat# 7074;Cell Signaling Technology) at room temperature for 1 hour.Immunoreactive proteins were visualized using an enhanced luminescence reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific).The net absorbance value for the target bands was analyzed using a gel image processing system (Liaoning Saias Technology Co.Ltd.,Shenyang,China).Protein expression levels were calculated as the optical density ratio of target protein to GAPDH protein.
Quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction
Four weeks after surgery,seven rats in each group were deeply intraperitoneally anesthetized with ethyl carbamate,and the SNpc of the left brain was separated.Tissues were homogenized and total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Takara Bio Inc.,Shiga,Japan).Total RNA was reverse transcribed into first-strand cDNA using a reverse-transcription reagent kit (Takara Bio) in accordance with the manufacturer’s procedure.Quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction was performed using the SYBR Green fluorescent dye (Takara Bio) methodology.The following primers (synthesized by the BGI Group,Beijing,China)specifically targeting rat genes were used.P2X4Rforward,5′-TTA CAA TGC TCA AAC GGA TCC C-3′;P2X4Rreverse,5′-GGA TAC CCA TGA TGC CTC CC-3′ (207 bp).NLRP3forward,5′-TTG GCT GCG GAT GGA ATT T-3′;NLRP3reverse,5′-TCT CGC AGT CCA CCT TCT-3′ (133 bp).Caspase-1forward,5′-CCA ATA ATG AAA ACA CCC ACT CGT-3′;Caspase-1reverse,5′-CAC AGT ATA CCC CAG ATC CTG CA-3′ (141 bp).IL-1βforward,5′-TGA TGA CGA CCT GCT AGT GTG TG-3′;IL-1βreverse,5′-TGT TGG CTT ATG TTC TGT CCA TTG-3′ (141 bp).IL-18forward,5′-TTC AGA AAC GTG TGC CAG GAC-3′;IL-18reverse,5′-ACG AGT TTG AAA GCA TCA TCT TCC-3′ (103 bp).Gapdhforward,5′-TGG CCT TCC GTG TTC CTA C-3′;Gapdhreverse,5′-GAG TTG CTG TTG AAG TCG CA-3′ (191 bp).
The quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction mixture (20 µL) contained RNase-free water,7.6 µL;SYBR Advantage qPCR Premix (Takara Bio),10 µL;forward primer,0.4 µL;reverse primer,0.4 µL;cDNA,1.6 µL.Thermal cycling conditions were pre-denaturation at 95°C for 10 minutes,followed by 45 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 seconds,and annealing at 60°C for 1 minute.Target gene expression was expressed relative to Gapdh expression.
Statistical analysis
Differences between group means were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test using GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software,San Diego,CA,USA).P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Effect of 5-BDBD on the number of TH-positive neurons in the SNpc
There were significantly fewer TH-positive neurons in the 6-OHDA and 5-BDBD+6-OHDA groups compared with the 5-BDBD and the control groups (allP<0.01).Compared with the 6-OHDA group,the quantity of TH-positive neurons increased significantly in the 5-BDBD+6-OHDA group (P<0.01).There were no significant differences in the number of TH-positive neurons in the 5-BDBD group compared with the control group (P>0.05;Figure 2).
Effect of 5-BDBD on inflammatory-and apoptosis-related mRNA and protein expression in the SNpc
We investigated the effect of 5-BDBD on the mRNA and protein expression levels of P2X4,NLRP3,caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 in the SNpc.The mRNA and protein levels of P2X4,NLRP3,caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 were significantly higher in the 6-OHDA and 5-BDBD+6-OHDA groups than the control and 5-BDBD groups (allP<0.01).The mRNA and protein levels of P2X4,NLRP3,caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 were significantly lower in the 5-BDBD+6-OHDA group than the 6-OHDA group(P<0.01).There were no significant statistical differences in P2X4 mRNA and protein expression between the control and 5-BDBD group (P>0.05;Figure 3andTable 1).

Table 1|Effect of 5-BDBD on the mRNA levels of P2X4R,NLRP3,caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 in the substantia nigra pars compacta
Effect of P2X4R overexpression and silencing on the number of TH-positive neurons in the SNpc
The numbers of TH-positive neurons were significantly lower in the 6-OHDA,P2X4R-NC+6-OHDA,P2X4R-RNA+6-OHDA,and P2X4R-siRNA+6-OHDA groups compared with the control,P2X4R-NC,P2X4R-RNA,and P2X4R siRNA groups (allP<0.01).Compared with the P2X4R-NC+6-OHDA group,there were significantly fewer TH-positive neurons in the P2X4R-RNA+6-OHDA group (P<0.01) and significantly more TH-positive neurons in the P2X4R-siRNA+6-OHDA group (P<0.01).There were no significant differences between the control and P2X4R-NC groups (P>0.05;Figures 4and5).
Effect of P2X4R overexpression and silencing on inflammatory-and apoptosis-related gene and protein expression levels in the SNpc

Table 2|Effect of the lentivirus carrying P2X4R on the mRNA levels of P2X4R,NLRP3,Caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 in the substantia nigra pars compacta

Table 3|Effect of the lentivirus carrying small interfering RNA for P2X4R on the mRNA levels of P2X4R,NLRP3,Caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 in the substantia nigra pars compacta
NLRP3,caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 protein levels were significantly higher in the 6-OHDA,P2X4R-NC+6-OHDA,P2X4R-RNA+6-OHDA,and P2X4R-siRNA+6-OHDA groups compared with the control,P2X4R-NC,P2X4R-RNA,and P2X4R siRNA groups (P<0.01).NLRP3,caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 protein levels were significantly higher in the P2X4R-RNA +6-OHDA group (P<0.01) and significantly lower in the P2X4RsiRNA+6-OHDA group (P<0.01).There were no significant differences in the expression of NLRP3,caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 proteins between the control and P2X4R-NC groups (P>0.05;Figures 6and7).
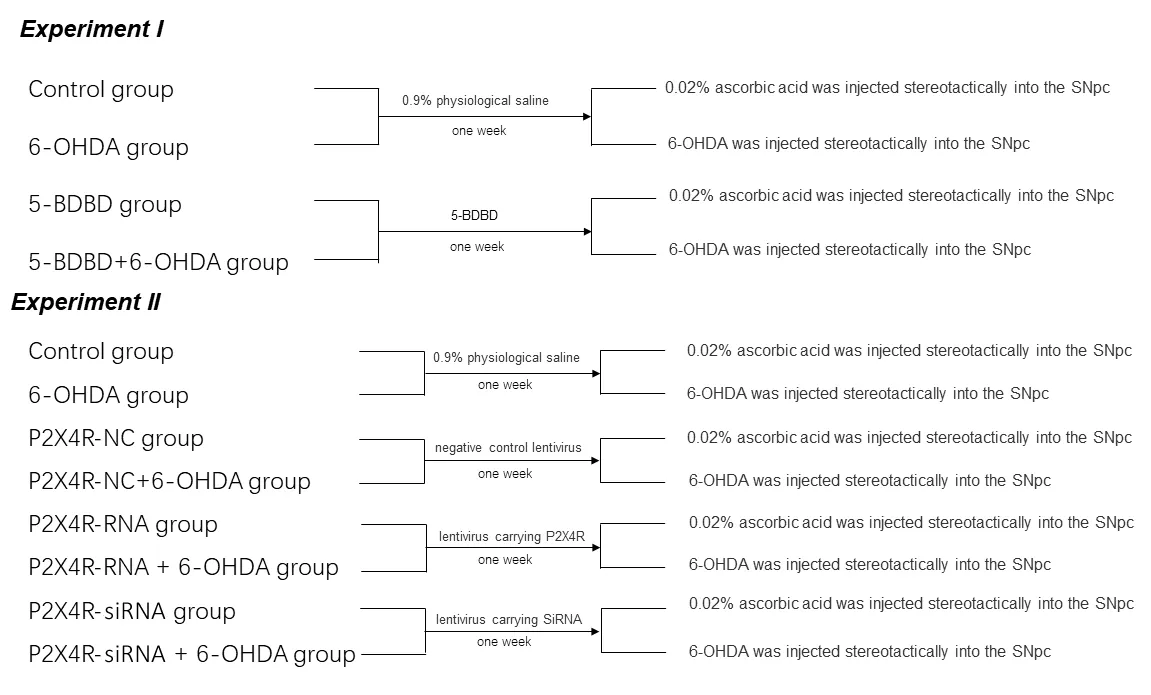
Figure 1|The study groups and interventions.

Figure 2|Effect of 5-BDBD on the number of tyrosine hydroxylasepositive neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.
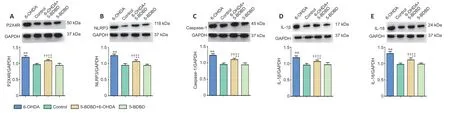
Figure 3|Effect of 5-(3-bromophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzofuro[3,2-e]-1,4-diazepin-2-one (5-BDBD) on the protein expression of P2X4R (A),NLRP3 (B),caspase-1 (C),IL-1β (D),and IL-18 (E) in the substantia nigra pars compacta.
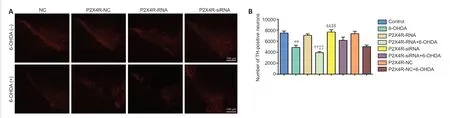
Figure 4|Effect of P2X4R overexpression and silencing on the number of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.

Figure 5|Distribution of the lentivirus in tyrosine hydroxylase-positive neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta in P2X4R-RNA and P2X4R-siRNA groups.
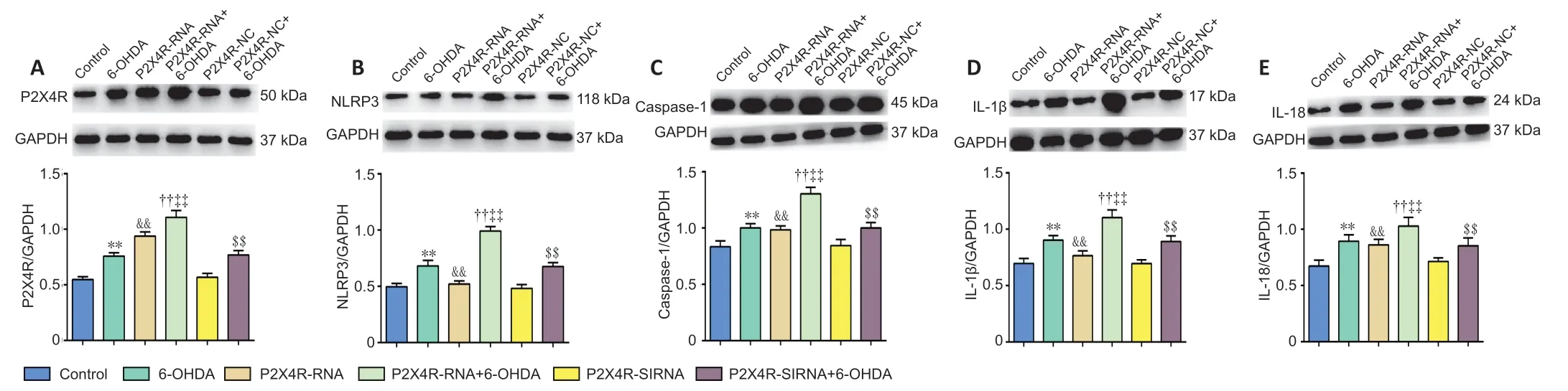
Figure 6|Effect of a lentivirus carrying P2X4R on the protein expression levels of P2X4R (A),NLRP3 (B),caspase-1 (C),IL-1β (D),and IL-18 (E) in the substantia nigra pars compacta.

Figure 7|Effect of the lentivirus carrying siRNA for P2X4R on the protein expression levels of P2X4R (A),NLRP3 (B),caspase-1 (C),IL-1β (D),and IL-18 (E)in the substantia nigra pars compacta.
Discussion
Neuroinflammation is critical for the onset of PD (Pradhan and Andreasson,2013).Microglial cells are central mediators of inflammatory effects in the brain and are regarded as stationary macrophages in the CNS;they derive from the yolk sac and are associated with myeloid immune cells(González et al.,2014).Extracellular ATP,an important signaling molecule,is mainly released by injured neurons or glial cells.ATP initiates a purinergic signaling pathway by binding to purinergic receptors and participates in the physiological or pathological processes of the nervous system(Bours et al.,2011).Purinergic signaling plays an important role in neuroimmune-related inflammation (Di Virgilio et al.,2009).The purinergic receptor family can be divided into two classes:P1 and P2 nucleotide receptors.P2 is further divided into P2X and P2Y.P2X receptors are mainly involved in pathological processes such as CNS injury,immune inflammation,metabolic disorders,and neurodegeneration(Köles et al.,2011).P2X4R was the first P2XR identified in the CNS and is expressed frequently on neurons and glial cells;it plays an important part in the modulation of synaptic transmission and exchange between CNS neurons and neighboring glial cells (Burnstock,2015).The molecular mechanism of P2X4R in microglial cells has had increasing attention over the last ten years,and it may regulate microglial cell activation and migration.Activated microglia play an important role in the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as PD.Therefore,P2X4R may contribute to the molecular mechanisms of these diseases by exacerbating inflammation in the CNS (Hirsch et al.,2012).We found that the mRNA and protein levels of P2X4R expression were upregulated in the rat model of PD,which we induced by 6-OHDA stereotactic injection.In line with our findings,P2X4R was also upregulated in the microglial cells of the CNS in an animal model of multiple sclerosis,and genes encoding P2X4R were upregulated in PC12 cells treated with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine for PD induction (Hracskó et al.,2011).
The NLRP3 inflammasome is an innate immune system complex activated by a variety of danger signals and is mainly expressed by myeloid cells.It consists of three main effectors:NLRP3,procaspase-1,and the apoptosis speck-like protein(Zahid et al.,2019).Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway is increasingly considered to be the basis of a variety of many inflammatory diseases.The mechanism underlying its activation is not fully understood,but the purinergic receptors P2X4 and P2X7 and damage-associated molecular patterns,such as ATP release,are involved (Chen et al.,2013).The NLRP3 inflammasome mediates the aggregation of caspase-1,which converts IL-1β into a mature form with biological activity (Juliana et al.,2012).Furthermore,IL-18 is significantly upregulated after NLRP3 inflammasome activation (Juliana et al.,2012).Therefore,we hypothesized that upregulation of the downstream signaling components of the NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to the pathogenesis of PD.Our data demonstrate that NLRP3 inflammasome components,including IL-1β and IL-18,are activated in PD-induced rats.The levels of P2X4R,NLRP3,caspase-1,IL-1β,and IL-18 were significantly increased in PD-induced rats overexpressing P2X4R and were significantly decreased in PD-induced rats treated with the selective P2X4R antagonist 5-BDBD and in P2X4R-knockdown rats.
Our study has some limitations.First,inflammasome activation in rat models of PD is not exactly equivalent to human brains,and more experiments are needed to investigate inflammasome activation in humans.Second,our current understanding of the potential beneficial effects of antagonizing P2X4R signaling is limited.We will continue to study the potential beneficial effects of antagonizing P2X4R signaling with the aim of attenuating neuropathological and behavioral impairment of PD-induced rats.
Based on our results,we conclude that ATP-P2X4R signaling mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation,resulting in CNS inflammation in a 6-OHDA-induced rat model of PD.In a wider perspective,we found that the ATP-P2X4R axis mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation to regulate glial cell activation,dopaminergic neurodegeneration,and dopamine levels.These findings reveal novel roles for the ATP-P2X4R axis in the pathogenesis of PD and provide new therapeutic targets for the disease.
Acknowledgments:We are grateful to the Central Laboratory of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University for providing experimental support and technical guidance.
Author contributions:Study design and manuscript draft:JW‚XNZ;experiment implementation and data acquisition:FFH‚JNF;data analysis:JYH‚ZQY;manuscript review:AMX.All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
For the first time she succeeded well, for the people were glad to buy the woman s wares27 because she was good-looking, and they paid her what she asked; many even gave her the money and left the pots with her as well. So they lived on what she had earned as long as it lasted, then the husband bought a lot of new crockery. With this she sat down at the corner of the market-place, and set it out round about her ready for sale. But suddenly there came a drunken hussar28 galloping23 along, and he rode right amongst the pots so that they were all broken into a thousand bits. She began to weep, and did now know what to do for fear. Alas! what will happen to me? cried she; what will my husband say to this?
Conflicts of interest:The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Financial support:This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China‚No.81971192 (to AMX).The funding source had no role in study conception and design‚data analysis or interpretation‚paper writing or deciding to submit this paper for publication.
Institutional review board statement:The study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Qingdao University‚China (approval No.QYFYWZLL 26119) on March 5‚2015.
Copyright license agreement:The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by all authors before publication.
Data sharing statement:Datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Plagiarism check:Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review:Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement:This is an open access journal‚and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License‚which allows others to remix‚tweak‚and build upon the work non-commercially‚as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
Open peer reviewers:Jeffrey Schweitzer‚Massachusetts General Hospital‚USA;Robert L.Haining‚Georgia Gwinnett College‚USA.
Additional files:
Additional file 1:Open peer review reports 1 and 2.
Additional Table 1:Results of the rotation of Parkinson’s disease model rats.
- 中国神经再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Towards a comprehensive understanding of p75 neurotrophin receptor functions and interactions in the brain
- Microglia regulation of synaptic plasticity and learning and memory
- Stroke recovery enhancing therapies:lessons from recent clinical trials
- Functional and immunological peculiarities of peripheral nerve allografts
- MicroRNA expression in animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and potential therapeutic approaches
- Significance of mitochondrial activity in neurogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases