Mechanism of Zixinyin oral liquid in the treatment of insomnia based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Shuang-Lin Qin,Xin Chen,Si-Wen Hui,Meng-Wei Xu,Rui Peng,Xiao-Ji Wang,Qing Min*
1School of Pharmacy,Hubei Engineering Research Center of Traditional Chinese Medicine of South Hubei Province,Xianning Medical College,Hubei University of Science and Technology,Xianning 437100,China.2School of Pharmacy,Jiangxi Science &Technology Normal University,Nanchang 330013,China.3Engineering Research Center of Health Food Design &Nutrition Regulation,School of Chemical Engineering and Energy Technology,Dongguan University of Technology,Dongguan 523808,China.
Abstract Objective: To explore the molecular mechanism of Zixinyin oral liquid (ZOL) in the treatment of insomnia.Methods: The compounds and action targets of four herbal medicines in ZOL were collected via Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform.Genes corresponding to the targets were queried from the UniProt database.Genecards database was searched to screen the related targets of insomnia.A Gene Ontology function enrichment analysis and a Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis were performed by Database for Annotation,Visualization and Integrated Discovery.AutoDock software was used for molecular docking to verify the results of network analysis.Results: A total of 47 effective compounds and 187 potential targets of ZOL were screened out from the four drugs.A total of 2592 disease targets were screened out from the genecards database,and there were 1576 genes whose relevance score ≥ 0.5.46 genes were obtained by taking the intersection of 187 potential targets of ZOL and 1,576 targets of insomnia.A total of 3,405 entries were obtained from Gene Ontology functional enrichment (P <0.05).A total of 195 signaling pathways were obtained through a Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis (P <0.05).Tumor necrosis factor,interleukin 17 and hypoxia inducible factor-1 signaling pathways were closely related to insomnia.The results of molecular docking show that all the core compounds of ZOL had a certain degree of affinity with gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-1 (GABRA1) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α).Paeoniflorgenone shows the highest affinity with GABRA1,and beta-sitosterol shows the highest affinity with TNF-α.ZOL may have a therapeutic effect on insomnia through its action on targets such as GABRA1 and TNF-α,meanwhile regulating many signaling pathways.
Keywords:Zixinyin oral liquid;insomnia;network pharmacology;molecular docking;GABRA1;TNF-α
Background
Insomnia is the most common sleep disorder,which is characterized by frequent and continuous difficulty in falling asleep and/or maintaining sleeping,resulting in dissatisfaction with sleep.The main clinical manifestations are difficulty in falling asleep,waking up easily and early,as well as difficulty in falling asleep after waking up [1].In recent years,with the rapid development of economic and social life,people bear more and more psychological pressure,leading to a series of psychosomatic diseases,including insomnia,headache,vertigo,anxiety,etc.Among them,insomnia is one of the most important diseases perplexing people's life.Long-term insomnia often leads to the decline of immunity and memory,fear,anxiety and other adverse emotions.At the same time,it also easily induces induce hypertension,neurasthenia and even sudden death.The risk factors of insomnia mainly include age,gender,family history and genetic factors,among which age is the most significant risk factor of insomnia [2,3].With the increase of age,the prevalence of insomnia increases gradually.The risk of insomnia among women is about 1.4 times that of men and even increases to 1.7 times among people over 45 years old [4,5].Statistics show that 10%–15% of adults meet the diagnostic criteria of insomnia,who have a chronic course of the disease.Nearly half of patients with severe insomnia have had symptoms for more than 10 years [6].
Chemotherapy has a quick effect and good effect,but there are some adverse reactions,such as drowsiness,ataxia,headache and so on.Many patients are troubled by the side effects of chemical drugs and drug dependence.Insomnia rebound will bring physical side effects and psychological conflicts to patients.Therefore,traditional Chinese medicine solutions for insomnia with slight side effects and no drug dependence have been recommended by medical workers and favored by the majority of patients.In recent years,great progress has been made in the treatment of insomnia through traditional Chinese medicine,at the same time,traditional Chinese medicine has many advantages in the treatment of insomnia,such as a low treatment cost,slight toxic and side effects,a good tolerance and so on.After long-term practice and exploration,a relatively perfect theoretical system has been formed for traditional Chinese medicine treatment of insomnia has been formed,with diverse treatment means are diverse and an accurate curative effect.
ZOL (Chinese patent medicine,state medical permitment number Z10910059) is composed of four traditional Chinese medicines:glehniae radix,radix paeoniae rubra,ophiopogon japonicus and panax notoginseng,which has the effect of nourishing heart-yin,promoting blood circulation and relieving pains.At present,it is mainly used for chest arthralgia caused by Yin deficiency and blood stasis,whose symptoms include chest tightness,chest pains,palpitation,five-heart upset heat,restless sleep at night and red tongue less moss;it is also used for coronary heart disease and angina pectoris with the above syndromes.In recent years,there are many reports on the clinical application of ZOL in the treatment of insomnia,whose clinical effect has been recognized.More and more evidence show that ZOL has a significant effect on insomnia,but its mechanism of action in the treatment of insomnia is not clear [7–9].
Network pharmacology is a network analysis of biological effects based on the theory of system biology,which emphasizes the prediction of drug targets and action pathways as a whole on the basis of multi-component,multi-target and multi-pathway networks [10,11].As an emerging discipline that can be used to effectively improve the efficiency of drug research and development,network pharmacology has been widely used in active ingredient screening,interpretation of drug action mechanism,research on disease pathogenesis and so on [12–16].Molecular docking technology is a theoretical simulation method to predict the binding mode and binding energy based on the characteristics of receptors and the interaction between receptors and drug molecules,which has been widely used in the field of computer-aided drug design in recent years[17,18].The study explored molecular mechanism of ZOL in the treatment of insomnia is explored in this study through network pharmacological analysis and molecular docking technology.
Materials and Methods
Databases and software
Databases:Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP,http://tcmspw.com/),protein database (UniProt) (https://www.uniprot.org/),small-molecule compound structure query database PubChem(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/),the Database for Annotation,Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID,https://david.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp),the US Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RCSB) Protein Data Bank(https://www.rcsb.org/) [19,20].Analysis software:topology analysis software Cytoscape 3.2.1,molecular docking software autodock Vina,autodock tools,data visualization software PyMOL,data visualization software Graphpad,and online mapping station Omishare.
Screening of active components and targets in ZOL
The main chemical components of ZOL were obtained through querying TCMSP and literature research.The chemical components in ZOL were screened with an oral bioavailability (OB) ≥ 30% and a drug likeness (DL) ≥ 0.18 [21,22].The target prediction function in TCMSP database is used to download the targets of these chemical components.
Intersection gene analysis of ZOL-insomnia
The screened component targets were imported into UniProt database,the species ess limited to "human",all the retrieved protein targets were corrected to the ID of UniProt,and the gene abbreviation was obtained corresponding to the target protein.Insomnia-related genes were retrieved from genecards website (https://www.genecards.org/)with insomnia as the keyword.The genes with a relevance score ≥ 0.5 and the main chemical component targets of ZOL obtained in 1.2 were used to obtain the intersection genes,and a Wayne diagram was drawn.
Target pathway analysis
In order to explore the biological function of the target protein,the potential target of ZOL was introduced into DAVID database.An enrichment analysis on Gene Ontology (GO) function and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway was carried out by inputting the name list of target genes and limiting the species to"home sapiens",the first 20 items were selected,a GO analysis histogram was drawn through graphpad software and a KEGG analysis advanced bubble chart was drawn through online mapping station omishare.
Docking of component target-molecular
According to the enrichment analysis results of KEGG signal pathway,the key proteins in the main pathway of ZOL were selected,and the PDB format file of the corresponding proteins was downloaded from the US Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RSCB)Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org/).PyMOL software was used to remove protein ligands and water and add hydrogen,which were saved as PDB format files,and autodock tools software was used to convert them into pdbqt-format files.The 2D structure of small-molecule compounds was obtained from the PubChem database,the energy was optimized by Sybyl software and transformed into pdbqt-format files through autodock tools.Then,autodock Vina was used for molecular docking,and an active ingredient with binding energy ≤–5.0 kJ/mol was selected as the screening basis for ZOL in the treatment of insomnia.
Results and Analysis
Screening of active ingredients and their targets
A total of 284 active compounds of 4 herbs in ZOL were retrieved through TCMSP retrieval and other databases,including 35 through glehniae radix,119 through radix paeoniae rubra,11 through ophiopogon japonicus and 119 through panax notoginseng [23–25].According to OB ≥ 30% and DL ≥ 0.18,a total of 47 active components were screened from ZOL,including 8 from glehniae radix,29 from radix paeoniae Rubra,2 from ophiopogon japonicus and 8 from panax notoginseng.See Table 1 for representative chemical compositions.Through the target prediction function of TCMSP database,187 core targets representing chemical components were downloaded,among which the compounds acting on the key target of insomnia GABRA1 were ammidin,cnidilin,beta sitosterol,stigmasterol,quercetin and paeoniflorinone.
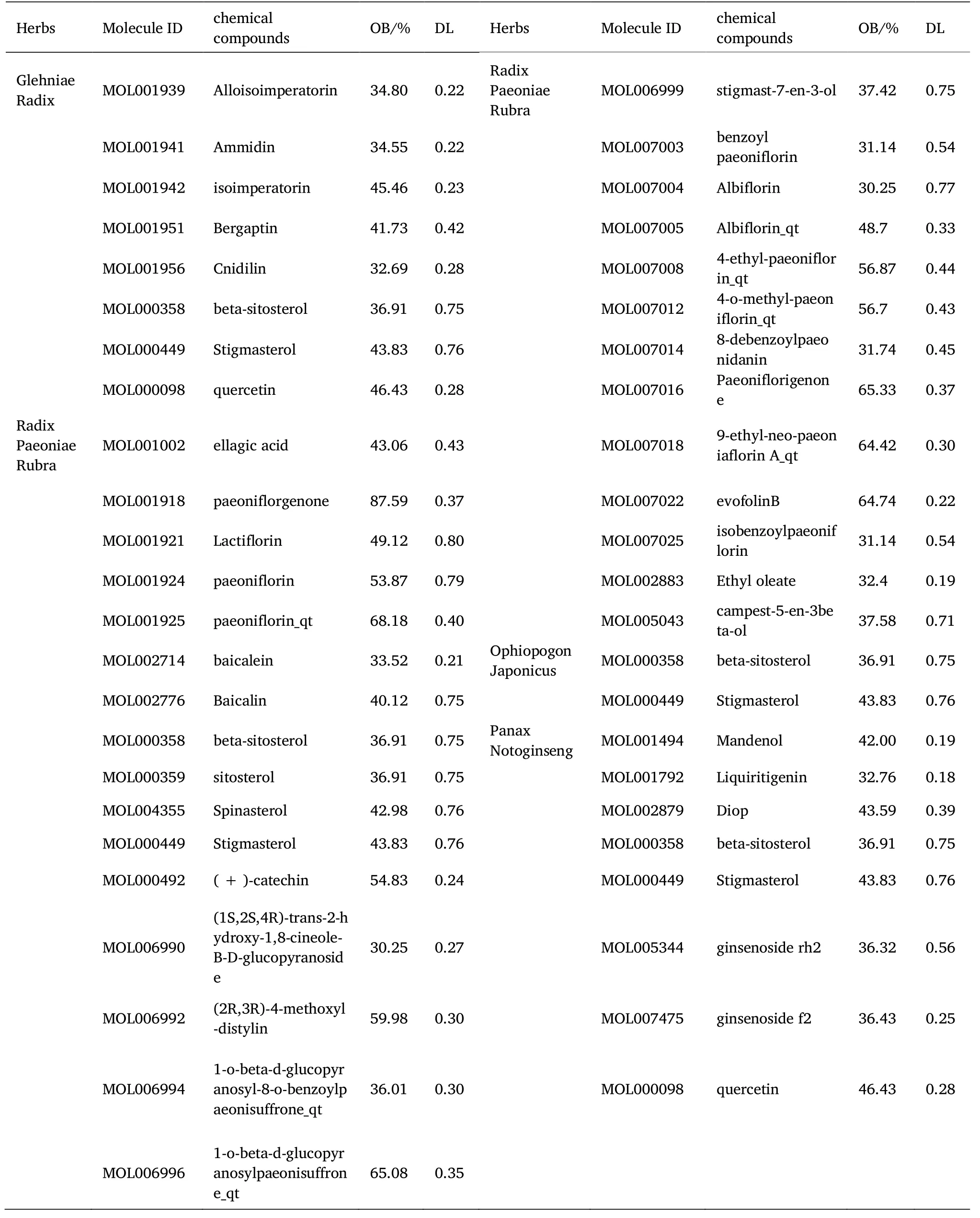
Table 1 Basic information of some chemical constituents in ZOL
Intersection gene analysis
2592 insomnia-related genes were retrieved from the genecards website with insomnia as the keyword,of which 1,576 genes were with a relevance score ≥ 0.5.These genes intersected with the 187 core targets in 2.1 to obtain the intersection genes,and a Wayne diagram was drawn,as is shown in Figure 1.Among the 187 targets of ZOL core components,46 were related to insomnia.
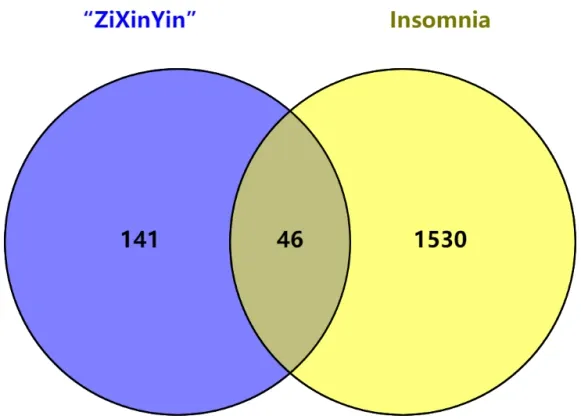
Figure 1 Gene analysis of the intersection between ZOL component target and insomnia

Figure 2 Go enrichment analysis of targets of ZOL
GO function enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
A Go function enrichment analysis was performed by DAVID to obtain GO entries (P<0.05),including 2,915 biological process (BP) entries,170 cellular components (CC) entries and 320 molecular functions(MF) entries,and 20 entries with a lowP-value were selected for visualization (Figure 2).BP mainly involves response to drugs,response to lipopolysaccharide,response to molecular of bacterial origin,multi-cellular organization process and cellular response to chemical stress,etc.;CC shows that the main action sites were cell membranes:membrane rafts,membrane microdomains,membrane regions,synaptic membranes and integral components of postsynaptic membranes,etc.;MF mainly involve:cytokine receptor binding,receptor-ligand activity,signaling receptor activator activity,cytokine activity and chloride transmembrane transporter activity,etc..These processes,parts and functions are closely related to the regulation of insomnia.
195 (P<0.05) signal pathways were screened through a KEGG pathway enrichment analysis,and 20 pathways with a low P-value were selected for visualization.The results are shown in Figure 3,which mainly involve the advanced glycation end products and the receptor for advanced glycation end products signaling pathway in diabetic complications,fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis,Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway,proteoglycans in cancers,relaxin signaling pathway and other related pathways,especially TNF signaling pathway and interleukin 17 (IL-17) signaling pathway,which are closely related to insomnia.Among them,the TNF signaling pathway is related to MMP9,CXCL10,IL6,IL1B,ICAM1,(c-Fos proto-oncogene protein) FOS,CASP3 and AKT1;IL-17 signaling pathway is related to MMP9,CXCL10,IL6,IL1B,Fos and CASP3,which are included in TNF signaling pathway.The relevant components of ZOL were obtained through a reverse search of these targets,as is shown in Table 2.
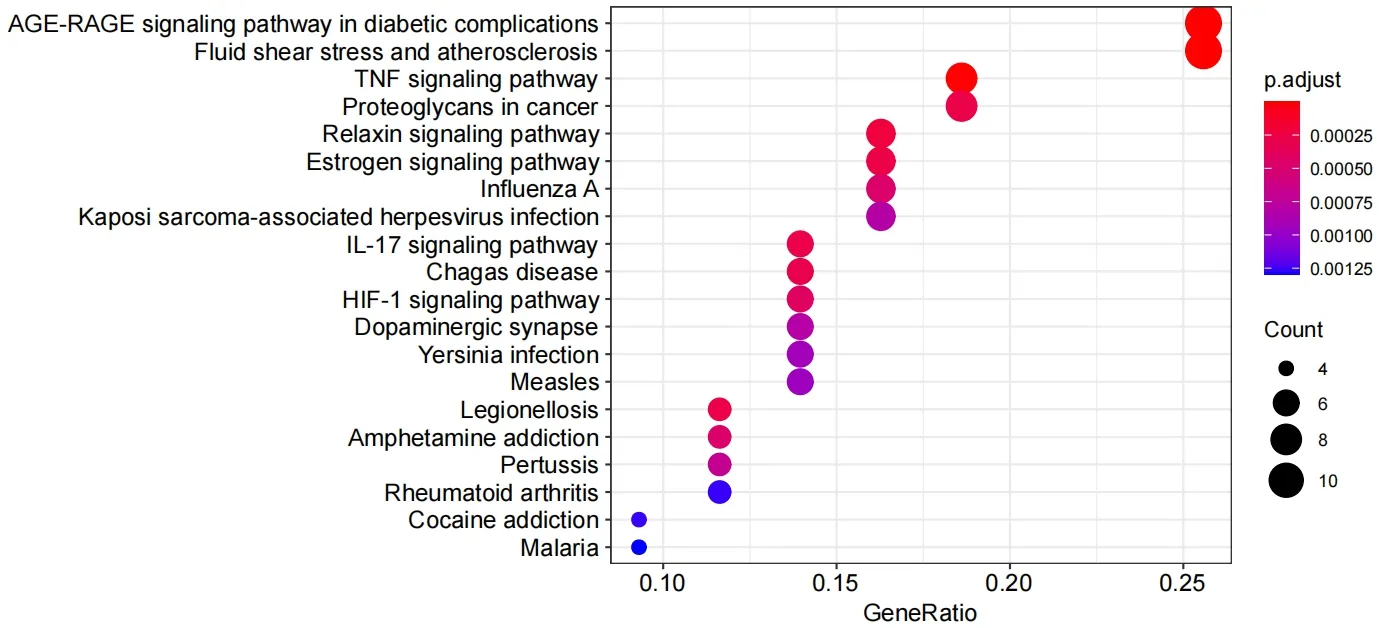
Figure 3 20 pathways for KEGG enrichment analysis of ZOL
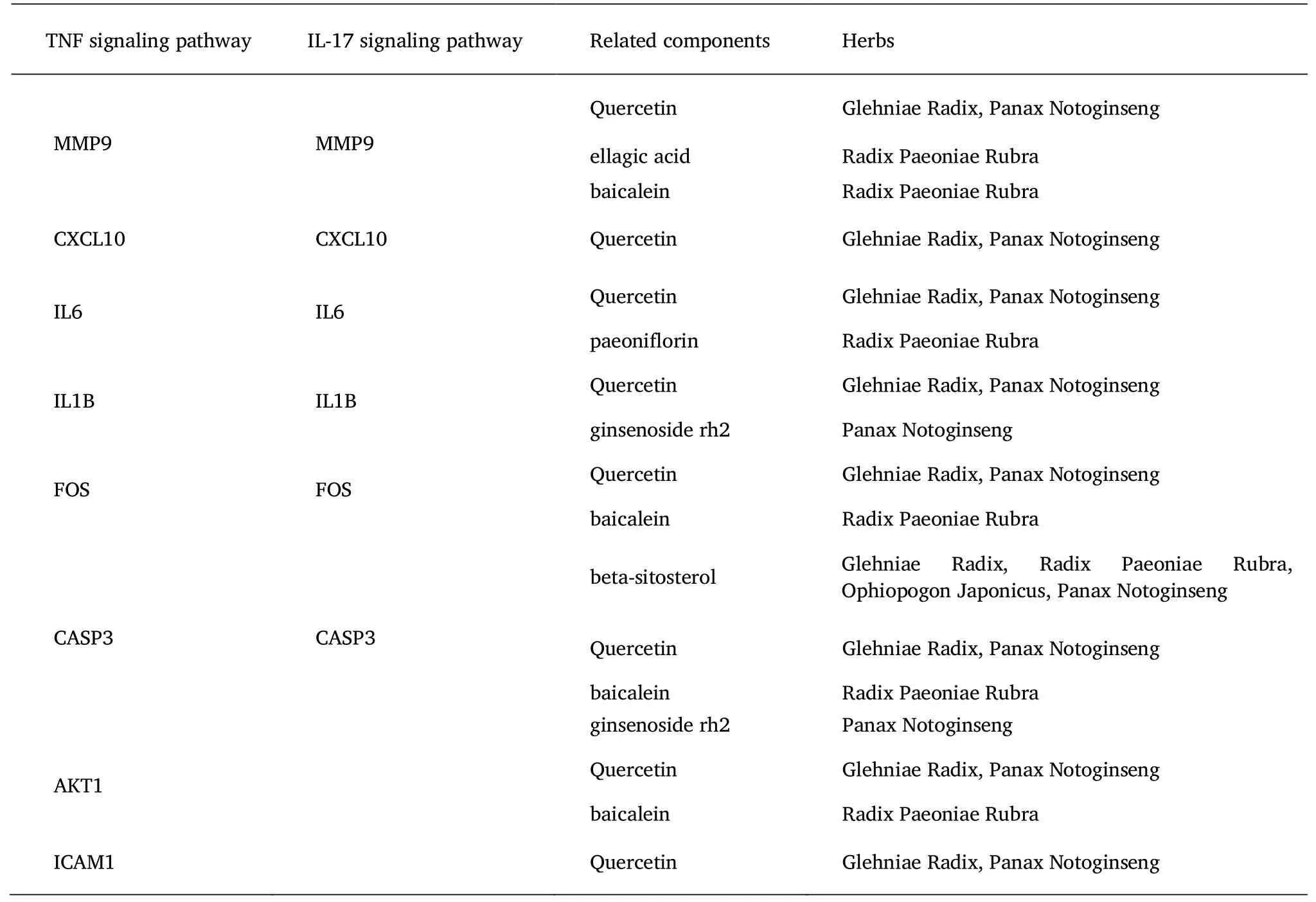
Table 2 Related components of related targets of TNF pathway
Molecular docking analysis of TNF-α and GABRA1 with the core compounds of ZOL
The lower the energy of the complex bound between ligands and receptors is,the more stable the structure and the greater the possibility of action will be.The related components of TNF and IL-17 signaling pathway obtained through a network pharmacological analysis (Table 2) and compounds acting on the key target of insomnia GABRA1 in ZOL screened in 2.1 were docked with the target GABRA1(PDB ID:6huk) and TNF-α (PDB ID:2az5).Taking the binding energy≤–5.0 kcal/mol as the screening standard,it can be seen from the results that the binding between core compounds of ZOL and receptor proteins has characteristics including a low energy,a stable structure and a high binding activity (Table 3).Among them,paeoniflorinone has the lowest binding energy with GABRA1 (binding energy=–9.0 kcal/mol),whose binding mode is shown in Figure 4,showing that paeoniflorinone has hydrogen bonds binding with thr261 amino acid residues of GABRA1,which has a hydrophobic effect with Leu259,Leu274,Thr256,Thr271,Ser267,Ala252,Ala248,Val257,Leu259,Ile255,Thr261 and Leu264.Stigmasterol has the lowest binding energy with TNF-α (binding energy=–9.1 kcal/mol),whose binding mode is shown in Figure 5,showing that stigmasterol has a hydrophobic effect with Ile155,Leu57,Leu120,Ser60,Gly121,Tyr59,Tyr119 and Tyr151.
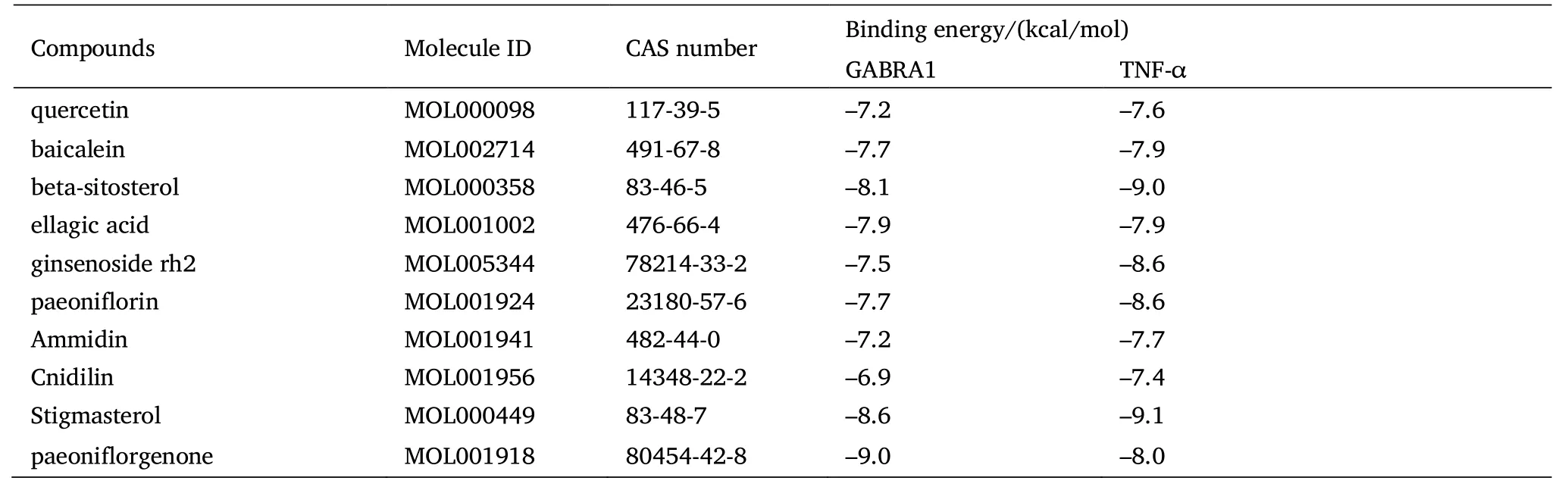
Table 3 Binding energy of core compounds of ZOL with GABAR1 and TNF-α
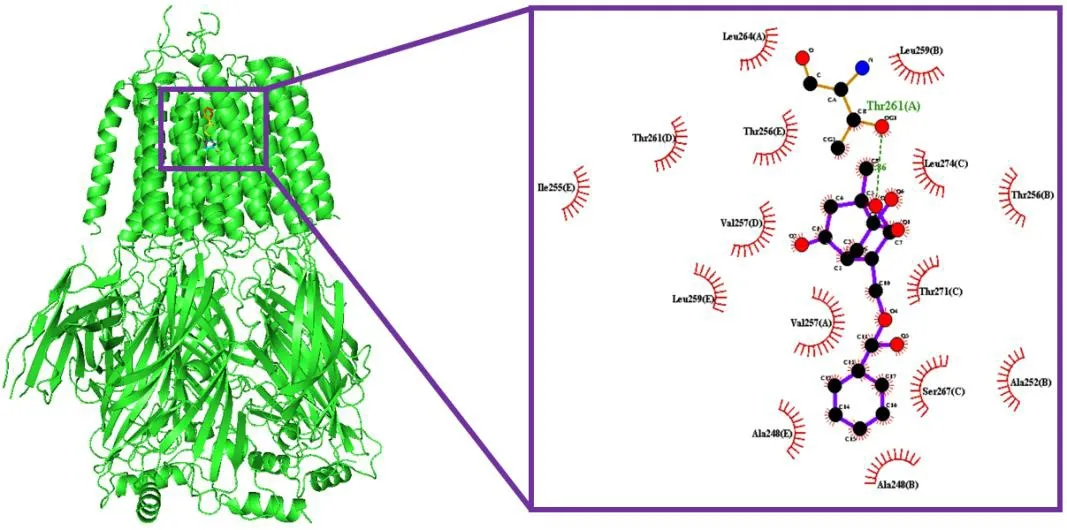
Figure 4 Paeoniflorgenone docking with GABRA1
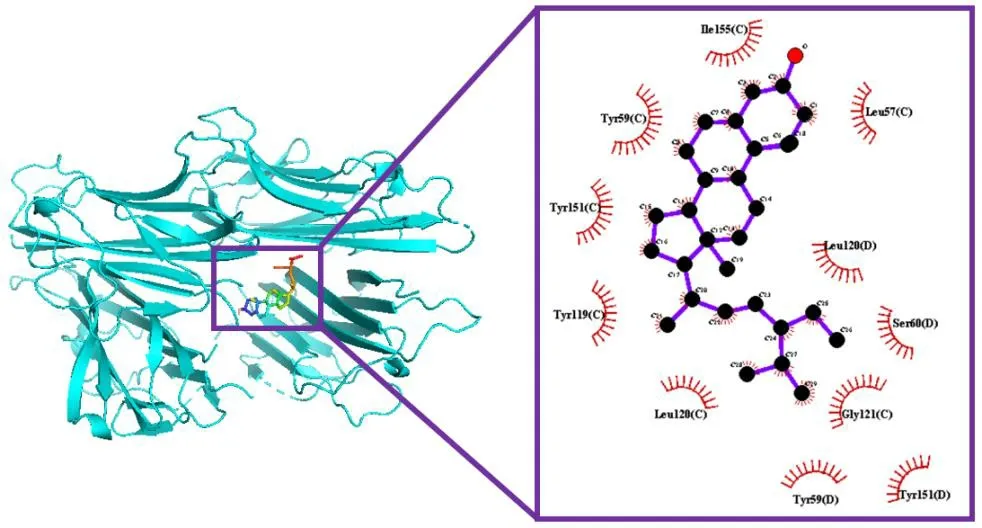
Figure 5 Stigmasterol docking with TNF-α
Discussion
All classical sedative and hypnotic drugs,such as benzodiazepines and phenobarbital drugs,have a certain degree of side effects,long-term use of which is prone to drug resistance and dependence [26].Traditional Chinese medicine has its own unique theoretical system for sleep cognition,which has an accumulated rich experience in the treatment of sleep disorders in the thousands of years of development process.In traditional Chinese medicine,insomnia is located in the heart and related to the liver,spleen as well as kidney,whose basic pathogenesis is that Yang does not enter Yin.There are many causes of insomnia,including the disturbance of liver Yang,excessive thinking,internal injuries to the heart and spleen,failure of Yang to cross Yin,Yin deficiency and fire as well as carduonephric cisharmony [27].Doctors often comprehensively analyze through four examination methods and treat according to syndrome differentiation.
At present,with the gradual deepening of research on the mechanism of insomnia,the basis and breakthrough of its treatment are gradually clear.γ-Aminobutyric acid is closely related to the occurrence and progression of insomnia,whose receptor GABRA1,as an inhibitory neurotransmitter receptor,also plays an important regulatory role in insomnia [28,29].ZOL is composed of four traditional Chinese medicines:glehniae radix,radix paeoniae rubra,ophiopogon japonicus and panax notoginseng,which has the effect of nourishing heart-Yin,promoting blood circulation and relieving pains.Through a component-target analysis,it was found that ammidin,cnidilin,beta sitosterol,stigmasterol,quercetin,paeoniflorinone and other compounds in ZOL could act on GABRA1,which was the key target of insomnia.
Insomnia can cause an increase in the expression of certain inflammatory factors,among which TNF-α and IL-17 are closely related to insomnia [30–32].At present,more and more studies show that the secretion of cytokines related to immune activation is closely related to mental diseases,especially insomnia [33,34].It has been found in studies that TNF-α and IL-1β can activate Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone-containing neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus to promote the release of adreno cortico-tropic-hormone (ACTH) from the adenohypophysis,thereby activating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis,leading to depression.At the same time,the imbalance of the HPA axis is also one of the mechanisms of insomnia.Through an intersection gene analysis,it can be known that the 46 targets of ZOL are closely related to insomnia.Through GO and KEGG enrichment analysis,the main related pathways of ZOL in the treatment of insomnia were found:TNF and IL-17 signaling pathway,of which TNF signaling pathway is related to the target of action of ZOL components MMP9,CXCL10,IL6,IL1B,ICAM1,FOS,CASP3 and AKT1;and IL-17 signaling pathway is related to that of ZOL components MMP9,CXCL10,IL6,IL1B,FOS and CASP3,all of which are included in TNF signaling pathway and closely related to insomnia.For example,the level of IL-6 is directly proportional to the time of wakefulness from sleep,which is related to both non-rapid eye movement sleep and sleep quality is inversely proportional [35].As the root of inflammatory reaction,interleukin cytokines will cause the release of more and more inflammatory mediators,destroy the normal sleep rhythm and finally lead to insomnia.The therapeutic effect and prognosis of sleep disorders can be evaluated based on the level of monitoring serum IL-6,IL-1β [36].FOS is a nucleophosphoprotein expressed by the proto-oncogene c-fos,which not only participates in physiological activities such as cell division,growth and differentiation,information recognition and transmission as well as learning and memory,but also closely related to animal behavior and the occurrence as well as development of various diseases.There is also a certain relationship with animals’level of sobriety [37].
Through a target-component reverse search,the related components of TNF and IL-17 signaling pathway were quercetin,baicalein,beta-sitosterol,ellagic acid,ginsenoside rh2 and paeoniflorin.These ingredients,together with those of ZOL that act on GABRA1,the key target of insomnia,are molecularly docked with the two key targets,namely GABRA1 and TNF-α.The results confirm that these core components have a high affinity with key targets GABRA1 and TNF-α,of which paeoniflorgenone has the strongest effect on GABRA1,and stigmasterol has the strongest effect on TNF-α.
To sum up,network pharmacology and molecular docking methods are used in this study to explore the mechanism of ZOL in the treatment of insomnia,and the relationship between ZOL and insomnia is analyzed as a whole,which provides a reference for molecular biological research related to ZOL and more in-depth pharmacological exploration,meanwhile proving that ZOL has a multi-component and multi-target regulation of insomnia.
 Drug Combination Therapy2022年2期
Drug Combination Therapy2022年2期
- Drug Combination Therapy的其它文章
- The potential of complementary and alternative medicine combination chemotherapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- Mechanism of Magnoliae Flos and Xanthii Fructus herb pair in treatment of allergic rhinitis based on network pharmacology
- Study on the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of white peony root and mucuna pruriens and their combinations in vivo
- Meta-analysis of curative effect of Sacubitril valsartan combined with Qiliqiangxin capsule in the treatment of patients with chronic cardiac failure
- Complex diseases demand novel treatment strategies:understanding drug combination
