APOE4 expression is associated with impaired autophagy and mitophagy in astrocytes
Schmukler Eran,Pinkas-Kramarski Ronit
Among the risk factors for late onset sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the expression of ε4 allele of apolipoprotein E (APOE4)gene (Mahley et al.,2006).Elevated amyloid processing and reduced degradation of Aβ,which lead to Aβ plaque deposition,are evident inAPOE4-positive AD patients and mice (Mahley et al.,2006).These features correlate with neuronal cell loss.Impaired mitochondrial activity and increased oxidative stress have long been recognized as additional hallmarks of AD pathology (Mahley et al.,2006).The effect ofAPOE4expression on autophagy and mitochondrial dynamics and activity in astrocytes is discussed in this perspective and is summarized inFigure 1.
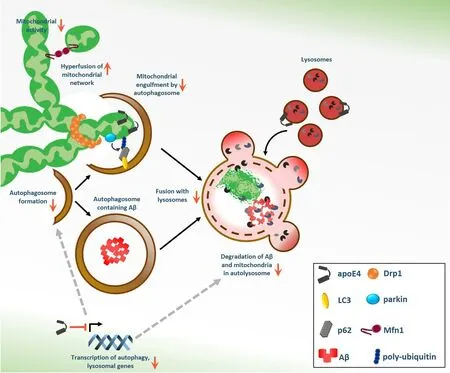
Figure 1|Schematic presentation of the effect of APOE4 on various aspects of autophagy,mitophagy and mitochondrial dynamics.
Impaired autophagy andAPOE4are both strongly associated with AD,and the possibility that the pathological effects ofAPOE4in AD,especially in the context of Aβ clearance,are related to autophagy was recently investigated (Simonovitch et al.,2016).Astrocytes have major protective roles under neuro-pathological conditions,such as neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration.Autophagy also acts as a protective mechanism,keeping cell homeostasis and promote survival under stress conditions (Klionsky and Emr,2000).Therefore,the effects ofAPOE3andAPOE4expression on autophagy in astrocytes under resting and stimulating conditions were determined,as well as the effect ofAPOE4on beta-amyloid plaques clearance and digestion (Simonovitch et al.,2016).In these astrocytes,autophagy was found to be defective at the initiation step(autophagosome formation) and at the cargo degradation step.TheAPOE4-expressing astrocytes were also impaired in the uptake of soluble Aβ and in the ability to clear insoluble Aβ plaques from brain sections of 5xFAD mice,compared to astrocytes expressingAPOE3(Simonovitch et al.,2016).Chloroquine,an inhibitor of autophagosomelysosome fusion,abolished the clearance of Aβ plaques by theAPOE3astrocytes,while rapamycin,an autophagy inducer,enhanced plaques removal byAPOE4astrocytes.These results pointed a possible link between autophagy and Aβ clearance.Importantly,additional studies demonstrated thatAPOE4expression may be associated with impaired autophagy,especially in astrocytes(Parcon et al.,2017).Parcon et al.(2017)have shown thatAPOE4AD patients exhibit lower brain mRNA levels of the autophagic proteins LC3 and p62,as well as of the lysosomal glycoprotein LAMP2.Consistently,mRNA levels of LC3,p62 and LAMP2 were upregulated following starvation-induced autophagy inAPOE3-expressing but not inAPOE4-expressing human glioblastoma cells and this upregulation was accompanied by clearance of protein aggregates (Parcon et al.,2017).Also,the autophagy inducer rapamycin was found to reduce learning impairment inAPOE4mice (Lin et al.,2017).The downregulation of autophagy byAPOE4may involve several mechanisms.Parcon et al.(2017) have suggested that apoE4 downregulates autophagy by acting as a transcriptional repressor of autophagic/lysosomal genes,which are normally upregulated by the transcription factor TFEB.Alternatively,the deleterious effect of apoE4 on autophagy may be due to its interaction and disruption of lysosome/autophagosome membranes disruption.
Since autophagy plays a key role in the clearance of redundant and damaged organelles including mitochondria (a process known as mitophagy),the effect ofAPOE4expression on mitochondrial dynamics was subsequently examined (Simonovitch et al.,2019;Schmukler et al.,2020).UsingAPOE3andAPOE4targeted replacement mice,the mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy related proteins expression was determined in brain sections and homogenates(Simonovitch et al.,2019).The levels of the mitochondrial fusion protein Mfn1 were higher,whereas the mitochondrial fission protein Drp1 were lower in theAPOE4brains indicating increased mitochondrial fusion and decreased fission.APOE4-dependent decrease in Drp1 was also observed in brain homogenates of AD patients (Simonovitch et al.,2019).In agreement with these results,altered mitochondrial dynamics inAPOE4-expressing astrocytes,including changes in the synthesis,mitochondrial recruitment,ubiquitination and degradation of proteins involved in mitochondrial fission,fusion and mitophagy was recently demonstrated(Schmukler et al.,2020).Reduced mitochondrial fission was evident by lower levels of Drp1 protein and mRNA levels as well as its interaction with the mitochondria inAPOE4astrocytes.Additionally,it was demonstrated thatAPOE4-expressing astrocytes exhibit higher levels of Mfn1,which are driven by reduced proteasomal degradation,and may interfere with normal mitophagy (Schmukler et al.,2020).Taken together,these findings suggest thatAPOE4is associated with decreased mitochondrial fission and elevated mitochondrial fusion in astrocytes and possibly in other CNS cells.
Parkin labels mitochondria for mitophagy by ubiquitination of specific mitochondrial proteins.APOE4mice brains exhibited higher levels of parkin compared withAPOE3mice(Simonovitch et al.,2019),and,consistently,APOE4astrocytes displayed increased levels of total and mitochondrial parkin (Schmukler et al.,2020).These finding suggest that parkin recruitment to mitochondria is intact inAPOE4astrocytes and might indicate impaired degradation of mitochondrial parkin,leading to its accumulation.Indeed,in these astrocytes,reduced proteasomal and lysosomal turnover of parkin underlie increased parkin levels (Schmukler et al.,2020),which was shown to impede its activity and result in mitophagy impairment(Durcan et al.,2014).In addition,the interaction of the autophagic proteins LC3-II and p62 with the mitochondria,and the lysosomal degradation of mitochondrial LC3-II and p62 were reduced inAPOE4astrocytes.Mitophagy induction following mitochondrial damage (CCCP treatment) was also reduced inAPOE4,further indicating altered mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy deficiency.Indeed,the mitochondrial network ofAPOE4astrocytes was shown to be hyperfused and mitochondria fromAPOE4mice brain sections were more elongated compared withAPOE3(Simonovitch et al.,2019;Schmukler et al.,2020).In agreement,fibroblast from AD patients also exhibit elongated mitochondria,highly connected network and decreased Drp1 levels (Zhu et al.,2013).The mechanism by whichAPOE4affects mitochondrial dynamics is yet unclear and may involve a detrimental interaction of apoE4 itself with the mitochondria,as was shown in both astrocytes and neurons(Schmukler et al.,2020).Alternatively,apoE4 may affect mitochondrial dynamics indirectly,by interfering with the basic autophagy/lysosomal machineries as discussed above.
Balanced mitochondrial dynamics and mitochondrial degradation through m i to p h a g y i s re q u i re d fo r p ro p e r mitochondrial function under basal,as well under mitochondrial stress conditions.Thus,altered mitochondrial dynamics and impaired mitophagy inAPOE4astrocytes may affect their functionality.In fact,APOE4astrocytes exhibit mitochondrial dysfunction,as judged by decreased mitochondrial metabolism,reduced MMP and lower levels of ATP (Schmukler et al.,2020).Moreover,APOE4astrocytes display reduced cleavage and accumulation of PINK1,a kinase that recruits parkin to damaged mitochondria.This feature is another hallmark of mitochondrial dysfunction.The impaired mitophagy and reduced removal of damaged mitochondria,which presumably underliesAPOE4astrocytes mitochondrial dysfunction,could be partially corrected by mitophagy induction using rapamycin treatment(Schmukler et al.,2020).Therefore,rapamycin-induced mitophagy in theAPOE4astrocytes may mediate the removal of dysfunctional mitochondria.
In this context ofAPOE4,autophagy and mitochondrial dynamics/function,therapeutic approaches could be employed.For example,it will be intriguing to examine the effect of other autophagy inducers onAPOE4-related pathologyin vitroandin vivo.Similarly,the naturally occurring compounds,urolithin A and actinonin,which were shown to improve mitochondrial activity and to induce mitophagy (Ryu et al.,2016;Fang et al.,2019) might prove to be beneficial inAPOE4models of AD.In fact,both utolithin A and actinonin were shown to have a therapeutic potential in other models of AD.Finally,the effect of apoE4-targeted agents,such as CS-6253 and bexarotene (Boehm-Cagan et al.,2016),on autophagy/mitophagy and mitochondrial dynamics/function could also be examined to further substantiate the relationship between apoE4 and these cellular features.
Collectively,the studies reviewed here indicate that the pathological effects ofAPOE4include autophagy/mitophagy impairments and could pave the way for identification of novelAPOE4-related therapeutic targets.
- 中国神经再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Towards a comprehensive understanding of p75 neurotrophin receptor functions and interactions in the brain
- Microglia regulation of synaptic plasticity and learning and memory
- Stroke recovery enhancing therapies:lessons from recent clinical trials
- Functional and immunological peculiarities of peripheral nerve allografts
- MicroRNA expression in animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and potential therapeutic approaches
- Significance of mitochondrial activity in neurogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases