丁苯酞对迟发性脑病患者精神、行为和认知的影响
陈艳坤 李慧 吴延芝 张友生 张宏丹 顾黎明
[摘要] 目的 探討丁苯酞对迟发性脑病患者精神、行为和认知的影响。 方法 选取2017年1月至2019年5月在菏泽市立医院就诊的120例一氧化碳中毒后迟发性脑病患者,随机分为两组。所有患者均置于绝对压力为0.25 MPa的高压氧室中,每天80 min,持续90 d;同时每天给予地塞米松5 mg,每周5 d,连续4周。另外,试验组前14 d给予丁苯酞注射液100 ml,每天2次;后76 d每天给予丁苯酞软胶囊200 mg,每天3次。治疗第14天、3个月、1年分别采用MMSE、MoCA、ADL对患者的行为和认知功能进行评估。在第3个月和1年后,用HAMA和HAMD评估患者的精神状态变化。 结果 治疗第14 d、3个月、1年,试验组的MMSE、MoCA、ADL评分均显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。在治疗后3个月和1年,试验组的HAMA和HAMD评分均显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。 结论 丁苯酞序贯疗法联合地塞米松、高压氧能明显改善一氧化碳中毒后迟发性脑病患者的精神、行为和认知功能,且无明显副作用。
[关键词] 丁苯酞;迟发性脑病;精神;高压氧;一氧化碳中毒
[中图分类号] R827.1 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2022)05-0022-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effects of butylphthalide on mental state, behavior and cognition of patients with delayed encephalopathy. Methods In this experiment, a total of 120 patients with DEACMP who attended Heze Municipal Hospital from January 2017 to May 2019 were randomly divided into two groups (all patients were arranged in a hyperbaric room with an absolute pressure of 0.25 MPa for 80 minutes per day for 90 days. Dexamethasone 5 mg was also given daily for 5 days per week for 4 weeks). In addition, the experimental group was given butylphthalide injection 100 ml twice a day for the first 14 days and butylphthalide softgels 200 mg three times a day for the last 76 days. The behavioral and cognitive functions of the patients were assessed using Mini-mental State Examination (MMSE) scale, montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA) scale,and activity of daily living (ADL) scale at 14 days,3 months,and 1 year of treatment, respectively.Changes in the mental state of patients were assessed by hamilton anxiety scale (HAMA) and hamilton cepression scale (HAMD) at 3 months and 1 year of treatment. Results At 14 days, 3 months, and 1 year of treatment,the MMSE,MoCA,and ADL scores in the experimental group were significantly higher than those in the control group, with statistically significant differences(P<0.001).At 3 months and 1 year after treatment, the HAMA and HAMD scores in the experimental group were significantly lower than those in the control group, with statistically significant differences(P<0.001). Conclusion Sequential butylphthalide therapy combined with dexamethasone and hyperbaric oxygen can significantly improve the mental, behavioral and cognitive functions of patients with DEACMP without significant side effects.
[Key words] Butylphthalide; Delayed encephalopathy; Mental state; Hyperbaric oxygen; Carbon monoxide poisoning
一氧化碳(carbon monoxide,CO)中毒的主要危害是其严重的临床影响、较高的毒性发生率和死亡率[1]。而急性脑损伤和CO中毒后迟发性脑病(delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning,DEACMP)是最常见的神经并发症[2-3]。CO中毒可导致神经、精神、行为和认知障碍,对患者的康复、功能恢复、生活质量甚至生存率都有显著的负面影响,给家庭和社会带来沉重的经济和情感负担。既往研究报道高压氧(hyperbaric oxygen chamber,HBO)对DEACMP有显著疗效[4-5],但仅使用HBO很难及时有效地控制DEACMP的进展。因此,探索更有效的药物治疗仍是当前研究的重点。
丁苯酞作为中国第一种神经病学领域的国家一类新药,是目前唯一获国家食品药品监督管理局批准治疗脑梗死的新药,是继青蒿素和双环醇之后中国第三个拥有自主知识产权的原创新药,国内第一个顺利进入美国FDAⅡ脑血管领域的临床试验药物。2010年和2014年,NBP(恩仪普,丁苯酞软胶囊)被列入中国预防脑卒中指南推荐药物,很快成为中国脑卒中一线治疗的重要辅助药物。经过对其应用的进一步研究,发现其有益作用远远超出了卒中的治疗范围[6-7]。最新研究表明,地塞米松(dexamethasone,DXM)和HBO[8]、NBP和HBO[9]对DEACMP认知功能的恢复有显著影响;此外,笔者课题组过去的研究[10]发现,NBP和DXM联合HBO治疗DEACMP可以改善患者的认知和运动功能。因此,笔者进一步研究NBP和DXM联合HBO对DEACMP患者的精神、行为和认知功能治疗的影响,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
本试验于2017年1月至2019年5月在菏泽市立医院进行;所有参与者均正式获得书面知情同意书,经过菏泽市立医院医学伦理委员会批准。中国临床试验注册:ChiCTR2000030608。纳入标准:①CO暴露2~60 d后发生DEACMP的临床症状;②双侧脑白质脱髓鞘病变的神经影像学证据。排除标准:①对丁苯酞过敏者;②简易精神状态检查(the mini-mental state examination,MMSE)>24分[11];③慢性肝或肾功能不全者;④遗传病;⑤短暂性脑缺血发作或中风者;⑥系统性或严重局部感染者;⑦胃肠道出血或凝血障碍者;⑧艾滋病毒感染、梅毒或其他传染病者;⑨妊娠或哺乳妇女。
患者被随机分配到两组,使用双盲、双假设计。所有患者置于绝对压为0.25 MPa的高压氧舱中,每天80 min,持续90 d;每天给予地塞米松5 mg,每周5 d,持续4周。另外,试验组给予NBP注射液100 ml,每日2次,连续14 d;随后给予软胶囊200 mg,每日3次,连续76 d。对照组在前14 d给予NBP注射安慰剂100 ml,每日2次;在接下来的76 d给予丁苯酞软胶囊安慰剂200 mg,每日3次。
所有患者都接受常规治疗(使用抗生素、调节水电解质和预防尿路感染等)。90 d后,治疗由临床医生或患者自己选择。
1.3 观察指标及评价标准
主要结果:治疗后第14天、3个月、1年通过MMSE、蒙特利尔认知评估(the montreal cognitive assessment,MoCA)、巴特尔日常生活活动指数(the barthel index of activities of daily living,ADL)评估患者认知和行为功能变化。治疗后3个月和1年用汉密尔顿焦虑量表(hamilton anxiety scale,HAMA)和汉密尔顿抑郁量表(hamilton depression scale,HAMD)评估患者精神病学状况。
次要结果:记录潜在不良事件,分析NBP序贯疗法联合DXM、HBO治疗DEACMP的安全性。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0统计学软件进行分析,计量资料用均数±标准差(x±s)表示。研究的人口和基线临床变量用t检验,计数资料采用χ2检验。进行协方差分析(ANCOVA)以评估治疗后MMSE、MoCA、ADL和HAMA、HAMD的差异。所有程序均为双尾检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组患者的基线特征和临床资料比较
共招募120例DEACMP患者,对照组失访1例,试验组失访7例;最终112例完成了整个治疗。两组患者在相关基线数据等方面比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。
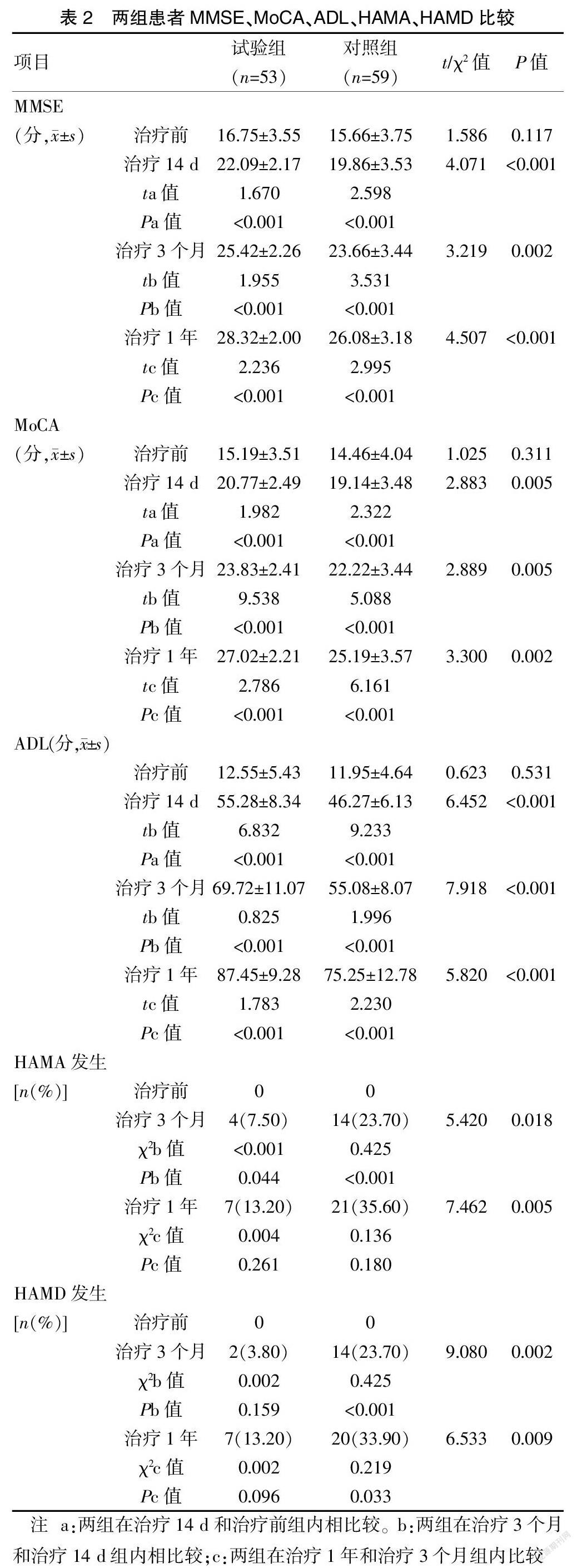
2.2 两组患者MMSE、MoCA、ADL、HAMA、HAMD比较
两组组内比较:两组均在治疗14 d、3个月、1年的MMSE、MoCA、ADL评分均顯著高于治疗前或上次评分结果,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。同时,试验组只在治疗的第3个月的HAMA评分略高于治疗前评估结果,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。对照组在治疗的第3个月、1年的HAMA和HAMD评分均显著高于上次评估结果,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表2。
两组组间比较:在治疗14 d、3个月、1年,试验组的MMSE、MoCA、ADL评分均显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。此外,在治疗第3个月和1年,试验组的HAMA和HAMD评分均显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。见表2。
2.3 两组不良事件比较
试验过程中所有患者的血糖、血脂、肝肾功能均无明显变化,可能是DXM使用剂量小、时间短。试验组出现食欲不振2例,轻度头痛2例,轻度皮肤刺激1例。对照组出现食欲减退1例,轻度头痛1例。两组比较,差异有统计学意义(P>0.05)。然而,这些患者均自行康复,并没有使用额外药物或特殊治疗。
3 討论
本研究发现该疗法可显著提高患者的MMSE、MoCA、ADL分值,降低HAMA、HAMD评分,这意味着该疗法可以显著改善DEACMP的行为和认知功能,降低心理障碍的发生。而ADL评分显著升高,提示添加NBP和DXM可能具有更好地保护和恢复神经功能的作用。结果表明,丁苯酞序贯疗法联合地塞米松、高压氧能明显改善CO中毒后迟发性脑病患者的精神、行为和认知功能,且无明显副作用。本研究应该被视为一种潜在的新疗法,但还需进一步探索。
DEACMP的发生是多种因素相互作用的结果,虽然具体发病机制尚不清楚,但认为主要是CO中毒后海马[12]萎缩和脑组织中[13]白质广泛脱髓鞘。海马CA1亚区延迟协同介导的神经病理学发病机制包括炎症、线粒体功能抑制及氧化应激、凋亡、神经递质异常、兴奋性氨基酸增加、脂质过氧化和对化学修饰的髓鞘碱性蛋白的适应性免疫反应等[6-7]。脑组织广泛白质脱髓鞘病理机制包括细胞因子和炎症分子在中枢神经系统中不平衡表达,氧自由基、过氧化物显著增加,细胞膜脂质过氧化反应和髓鞘基本蛋白质结构和功能变化,髓鞘衍生轴突生长抑制剂异常表达(如Nogo、NgR和Ogmp)[14-16],导致脱髓鞘神经细胞和继发性神经细胞死亡。此外,Ischiropoulos等[17]报道CO中毒改变了一氧化氮(NO)水平和NO合酶活性,提示NO可能与脑组织破坏或损伤有关。NBP作用于DEACMP的机制可能与其独特的药理作用有关,抑制血小板聚集、减少血栓形成、改善微循环、减少脑梗死体积、抵抗氧化应激、保护线粒体功能、减少神经元凋亡、减轻炎症反应、介导神经元自噬、促进神经发生等多种病理生理机制上发挥多靶向作用,表现出明显的神经保护作用[18-24]。
本研究局限性:①样本量相对较小;②所有患者来自同一城市;③仅考察了该疗法的短期疗效。因此,需要通过多中心、大样本、长期纵向随访的研究进一步证实丁苯酞序贯疗法联合地塞米松、高压氧治疗CO中毒后迟发性脑病的疗效和安全性。
[参考文献]
[1] Kalay N,Ozdogru I,Cetinkaya Y,et al.Cardiovascular effects of carbon monoxide poisoning[J].Am J Cardiol,2007,99:322-324.
[2] Geraldo AF,Silva C,Neutel D,et al.Delayed leukoence phalopathy after acute carbon monoxide intoxication[J].J Radiol Case Rep,2014,8(5):1-8.
[3] Goldstein M.Carbon monoxide poisoning[J].J Emerg Nurs,2008,34(6):538-542.
[4] Weaver LK,Valentine KJ,Hopkins RO.Carbon monoxide poisoning:Risk factors for cognitive sequelae and the role of hyperbaric oxygen[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2007,176:491-497.
[5] Weaver LK.Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for carbon mono- xide poisoning[J].Undersea Hyperb Med,2014,41:339-354.
[6] Raub JA,Mathieu-Nolf M,Hampson NB,et al.Carbon monoxide poisoning-a public health perspective[J].Toxi- cology,2000,145:1-14.
[7] Hampson NB,Piantadosi CA,Thom SR,et al.Practice recommendations in the diagnosis,management,and prevention of carbon monoxide poisoning[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2012,186:1095-1101.
[8] Xiang W,Xue H,Wang B,et al.Combined application of dexamethasone and hyperbaric oxygen therapy yields better efficacy for patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning[J].Drug Des Devel Ther,2017,11:513-519.
[9] Xiang W,Xue H,Wang B,et al.Efficacy of N-Butyl phthalide and hyperbaric oxygen therapy on cognitive dysfunction in patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning[J].Med Sci Monit,2017, 23:1501-1506.
[10] Zhang J,Guo Y,Li W,et al.The efficacy of N-Buty- lphthalide and dexamethasone combined with hyperbaric oxygen on delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning[J].Drug Des Devel Ther,2020,14:1333-1339.
[11] Shu AH,Wang Q,Chen XB.Effect of different depths of anesthesia on postoperative cognitive function in laparoscopic patients:A randomized clinical trial[J].Curr Med Res Opin,2015,31:1883-1887.
[12] Pulsipher DT,Hopkins RO,Weaver LK.Basal ganglia volumes following CO poisoning:A prospective longitudinal study[J].Undersea Hyperb Med,2006,33:245-256.
[13] Kim JH,Chang KH,Song IC,et al.Delayed encephalo pathy of acute carbon monoxide intoxication:Diffusivity of cerebral white matter lesions[J].AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2003,24(8):1592-1597.
[14] Gorman D,Drewry A,Huang YL.The clinical toxicology of carbon monoxide[J].Toxicol,2003,187:25-38.
[15] Li Q,Cheng Y,Bi MJ,et al.Effects of N-Butylphthalide on the expressions of Nogo/NgR in rat brain tissue after carbon monoxide poisoning[J].Environ Toxicol Pharmacol,2015,39(2):953-961.
[16] Yang Y,Liu Y,Wei P,et al.Silencing Nogo-A promotes functional recovery in demyelinating disease[J].Ann Neurol,2010,67(4):498-507.
[17] Ischiropoulos H,Beers MF,Ohnishi ST,et al.Nitric oxide production and perivascular nitration in brain after carbon monoxide poisoning in the rat[J].J Clin Invest,1996,97:2260-2267.
[18] Yang H,Xu S,Li J,et al.Potassium 2-(1-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate inhibits ADP-induced rat platelet aggregation through P2Y1-PLC signaling pathways[J].Naunyn Schm iedebergs Arch Pharmacol,2015,388(9):983-990.
[19] Ma F,Gao Y,Qiao H,et al.Antiplatelet activity of 3-butyl-6-bromo-1(3H)-isobenzofuranone on rat platelet agg- regation[J].J Thromb Thrombolysis,2012,33(1):64-73.
[20] Ye J,Zhai L,Zhang S,et al.DL-3-n-butylphthalide inhibits platelet activation via inhibition of cPLA2-mediated TXA2 synthesis and phosphodiesterase[J].Plate- lets,2015,26(8):736-744.
[21] Lu XL,Luo D,Yao XL,et al.dl-3n-Butylphthalide promotes angiogenesis via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-endothelial nitric oxide synthase signaling pathways[J].J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2012,59(4):352-362.
[22] Dawson TM,Dawson VL.Mitochondrial mechanisms of neuronal cell death:Potential therapeutics[J].Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,2017,57:437-454.
[23] Li J,Li Y,Ogle M,et al.dl-3n-Butylphthalide prevents neuronal cell death after focal cerebral ischemia in mice via the JNK pathway[J].Brain Res,2010,1359:216-226.
[24] Zhang P,Guo ZF,Xu YM,et al.N-Butylphthalide (NBP) ameliorated cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced brain injury via HGF-regulated TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2016,83:658-666.
(收稿日期:2021-09-28)

