卵形鲳鲹卵巢不同发育时期的转录组测序分析
李蔚 何苹萍 韦嫔媛 朱鹏 蒋伟明 胡珅华 韦友传 韦明利 彭金霞


摘要:【目的】鑒定筛选出与卵形鲳鲹卵巢发育相关的候选基因及信号通路,为揭示其卵巢性成熟过程的分子机制打下基础。【方法】挑选卵巢发育处于?期和Ш期的雌性卵形鲳鲹,分别构建卵形鲳鲹卵巢?期和Ш期的cDNA文库,采用Illumina HiSeqTM 2500进行转录组测序,经过滤、质量控制及拼接组装后获得的Unigenes在七大数据库(Nr、Nt、Pfam、KOG/COG、Swiss-Prot、KEGG和GO)中进行比对;通过FPKM及DEGseq筛选出差异表达基因,以GOseq和KOBAS对差异表达基因分别进行功能注释及信号通路富集分析,并采用MISA和GATK3进行SSR鉴定及SNP分析。【结果】卵形鲳鲹卵巢组织转录组测序获得的325156432条Raw reads,经过滤筛选得到317206752条Clean reads,拼接组装后得到59554条Unigenes;69.65%的Unigenes在Nr、Nt、Pfam、KOG/COG、Swiss-Prot、KEGG和GO等七大数据库中注释成功,其中有24599条Unigenes被注释到GO数据库,15997条Unigenes被注释到KEGG数据库。在卵形鲳鲹卵巢组织的2个发育时期共鉴定获得56115个基因,经差异表达分析后获得17737个差异基因,其中8169个基因在卵巢Ш期上调表达、9568个基因在卵巢Ш期下调表达。GO功能注释分析发现,卵形鲳鲹卵巢差异表达基因主要注释在细胞过程、氮化合物代谢过程、初级代谢过程、核、核部分、离子结合及水解酶活性等条目上;而KEGG信号通路富集分析结果显示,17737个差异表达基因显著富集在318条代谢途径上,其中前20条KEGG信号通路包括2-氧代羧酸代谢、PI3K-Akt信号通路、甲状腺激素信号通路、磷脂酶D信号通路、Fc εRI信号通路和细胞周期等。卵形鲳鲹卵巢转录组(59554条Unigenes)中共存在30133个SSRs和82490个SNPs。【结论】GnRHR、FSHR、FSHβ、CYP11A、SIRT3和PEG3等差异表达基因及PI3K-Akt信号通路和VEGF信号通路等与卵形鲳鲹卵巢的发育密切相关,共同调节卵巢的发育与成熟,在卵巢性成熟过程中发挥重要作用。
关键词: 卵形鲳鲹;卵巢;发育;差异表达基因;信号通路;转录组测序
中图分类号: S917;S965.331 文献标志码: A 文章编号:2095-1191(2022)03-0714-11
Transcriptome analysis of ovaries at the different developmental stages of Trachinotus ovatus
LI Wei HE Ping-ping WEI Pin-yuan ZHU Peng JIANG Wei-ming
HU Shen-hua WEI You-chuan WEI Ming-li PENG Jin-xia
(1Guangxi Academy of Fisheries Sciences, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Aquatic Genetic Breeding and Healthy Aquaculture, Nanning, Guangxi 530021, China; 2College of Oceanography, Beibu Gulf University,
Qinzhou, Guangxi 535011, China; 3College of Animal Science and Technology of Guangxi University,
Nanning, Guangxi 530004, China)
Abstract:【Objective】The candidate genes and pathways related to the ovarian development of Trachinotus ovatus were identified, so as to lay the foundation of revealing the molecular mechanism on ovarian sexual maturation. 【Method】The stage ? and stage Ш ovarian tissue of T. ovatus were selected to construct the cDNA library for stage ? and stage Ш, respectively. Transcriptome sequencing was performed by Illumina HiSeqTM2005. After filtering, quality control, and assembly, the unigenes obtained were mapped to the seven databases (Nr, Nt, Pfam, KOG/COG, Swiss-Prot, KEGG and GO). The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified by FPKM and DEGseq. The GOseq and KOBAS were used for functional annotation and signal pathway enrichment analysis of DEGs, respectively. And the simple sequence repeat (SSR) identification and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) analysis were performed by MISA and gatk3. 【Result】The results showed that a total of 325156432 raw reads were generated from ovarian tissues. After filte-ring, 317206752 clean reads were selected, and then were assembled into 59554 unigenes, 69.65% of which were successfully annotated in Nr, Nt, Pfam, KOG/COG, Swiss-Prot, KEGG and GO databases. 24599 and 15997 unigenes were annotated to the GO database and KEGG database, respectively. The analysis showed that a total of 17737 DEGs were found in the ovaries of T. ovatus, among which 8169 DEGs were up-regulated at stage Ш ovary, and 9568 DEGs were down-regulated in stage Ш ovary. The GO functional annotation analysis demonstrated that, cellular process, nitrogen compound metabolic process, primary metabolic process, nucleus, nuclear part, ion binding and hydrolase activity. The results of KEGG signaling pathway enrichment analysis showed that 17737 DEGs were significantly enriched on 318 metabolic pathways. The top 20 KEGG signaling pathway including 2-Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism, PI3K-Akt signa-ling pathway, thyroid hormone signaling pathway, phospholipase D signaling pathway, Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway and cell cycle. Finally, a total of 30133 SSRs and 82490 SNPs were obtained from the 59554 unigenes of ovarian transcriptome of T. ovatus. 【Conclusion】Six DEGs, including GnRHR, FSHR, FSHβ, CYP11A, SIRT3 and PEG3,as well as two KEGG pathways such as PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and VEGF signaling pathway are closely involved in the ovarian development of T. ovatus, which co-regulates ovarian development and maturation.7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
Key words:Trachinotus ovatus;ovaries;development;differentially expressed genes;signal pathway;transcriptome sequencing
Foundation items: Natural Science Foundation of China (31660740, 31860736); Guangxi Science and Technology Major Project (Guike AA17204094-4); Guangxi Key Laboratory of Aquatic Genetic Breeding and Healthy Aquaculture Opening Fund (GXKEYLA2019-03)
0 引言
【研究意義】卵形鲳鲹(Trachinotus ovatus)俗名金鲳鱼,属于广盐暖水性鱼类,在我国南海、东海和黄海均有分布(陈伟洲等,2007;张永德等,2020),尤其在广西、广东和海南等地分布较广泛。卵形鲳鲹因具有无肌间刺、肉质细嫩、味道鲜美、抗逆性强、营养价值高等特点,而深受消费者青睐,是我国重要的海水养殖经济鱼类(郭萌萌等,2018)。至今,有关卵形鲳鲹的人工养殖和育苗技术已有较多报道(陈伟洲等,2007;林川等,2017;彭俊耀等,2017),对其胚胎发育和性腺发育也有相关研究(区又君和李加儿,2005;Xie et al.,2014;蒋小珍等,2015)。大多数硬骨鱼类以卵生方式进行繁殖,而卵巢是卵子形成和雌性激素分泌的重要场所。因此,研究卵形鲳鲹卵巢发育过程的分子机制,对发展新的繁殖相关技术对具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】近年来,转录组测序技术得到快速发展,已广泛应用于鱼类的相关研究领域,包括病毒致病机理、免疫应答、生殖发育及遗传育种等方面(Bar et al.,2016;Zhang et al.,2017;Wang et al.,2019),或将转录组测序技术作为研究鱼类性腺发育的重要手段,旨在筛选出相关的候选基因和信号通路。Socorro等(2007)对欧洲鲈鱼(Dicentrachus labrax)的精巢组织进行转录组测序分析,结果发现CYP11B和CYP19A基因在精巢中高度表达,编码调控雄激素的分泌,且对精子的发生和成熟起重要作用。Tao等(2013)通过转录组测序研究尼罗罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)不同发育阶段性腺的特异性,发现cyp19a1a和cyp19a1b基因在卵巢早期发育过程中发挥着重要作用。Fan等(2014)基于转录组测序探讨牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)性别决定和性腺发育的分子机制,证实卵巢类固醇生成和雌激素信号通路在牙鲆的性腺发育过程中发挥重要调控作用。Du等(2017)通过转录组测序技术研究斑石鲷(Oplegnathus punctatus)性腺发育和配子产生的分子机理,结果发现foxl2、bmp15、nanos3、sox9、amh等基因在斑石鲷性腺发育及生殖细胞的产生和维持方面起重要调控作用。Yue等(2017)基于转录组测序技术研究中华鲟(Acipenser sinensis)早期配子发生机制,结果发现sox、载脂蛋白和细胞周期蛋白等3个基因家族参与其生殖调控。姚汶励等(2019)基于高通量转录组测序分析草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idella)雌雄性腺差异表达基因,结果发现cyp19a1a和foxl2基因在其卵巢中显著高表达。He等(2019)基于转录组测序挖掘调控金钱鱼(Scatophagus argus)生殖发育的候选基因,结果发现foxl2、zar1及figla等6个基因与卵巢发育和卵子产生相关。李营等(2020)通过转录组测序分析,证实Dmrt1、Sox9、Bmp15和Gdf9等基因及卵母细胞成熟、卵母细胞减数分裂和卵巢类固醇合成等通路参与调控施氏鲟(Acipenser schrenckii Brandt)的性腺发育及性别分化过程。此外,已有研究通过转录组测序证实amh、foxl2及foxl3等基因在硬骨鱼类的性腺发育过程中发挥着重要作用(Crespo et al.,2013;张升利等,2014;Pfennig et al.,2015)。【本研究切入点】卵形鲳鲹生长速度快,鱼苗投放1年以内即可达商品鱼规格,但其性腺在自然条件和人工养殖下分别需要8年和3~5年才能发育成熟,性成熟周期较长(蒋小珍等,2015)。因此,了解卵巢发育的分子机制,探寻提升卵形鲳鲹繁殖性能的新途径,有利于促进其产业的可持续发展。【拟解决的关键问题】通过对卵形鲳鲹不同发育时期的卵巢组织进行转录组测序,鉴定筛选出与卵巢发育相关的候选基因及信号通路,为揭示其卵巢性成熟过程的分子机制打下基础。
1 材料与方法
1. 1 试验材料
供试卵形鲳鲹来源于中国—东盟海洋水产种业研发基地(北海竹林),以1龄鱼及3龄鱼为研究对象。1龄鱼的平均体重360.00±20.00 g,平均体长21.67±0.82 cm;3龄鱼的平均体重1990.00±2100.00 g,平均体长35.40±16.53 cm。将卵形鲳鲹的部分性腺组织保存于4%多聚甲醛中,用于组织切片制作及观察分析,以确定性腺发育阶段。另外,取部分性腺组织保存于RNAlater中,用于性腺转录组测序分析。根据组织切片显微观察结果,挑选卵巢发育处于?期和Ш期的雌性卵形鲳鲹各3尾。卵巢以卵原细胞为主鉴定为Ⅰ期;同时包含卵原细胞、初级卵母细胞和次级卵母细胞,但以次级卵母细胞为主则鉴定为Ш期。
1. 2 cDNA文库构建及RNA-Seq测序
利用TRIzol试剂(美国Invitrogen公司)提取6尾卵形鲳鲹卵巢组织中的总RNA,cDNA文库构建和RNA-Seq测序均委托广西普斐信息科技有限公司完成。RNA质量检测合格后,用带有Oligo(dT)的磁珠与mRNA的poly(A)尾端特异性结合,进一步对mRNA进行富集。随后加入破碎缓冲液将mRNA打断成短片段,以其为模板合成双链cDNA,采用AMPure XP磁珠进行纯化;纯化的cDNA经末端修复、加3'端poly(A)尾及连接接头后,以AMPure XP磁珠对DNA片段进行选择;最后进行PCR扩增,并以AMPure XP磁珠纯化产物,得到最终的cDNA文库。cDNA文库质量检测合格后,上机进行Illumina HiSeqTM 2500测序。7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
1. 3 测序数据组装及基因功能注释
为保证RNA测序分析的准确性,对原始序列(Raw read)进行过滤,去除带接头、N(无法确定碱基信息)比例高于10%、低质量序列(有50%以上碱基的质量值sQ≤5),有效序列获得(Clean reads)。使用Trinity对Clean reads进行拼接组装,即获得转录本(Grabherr et al.,2011),取同1个Cluster中最长的转录本作为Unigenes,并将其进行七大数据库(Nr、Nt、Pfam、KOG/COG、Swiss-Prot、KEGG和GO)的功能注释。
1. 4 差异表达基因筛选
以获得的转录组数据作为参考序列,采用RSEM将每个样本的Clean reads与其进行比对分析(Li and Dewey,2011)。根据比对结果将获得的Read count数目进行FPKM转换(Trapnell et al.,2010),标准化处理后,再利用DEGseq进行差异表达分析(Wang et al.,2010);同时以GOseq和KOBAS对差异表达基因分别进行功能注释及信号通路富集分析(Mao et al.,2005;Young et al.,2010)。
1. 5 SSR和SNP检测
采用MISA对卵形鲳鲹卵巢转录组数据拼接所得的Unigenes进行SSR检测,单核苷酸、二核苷酸、三核苷酸、四核苷酸、五核苷酸、六核苷酸重复所对应的最少重复次数分别为10、6、5、5、5或5,详见http://pgrc.ipk-gatersleben.de/misa/misa.html。通过SAMtools和Picard-Tools等进行分类及去除重复的Reads,再利用变异检测GATK3鉴定出转录组数据中SNP位置和突变类型(van der Auwera et al.,2013)。
2 结果与分析
2. 1 卵形鲳鲹卵巢组织切片观察结果
通过对卵形鲳鲹的卵巢组织切片进行观察,挑选性腺发育处于?期和Ш期的雌性卵形鲳鲹各3尾。性腺发育?期,卵形鲳鲹卵巢中的生殖细胞以卵原细胞为主,其体积较小,呈圆形,细胞核较大,细胞质很少(图1-A)。性腺发育Ш期,卵形鲳鲹卵巢中的生殖细胞以次级卵母细胞为主,细胞呈圆形,排列松散,细胞体积相应增大,大部分核仁沿核膜内缘分布,核外周胞质中油滴增多,细胞质中有细小的卵黄核(图1-B)。
2. 2 卵形鲳鲹卵巢转录组数据统计结果
卵形鲳鲹卵巢转录组测序获得的325156432条Raw reads经过滤筛选得到317206752条Clean reads(表1),各样品筛选获得的有效碱基(Clean bases)均在3.00 Gb以上,Q20碱基占比在90.00%以上,Q30碱基占比在82.50%以上,GC含量平均为50.47%,数据质量较高,可用于后续研究。
2. 3 卵形鲳鲹卵巢转录组序列注释结果
将拼接得到的59554条Unigenes在七大数据库(Nr、Nt、Pfam、KOG/COG、Swiss-Prot、KEGG和GO)中进行比对,结果发现有41482条Unigenes至少在1个数据库中被注释。在Nr、Nt、KEGG、Swiss-Prot、 Pfam、GO及KOG等数据库注释成功的Unigenes分别有29607、37366、15997、24768、24255、24599和11949条(表2),说明注释到七大数据库的基因较多,有利于后续研究。共有24599条Unigenes在GO功能注释中被分成三大类[分子功能(Molecular function)、细胞组分(Cellular component)及生物学过程(Biological process)],共涉及54个功能组(图2)。其中,752条Unigenes参与发育过程(Developmental process),408条Unigenes参与生殖过程(Reproductive process),389条Unigenes参与生殖(Reproduction)。同时有15997条Unigenes被注释到KEGG数据库,共涉及五大分支32种代谢途径(图3),主要参与信号转导(Signal transduction)、细胞免疫(Cellular immunity)、信号分子与相互作用(Signaling molecules and interaction)等代谢通路。
2. 4 卵形鲳鲹卵巢差异基因表达分析结果
在卵形鲳鲹卵巢组织的2个发育时期共鉴定获得56115个基因,经差异表达分析后获得17737个差异基因(图4),其中,8169个基因在卵巢Ш期上调表达,9568个基因在卵巢Ш期下调表达,包括GnRHR (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor)、FSHβ (Follicle stimulating hormone beta subunit)、FSHR (Follicle stimulating hormone receptor)、CYP11A (Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme,mitochondrial)、SIRT3(NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-3,mitochondrial)和PEG(Paternally-expressed gene 3 protein-like)等基因(表3)。
2. 5 卵形鯧鲹卵巢差异表达基因GO功能注释分析结果
为进一步挖掘与卵形鲳鲹卵巢发育相关的基因,对卵巢?期和卵巢Ш期的差异表达基因进行GO功能注释分析。由图5可知,卵形鲳鲹卵巢差异表达基因主要注释在细胞过程(Cellular process)、氮化合物代谢过程(Nitrogen compound metabolic process)、初级代谢过程(Primary metabolic process)、核(Nucleus)、核部分(Nuclear part)、离子结合(Ion binding)及水解酶活性(Hydrolase activity)等条目上。7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
2. 6 卵形鲳鲹卵巢差异表达基因KEGG信号通路富集分析结果
在生物体内,不同基因调控不同的生物学功能,且这些基因相互协调以维系生命活动能正常进行。KEGG信号通路富集分析结果显示,17737个差异表达基因显著富集在318条代谢途径上,其中前20条KEGG信号通路(表4)包括2-氧代羧酸代谢(2-Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism)、PI3K-Akt信号通路(PI3K-Akt signaling pathway)、甲状腺激素信号通路(Thyroid hormone signaling pathway)、磷脂酶D信号通路(Phospholipase D signaling pathway)、Fc εRI信号通路(Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway)和细胞周期(Cell cycle)等。
2. 7 卵形鲳鲹卵巢转录组序列SSR鉴定和SNP分析结果
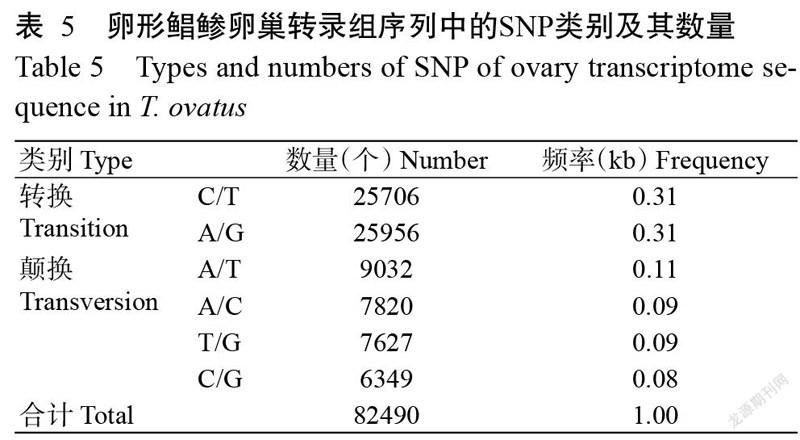
对卵形鲳鲹卵巢转录组序列进行SSR鉴定,结果表明59554条Unigenes中共存在30133个SSRs,其中6569条Unigenes包含1个以上SSR的序列数。6种核苷酸重复类型的SSR出现频率各不相同,以单核苷酸重复SSR的出现频率最高,其次是二核苷酸重复SSR(图6)。其中,A/T在单核苷酸重复SSR中最常见,AC/GT在二核苷酸重复SSR中最常见,AGG/CCT在三核苷酸重复SSR中最常见,AAAT/ATTT在四核苷酸重復SSR中最常见。SNP分析结果(表5)表明,卵形鲳鲹卵巢转录组中共有82490个SNPs,其中C/T、A/G分别有25706和25956个,A/T、A/C、T/G和C/G分别有9032、7820、7627和6349个。
3 讨论
转录组测序技术对于鉴定筛选不同生物、不同发育时期或不同组织间的差异表达基因至关重要(吴小梅等,2017;夏晓培,2017;张涛等,2018;肖韵铮等,2020)。卵形鲳鲹是一种重要的海水养殖鱼类,但其卵巢发育的分子机理尚未明确,因此亟待挖掘相关的候选基因和信号通路。本研究利用Illumina HiSeq测序技术对卵形鲳鲹?期和Ш期卵巢组织进行转录组测序,共得到59554条Unigenes,注释成功率为69.65%;尚有30.35%的Unigenes未得到功能注释,可能是由于数据库现有的鱼类基因信息不够丰富,或是包含特有且未被发现的新基因(Li et al.,2016),具体原因有待进一步探究。其中,有24599条Unigenes在GO数据库中被注释,主要涉及发育过程、生殖过程和生殖等GO功能条目,表明这些基因在卵形鲳鲹卵巢生殖细胞的发育过程中至关重要。
本研究筛选出多个与卵形鲳鲹卵巢发育相关的差异表达基因,共同调节卵巢的发育与成熟。其中,GnRHR、FSHR、FSHβ、CYP11A和SIRT3等5个差异表达基因在?期卵巢中高丰度表达,表明这5个基因参与调控卵形鲳鲹卵巢的早期发育;PEG3基因在Ш期卵巢中高表达,则可能参与调控卵巢的后期发育过程。已有研究表明,下丘脑—垂体—性腺轴(HPG)不仅与哺乳动物卵泡和卵母细胞的发育过程相关,还与鱼类的生殖发育有关(Daftary and Gore,2005;Ji et al.,2013;Liu et al.,2016)。促性腺激素释放激素受体(GnRHR)是垂体分泌的G-蛋白偶联受体,与下丘脑分泌的促性腺激素释放激素(GnRH)结合后通过刺激一系列的激素级联反应,而促进促性腺激素释放,使得性腺发育成熟,达到调控性腺发育的目的。Madigou等(2000)研究发现,GnRHR基因在虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)卵巢中有较高的表达水平,即在卵巢发育过程中起关键作用。卵泡刺激素(FSH)是垂体分泌的糖蛋白激素,其β亚基(FSHβ)具有特异性表达调控的作用,从而促使FSH在性腺发育的过程中发挥生物功能。卵泡刺激素受体(FSHR)是性腺上的促性腺激素受体,也属于G-蛋白偶联受体。FSH与FSHR结合能促进卵泡的生长与成熟,有效刺激滤泡细胞合成类固醇激素,对哺乳动物和鱼类的性腺生殖发育活动均具有重要作用(Santos et al.,2001;何小龙,2010)。FSHβ基因可促进新澳鳗鲡(A. australis schmidti)卵巢的早期发育(Setiawan et al.,2012);而FSHR基因在斑马鱼(Danio rerio)及庸鲽(Hippoglossus hippoglossus)的卵母细胞生长及卵黄生成的中前期高表达(So et al.,2005;Kobayashi et al.,2008)。
性类固醇激素由胆固醇转化而成,在性腺中合成分泌,主要包括雌激素、孕激素和睾酮类,对鱼类的性腺发育分化起重要作用(Tokarz et al.,2015;Toit et al.,2017)。胆固醇侧链裂解酶基因(CYP11A)参与类固醇激素的合成,类固醇激素合成急性调节蛋白(StAR)携带胆固醇进入细胞后,通过CYP11A转换成孕酮,再经过一系列的芳香化反应,最终合成雄激素和雌激素。CYP11A基因在斑马鱼卵巢成熟前期高表达(陈孝红等,2015)。SIRT3基因通过阻止活性氧(ROS)的激活,而在雌性牦牛繁殖发育过程中发挥调控作用,促进卵丘细胞的增殖凋亡、氧化应激及孕酮分泌(王斌,2020);SIRT3基因在山羊卵巢中高表达,具有基因型多态性,其表达水平与山羊的产羔量紧密相关,可能是山羊遗传改良的潜在候选基因(Silpa et al.,2020)。基因印迹是指不遵从孟德尔定律,某些基因的单等位基因表达取决于其亲本来源的现象(Song et al.,2009)。PEG3基因作为哺乳动物的印迹基因,在其繁殖活动中发挥重要作用。宋振华等(2010)研究发现,PEG3基因是雌性小鼠生殖细胞的印迹基因,其甲基化印迹发生在次级卵母细胞发育阶段;Jiang等(2011)研究表明,PEG3基因是猪的印迹基因,在卵巢中表达双等位基因。7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
卵巢的发育涉及多个生物学途径。本研究的KEGG信号通路富集分析结果显示,卵形鲳鲹卵巢差异表达基因显著富集到PI3K-Akt信号通路、甲状腺激素信号通路和VEGF信号通路等。其中,PI3K-Akt信号通路主要是由磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)、中间效应因子及蛋白激酶B(Akt)所构成。PI3K-Akt信号通路对卵巢卵泡的发育和卵母细胞的成熟起重要作用(Wen et al.,2018)。在卵泡的发育过程中,卵原细胞进行减数分裂,而PI3K-Akt信号通路在卵母细胞减数分裂过程中发挥关键调控作用,从而影响卵母细胞的成熟分化程度(Song et al.,2018)。PI3K-Akt信号通路除了在哺乳动物,如猪、牛及小鼠的卵泡发育过程中起重要调控作用(Tomek and Smiljakovic,2005;Liu et al.,2018)外,在小菜蛾等昆虫的卵巢发育和卵子发生方面也发挥着潜在作用(Peng et al.,2017)。此外,VEGF信号通路与卵巢发育密切相关(Qiu and Liu,2009)。Jung等(2016)研究表明,VEGF信号通路在罗氏沼虾(Macrobrachium rosenbergii)的卵子发生和卵巢发育成熟过程中扮演重要角色。可见,PI3K-Akt信号通路和VEGF信号通路在卵形鲳鲹的卵巢性成熟过程中发挥重要作用。
4 结论
GnRHR、FSHR、FSHβ、CYP11A、SIRT3和PEG3等差异表达基因及PI3K-Akt信号通路和VEGF信號通路等与卵形鲳鲹卵巢的发育密切相关,共同调节卵巢的发育与成熟,在卵巢性成熟过程中发挥重要作用。
参考文献:
陈伟洲,许鼎盛,王德强,邓用谋,佘忠明,丘广艳,李远友. 2007. 卵形鲳鲹人工繁殖及育苗技术研究[J]. 台湾海峡,26(3):435-442. [Chen W Z,Xu D S,Wang D Q,Deng Y M,She Z M,Qiu G Y,Li Y Y. 2007. Study on the spawning and hatching technique for Trachinotus ovatus[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait,26(3):435-442.] doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2007.03.019.
陈孝红,仇雪梅,郝薇薇,王秀利. 2015. 斑马鱼CYP11a1基因在不同性腺发育时期的表达[J]. 大连海洋大学学报,30(1):13-17. [Chen X H,Qiu X M,Hao W W,Wang X L. 2015. Expression of CYP11a1 in different developmental phases of gonad in zebrafish Danio rerio[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University,30(1):13-17.] doi:10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-1388.2015.01.003.
郭萌萌,何晨,张诗苑,吴继香,林格儿,李川,曹君. 2018. 金鲳鱼不同组织脂肪酸组成比较[J]. 食品工业科技,39(9):45-50. [Guo M M,He C,Zhang S Y,Wu J X,Lin G E,Li C,Cao J. 2018. Fatty acids composition in diffe-rent tissues of Trachinotus ovatus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,39(9):45-50.] doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.09.009.
何小龙. 2010. 蒙古羊BMPR-IB、FSHβ基因克隆与表达及卵巢组织差异表达基因研究[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学. [He X L. 2010. Study on cloning and expression of BMPR-IB,FSHβ gene and differentially expressed genes of ovary in Mongolian sheep[D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University.] doi:10.7666/d.d197931.
蒋小珍,韦嫔媛,陈晓汉,彭敏,蒋伟明,李咏梅,彭金霞. 2015. 卵形鲳鲹性腺组织学观察及简易性别判定方法建立[J]. 西南农业学报,28(1):428-432. [Jiang X Z,Wei P Y,Chen X H,Peng M,Jiang W M,Li Y M,Peng J X. 2015. Histological observation of Trachinotus ovatus and methodical construction of simple method of early sex identification[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,28(1):428-432.] doi:10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2015. 01.080.
李营,阮瑞,艾成,岳华梅,叶欢,杜浩,李创举. 2020. 养殖施氏鲟的性腺转录组特征分析[J]. 水生生物学报,44(2):310-318. [Li Y,Ruan R,Ai C,Yue H M,Ye H,Du H,Li C J. 2020. Characteristics of the gonadal transcriptome of Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii) under artificial culture[J]. Acta Hydrobiologuca Sinica,44(2):310-318.] doi:10.7541/2020.038.7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
林川,王小兵,黄海. 2017. 卵形鲳鲹鱼种大型网箱阶梯式中间培育技术[J]. 热带生物学报,8(4):383-389. [Lin C,Wang X B,Huang H. 2017. The stepwise intermediate culture of Trachinotus ovatus fingerlings in large cage[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology,8(4):383-389.] doi:10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2017.04.002.
区又君,李加儿. 2005. 卵形鲳鲹的早期胚胎发育[J]. 中国水产科学,12(6):786-789. [Ou Y Q,Li J E. 2005. Early embryonic development in Trachinotus ovatus[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China,12(6):786-789.] doi:10. 3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2005.06.019.
彭俊耀,梁怡姬,欧小华. 2017. 卵形鲳鲹人工繁殖及育苗技术[J]. 海洋与渔业,(4):54-55. [Peng J Y,Liang Y J,Ou X H. 2017. Study on the spawning and hatching technique of Trachinotus ovatus[J]. Ocean and Fisheries,(4):54-55.] doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4046.2017.04.020.
宋振华,闵令江,荣美洁,潘庆杰,沈伟. 2010. 小鼠卵泡颗粒细胞分化不影响卵母细胞印迹基因DNA甲基化进程[J]. 青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版),27(1):6-10. [Song Z H,Min L J,Rong M J,Pan Q J,Shen W. 2010. DNA methylation of imprint genes in the oocytes was not affec-ted by the differentiation of granulose cells[J]. Journal of Qingdao Agricultural University(Natural Science),27(1):6-10.] doi:10.3969/J.ISSN.1674-148X.2010.01.002.
王斌. 2020. 牦牛SIRT3基因的特征分析以及對卵丘细胞的影响[D]. 成都:西南民族大学. [Wang B. 2020. Characteristic analysis of yak SIRT3 gene and its effect on cumulus cells[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Minzu University.] doi:10.27417/d.cnki.gxnmc.2020.000239.
吴小梅,张昕,李南羿. 2017. 双孢蘑菇子实体不同发育时期的转录组分析[J]. 菌物学报,36(2):193-203. [Wu X M,Zhang X,Li N Y. 2017. Transcriptome analysis of Agaricus bisporus fruiting at different stages[J]. Mycosystema,36(2):193-203.] doi:10.13346/j.mycosystema.150275.
夏晓培. 2017. 泥鳅发育不同时期性腺转录组学研究及Wnt4基因的生物信息学分析[D]. 新乡:河南师范大学. [Xia X P. 2017. Transcriptome study of gonads in different stages of loach development and bioinformatics analysis of Wnt4 gene[D]. Xinxiang:Henan Normal University.]
肖韵铮,韩世明,秦昭,李春奇. 2020. 滇黄精转录组测序及类黄酮合成相关基因的分析[J]. 河南农业大学学报,54(6):931-940. [Xiao Y Z,Han S M,Qin Z,Li C Q. 2020. Analysis of transcriptome sequencing and related genes of flavonoids biosynthesis from Polygonatum kingianum[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University,54(6):931-940.] doi:10.16445/j.cnki.1000-2340.2020.06.004.
姚汶励,姜鹏,白俊杰,马冬梅. 2019. 基于高通量转录组测序的草鱼雌雄性腺差异表达基因分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,38(9):3901-3911. [Yao W L,Jiang P,Bai J J,Ma D M. 2019. Analysis of differential expressed genes between male and female gonads of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) based on high throughput transcriptome group sequencing[J]. Genomics and Applied Bio-logy,38(9):3901-3911.] doi:10.13417/j.gab.038.003901.7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
張升利,付成东,梁拥军,李文通,孙砚胜,史东杰,张欣. 2014. 长尾草金鱼成熟期雌雄性腺RNA-Seq转录组分析[J]. 水产科学,33(12):750-756. [Zhang S L,Fu C D,Liang Y J,Li W T,Sun Y S,Shi D J,Zhang X. 2014. The RNA-Seq transcriptome analysia in mature gonads of long-tailed goldfish Carassius auratus[J]. Fisheries Science,33(12):750-756.] doi:10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.2014.12.006.
张涛,杨理凯,路宏朝,王令,刘欢,左甜甜. 2018. 小鼠中年期和老年期睾丸组织转录组分析[J]. 西北农业学报,27(8):1088-1096. [Zhang T,Yang L K,Lu H C,Wang L,Liu H,Zuo T T. 2018. Transcriptome analysia of mouse testis tissue in middle age and old age[J]. Acta Agriculture Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,27(8):1088-1096.] doi:10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2018.08.002.
张永德,文露婷,罗洪林,林勇,杜雪松,余艳玲,韦孜娜,黄姻. 2020. 卵形鲳鲹基因组调研及其SSR分子标记的开发应用[J]. 南方农业学报,51(5):983-994. [Zhang Y D,Wen L T,Luo H L,Lin Y,Du X S,Yu Y L,Wei Z N,Huang Y. 2020. Genome survey and development of SSR molecular markers for Trachinotus ovatus[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,51(5):983-994.] doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2020.05.001.
Bar I,Cummins S,Elizur A. 2016. Transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed genes associated with germ cell and gonad development in the southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii)[J]. BMC Genomics,17(1):217. doi:10.1186/s12864-016-2397-8.
Crespo B,Lan-Chow-Wing O,Rocha A,Zanuy S,Gómez A. 2013. foxl2 and foxl3 are two ancient paralogs that remain fully functional in teleosts[J]. General and Compa-rative Endocrinology,194:81-93. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen. 2013.08.016.
Daftary S S,Gore A C. 2005. IGF-1 in the brain as a regulator of reproductive neuroendocrine function[J]. Experimental Biology and Medicine,230(5):292-306. doi:10. 1177/153537020523000503.
Du X X,Wang B,Liu X M,Liu X B,He Y,Zhang Q Q,Wang X B. 2017. Comparative transcriptome analysis of ovary and testis reveals potential sex-related genes and pathways in spotted knifejaw Oplegnathus punctatus[J]. Gene,637:203-210. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2017.09.055.
Fan Z F,You F,Wang L J,Weng S D,Wu Z H,Hu J W,Zou Y X,Tan X G,Zhang P J. 2014. Gonadal transcriptome analysis of male and female olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)[J]. BioMed Research International,2014:291067. doi:10.1155/2014/291067.
Grabherr M G,Haas B J,Yassour M,Levin J Z,Thompson D A,Amit I,Adiconis X,Fan L,Raychowdhury R,Zeng Q D,Chen Z H,Mauceli E,Hacohen N,Gnirke A,Rhind N,di Palma F,Birren B W,Nusbaum C,Lindblad-Toh K,Friedman N,Regev A. 2011. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome[J]. Nature Biotechnology,29(7):644-652. doi:10.1038/nbt.1883.7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
He F X,Jiang D N,Huang Y Q,Mustapha U F,Yang W,Cui X F,Tian C X,Chen H P,Shi H J,Deng S P,Li G L,Zhu C H. 2019. Comparative transcriptome analysis of male and female gonads reveals sex-biased genes in spotted scat(Scatophagus argus)[J]. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry,45(6):1963-1980. doi:10.1007/s10695-019- 00693-8.
Ji K,Liu X S,Lee S,Kang S,Kho Y,Giesy J P,Choi K. 2013. Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on hormones and genes of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad axis,and reproduction of zebrafish[J]. Journal of Hazar-dous Materials,254-255:242-251. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat. 2013.03.036.
Jiang C D,Li S,Deng C Y. 2011. Assessment of genomic imprinting of PPP1R9A,NAP1L5 and PEG3 in pigs[J]. Genetika,47(4):537-542. doi:10.1134/S1022795411040053.
Jung H,Yoon B H,Kim W J,Kim D W,Hurwood D A,Lyons R E,Salin K R,,Kim H S,Baek I,Chand V,Mather P B. 2016. Optimizing hybrid de Novo transcriptome assembly and extending genomic resources for giant freshwater prawns(Macrobrachium rosenbergii):The identification of genes and markers associated with reproduction[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,17(5):690. doi:10.3390/ijms17050690.
Kobayashi T,Pakarinen P,Torgersen J,Huhtaniemi I,Ander-sen ?. 2008. The gonadotropin receptors FSH-R and LH-R of atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus)-2. Differential follicle expression and asynchronous oogenesis[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology,156(3):595-602. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.02.010.
Li B,Dewey C N. 2011. RSEM:Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome[J]. BMC Bioinformatics,12(1):323. doi:10. 1186/1471-2105-12-323.
Li Y P,Zhang L L,Sun Y,Ma X L,Wang J,Li R J,Zhang M W,Wang S,Hu X L,Bao Z M. 2016. Transcriptome sequencing and comparative analysis of ovary and testis identifies potential key sex-related genes and pathways in scallop Patinopecten yessoensis[J]. Marine Biotechno-logy,18(4):453-465. doi:10.1007/s10126-016-9706-8.
Liu W J,Chen C Y,Chen L,Wang L,Li J,Chen Y Y,Jin J N,Kawan A,Zhang X Z. 2016. Sex-dependent effects of microcystin-LR on hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad axis and gametogenesis of adult zebrafish[J]. Scientific Reports,6:22819. doi:10.1038/srep22819.
Liu Y,Li M X,Bo X W,Li T,Ma L P,Zhai T J,Huang T. 2018. Systematic analysis of long non-coding RNAs and mRNAs in the ovaries of duroc pigs during different follicular stages using RNA sequencing[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,19(6):1722. doi:10.3390/ijms19061722.7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
Madigou T,Ma?anos-Sanchez E,Hulshof S,Anglade I,Zanuy S,Kah O. 2000. Cloning,tissue distribution,and central expression of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor in the rainbow trout(Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J]. Bio-logy of Reproduction,63(6):1857-1866. doi:10.1095/biolreprod63.6.1857.
Mao X Z,Cai T,Olyarchuk J G,Wei L P. 2005. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology(KO) as a controlled vocabulary[J]. Bioinformatics,21(19):3787-3793. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti430.
Peng L,Wang L,Yang Y F,Zou M M,He W Y,Wang Y,Wang Q,Vasseur L,You M S. 2017. Transcriptome profiling of the Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera:Plutellidae) ovary reveals genes involved in oogenesis[J]. Gene,637:90-99. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2017.09.020.
Pfennig F,Standke A,Gutzeit H O. 2015. The role of Amh signaling in teleost fish—Multiple functions not restricted to the gonads[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology,223:87-107. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2015.09.025.
Qiu G F,Liu P. 2009. On the role of Cdc2 kinase during meio-tic maturation of oocyte in the Chinese mitten crab,Eriocheir sinensis[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Phy-siology. Part B:Biochemistry & Molecular Biology,152(3):243-248. doi:10.1016/j.cbpb.2008.12.004.
Santos E M,Mariann R W,Tyler C R. 2001. Follicle-stimula-ting hormone and its α and β subunits in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss):Purification,characterization,development of specific radioimmunoassays,and their seasonal plasma and pituitary concentrations in females[J]. Biology of Reproduction,65(1):288-294. doi:10.1095/biolreprod65.1.288.
Setiawan A N,Ozaki Y,Shoae A,Kazeto Y,Lokman P M. 2012. Androgen-specific regulation of FSH signalling in the previtellogenic ovary and pituitary of the New Zealand shortfinned eel,Anguilla australis[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology,176(2):132-143. doi:10.1016/ j.ygcen.2011.12.041.
Silpa M V,Naicy T,Aravindakshan T V,Radhika G,Joan J,Jinty S. 2020. Ovarian expression,polymorphism identification and association of SIRT3 gene with reproduction traits in goats[J]. Animal Biotechnology,32(5):544-549. doi:10.1080/10495398.2020.1726363.
So K W,Kwok H F,Ge W. 2005. Zebrafish gonadotropins and their receptors:Ⅱ. Cloning and characterization of zebrafish follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone subunits—Their spatial-temporal expression patterns and receptor specificity[J]. Biology of Reproduction,72(6):1382-1396. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.104.038 216.7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
Socorro S,Martins R S,Deloffre L,Mylonas C C,Canario A V M. 2007. A cDNA for European sea bass (Dicentrachus labrax) 11beta-hydroxylase:Gene expression during the thermosensitive period and gonadogenesis[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology,150(1):164-173. doi:10.1016/ j.ygcen.2006.07.018.
Song B S,Jeong P S,Lee J H,Lee M H,Yang H J,Choi S A,Lee H Y,Yoon S B,Park Y H,Jeong K J,Kim Y H,Jin Y B,Kim J S,Sim B W,Huh J W,Lee S R,Koo D B,Chang K T,Kim S U. 2018. The effects of kinase modulation on in vitro maturation according to different cumulus-oocyte complex morphologies[J]. PLoS One,13(10):e0205495. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0205495.
Song Z H,Min L J,Pan Q J,Shi Q H,Shen W. 2009. Maternal imprinting during mouse oocyte growth in vivo and in vitro[J]. Biochemcal and Biophysical Research Communications,387(4):800-805. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009. 07.131.
Tao W J,Yuan J,Zhou L Y,Sun L N,Sun Y L,Yang S J,Li M H,Zeng S,Huang B F,Wang D S. 2013. Characterization of gonadal transcriptomes from Nile tilapia(Oreochromis niloticus) reveals differentially expressed genes[J]. PLoS One,8(5):e63604. doi:10.1371/journal.pone. 0063604.
Toit R L D,Storbeck K H,Cartwright M,Cabral A,Africander D. 2017. Progestins used in endocrine therapy and the implications for the biosynthesis and metabolism of endogenous steroid hormones[J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,441:31-45. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2016.09. 004.
Tokarz J,M?ller G,de Angelis M H,Adamski J. 2015. Steroids in teleost fishes:A functional point of view[J]. Steroids,103:123-144. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2015.06.011.
Tomek W,Smiljakovic T. 2005. Activation of Akt (protein kinase B) stimulates metaphase I to metaphase II transition in bovine oocytes[J]. Reproduction,130(4):423-430. doi:10.1530/rep.1.00754.
Trapnell C,Williams B A,Pertea G,Mortazavi A,Kwan G,van Baren M J,Salzberg S L,Wold B J,Pachter L. 2010. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching du-ring cell differentiation[J]. Nature Biotechnology,28(5):511-515. doi:10.1038/nbt.1621.
van der Auwera G A,Carneiro M O,Hartl C,Poplin R,del Angel G,Levy-Moonshine A,Jordan T,Shakir K,Roazen D,Thibault J,Banks E,Garimella K V,Altshuler D,Gabriel S,DePristo M A. 2013. From FastQ data to high confidence variant calls:The Genome Analysis Toolkit best practices pipeline[J]. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics,43:11.10.1-11.10.33. doi:10.1002/0471250953.bi1110s43.7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D
Wang L K,Feng Z X,Wang X,Wang X W,Zhang X G. 2010. DEGseq:An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data[J]. Bioinformatics,26(1):136-138. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp612.
Wang W W,Tan S X,Luo J,Shi H T,Zhou T,Yang Y J,Jin Y L,Wang X Z,Niu D H,Yuan Z H,Gao D Y,Dunham R,Liu Z J. 2019. GWAS analysis indicated importance of NF-κB signaling pathway in host resistance against motile aeromonas septicemia disease in catfish[J]. Marine Biotechnology,21(3):335-347. doi:10.1007/s10126-019-09883-0.
Wen X W,Xie J,Zhou L X,Fan Y,Yu B F,Chen Q J,Fu Y L,Yan Z,Guo H Y,Lü Q F,Kuang Y P,Chai W R. 2018. The role of combining medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate with human menopausal gonadotropin in mouse ovarian follicular development[J]. Scientific Reports,8(1):4439. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-22797-6.
Xie Z Z,Xiao L,Wang D D,Fang C,Liu Q Y,Li Z H,Liu X C,Zhang Y,Li S S,Lin H R. 2014. Transcriptome analysis of the Trachinotus ovatus:Identification of reproduction,growth and immune-related genes and microsatellite markers[J]. PLoS One,9(10):e109419. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109419.
Young M D,Wakefield M J,Smyth G K,Oshlack A. 2010. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq:Accounting for selection bias[J]. Genome Biology,11(2):1-12. doi:10. 1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14.
Yue H M,Li C J,Du H,Zhang S H,Wei Q W. 2017. Sequencing and de novo assembly of the gonadal transcriptome of the endangered Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis)[J]. PLoS One,10(6):e0127332. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0127332.
Zhang X,Mu Y N,Mu P F,Ao J Q,Chen X H. 2017. Transcriptome analysis reveals comprehensive insights into the early immune response of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) induced by trivalent bacterial vaccine[J]. PLoS One,12(1):e0170958. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170958.
(責任编辑 兰宗宝)7961F3CB-8156-4CEE-B097-F27409C0EE5D

