Identification of Resistance of Powdery Mildew and Stripe Rust of Winter Wheat Strains in Xinjiang
Wei SANG, Pengpeng LIU, Yingbin NIE, Dezheng KONG, Fengjuan CUI, Xinnian HAN, Hongjun XU, Peiyuan MU
Institute of Crop Research, Xinjiang Academy of Agri-Reclamation Sciences/Key Laboratory of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps for Cereal Quality Research and Genetic Improvement, Shihezi 832000, China
Abstract Wheat powdery mildew and stripe rust are the major diseases in wheat producing area in Xinjiang. To obtain wheat germplasm resources and varieties resistant to powdery mildew and rust, 36 high-generation stable strains of Xinjiang winter wheat were evaluated using the method of natural inducement from 2018 to 2020. A total of 5 strains with high resistance to powdery mildew, 4 strains with slow stripe rust and 1 strain with resistance to powdery mildew and adult plant slow stripe rust were obtained. And the parental combination of disease-resistant varieties was analyzed. These studies will provide theoretical basis for the breeding of resistant wheat varieties in Xinjiang.
Key words Xinjiang winter wheat strains; Powdery mildew; Stripe rust; Resistance identification
1 Introduction
Wheat is the largest food crop planted in the world, while wheat disease is an important factor affecting the healthy development of agriculture. Powdery mildew and stripe rust of wheat are fungal diseases caused byBlumeriagraminisandPucciniastriiformis, which are important factors affecting wheat production. They are widely distributed in the world because of strong climate adaptability. Powdery mildew and stripe rust occur to varying degrees in many countries and major wheat producing areas in China, and can result in the yield reduction of 10%-20% in epidemic years, or even no harvest in severe cases, which seriously affect the stable and high yield of wheat, being the two most serious diseases affecting wheat production in China[1-2].
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (hereinafter referred to as Xinjiang) is a high wheat producing area in China and an important grain production base, which plays an important role in ensuring national food security. In recent years, due to the global climate changes and the large-scale application of drip irrigation technology, the occurrence of powdery mildew and stripe rust in Xinjiang wheat producing areas has become more and more serious, from occasional to frequent. At present, there are few varieties that are resistant to both diseases in wheat production in Xinjiang, and the climatic conditions are more and more suitable for the occurrence and spread of powdery mildew and stripe rust, which have become the main diseases harming wheat production in Xinjiang. The use of disease-resistant varieties is the most economical, effective and fast way to reduce the damage of powdery mildew and stripe rust of wheat[1,3-4]. Xinjiang wheat breeding units realize disease resistance and yield increase by continuously introducing new materials for variety improvement. However, most wheat varieties grown in large areas and important resistance sources in Xinjiang do not have dominant races resistant to powdery mildew and stripe rust, and it is urgent to explore the resistance sources of powdery mildew and stripe rust to enrich the resistance genes of wheat and ensure the safety of wheat production. Therefore, it is of great importance to continuous control of powdery mildew and stripe rust of wheat and the safe production of wheat in Xinjiang by strengthening the study on resistance to powdery mildew and stripe rust of wheat varieties or strains in Xinjiang.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 MaterialsA total of 36 Xinjiang winter wheat strains were tested, and new winter wheat strains developed since 2017 by the wheat research laboratory of Institute of Crop Research, Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Reclamation Sciences (hereinafter referred to as institute of crop research) were mainly selected (Table 1). The tested new strains were obtained by propagation in the experimental station of institute of crop research in 2017, 2018 and 2019, respectively.
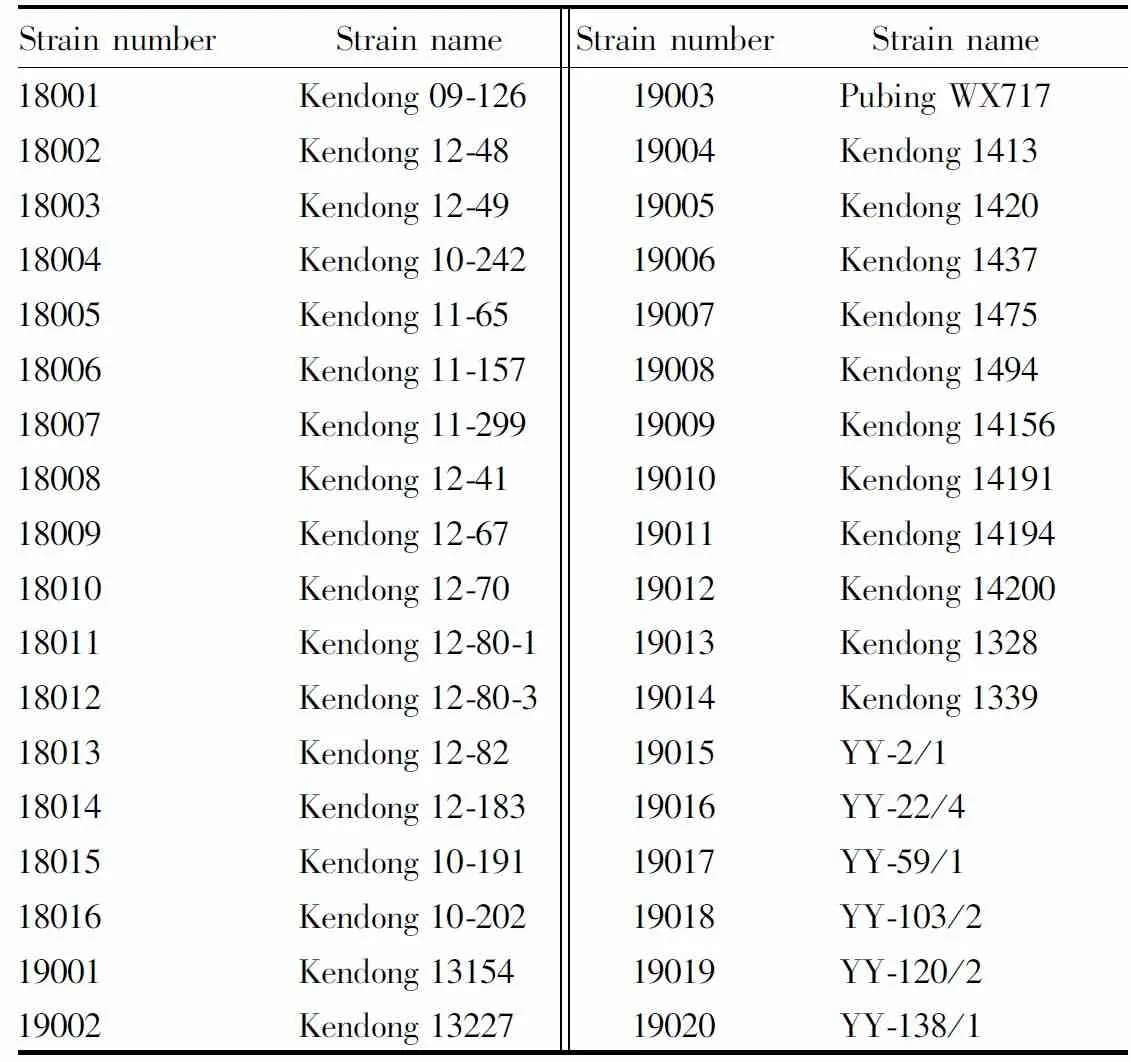
Table 1 Names and numbers of Xinjiang winter wheat strains tested
2.2 Identification of disease resistance
2.2.1Identification of powdery mildew resistance. The resistance of 20 materials to powdery mildew was tested at Changping experimental base of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. All materials were planted before October 2019.B.graminisstrain was a mixed strain provided by Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences for identification of powdery mildew resistance in national winter wheat regional test,which was inoculated after wheat turning green. The reaction type was recorded according to 9-level standard at milk ripe stage of wheat, and rechecked once. Specifically, 0 represented immune (M); 1-2 represented highly resistant (HR); 3-4 represented moderately resistant (MR); 5-6 represented moderately susceptible (MS); 7-9 represented highly susceptible (HS).
2.2.2Identification of stripe rust resistance. The resistance of 36 materials to stripe rust was identified in Qingshui breeding base of Wheat Research Institute, Gansu Academy of Agricultural Sciences. In order to investigate the actual effect of stripe rust on grain yield of each strain, the test was divided into two groups: naturally induced susceptible group (I) and spray protection group (II). The two groups were compared and planted adjacent to each other, three replicates each group, and various materials in each replicate were randomly arranged. Wheat strains were sown in drill by manual ditching, with equidistant line (line length 1 m, line spacing 0.2 m), 2 lines each material. A line of rapidly susceptible control "Huixianhong" was planted for each 50 materials; a line of "Huixianhong" was planted in the middle of each group of materials; and "Huixianhong" was planted around the identification area as the inducement line. The sowing was synchronous with the field operation, and the sowing date of different materials was adjusted appropriately. Winter materials were normally sown in autumn according to the local climate, while weak winter materials or spring materials were delayed for one month.
In the middle and late April of the next year when there was no wind after rain, the mixed strain of stripe rust were inoculated to inducement lines around the identification area by powder spraying method (2018) or uredospore spraying method (2019, 2020). At 20-30 d post inoculation, the disease state was identified by stages according to the incidence. According to the national standard NY/T1443.1-2007TechnicalSpecificationforEvaluationofWheatResistanceagainstStripeRust, the incidence was identified and evaluated from three indexes of reaction type, severity and prevalence rate. The reaction type could be divided into 6 types: 0, 0’, 1, 2, 3 and 4, and the highest grade found on the diseased leaves shall prevail. The severity was divided into 8 grades: 1% (t), 5%, 10%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100%. The lowest and highest values were recorded without taking an average. The prevalence rate was estimated as the percentage of the number of diseased leaves in the total number of investigated leaves. Every identification of all materials was done on the same day or the next day. Each index of each material appraisal should be subject to the highest value in the three replicates. Evaluation of disease resistance relied on reaction type and severity, regardless of prevalence rate. For the material with relatively prominent resistance, it should be evaluated according to the standard. For the materials showing partial resistance or slow stripe rust, the severity was reduced by 2 grades according to the actual identification results, with Huixianhong as the control, which was divided into 3 grades of highly slow stripe rust, moderately slow stripe rust, and low slow stripe rust.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Identification of resistance to powdery mildewAs shown in Table 2, 5 out of 20 winter wheat strains tested were highly resistant materials, including Kendong 13154, Kendong 1339, YY-2/1, YY-22/4 and YY-120/2, accounting for 25%; there were 9 moderately resistant materials, including Kendong 13227, Pubing WX717, Kendong 1420, Kendong 1494, Kendong 14156, Kendong 14200, Kendong 1328, YY-59/1 and YY-138/1, accounting for 45%; there were 6 susceptible materials, including Kendong 1413, Kendong 1437, Kendong 1475, Kendong 14191, Kendong 14194 and YY-103/2, accounting for 30%; and there was no highly sensitive materials or immune materials. Kendong 13154, Kendong 13227, Kendong 1339 and YY-120/2 were used as experimental materials in winter wheat regional test in southern and northern Xinjiang, and showed moderate and high resistance to powdery mildew in regional test, which was consistent with the resistance identification of powdery mildew by Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Analyzed from parental combination, the male parent of the 4 materials was Xindong 51, which was approved and named by Xinjiang Province in 2016. Xindong 51 was an immune-highly resistant material in field resistance identification by institute of crop research for many years, with stable resistance and good agronomic characters, which could be directly used as resistant parent of powdery mildew. The 4 regional test materials were hybridized by Xindong 51 resistant source with Xindong 18 and Xindong 41, the main varieties promoted in Xinjiang, all of which had good performance in resistance and multi-point adaptability of regional test.
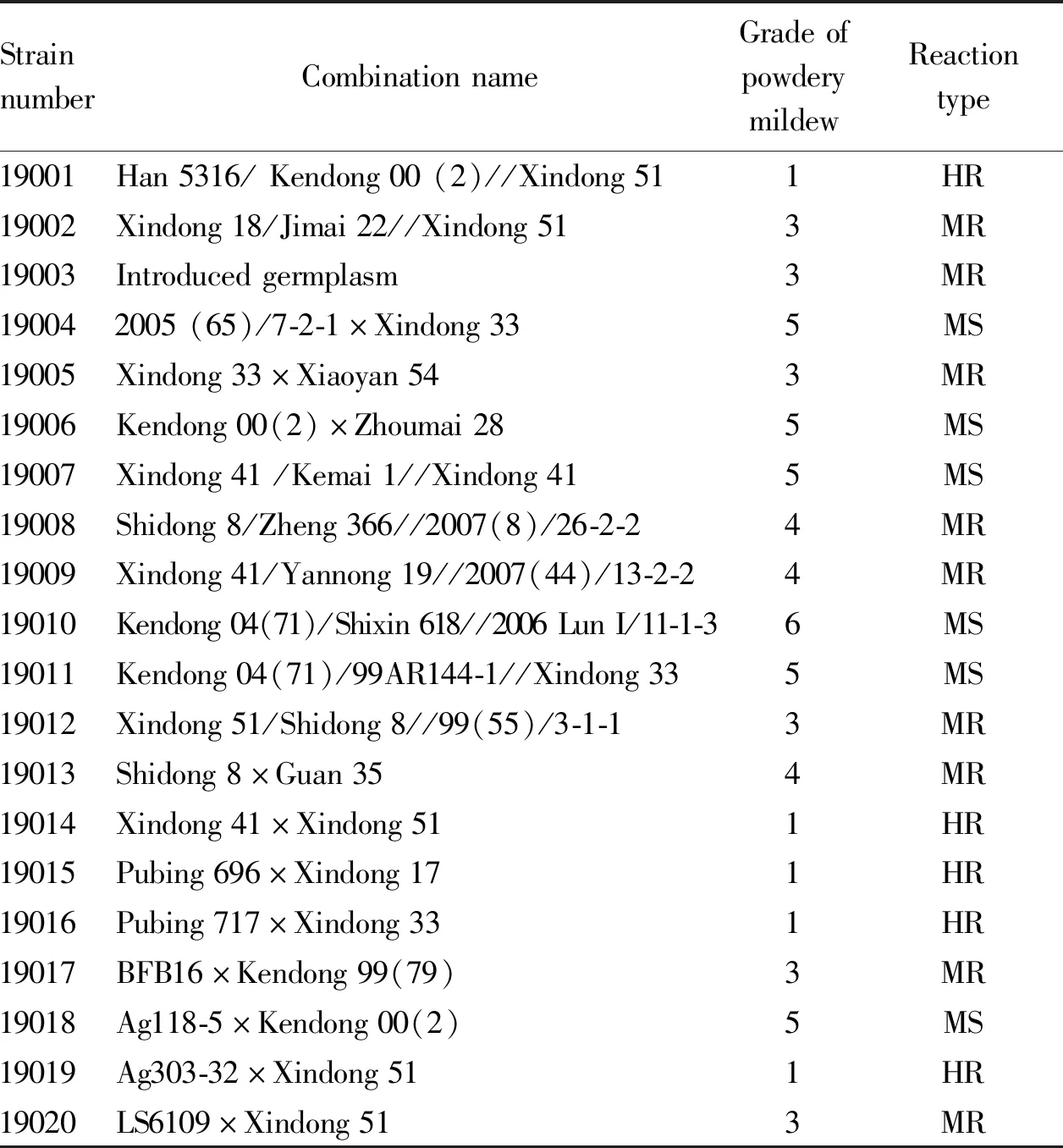
Table 2 Performance of adult-plant resistance of Xinjiang winter wheat strains to powdery mildew
3.2 Identification of resistance to stripe rustAs shown in Tables 3-4, the identification results of resistance of 16 materials tested to stripe rust were listed in 2018, while only 5 materials with slight resistance were listed in 2019. The comparative analysis results demonstrated that there were 4 materials with slightly resistance and slow stripe rust, including Kendong 12-48, Kendong 12-49, Kendong 10-242 and Kendong 12-67, accounting for 25%. Kendong 11-65 was susceptible in 2018 and slightly resistant in 2019. The remaining 11 materials were all susceptible to stripe rust within 2 years, with a reaction type of grade 4, a severity of over 40 and a prevalence rate of 100%, indicating that 68.7% of the tested winter wheat strains were susceptible to stripe rust. Based on the analysis of the parental combinations of 5 materials with slight resistance and slow stripe rust in the past 2 years, the parents of Kendong 12-48, Kendong 12-49 and Kendong 11-65 were all introduced from Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei provinces, belonging to the varieties and high generation stable strains selected before the 12thFive-Year Plan in northern wheat region; the female parent of Kendong 12-67 was approved by Hebei Province, and the male parent was widely promoted in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region; the parents of Kendong 10-242 were self-bred high-generation strain and Xinjiang local variety. Comprehensive analysis showed that all the tested materials were hybrid combinations prepared by institute of crop research from 2010 to 2012, and poor disease resistance performance of the hybrid offspring may be due to the lack of resistance of the parents themselves.
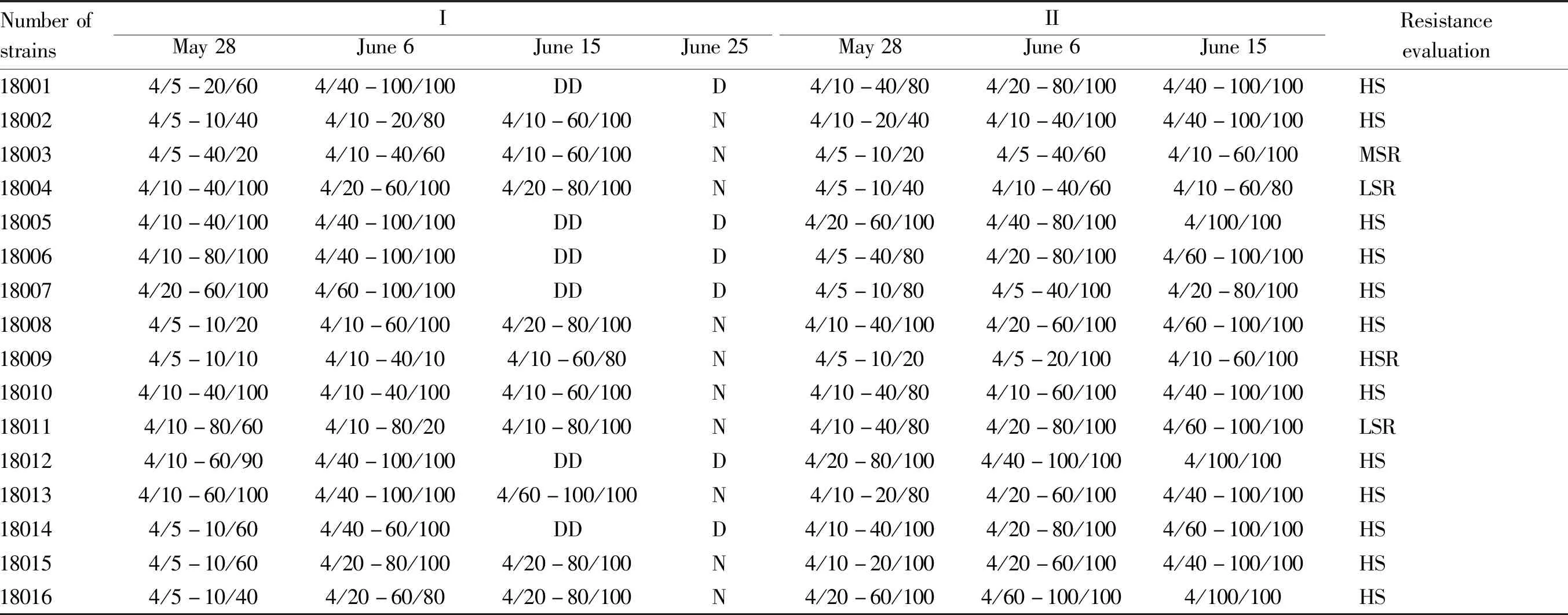
Table 3 Identification results of stripe rust resistance of Xinjiang winter wheat strains in 2018
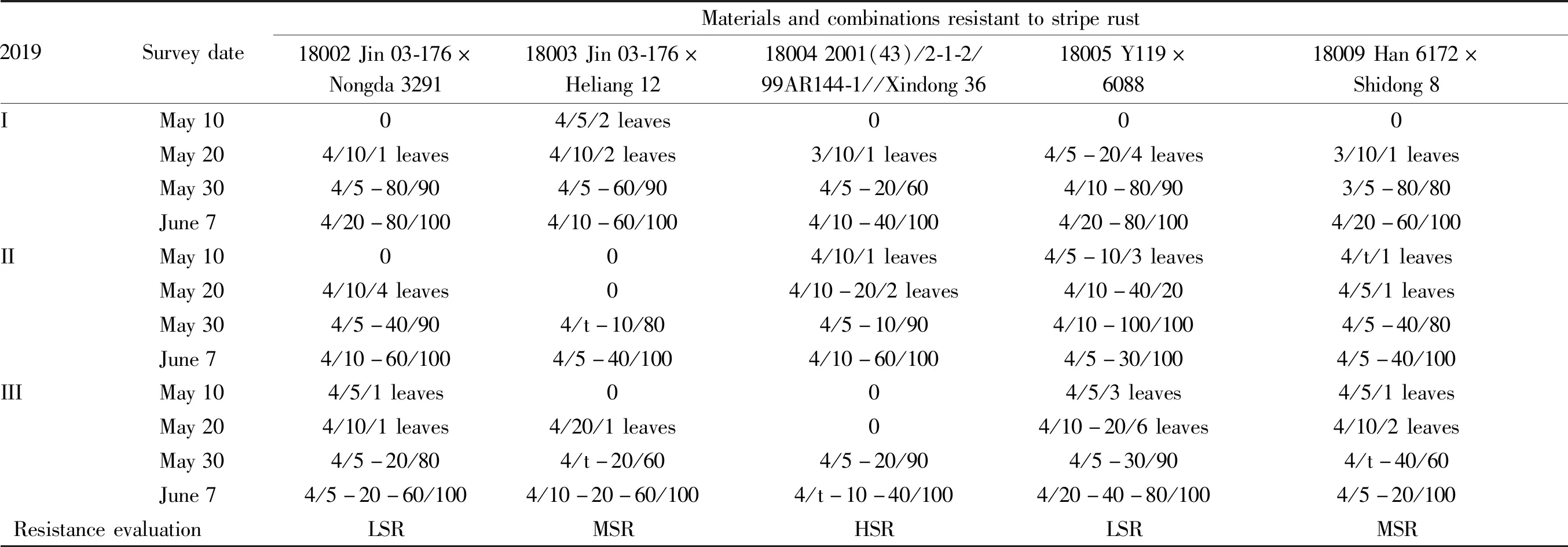
Table 4 Identification results of stripe rust resistance of Xinjiang winter wheat strains in 2019
The research on the disease resistance of wheat varieties in Xinjiang began from 2005. Powdery mildew and leaf rust, the main diseases harming wheat production, mainly occurred in the Yili Valley, and the incidence in other regions varied among different years. Chemical control is still the major measure against powdery mildew and leaf rust. Due to the lack of preliminary study on the disease resistance of wheat varieties and the lack of related resistant varieties breeding, varieties and high-generation stable strains developed by institute of crop research before the 12thFive-Year Plan showed poor resistance to stripe rust.
The identification results of stripe rust resistance of 20 tested strains in 2020 showed that Kendong 1339, YY-59/1 and YY-103/2 had adult-plant slow stripe rust, accounting for 15% of the total; the remaining 85% of the tested materials were susceptible. From analysis of the parental combinations of the 3 materials, the parents of Kendong 1339 were all varieties widely promoted in Xinjiang; the female parent of YY-59/1 was BFB16 containing powdery mildew resistance gene and the male parent was a crop self-bred line, while the female parent of YY-103/2 was a polygenic resistance material and the male parent was a crop self-bred line. Compared with Kendong 12-48, Kendong 12-49, Kendong 10-242 and Kendong 12-67, the disease resistance of the combination offspring was also enhanced with the increase of the parents’ disease resistance, which was manifested as adult plant slow stripe rust.
4 Conclusions and discussion
Five powdery mildew resistant materials were preliminarily screened out in the identification of induced resistance of powdery mildew and stripe rust. Four slow stripe rust materials were screened out, probably attributed to the transmission from the infected seedlings to the strain to be identified after the incidence of the infected control, in which there were differences in the infection time, and the difference in the resistance of the strain would also affect the transmission rate of the disease. The test suggested that induced identification used for screening of disease resistance identification could reduce the workload of identification of progeny lines. In addition, good resistant materials were also obtained through the screening of high generation strains, such as Kendong 1339, which showed high resistance to powdery mildew, slight resistance to stripe rust and adult plant slow stripe rust.
Yili Valley is the main birthplace of wheat stripe rust in Xinjiang, and also the main bacterial source base in the wheat areas in southern and northern Xinjiang[3-5]. With the increase of temperature, the occurrence of wheat rust in Xinjiang wheat region is aggravating, while most varieties widely planted in production are susceptible to stripe rust. Moreover, powdery mildew, as the most common wheat disease in Xinjiang, has rapid changes in physiological races, and varieties will easily lose their disease resistance. Therefore, breeding varieties resistant to powdery mildew and stripe rust is one of the main breeding objectives in this region.
Currently, wheat breeders in Xinjiang have cultivated varieties with high resistance to powdery mildew, such as Xindong 38, Xindong 41, Xindong 51 and Xindong 53. The parents are Xindong 18, Yinong 16 and Shidong 8, which have good resistance to powdery mildew. Planting resistant varieties in powdery mildew epidemic years has better protection against yield loss. Only the institute of crop research and Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences has conducted screening, identification and combination breeding of resistant germplasm resources against stripe rust since 2010. At present, a few strains show slow stripe rust and no resistant varieties have been bred. Previous results show that barley germplasm resources, wild wheat related varieties, and wheat derived lines containing wheatgrass and other exogenous species have strong resistance to powdery mildew and stripe rust, and might have certain resistance genes. Therefore, it is necessary to further conduct introduction, identification, evaluation and utilization of resistant germplasm resources. Meantime, because the resistance of wheat toB.graminisandP.striiformisvaries greatly in different environments, different growing periods and different genetic conditions[4-5], the selection of resistant varieties requires multi-point identification and screening of hybrid progenies in different areas of Xinjiang for many years.
- 植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Grafting and Seedling Cultivation Technique of Bitter Gourd for Disease Prevention in Hainan
- Key Technical Points of Wheat Moisture-resistant Strain Sowing and Management of Promoting Seedlings from Weak to Strong in Daiyue District
- Rodent Damage and Control Methods in Hami Grassland of Xinjiang
- Contrast Test of Precision Electric Mist Duster and Electric Sprayer
- Study on Toxicity of 9 Biocontrol Microbial Products to Adult Population of Tobacco Beetle, Lasioderrma serricorne (Fabricius)
- Screening of Chemical Agents for Controlling Spodoptera frugiperda in Corn Fields of Panmao Township, Yunnan Province

