Visualization analysis of the international standard ISO/TC 249 for traditional Chinese medicine
ZHAO Shuting,ZHONG Ynmei,HU Yunzhng,SUN To,d,e,WU Chunjie,WEN Chunbio*
a. School of Intelligent Medicine,Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu,Sichuan 611137,China
b. Sichuan Provincial Engineering Research Center for Digitalization of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu,Sichuan 610075,China
c. Medical Records and Statistics Room,The First People's Hospital of Yibin,Yibin,Sichuan 644000,China
d. Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Standardization,Ministry of Education,Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu,Sichuan 611137,China
e. State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Resources with Southwest Characteristics,Chengdu,Sichuan 611137,China
f. School of Pharmacy,Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu,Sichuan 611137,China
ABSTRACT Objective This study proposes to visually review the current situation and progress of standards sets by the International Organization for Standardization/Technical Committee on Traditional Chinese Medicine (ISO/TC 249). The review aims to explore the development strategies of the standards,which will exhibit the considerable impact on the economy,trade and exchanges,and cooperation in the area of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).Methods ISO/TC 249 standards were searched on the ISO website,and their title,proposed time,current stage,scope,and classification were obtained for further summarization. Gephi was utilized to portray the co-occurrence network graph of the ISO/TC 249 standards subject.Results In ISO/TC 249,there were 116 standards,including 81 published standards and 35 developing standards by April 30,2022. Two withdrawal standards were published after revision,which were not counted in the total standards. The number of published standards has been increasing since the first standard was published in 2014,whose title was “Sterile acupuncture needles for single use”. Among these standards,17.24% (20/116) standards were in review,56.03% (65/116) in publication,3.45% (4/116) in approval,5.17% (6/116) in enquiry,3.45% (4/116) in committee,and 14.66% (17/116) in preparation,respectively. With 116 standards,most of the research focused on the medicament,as its classification of the International Classification for Standards (ICS) showed the proportion reaching 49.54%. The network analysis data revealed that the top five most frequent words were “materials” “root” “requirements” “products” and “system”,after removing the noise data,such as prepositions,conjunctions,and pronouns. Additionally,the word “system” co-exists with the terms “computerized” “coding” “image” “tongue” and “analysis”; the word “requirement” co-exists with“manufacturing” “decoction” “process” and “materials”; whereas the word “devices” coexists with “pulse” “electric” “skin” and “measurement”.Conclusion With the increased diversification and complexity of problems,the development of standards is also oriented to multidisciplinary fields to cultivate the interdisciplinary talents,and especially the international standardization talents of compound TCM. Multi-angle analysis,formulation,and demonstration of standards,in line with industry needs in different disciplines,enhance the availability of standards and the ability to serve the industry.
Keywords International Organization for Standardization/Technical Committee on Traditional Chinese Medicine (ISO/TC 249) Visualization analysis Standard subject distribution International Classification for Standards (ICS) Interdisciplinary talents
1 Introduction
As an independent,international,and non-governmental organization with a membership of 164 national standards bodies based in Geneva,Switzerland,the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is dedicated to supporting innovation,providing solutions to global challenges,and promoting voluntary,consensusbased,market-relevant international standards through bringing global experts together to share knowledge[1]. It has published nearly 24 320 standards covering almost every industry (such as technology,food safety,agriculture,and health care),except electrical and electronic engineering [the responsibility of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)][2].
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been rigorously practiced for thousands of years and benefited human health care owing to its comprehensiveness,affordability,and accessibility[3]. Thus,the medical community has acknowledged the advantages of TCM,and various types of TCM clinics and research centers have been established in many countries and regions[4-7]. As the popularity of TCM increases,countries,industry experts,and governments globally have started to cast great concentration on TCM[8,9]. Standards will serve as foundations to underpin the international practice of TCM for the benefit of both technical consumers and trade[10]. While some countries have their own operating standards for TCM practitioners,and regulations for TCM products,the industry remains fragmented. Thus,the International Organization for Standardization/Technical Committee on Traditional Chinese Medicine (ISO/TC 249) was approved in 2009[11]. Each standard published by the ISO is classified by the International Classification for Standards (ICS),a hierarchical classification method[12],aiming to recommend a universally applicable taxonomy to countries worldwide,regardless of their existing standard catalogs and database classification systems. It can solve the problems caused by the lack of an international unified standard document classification method and considerable differences in classification systems and identification systems in these standard catalogs,indexes,and databases,as well as language barriers.
This study of the ISO/TC 249 network analysis and exploration can help understand the international standardization activities,and provide new insight into the researches,which can help scholars,enterprises,and governments to discover the rules and procedures of ISO/TC 249,and improve the efficiency and innovation ability of the ISO/TC 249 participants. Moreover,the findings depict the subject distribution of ISO/TC 249 and provide a practical basis for researchers to formulate scientific and technological strategies,as well as for decisionmakers to consider the innovations in TCM.
2 Methods
2.1 Data source
The standards and standard projects of ISO/TC 249 were acquired on the official website of ISO (https://www.iso.org/committee/598435/x/catalogue/p/0/u/1/w/0/d/0)on April 30,2022. The title,proposed time,current stage,scope,and classification were documented in Excel 2010 for further analysis.
2.2 Visualization analysis of standards and standard projects
The classification of ISO/TC 249 standards follows the ICS. Developed and maintained by the ISO,ICS is a threelevel hierarchical system for technical standards classification: fields (level 1),groups (level 2),and subgroups(level 3). There are 41 items in the fields,taking a logical sequence from total to points,from general to specific. If the standard is not specific to classify,but it has a broad guiding significance,such as comprehensive basic standards,vocabulary,quantity and unit,graphic symbols,and general technology. Then,we can list the “Item 1” in the first place to represent the categories of “synthesis,vocabulary,standardization,and literature” to solve the problem of commonality.
Visual representation is processed quickly in the brain and requires less effort than textual information[13]. Accordingly,the graphing functions of Excel 2010 and the visualization tool Gephi[14,15]were employed for performance analysis and interactive trace visualization of ISO/TC 249 standards. The Fruchterman-Reingold algorithm[16],a force-directed layout algorithm,is applied to create an overall favorable layout graph,guaranteeing that near nodes are topologically placed in the same vicinity,whereas far nodes are placed far from each other.
3 ISO/TC 249 working group (WG) and life cycle
3.1 WG and task force (TF)
The ISO/TC 249 established six WG and one TF to conduct the following tasks shown in Table 1. WG 1 to WG 5 were all established in May 2011. With the integrated development of TCM and information technology,a joint WG,that is JWG 1: “Traditional Chinese medicine (informatics)”,was established in December 2012[17].
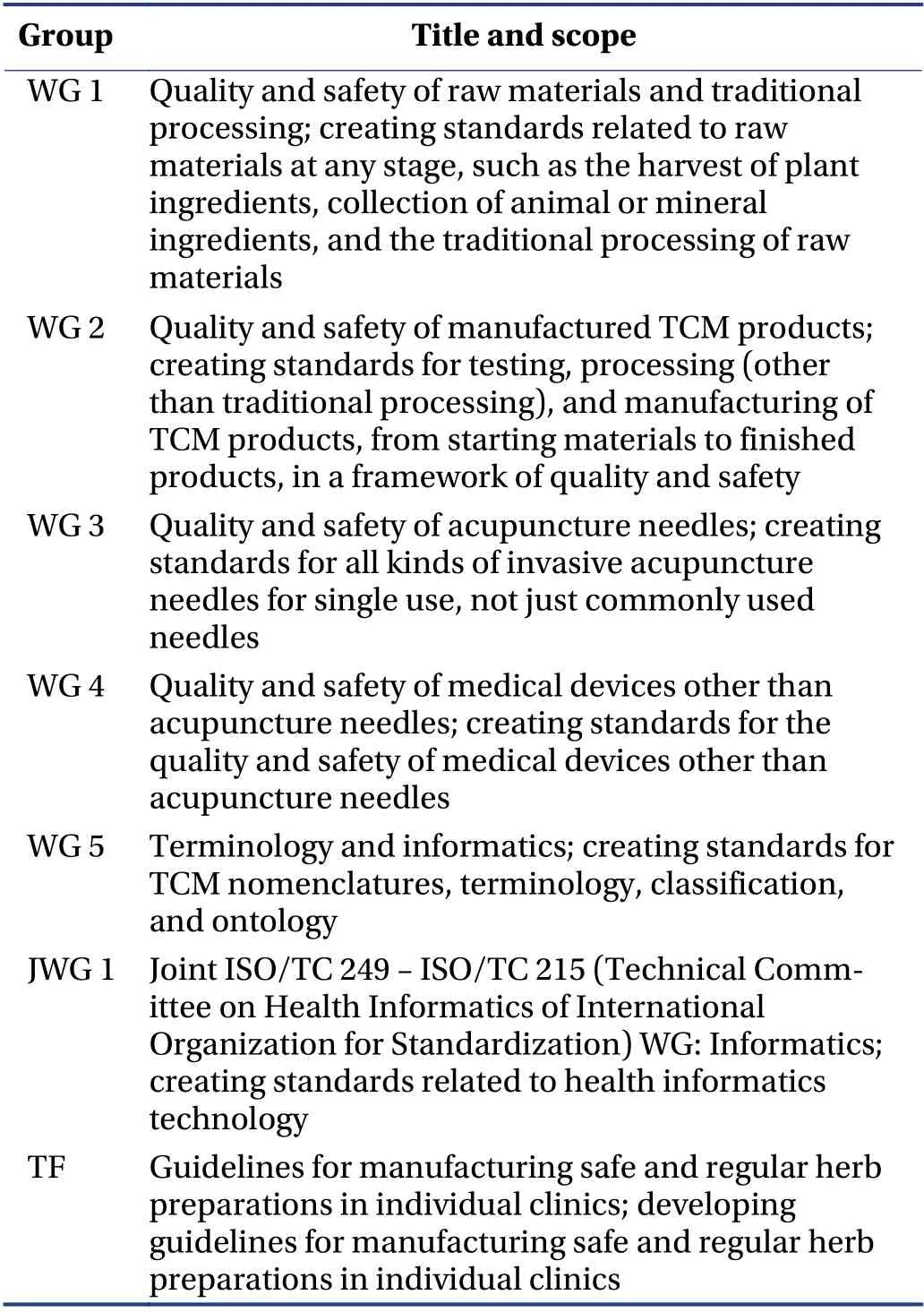
Table 1 WG and TF of ISO/TC 249
3.2 Life cycle and current stage
The life cycle of ISO/TC 249,which is also known as international harmonized stage codes,can be divided into nine stages: preliminary,proposal,preparatory,committee,enquiry,approval,publication,review,and withdrawal. What is more,each stage can be roughly divided into four substages: registration,start of the main action,completion of the main action,and decision.
Each published standard is reviewed at least every five years. Correspondingly,the review results are divided into three categories: to be confirmed,revised,and withdrawn. Table 2 lists the subitems of every stage.

Table 2 Life cycle of ISO/TC 249 standards
4 Results
One hundred and eighteen standard subjects were identified,including 81 published standards,35 standards under development,and two withdrawn standards. For two withdrawn standards,the revision was completed to be published. One is ISO 18665:2015 “Herbal decoction apparatus”,which was revised and published in 2021 and 2022,respectively. The other is ISO 18666:2015 “General requirements of moxibustion devices”,which was revised and published in 2021.
Table 3 shows 18 published standards in 2021 and 2022. The first five standards listed in Table 3 will be published in May 2022. The above standards can give a glance at the development trend of international standards of TCM in a short period. More specifically,the data in Table 3 show that the standard research on equipment is 16.7% (3/18). Remarkably,a standard for herbal decoction apparatus was published for the first time. The development of standards is aimed at solving the problems existing in the field of TCM. The trend of the proposal is focused on the medicaments,medical equipment,and general requirements or guidelines.
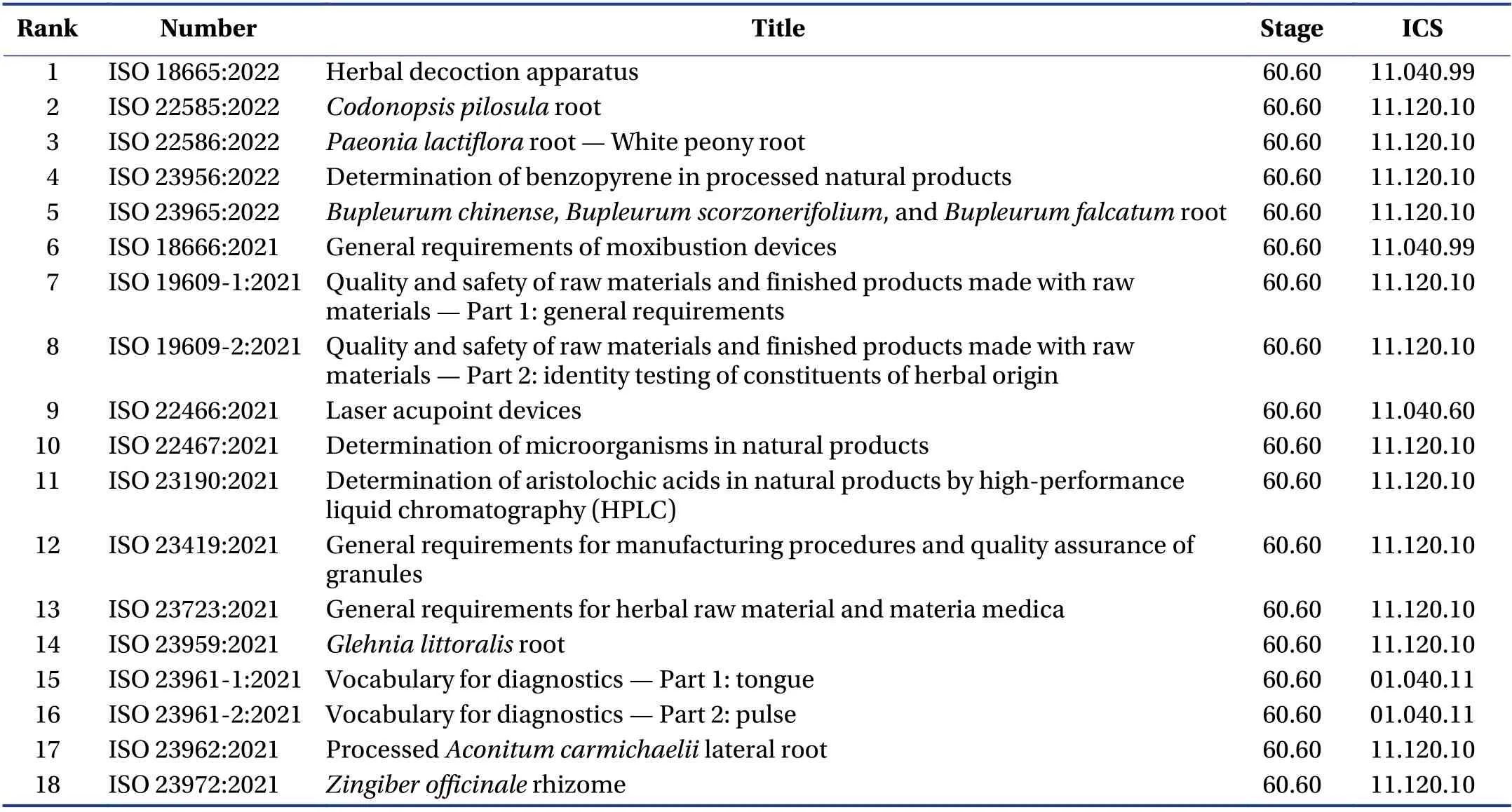
Table 3 Eighteen published TCM standards in 2021 and 2022
4.1 Year of proposal
In 2014,with the release of the first international standard for TCM,“Sterile acupuncture needles for single use”(ISO 17218:2014),which was formulated by China,the formulation of the ISO/TC 249 international standard has entered a rapid development stage. At this stage,the number of project approvals and publications of international standards has been increasing annually (Figure 1).
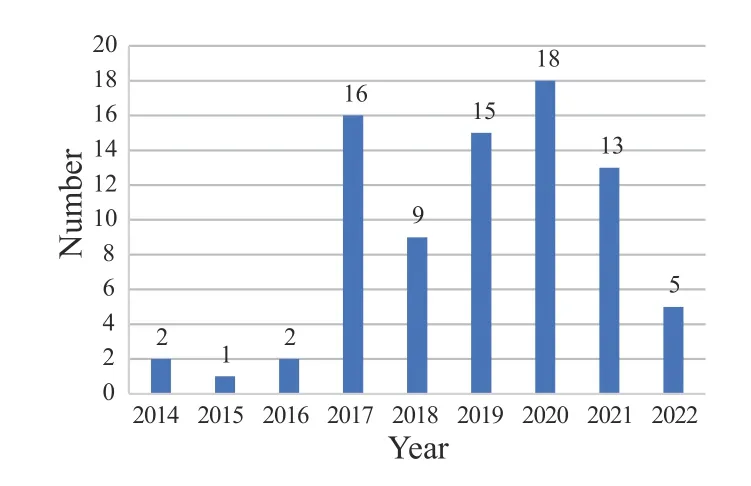
Figure 1 Proposed time of 81 published ISO/TC 249 standards
It illustrates the annual publication output. Overall,the publication number accounts for 69.83% (81/116) of all published and developing standards,which increased by approximately 5.6% compared with the data in 2019.Especially from 2019 to 2021,the publication number accounted for over 50% (46/81) of all published standards. Moreover,two standards,which were published in 2015,underwent the review stage in 2021. The two standards were voted to be revised by initiating a new project process,and the first publication was withdrawn when the revision was published.
As shown in Figure 2,20 standards were in the review stage. Moreover,four of them had been confirmed,15 were under periodical review,and for the other,the review was closed. Additionally,reviewing and revising standards in a timely manner can ensure their suitability and effectiveness to meet the needs of industrial development. In addition to the 81 published standards and the two withdrawn standards,the other 35 standards under research were in different stages. Recently,there were 17.24% (20/116) standards in review,56.03% (65/116) in publication,3.45% (4/116) in approval,5.17% (6/116) in enquiry,3.45% (4/116) in committee,and 14.66%(17/116) in preparation,respectively.

Figure 2 Status quo of 116 ISO/TC 249 standards
4.2 Classification of standards
Regarding ISO/TC 249,the classification mainly focused on No. 11,which represents medical and health technology. The standards belong to different areas according to the field,and the ICS number is set to at least one category. At present,the ISO/TC 249 standards are shown at most three ICS numbers,belonging to the same or different fields.
Figure 3 shows the detailed classification of 109 standards. The ICS No. 11.120.11 is on behalf of medicaments,including medical prescriptions and medicinal herbs.Therefore,the percentage of medicaments is up to 49.54% (54/109),implying that the standard proposer pays considerable attention to the medicaments,such as the Chinese medicinal materials with large international demand and high market demand to establish corresponding international standards. More precisely,the majority of the standard proposers are engaged in medicaments activities. Furthermore,the development of TCM equipment standards has become an industry consensus.Along with the research and development of technologies and products,the corresponding standard research accounts for 27.52% (30/109),such as the ICS of syringes,needles,and catheters (11.040.25),diagnostic equipment(11.040.55),therapy equipment (11.040.60),and other medical equipment (11.040.99). Moreover,other 11 standards are at the stage of Approved Work Item (AWI),with no ICS (Table 4).
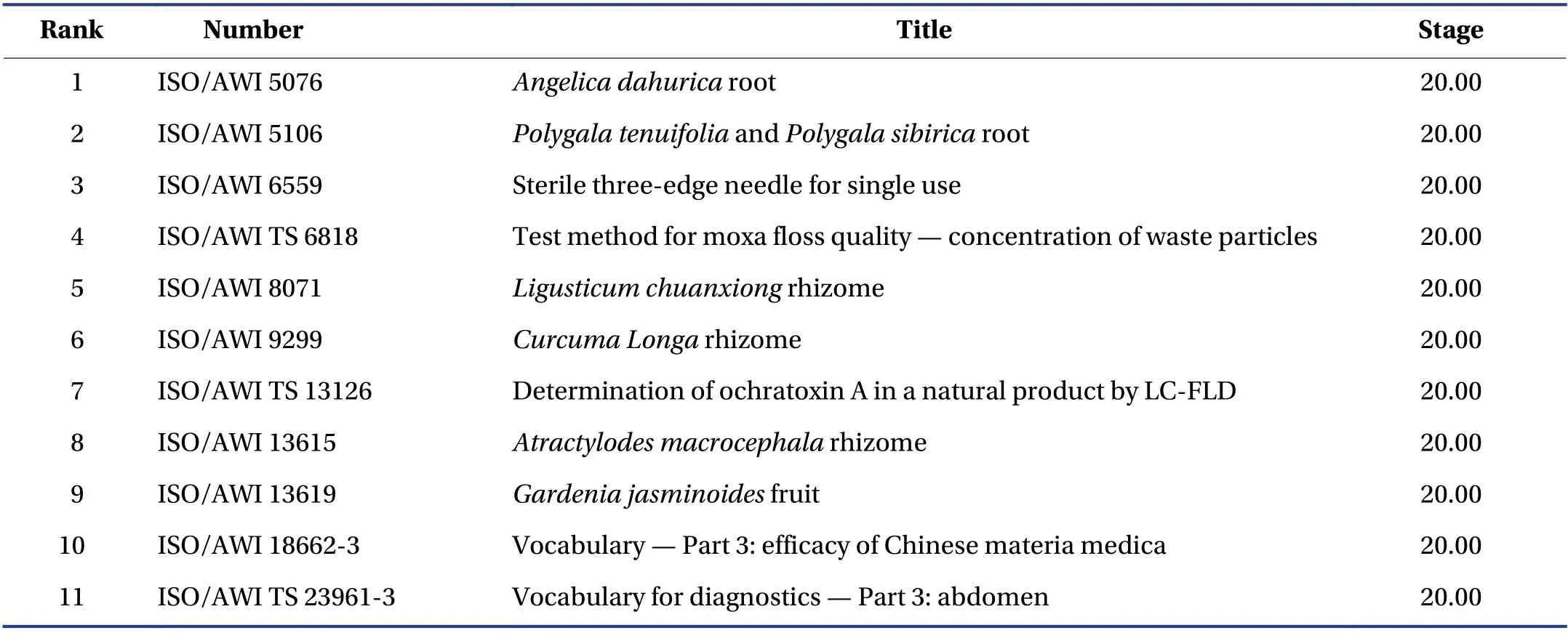
Table 4 AWI standards with no ICS
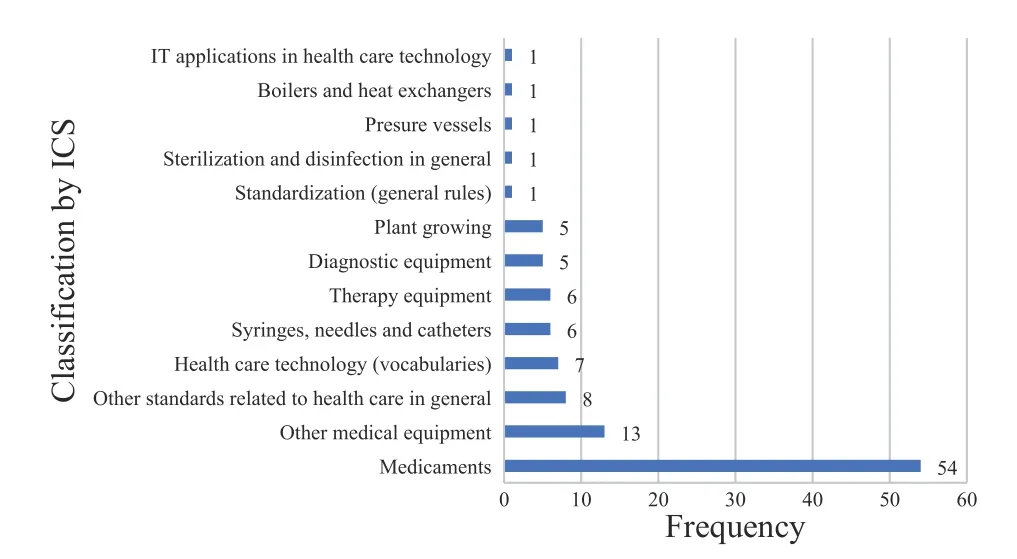
Figure 3 Classification of ISO/TC 249 standards
4.3 Network analysis of standard subjects
The name of the standard can directly reflect the scope and characteristics of the standardization object,which is related to the dissemination effect of the standard information. We split the standard title name in Excel 2010 and then imported the data into the Gephi tool for analysis. A total of 279 words were identified after splitting the title names. According to the frequency of occurrence,the 20 most frequent words in the title are shown in Table 5.
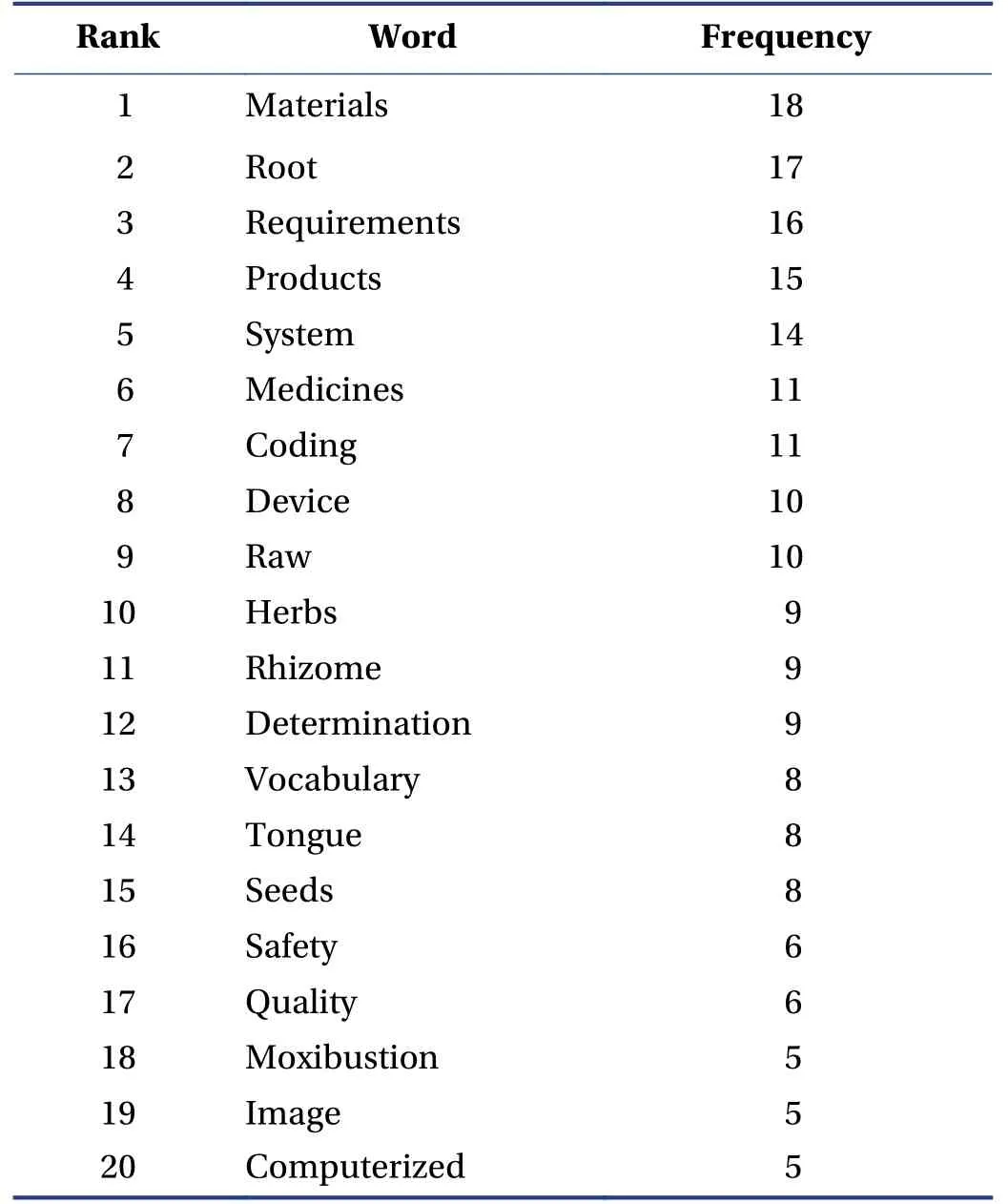
Table 5 Top 20 frequent words in the title of ISO/TC 249
After filtering unconnected nodes,we created the cooccurrence diagram (Figure 4) to show the relationship between subjects. The top five most frequent words were“materials” “root” “requirements” “products” and “system”,after removing the noise data,such as prepositions,conjunctions,or pronouns. The word “requirement”most co-exists with “manufacturing” “decoction” “process” “pieces” and “materials”. The word “products” coexists with “storage” “quality” “safety” and “determination”. The word “system” most co-exists with the words such as “computerized” “coding” “image” “tongue” and“analysis”. Furthermore,the word “devices” co-exists with “pulse” “electric” “skin” and “measurement”. Nodes of acupuncture and ginseng are also illustrated in Figure 4 as core nodes.
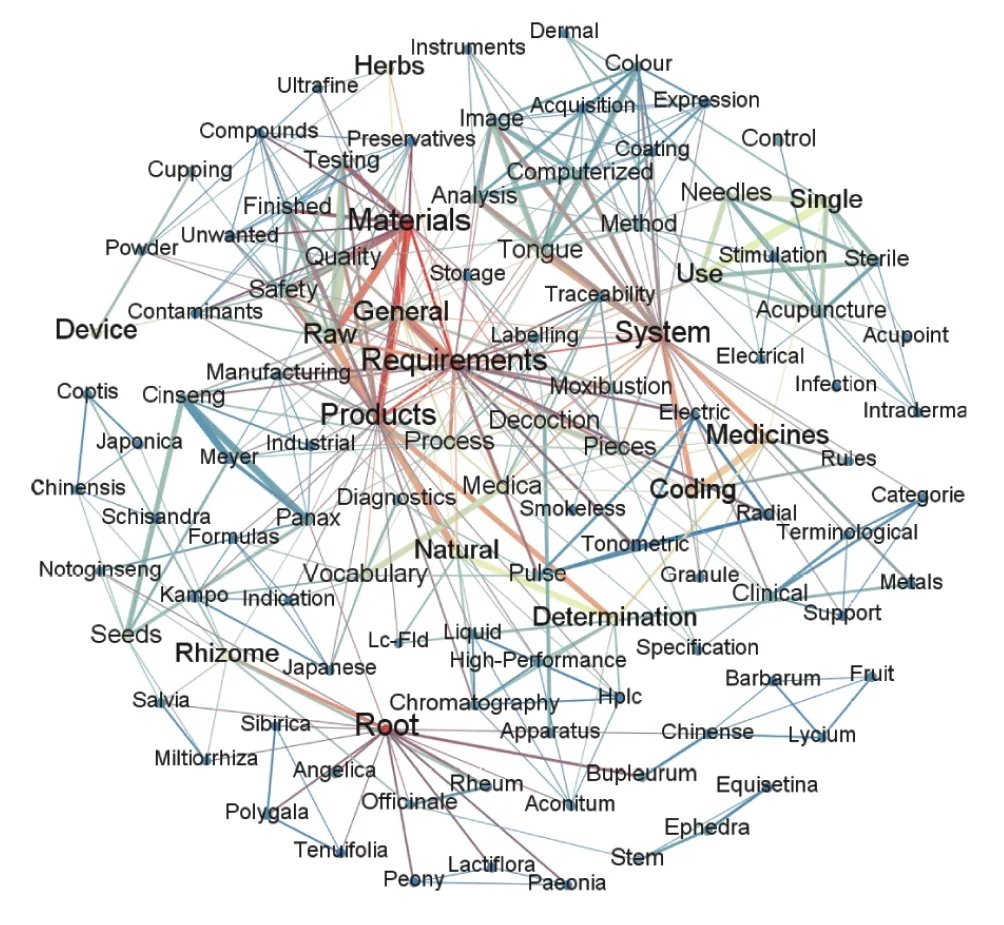
Figure 4 Visualization graph of ISO/TC 249 standard subjects
5 Discussion
Based on the standard data collected on the ISO/TC 249 website,we provided a visualization overview of the published standards,standard projects,and standard proposals. First,almost one-third of standard subjects were in the preparatory,committee,and enquiry stages,and four standards related to Chinese materia medica(CMM) were published in 2022. This demonstrates that international standards are in the stage of rapid development in CMM,and there will be a further increase corresponding to the seed,planting,processing,and circulation.Furthermore,the increment of standards manifests the increasing interest of the participating members,such as contribution to TCM international standardization and cooperation with other international organizations. This may facilitate the market need for TCM standards to enhance trade and industry growth. More and more people abroad recognize Chinese medicine treatment for its curative effect,such as acupuncture[18,19]. Therefore,it is necessary to further strengthen the development of standards in the direction of TCM,such as diagnosis and treatment equipment. The current standards of the four diagnoses of TCM,namely inspection,auscultation and olfaction,interrogation,and palpation equipment,represent an excellent case example in standard research. This shows that TCM standardization is an interdisciplinary area and requires the cooperation of experts from different fields. The efforts for international standards for TCM are essential to boost people’s confidence in TCM.
Second,116 standards can be divided into 13 types.Among them,medical care equipment and technology are related to internet technology,plant growing,and engineering. The visualization graph of standard subjects shows that the safety and quality of CMM (storage requirement,quality and safety,ginseng seeds,and seedlings),manufactured products (labeling requirements,detection,and indication codes),medical devices (electric radial pulse tonometry,smokeless/moxibustion,skin electrical resistance measurement,and therapeutic fumigation devices),and computer analysis system (coding,image analysis,categories of clinical terminological,and traceability system) are of great concern in ISO/TC 249. There are major risks due to unprofessional practitioners or inappropriate treatments in poorly regulated markets,thus undermining the public safety,the image and trustworthiness of TCM,and the crossborder flow of TCM products and services. ISO/TC 249 can provide a performance framework and the regulation of treatment as the solution.
In summary,ISO/TC 249 covers a broad range of subjects and has been increasing its yearly outcomes. It especially benefits from the data exchange and various technological methods derived from fields such as artificial intelligence (AI),machine learning,statistics,and database systems. Many research projects have developed massive computerized tongue image analysis system(CTIS),and ISO/TC 249 has published a series of standards encompassing light environment,color chart,peripheral visual instruments,and methods of acquisition and expression of tongue color and tongue coating color to improve CTIS performance and clinical approach[20-23].In the future,for such a traditional yet modern field,as more modern technologies are being applied in TCM,there is an increasing need for consistent efforts to seek“consensus”,which would bring regenerated eyes to look at the world.
6 Conclusion
As the international standardization of TCM is highly valued by the global industry,more global experts will make suggestions regarding ISO/TC 249 to develop more wellestablished international standards for TCM. Moreover,the formulation and publication of international standards belong to the top-level design for industrial development. Promulgation of international standards will reduce the regulatory and supervisory barriers technically,place the industry under effective management,and ensure the quality and efficacy of TCM-related products and services. The development of these standards is,therefore,a critical step toward breathing new life into the time-honored practice of TCM in a modern world for the benefit of all human beings.
In conclusion,the international standardization of TCM as a new area encounters numerous challenges and,requires the participation of professional talents who are qualified with a well-organized,multi-aspect knowledge structure and high-level expertise. Besides,it is necessary to improve the cultivation of interdisciplinary talents,especially the international standardization talents of compound TCM. Additionally,the standards released and formulated by ISO/TC249 only cover the fields such as terminology,facilities and equipment,and service supplies. Accordingly,there are still many blank areas to be further supplemented and improved.
Fundings
National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1707606),Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2022MS500),Chengdu Science and Technology Department Project(2019-YF09-00185-SN),and Xinglin Scholar Research Promotion Project of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (MPRC2021022).
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Digital Chinese Medicine2022年2期
Digital Chinese Medicine2022年2期
- Digital Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- MEDICLOUD: a holistic study on the digital evolution of medical data
- Ancient and modern medication laws of aromatic Chinese medicines in treating angina pectoris based on data mining
- Intra-set correlation analysis of medical records of thyroid cancer treated by traditional Chinese medicine Master ZHOU Zhongying
- Traditional Chinese medicine Master XIONG Jibo’s medication experience in treating arthralgia syndrome through data mining
- Screening influencing factors of blood stasis constitution in traditional Chinese medicine
- Mechanisms of Dihuang (Rehmanniae Radix) in treating diabetic nephropathy complicated with depression based on network pharmacology
