Effect of precise nursing service mode on postoperative urinary incontinence prevention in patients with prostate disease
Xi-Chun Zheng,Ting-Ting Luo,Dan-Dan Cao,Wen-Zhi Cai
Xi-Chun Zheng,Ting-Ting Luo,Dan-Dan Cao,Department of Urology,Shenzhen Hospital of Southern Medical University,Shenzhen 518000,Guangdong Province,China
Wen-Zhi Cai,Nursing Department,Southern Medical University,Shenzhen 518000,Guangdong Province,China
Abstract BACKGROUND Patients with benign prostatic disease often experience detrusor morphological changes and dysfunction.In severe cases,it leads to bladder detrusor dysfunction,resulting in dysuria,frequent urination,urgent urination,incomplete urination,and other symptoms including renal function injury.An operation to restore normal urination function and to control postoperative complications,as far as possible,is the most common method for benign prostatic disease.AIM To observe the effect of precise nursing service mode on postoperative urinary incontinence prevention in patients with prostate disease.METHODS In total,130 patients diagnosed with benign prostatic disease,from January 2018 to June 2021,in our hospital,were selected and divided into observation and control groups according to their treatment options.Sixty-five cases in the control group were given routine nursing mode intervention and 65 cases in the observation group received precise nursing service mode intervention.The intervention with the observation group included psychological counseling about negative emotions,pelvic floor exercises,and post-hospital discharge care.The complications of the two groups were counted,and the general postoperative conditions of the two groups were recorded.The urinary flow dynamics indexes of the two groups were detected,and differences in clinical international prostate system score(IPSS)and urinary incontinence quality of life questionnaire(I-QOL)scores were evaluated.RESULTS Postoperative exhaust time(18.65 ± 3.23 h and 24.63 ± 4.51 h),the time of indwelling catheter(4.85 ± 1.08 d and 5.63 ± 1.24 d),and hospitalization time(8.78± 2.03 d and 10.23 ± 2.28 d)in the observation group were lower than in the control group.The difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05).After the operation,the maximum urinary flow rate(Qmax)increased(P < 0.05),the residual urine volume(RUV)decreased(P < 0.05),and the maximum closed urethral pressure(MUCP)was not statistically significant(P > 0.05)compared to pre-operation.The Qmax of the observation group was higher than that of the control group,while the RUV was lower than that of the control group.There was no significant difference in MUCP between the observation and control groups(P> 0.05).The I-QOL score of the two groups improved(P < 0.05),and the IPSS decreased(P < 0.05).After the operation,the I-QOL score of the observation group was higher than that of the control group,and the IPSS was lower than that of the control group(P < 0.05).There were no significant differences in the incidence of urethral injury(1.54% and 3.08%),bladder spasm(0.00% and 1.54%),and secondary bleeding(1.54% and 4.62)between the observation and control groups(P > 0.05).CONCLUSION The precise nursing service mode can reduce the incidence of postoperative urinary incontinence in patients with prostate disease,thus improving postoperative urodynamics and rehabilitation,and quality of life.
Key Words:Precise nursing service mode;Prostate disease;Urinary incontinence;Urodynamics;Life quality
lNTRODUCTlON
Urinary incontinence is one of the most common postoperative complications in patients with benign prostate disease who fail to respond to conservative treatment.Urinary incontinence can not only cause local skin eczema,erosion,incontinence dermatitis,and other complications but also exert psychological pressure on patients,seriously affecting their physical and mental health after surgery[1,2].Previous studies have found that postoperative local edema,a long catheter indwelling time,hyperplastic gland compression,hemostatic balloon placement,and psychological factors were related to urinary incontinence.The postoperative nursing quality has greatly influenced the care for urinary incontinence;however,routine nursing mode focuses on basic nursing.Therefore,targeted interventions for urinary incontinence are often inadequate[3].
Precise nursing service mode is a novel nursing mode,providing care based on patients’ needs rather than care being imposed on them by the nursing staff.Hence,this intervention administers the right care to the right patient at the right time.Comprehensive precision nursing intervention helps to improve patients' cognition,compliance,and satisfaction while reducing complications.It has been applied in many areas such as in intensive care units,surgery,orthopedics,gynecology,and pediatrics,and has achieved beneficial results[4,5].Neurogenic bladder,caused by dysuria,has no completely effective treatment in China or abroad.Urinary incontinence can be alleviated by using a bladder therapy instrument after the prostate operation.Our study aimed to observe the effect of precise nursing service mode on the prevention of postoperative urinary incontinence in patients with prostate disease.
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Case data
A total of 130 patients,on average(62.89 ± 11.71)years old,diagnosed with benign prostatic disease from January 2018 to June 2021,in our hospital,were selected and divided into observation and control groups according to their treatment options.Sixty-five cases in the control group were given routine nursing mode intervention,and 65 cases in the observation group received precise nursing service mode intervention.There was no statistical significance of the baseline data between the two groups(P> 0.05).Written informed consent was given by patients in this study.
Selection of cases
Inclusion criteria:(1)Preoperative biopsy was performed on patients with prostate specific antigen < 4 ng/mL,which met the criteria of benign prostatic hyperplasia in The Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Diseases of Urology in China.Cystoscopy,urodynamic examination,and digital rectal examinations were performed to confirm the diagnosis;(2)Patients were ≥ 50 years old,≤ 85 years old;(3)Electro prostatectomy was performed after invalid conservative observation and drug treatment;(4)Neurogenic bladder was excluded;(5)Patients had no history of lower urinary tract trauma;and(6)They understood the purpose and methods of this study,voluntarily participated in it,and signed the informed consent.
Exclusion criteria:(1)Obstruction of urination due to urinary calculi,urethral stricture,and other reasons;(2)skin disease or severe skin damage in the perineal region;(3)psychological urinary incontinence or previous urethral trauma;(4)mental abnormalities;and(5)serious heart,liver,kidney,and other organ diseases.
Methods
The control was given routine nursing mode intervention,including vital signs’monitoring,proper catheter fixation and unobstructed,continuous bladder irrigation,dietary guidance,psychological counseling,prevention of falls and pressure sores,and analgesic drugs as directed by doctors.
The observation group was given precise nursing service mode intervention.Moreover,psychological intervention occurred first to understand the factors causing patients' negative emotions,to correct patients' wrong ideas through health education,to ensure patients realize the impact of negative emotions on postoperative urinary incontinence,and to help patients establish recovery confidence.
Stepped pelvic floor functional exercise was adopted,and patients were guided to engage in pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation training three days before the operation.Training method:the nursing staff wore disposable gloves;inserted the right index finger into the patient's anus after smearing paraffin oil and asked the patient to relax the abdominal and thigh muscles,contract the anus and urethra,relax for 5-10 s after holding for more than 3 s,and gradually extended the contraction time for 5-10 s,depending on the feeling of tightness of the anus by the pressure on the fingers.The training time was 20 min/t,3 times/d.The training was suspended from the day of the operation to 2d after the operation,and the tube training was started on the third day after operation.The duration and intensity of the exercise was gradually increased.
Patients were guided to conduct bladder function training.When the urinary catheter was just removed,the nurse responsible told the patients to urinate again immediately after urination,to avoid holding urine,to urinate regularly within a short time,and then gradually extend the interval.Once urination had occurred,they did not urinate again immediately,but maintained a relaxed and pleasant mood to relax the bladder and inhibit urination.
Intermittent micturition training was conducted to stop or slow down the speed of urinary flow during micturition.Attention was paid to contract the pelvic floor muscles to prevent urine outflow before urinary incontinence caused by coughing,laughing and other actions.For patients with urinary incontinence,clothes were changed in time and perineum area cleaned,to prevent urine odor and skin irritation.
The patient was guided to use the Lihe household low-frequency electronic pulse bladder instrument correctly after discharge from the hospital.Precision nursing permeates all stages of preoperative nursing,postoperative nursing,and continuous nursing to establish an out of hospital follow-up platform for specific diseases and to build a patient discharge system on effective supervision and communication.
Observation indexes and test method
The postoperative exhaust time,time of indwelling catheter,hospitalization time,urethral orifice injury,bladder spasm,secondary hemorrhage,and urinary incontinence were recorded.
Clinical international prostate system score(IPSS)and urinary incontinence quality of life questionnaire(I-QOL)scores were used to evaluate the symptoms and life quality[6,7].There are 7 IPSSs,and the individual score is 0-5.The lower the score,the lighter the symptoms.There are 22 questions in the I-QOL score,with a total score of 0-100.The higher the score,the better the quality of life.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 19.0 was used for data analysis;measurement data were expressed by mean ±SD;t-test was used for comparative application;enumeration data were expressed by the number of cases(percentage);χ2test was used for comparative application.The inspection level was 0.05.
RESULTS
The comparison of baseline data between the two groups
There were no significant differences in age,course of the disease,IPSS,prostate volume,rectal digital examination,and basic diseases between the two groups(P>0.05),as indicated in Table 1.
The comparison of postoperative outcomes between the two groups
Postoperative exhaust time,time of indwelling catheter,and hospitalization time for the observation group were lower than for the control group.The difference was significant(P< 0.05)(Table 2).
Comparisons of urinary flow mechanics index,IPSS,and I-QOL scores of the twogroups
The urinary flow mechanics index before the operation was consistent(P> 0.05),After the operation,the maximum urinary flow rate(Qmax)increased(P< 0.05),the residual urine volume(RUV)decreased(P< 0.05),and the maximum closed urethral pressure(MUCP)was not statistically significant(P> 0.05)compared with during preoperation.The Qmax of the observation group was higher than that of the control group,while the RUV was lower than that of the control group.There were no significant differences in MUCP between the observation and control groups(P>0.05).Preoperative IPSS and I-QOL scores were similar(P> 0.05).After the operation,the I-QOL score of the two groups improved(P< 0.05),and the IPSS decreased(P<0.05).The I-QOL score of the observation group was higher than that of the control group,and the IPSS was lower than that of the control group(P< 0.05),as demonstrated in Table 3.
Comparison of complications between two groups
There were no significant differences in urethral orifice injury,bladder spasm,and secondary bleeding between the two groups(P> 0.05)(Table 4).
Comparison of urinary incontinence between the two groups
In the observation group,there were 14 cases of temporary urinary incontinence on the day the catheter was introduced;the incidence rate was 21.54%;mainly mild.Among the 14 cases of urinary incontinence in the observation group,9 cases returned to normal within 1 wk,and 5 cases returned to normal within 1 to 4 wk.In the control group,25 cases of temporary urinary incontinence occurred on the same day;the incidence rate was 38.46%;mainly moderate.Among the 25 cases of urinary incontinence in the control group,13 cases returned to normal within 1 wk,and 8 cases returned to normal within 1 to 4 wk.The incidence of urinary incontinence in the observation group was lower than that in the control group,and there was nosignificant difference in the duration of urinary incontinence between the observation and control groups(P> 0.05)as indicated in Table 5.
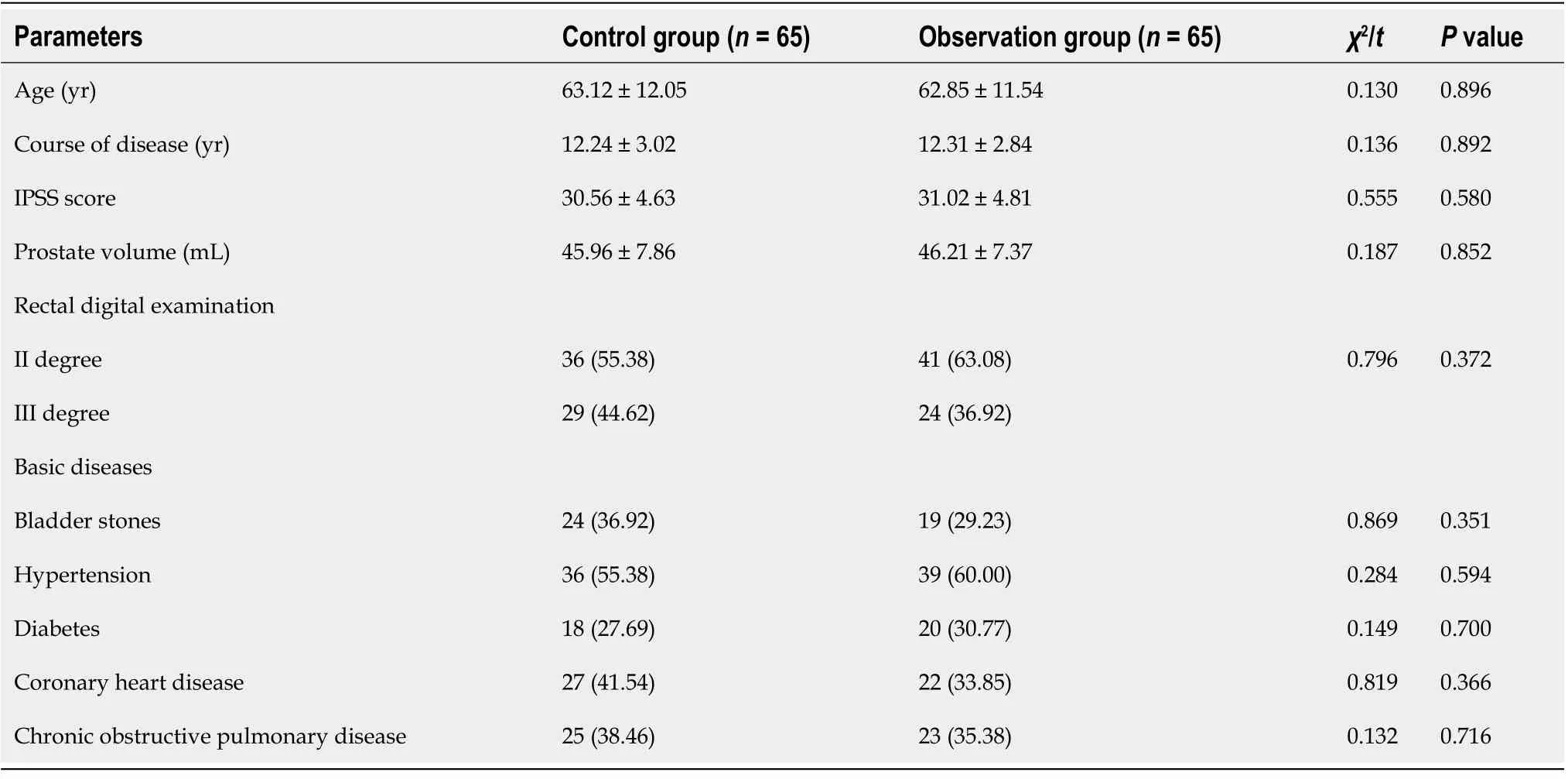
Table 1 Comparison of baseline data between the two groups,n(%)
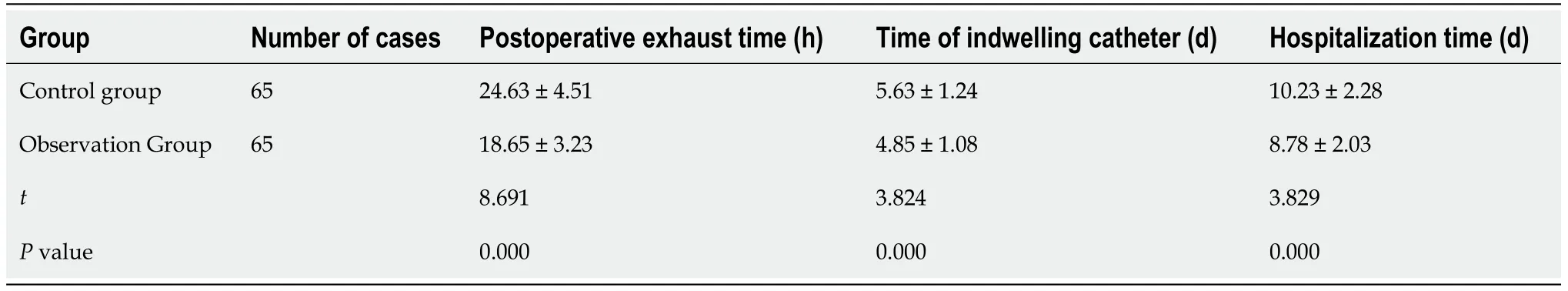
Table 2 Comparison of postoperative outcomes between the two groups(mean ± SD)

Table 3 Comparison of urinary flow mechanics index,international prostate system score and incontinence quality of life questionnaire score in the two groups(mean ± SD)

Table 4 Comparison of complications between two groups,n (%)
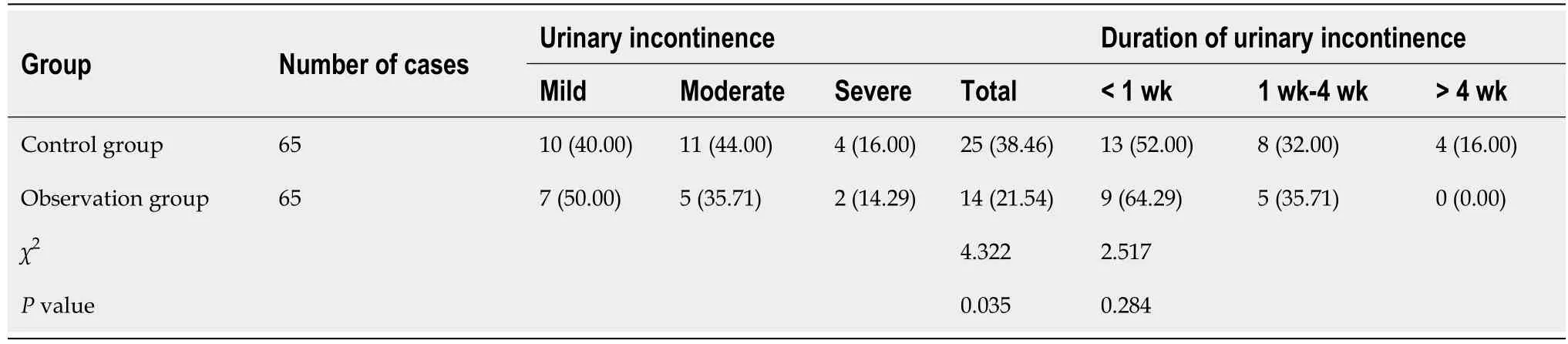
Table 5 Comparison of urinary incontinence between two groups,n (%)
DlSCUSSlON
Postoperative urinary incontinence is the common complication affecting the quality of life,with a harmful influence on patients' bodies and minds[8,9].The main treatment for postoperative urinary incontinence is prevention,and nursing intervention plays a vital role in this process[10].The Lihe household low-frequency electronic pulse bladder instrument provides a type of intervention.It is a noninvasive,painless physical therapeutic apparatus,multidimensional bladder stimulus with a low frequency,which can help patients to improve the bladder smooth muscle,pelvic floor muscles,and urethral sphincter function,to solve the increased residual urine,urinary retention,and urination dysfunction.The instrument can be used in professional medical institutions and at home.
In the postoperative care of patients with prostate disease,it is necessary to consider patients as the center and to implement the targeted nursing plan based on fully evaluating the patient's condition,which is the essence of the precision nursing model[11].Since its advent,the precise nursing service mode has played a key role in various clinical fields.The precision nursing emergency management system in emergency rescue,and found that it could improve the emergency response rate and overall standards of nursing staff and ensure the safety of patients’ lives[12,13].Moreover,Spierset al[14]applied the improved scheme based on precision nursing to the care of patients with the replantation of an amputated finger,and found that it could effectively reduce the risks of complications such as vascular crisis,postoperative infection,constipation,and could help relieve the pain.
In our study,precise nursing service mode was applied to prevent postoperative urinary incontinence in patients with prostate disease,and it was found to shorten postoperative exhaust time,the time of indwelling catheter and hospitalization time,and the incidence of urinary incontinence.However,there were no significant differences in urethral orifice injury,bladder spasm,and secondary bleeding between the two groups.This is because the psychological intervention was given first under the precision nursing service mode,which could have helped patients to reduce psychological pressure and to reduce the adverse psychological effects on urinary incontinence.
Before and after the operation,patients were guided to implement intervention measures such as pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation training to improve the strength of pelvic floor muscle groups and to reduce urinary incontinence caused by pelvic floor muscle relaxation.They were guided to increase urinary continence with intermittent training.Furthermore,patients were educated on how to use Lihe household lowfrequency electronic pulse bladder instrument correctly after discharge.This was to help them improve urinary continence ability,to promote local blood circulation,accelerate the damage of nerve repair which can help patients recover automatic micturition function as soon as possible,and accelerate the removal of catheters.The removal of the urethra is more conducive to the early cessation of the patient's rehabilitation,which can promote the faster recovery of intestinal function[15].
The urinary flow mechanics index is important to evaluate the effects of the operation and assess patients’ urination function.In patients with prostate disease,the abnormality of the urinary flow mechanics index is related to not only the prostate disease but also the surgical trauma[16,17].In our study,the urination function was evaluated through Qmax,RUV,and MUCP testing in the two groups.IPSSs were used to evaluate the prostate symptoms,and I-QOL scores were used to evaluate the quality of life.We found that the precision nursing service model could improve postoperative urinary flow mechanics,promote rehabilitation,and improve the quality of life of patients.This is because this nursing model can guide patients to avoid the occurrence of urinary incontinence Furthermore,it provides timely treatment after the occurrence of urinary incontinence,thus relieving the pain of patients and allowing their quality of life to improve[18].The early removal of the catheter can not only reduce the triggering factors of urinary incontinence but also help patients to implement urination training and improve the urinary flow mechanics index.Operation on the prostate may affect the sexual function of patients,which is related to the damage of the penile anatomy,penile blood vessels,and the erectile nerve[19,20].
Nursing care for patients with prostate disease who have undergone surgery has a direct and important impact on patients’ rehabilitation.However,existing conventional nursing interventions fail to achieve satisfactory results and have no significant effect on the prevention of patient complications.Precision nursing through psychological intervention,stepped pelvic floor exercises,and home training after discharge facilitates recovery and yields satisfactory results.Compared with conventional care,precision care encompasses all stages of preoperative,postoperative,and continuous care.Moreover,it is effective in preventing urinary incontinence.However,the findings are limited by the study sample because only patients who underwent prostatectomy for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia were included.Patients with urinary dysfunction caused by urinary calculi,urethral stricture,and other reasons;skin diseases or severe skin damage in the perineum;psychological urinary incontinence;a previous history of urethral trauma;mental disorders;severe heart,liver,kidney,and other organic diseases were excluded.However,such patients are not uncommon in clinical settings,so future studies should explore targeted and precise care for such patients.
CONCLUSlON
The precise nursing service mode can reduce the incidence of postoperative urinary incontinence in patients with prostate disease;thus,it improves postoperative urodynamics and rehabilitation,and the patients’ quality of life.
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research background
An operation to restore normal urination function and to control postoperative complications,as far as possible,is the most common method for benign prostatic disease.The postoperative nursing quality has greatly influenced the care for urinary incontinence.
Research motivation
In order to find a reasonable nursing way to improve postoperative urinary incontinence of patients with prostate disease.
Research objectives
This study aimed to observe the effect of precise nursing service mode on postoperative urinary incontinence prevention in patients with prostate disease.
Research methods
A total of 130 patients diagnosed with benign prostatic disease were selected and divided into observation and control groups according to their treatment options.The control was given routine nursing mode intervention;The observation group was given precise nursing service mode intervention.The postoperative exhaust time,time of indwelling catheter,hospitalization time,urethral orifice injury,bladder spasm,secondary hemorrhage,and urinary incontinence were recorded.Clinical international prostate system score(IPSS)and urinary incontinence quality of life questionnaire(IQOL)scores were used to evaluate the symptoms and life quality.
Research results
Postoperative exhaust time,time of indwelling catheter and hospitalization time in the observation group were lower than in the control group.After the operation,the maximum urinary flow rate increased,the residual urine volume decreased,and the maximum closed urethral pressure was not statistically significant compared with during pre-operation;After the operation,the I-QOL score of the two groups improved,and the IPSS decreased.The I-QOL score of the observation group was higher than that of the control group,and the IPSS was lower than that of the control group.The incidence of urinary incontinence in the observation group was lower than that in the control group,and there was no statistical significance in the duration of urinary incontinence between the observation group and the control group.
Research conclusions
The precise nursing service mode can reduce the incidence of postoperative urinary incontinence in patients with prostate disease;thus,it improves postoperative urodynamics and rehabilitation,and the patients’ quality of life.
Research perspectives
Next,we want to explore the improvement effect of precision nursing service mode on the prognosis of patients undergoing surgery for other urinary diseases
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年5期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年5期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Subclavian artery stenting via ilateral radial artery access:Four case reports
- Neurothekeoma located in the hallux and axilla:Two case reports
- Diffuse invasive signet ring cell carcinoma in total colorectum caused by ulcerative colitis:A case report and review of literature
- Tacrolimus treatment for relapsing-remitting chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy:Two case reports
- Aseptic abscess in the abdominal wall accompanied by monoclonal gammopathy simulating the local recurrence of rectal cancer:A case report
- Unusual magnetic resonance imaging findings of brain and leptomeningeal metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma:A case report
