Study on Antibacterial Effects of Purple, Yellow and White-skinned Onions
Guo Qian-qian, Wu Peng*, Zhang Bao-cheng, Zhu Kun, Pan Lin, and Zhang Yan-ling
1 College of Life Science, Agriculture and Forest, Qiqihar University, Qiqihar 161006, Heilongjiang, China
2 Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Resistance Gene Engineering and Protection of Biodiversity in Cold Areas, Qiqihar 161006, Heilongjiang,China
3 College of Basic Medicine, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang, China
Abstract: Onion (Allium cepa L.) is a common biennial herb, and contains allicin compounds which can kill harmful microorganism.The antibacterial effects of raw and mature onion juice of purple, yellow and white-skinned onions at different concentrations on Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) were studied. There were differences among the antibacterial effects of raw and mature onion juice of purple, yellow and white-skinned onions at different concentrations. What was more, the antibacterial effects of raw onion juice were better than those of the mature one. The antibacterial effects of high concentration onion juice were better than those of the low one. The content of the total flavonoids in raw purple onion was higher than that in mature onion, and reached extremely significant levels in 50%, 75% and 100%, respectively. Through comparison, it was found that onion juice of purple-skinned had the best suppression effects on S. aureus (gram-positive bacterium) and E. coli (gram-negative bacterium),and gram-positive bacterium had better suppression effects than gram-negative bacterium. It wound provide the basis about bioactive function and antibacterial drugs.
Key words: onion, S. aureus, E. coli, antibacterial effect
Introduction
Onion (Allium cepaL.) is a common vegetable crop.According to the differences of bulbous morphology,onion can be divided into tiller onion and ball onion(Teyssieret al., 2001). The ball onion can also be divided into red, purple and yellow onions according to the skin color. Allicin is the main antibacterial substance in onion. In addition, onion has medicinal effects which may be important in the prevention and amelioration of coronary problems (Augusti, 1990).The onion and its chemical composition have excellent pharmacological effects, such as inhibiting bacteria,resisting tumors, reducing blood sugar and blood fat,oxidation resistance, etc (Hu and Yu, 2012). Over 50%of these crops are grown in Asia, and China and India are the major producers of bulb onions (Guptaet al., 1991).
Staphylococcus aureus(S. aureus) is an important pathogenic bacterium. It is the representation of a grampositive bacterium, which can cause many serious infections. The main components ofStaphylococcusaureus's cell wall are peptidoglycan and teichoic-acid,compared to gram-negative bacteria, the peptidoglycan ofS. aureushas a denser network structure.S. aureushas low nutrient requirements and high salt tolerance.The optimum growth temperature and pH are 37℃and 7.4, respectively.S. aureuscan be found in air,water, dust and animal excrement. Hence, there are a lot of opportunities for food to be polluted. The US Centers for Disease Control reported thatS. aureusaccounted for the second of all the infections.S. aureuscan invade the body through many pathways, resulting in multiple infections of the skin or organs, and even sepsis.Escherichia coliis calledE. colicommonly,which is a common prokaryotic bacterium. It belongs to gram-negative bacterium and the body has flagella,can move, no spores. The main component ofE. coli's cell wall is peptidoglycan, and it has only simple organelles. Under normal circumstance,E. colidoes not harm the human body, and has a mutually beneficial relationship with the human body. When the body's immunity is down, it will cause damage to these parts of the body outside the intestines.E. colimainly causes diseases, such as extraintestinal infection,acute diarrhea, etc.
In recent years, the antibacterial peptides have been found in onion. The reports indicated that antibacterial peptides have antibacterial, antifungal and antitumor effects (Wanget al., 2005). At present, all the conventional antibiotics have developed corresponding drugresistant strains, and the resistance of pathogenic bacteria has been a serious threat to people's health.For example, many achievements in modern animal husbandry and veterinary medicine are based on the application of antibiotics. The past decades can be called the "antibiotic era". However, long term use of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic residues in animal products and cause bacterial resistance. It has brought great harm to the animal husbandry and human health. Therefore, finding new types of antibiotics is an effective way to solve the problem of drug resistance.Antimicrobial peptides have a good development prospect because of their high antimicrobial activities,wide spectrum of antimicrobial spectrum, a wide range of species and a wide range of selection, and the target strains are not easy to produce resistance mutation. The use of biological antimicrobial peptides instead of traditional antibiotics will surely become a trend in the future development of life. Therefore,the study of the antibacterial effects of onion has high practical significance. Due to the nutritional value and medicinal value of the onion, reports of onions have been frequently reported in recent years, but studies on onions are mostly focused on high-yield cultivation and management (Haoet al., 2008), selection and breeding of new varieties (Xu and Qian, 2007), and extraction and analysis of onion chemical components(Gao and Liu, 2008). Some studies have shown that some ingredients in onion have a certain inhibitory effect, such as organic sulphides in onions, which have a better inhibitory effect onS. aureusandBacillus subtilis(Jianget al., 2008). The ethanol extract of onion has different inhibitory effects onBacillus subtilis,S. aureus,E. coliand yeasts (Tanget al.,2012). However, there are relatively few reports on the bacteriostatic effects of raw and mature onion juice.
Onion is a special vegetable crop that combines health care and nutrition. It not only contains rich nutrients, but also has the function of antiseptic, anticancer and so on (Sunet al., 1992). Fresh onions contain allicin compounds that act as a proper bactericidal effect. Allicin can react with sulfhydryl compounds to prevent its binding to proteins and inhibit bacterial proliferation (Yuet al., 1997).Sulfur-containing amino acids in onions can deplete hydrogen and sulfur-containing enzymes necessary for the synthesis of cholesterol and lipids to prevent insulin from being destroyed, thereby reducing blood glucose (Ling and Zhang, 2008). In addition, onion juice also has an elimination effect on nitrite, as well as treatment of scurvy, heavy metal poisoning and skin ulceration (Chuet al., 2017). Onion and its deepprocessed products have many physiological functions,such as onion oil contains a significant anti-platelet coagulation component (Kaminie and Syeda, 1983).But there are few real onion processing products,and few reports about the antibacterial effects of raw and mature onion juice. Therefore, the antibacterial effects of raw and mature onion juice were studied.This experiment was conducted to study the inhibition effects of onion juice on the two common bacteria,E. coliandS. aureusand hope to provide scientific basis for the further processing of onions in the food industry and the development of health products.
Materials and Methods
Materials of experiment
This experiment was conducted at the laboratory of Life Science and Agriculture and Forestry College,Qiqihar University. The selected onions included purple-skinned onions (Zhixing, Hongxiuqiu and Hongzhuangyuan), yellow-skinned onions (Golden Ball No. 2, Tianzheng 105 and Laixuan 13) and whiteskinned onions (Hami, Baizhengzhu No.1 and Baiyu).E. coliandS. aureuswere provided by the laboratory of the microorganism in Life Science and Agriculture and Forestry College, Qiqihar University.
Methods of experiment
Preparation of raw and mature onion juice
At first, the purple, yellow and white-skinned onions were washed, and put on the clean bench and peel offtheir skin, then weigh 500 g of chips on an electronic balance. Meanwhile, checked juicer that was washed three times by clear water, and ended up with sterile water. Juiced the onions, then filtered them with sterile gauze. Finally, got raw onion juice after suction filtration by vacuum extractor. Then reserved them at 4℃.Poured the part raw onion juice into the autoclave in 121℃ and heated them to get mature onion juice.Reserved them at 4℃.
Production of culture medium
The culture medium was the beef extract peptone in this experiment. The beef extract 3 g, peptone 10 g,NaCl 5 g and agar powder 15 g were mixed and diluted to 1 000 mL with distilled water. The solution pH was adjusted to 7.2-7.4. After the above steps were completed, the medium was transferred to the four 250 mL conical bottles. The sealed medium was sterilized and reserved.
Preparation of E. coli and S. aureus suspension
E. coliand andS. aureuswere activated. Part of them were taken from the inoculation ring to be diluted with 1 000 mL sterile saline, and shaked for 5 min to make it uniform. Moreover, four sterilize tubes were taken and poured 1 mL bacterial suspension and 9 mL sterile saline. In this way, bacterial suspension was diluted four times and repeated the process. Finally,E. coliandS. aureussuspension was gotten.
Determination of bacteriostasis effects
Ethanolic extracts of onion was done by agar well diffusion assay. Broth cultures equal to 0.5 McFarland standards were prepared according to method described by Hannanet al. (2010) and Wang (2010).Five wells of equal size on each Mueller-Hinton (MH)agar plate were made by 9 mm cork borer. A total of 120 µL of extract from each dilution (100%, 75%,50%, 25% and CK) was poured into each well with micropipette. The normal saline were used as the control. The diameter of the clear zone around each well was measured in cm by digital calipers (sylvac fowler ultra-cal II). The experiment was performed in five replicates.
Analysis of the total flavonoids
The total flavonoids were determined by the colorimetric method of Changet al(2002). Onion extracts(0.5 mL) were mixed with 1.5 mL of 75% ethanol, 0.1 mL of 10% aluminum chloride, 0.1 mL of 0.1 mol • L-1potassium acetate and 2.8 mL of distilled water. The reaction mixture was maintained for 30 min at room temperature. The absorbance was measured against a blank at 415 nm using the UV spectrophotometer.Quercetin was used for the standard calibration curve and the total flavonoid content was expressed in mg of quercetin equivalents per gram dry weight (mg Q • g-1DW) (Sharmaet al., 2015).
Results
Inhibition of S. aureus and E. coli by raw onion juice of different concentrations
The inhibitory effects of 25%, 50%, 75% and 100% raw onion juice onE. coliandS. aureuswere compared and the antimicrobial diameters were measured. The results showed that the raw onion juice could inhibit the growth ofS. aureusandE. coliand form bacteriostasis. Inhibition ofS. aureusby raw onion juice of different concentrations (100%,75%, 50% and 25%) is shown in Fig. 1. The results showed that purple onion had the largest antimicrobial diameter at all the concentrations (from 25% to 100%),followed by yellow onion, and white onion had the smallest antimicrobial diameter. In addition, as the concentration of onion juice increased from 25% to 100%, the bacteriostatic diameter increased. The 100%of the purple raw onion juice had the best antibacterial effects onS. aureus.
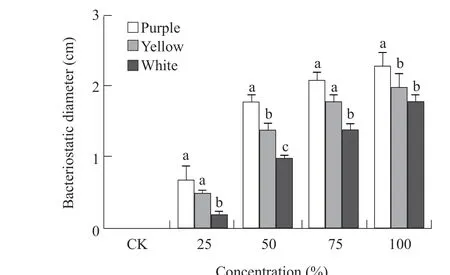
Fig. 1 Inhibition of S. aureus by raw onion juice of different concentrations
Inhibition ofE. coliby raw onion juice of different concentrations is shown in Fig. 2. The results showed that purple onion had the largest antimicrobial diameter at all the concentrations (from 25% to 100%),followed by yellow onion, and white onion had the smallest antimicrobial diameter. The 25% white onion juice had no bacteriostasis againstE. coli. In addition,as the concentration of onion juice increased from 25% to 100%, the bacteriostatic diameter increased.The 100% of the purple raw onion juice had the best antibacterial effects onE. coli. The general inhibition trend of raw onion juice onS. aureusandE. coliwas the same, but the inhibition diameters of raw onion juice on each concentration ofS. aureuswere larger than those ofE. coli. Therefore, as shown in Figs.1 and 2, 100% purple raw onion juice had the best antibacterial effects onS. aureus, the effects of raw onion juice onS. aureuswere better than those onE. coli, which could be used for the further development of antibacterial drugs.
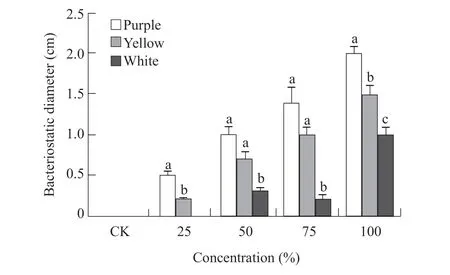
Fig. 2 Inhibition of E. coli by raw onion juice of different concentrations
Inhibition of S. aureus and E. coli by mature onion juice of different concentrations
The inhibitory effects of mature onion juice of different concentrations onS. aureusandE. coliare shown in Figs. 3 and 4. The results of Fig. 3 showed 100%, 75% and 50% of the three mature onion juice could inhibit the growth ofS. aureusto form the inhibition zone, and the diameter of the inhibition zone increased with the increase of onion concentration.Specially, 25% concentration of mature onion juice had no inhibitory effects onS. aureus. It could be seen from Fig. 3 that the bacteriostatic effects of mature onion juice were better as the concentration of 100%purple onion juice. However, the bacteriostasis effects of 100% mature purple onion juice were lower than those of raw purple onion juice (Figs. 1 and 3).

Fig. 3 Inhibition of S. aureus by mature onion juice of different concentrations

Fig. 4 Inhibition of E. coli by mature onion juice of different concentrations
The inhibition effects of mature onion juice of different concentrations onE. coliare shown in Fig. 4.The results showed that 100% and 75% mature onion juice could inhibit the growth ofE. coliand form the inhibition zone, and the diameter of the inhibition zone increased with the increase of onion concentration.Especially, 25% and 50% mature onion juice had no inhibitory effects onE. coli. At the same time, when the concentration of mature onion juice was less than or equal to 25%, it had no inhibition effects onS. aureus(Figs. 2 and 4). It could be seen from Fig. 4 that the bacteriostatic effects of mature onion juice were best as the 100% purple mature onion juice.However, the bacteriostasis effects of 100% mature purple onion juice were lower than those of raw purple onion juice (Figs. 2 and 4). On the whole, the effects of inhibitingS. aureusby raw and mature purple onion juice were obviously better than those ofE. coli.
Comparison of bacteriostasis effects of purple onion juice on S. aureus and E. coli
Through previous studies, it was found that 100%raw and mature purple onion juice had the strongest antibacterial effect in the same group. The results of Fig. 5 showed that the antibacterial effects of raw and mature purple onion juice onS. aureuswere significantly higher than those onE. coli(P<0.01).Further, 100% raw purple onion juice had the best inhibitory effect onS. aureus.

Fig. 5 Comparison of bacteriostasis effects of purple onion juice on S. aureus and E. coli
Analysis of the total flavonoids in raw and mature purple onion juice of different concentrations
The total flavonoids in the raw and mature purple onion juice of different concentrations varied in the range from 220.15±48.25 mg Q • g-1DW to 2 272.87±189.65 mg Q • g-1DW. The results of Fig. 6 showed that the total flavonoid content gradually increased with 25%, 50%, 75% and 100% of raw and mature purple onion. The content of the total flavonoids in raw purple onion was higher than that in mature onion, and reached extremely significant levels in 50%, 75% and 100%, respectively. After heating and causing onion mature, there was a decrease in the total flavonoids, which indicated that some flavonoids were probably destroyed. In most fruits and vegetables, the flavonoids contained ceglycoside bonds and existed as dimers and oligomers, and the industrial processing,such as heating or boiling, resulted in the formation of monomers by the hydrolysis of ceglycoside bonds(Manachet al., 2004). Our results were consistent with the findings of Manachet al.(2004) who found that the total flavonoids decreased after heating at a certain temperature and magnitude of the time. The reason for the decrease in the total flavonoids at higher temperature could be because of the degradation of flavonoids. It also depended on the structure of particular flavonoids.
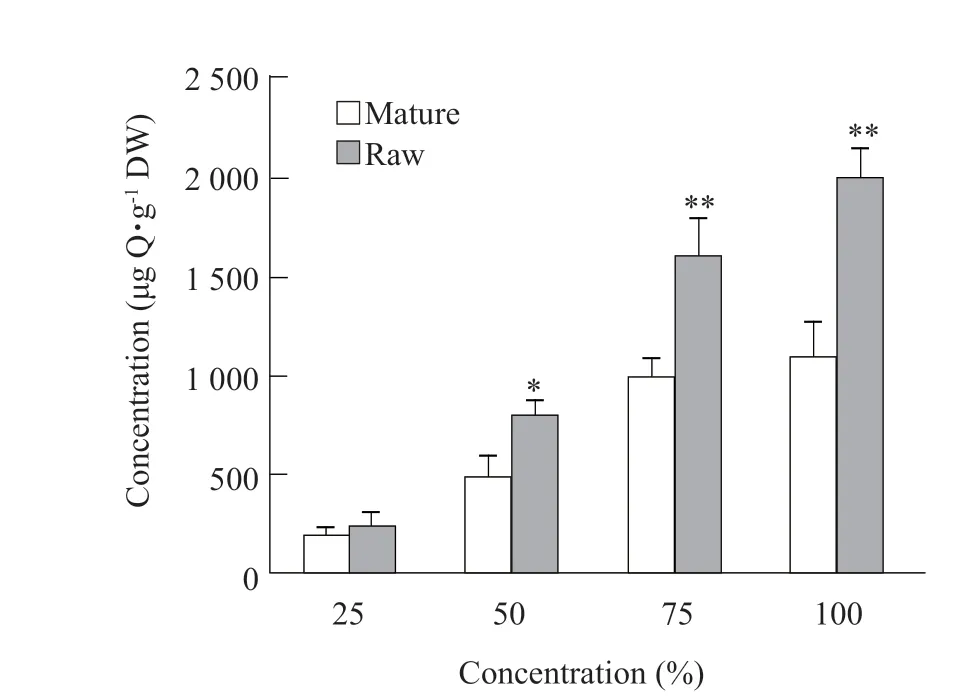
Fig. 6 Analysis of the total flavonoid content in raw and mature purple onion juice of different concentrations
Discussion
Onion extract is a source of bioactive compounds demonstrating a high antioxidant activity (Piechowiak and Balawejder, 2019). Nowadays, with regard to the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, there is a greater need for alternative treatments. Thus, new approaches for finding novel compounds are needed. One of the recent approaches focused on traditional herbal medicine in order to develop new medications (Nejabatet al., 2014).Onion (Alium cepa), one of the herbs that have medicinal value, has often been discussed in traditional literature, and it has also been scientifically studied in recent decades. Studies in this area can be roughly divided into two categories: those which are done and investigated the antimicrobial properties of onion, and those which evaluate the antibacterial effects of onion juice on gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus) and gramnegative bacteria (E. coli).
Onion is mainly divided into three types according to peel colors: purple, yellow and white. Purple onion contains anthocyanins, a type of strong antioxidant phytochemicals, can protect the human body from free radical damage, but also enhance vascular elasticity,improve the circulation system and enhance skin smoothness, inhibit inflammation and allergy, and improve joint flexibility. The content of organic sulfur compounds in purple onion is higher than that in the other two, so its pungent flavor is heavier. Organic sulfur compounds have antibacterial, anti-cancer, antiatherosclerosis and anti-inflammatory effects, and can eradicate free radicals in the body, with antioxidant effects. Generally speaking, the nutritional value of purple onion is higher than that of white and yellow onions. In addition to the high nutritional value, the results of this study showed that 100% raw purple onion juice had the strongest antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacterium (S. aureus), which was useful for the development of antibacterial agents against gram-positive bacteria.
It is found that the antimicrobial effects of onion are due to the action of onion antimicrobial peptides. The cytoplasm of onion contains sulfur compounds called alliin, and the cell wall contained alliinase. When the fresh onion cell broke down, alliin produced a series of sulfur metabolism, such as allicin and ahoene under the action of alliinase product (Chenet al., 2003). Allicin in onions may be the main antimicrobial substances,these substances are also the main components of onion antimicrobial peptides. Because the extract of onion is sensitive to temperature, high temperature may destroy the antibacterial structure of onion, so the temperature is not too high when extracting the active substance of onion. It was reported that allicin would lose a great deal or even all of it after high temperature sterilization at 121℃ for 20 min, thus completely losing its bactericidal effect. In this experiment, the mature onion juice after high temperature sterilization still had certain bacteriostatic effect, and was not as spicy as raw onion stimulation, therefore, people with gastrointestinal discomfort could eat mature onion or semi-cooked onion for dietary therapy and health care, but the actual amount of edible to achieve health effects to be further studied.
The cytoplasm and cell wall of onion contains flavonoids. When fresh onion cells ruptured, the flavonoids could produce a series of sulfur-containing metabolites (Tanget al., 2015), and it was generally believed that these compounds might be the main antimicrobial substances (Kim, 1997). They could react with cysteine and other sulfhydryl compounds to prevent their binding to proteins and thus inhibit bacterial reproduction. This study tested the antimicrobial activity of raw and mature purple, yellow and white onion juice, and confirmed that raw onion juice had stronger antimicrobial activity than mature onion juice, of which 100% purple onion juice had the strongest antimicrobial activity. In addition, in the bacteriostatic test of onion juice, it was confirmed that the concentration of onion juice was positively correlated with its bacteriostatic effects, and the bacteriostatic effects of different varieties were also different. The effects of purple onion juice were better than those of yellow and white onion juice. The results of Kang (2012) also confirmed it. Hannanet al.(2010) used two different onion extracts (purple onion and yellow onion) to study the bacteriostatic effects ofVibrio cholerae, and the results showed that the bacteriostatic activity of purple onion extract was much greater than that of yellow onion extract, which was similar to our results.
Conclusions
In this study, purple onion juice had significant inhibitory effects onS. aureusandE. coli. Bacteriostatic activity was positively correlated with onion juice concentration. Under the same concentration, the bacteriostatic effects of raw onion juice were obviously better than those of mature onion juice. And inhibition effects of the same concentration of onion juice onS. aureuswere better than those onE. coli. The antimicrobial activity of purple onion juice was better than that of white and yellow onion juice. The results showed that 100% purple raw onion juice had higher total flavonoid content and was more suitable for the inhibition ofS. aureus. The results had certain guiding significance for food preservation and health care. It was suggested that 100% raw onion could be eaten properly. This study might be a starting point for further investigations on this herb.
 Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2022年2期
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2022年2期
- Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Effects of Different Ventilation Modes and Outlet Height on Nursery Piggery Environment
- Measurement of Grain Production Efficiency in Main Grain-producing Areas and Analysis of Inter-provincial Differences
—— A Study Based on Super-SBM Model and Malmquist Index - Effects of Planting Density and Cutting Time on Hay Yield and Nutritional Value of Forage Soybean HN389
- Effects of Encapsulated Enzyme and Yeast Products on in Vitro Rumen Fermentation
- Attribution of Antioxidation of Quercetin in Vitro and Arbor Acre Broilers
- Study on Exogenous Ethylene Induced Rice Resistance to Rhizoctonia solani
