Neurothekeoma located in the hallux and axilla:Two case reports
lNTRODUCTlON
Neurothekeomas(NTKs)are rare,benign,superficial soft tissue tumours that typically present as solitary nodules with a predilection for the head,neck,and upper limbs of females[1,2].Due to the low prevalence and undefined clinical symptoms of NTKs,it is difficult to accurately distinguish them from other skin tumours.NTKs rarely occur in the lower limbs or axillae and have been reported only once in the areas of the toes and axillae[3,4].In this report,we describe two different types of NTKs arising in the hallux of a 47-year-old female and the axilla of a 6-year-old boy.Both patients underwent surgical resection,and the final diagnosis was confirmed through histopathological examination.
The Princess was surprised and anxious, and fearing the parrot, who was her greatest comfort, had fallen ill, she took him in her hand and caressed46 him
CASE PRESENTATlON
Chief complaints
A 47-year-old woman complained of a painless,verrucous bulge on the plantar side of the left hallux for 3 years.
A 6-year-old boy visited our hospital and complained of a gradually increasing subcutaneous mass in the axilla for 2 years.
History of present illness
The verrucous mass appeared on the plantar side of the left hallux three years previously,and the surface skin of the tumour was abraded due to poor wound healing.Inflammatory granulation tissue formation was observed in the wound.The patient intermittently adhered to conservative treatment,but her condition was not relieved.
The subcutaneous mass was found in the axilla two years previously,and the colour of the mass was the same as that of the normal skin.The mass was only 1 cm in diameter when it was first discovered but gradually grew to 2 cm within two years.
At the cross roads the two elder brothers debated if they should go the same way as the youngest, but when they saw how dreary and deserted25 it looked they made up their minds that it would be impossible to find what they sought in these wilds, and so they stuck to their former paths
History of past illness
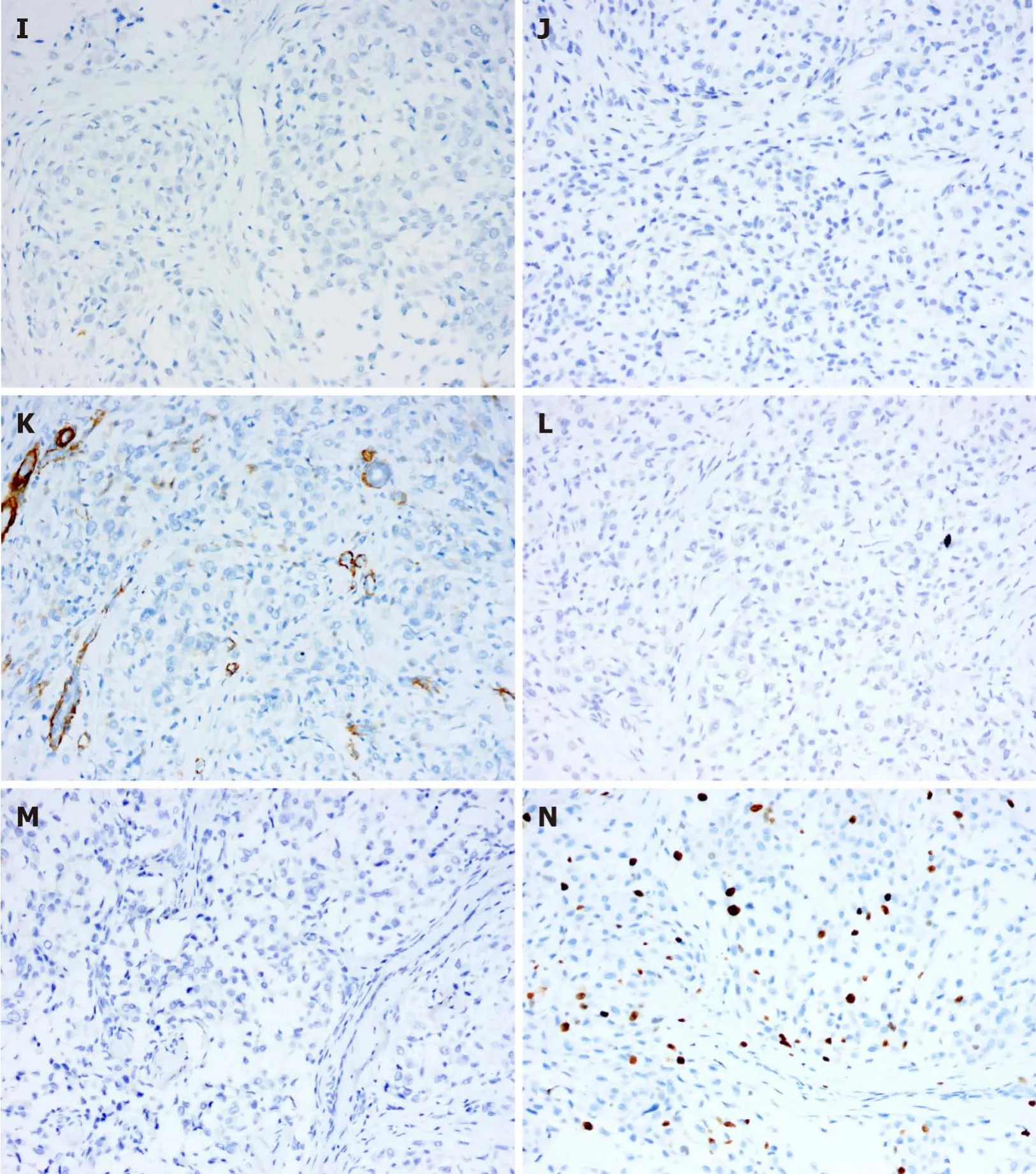
Histopathological examination of the specimen showed that the tumour tissue was composed of multiple small nodules,and the nodules were separated by hyalinized collagen fibres(Figure 2A).The nodules were composed mainly of uniformly sized eosinophilic oval cells,in which nucleoli and mitosis were observed.A small number of multinucleated giant cells infiltrated the nodules,and no myxoid matrix was observed in the interstitium(Figure 2B and C).Immunohistochemical examination revealed positive staining for CD10,CD68,TFE3,p63 and vimentin(Figure 2D-H)and negative staining for S-100,CK,SMA,glial fibrillary acidic protein(GFAP)and CD1a(Figure 2I-M).The Ki-67proliferation index was approximately 15%(Figure 2N).
The patient did not complain of any prior specific symptoms.
Personal and family history
Both patients denied any history of smoking,drinking,or drug abuse.Underlying systemic disease and family genetic history were denied.
26.Ring this bell, and what she wanted would appear: The magical castle, with its invisible servants, appears in Cupid and Psyche as well as Beauty and the Beast. Psyche receives the omnipresent service since she is in the home of a god, Cupid, with the divine powers associated with a mythological81 god. The other heroines live in a home of enchantment where every physical desire is met. They have moved from poverty to complete luxury. Supposedly they should be content and feel no more want, but they also know there is more to life than physical luxury.Return to place in story.
Physical examination
The patient's general condition was stable with normal vital signs(body temperature 36.8 °C,blood pressure 140/80 mmHg,pulse 110 bpm).A red solid mass with a diameter of 0.8 cm was found on the plantar side of the left hallux with a tough texture,normal skin temperature,and good dorsal artery pulsation.
The patient's general condition was stable with normal vital signs(body temperature 36.7 °C,blood pressure 95/65 mmHg,pulse 103 bpm).A subcutaneous mass with a diameter of 2 cm was observed in the left armpit with good mobility,normal surface skin colour and temperature,and mild palpable pain.The superficial lymph nodes were not enlarged.
Laboratory examinations
Surgical treatment was performed with local infiltration anaesthesia.The 0.8-cm tumour was located in the superficial layer of the flexor tendon and had an incomplete capsule.The tumour was completely resected and submitted for pathological examination.
Just six weeks after our Christmas visit, Daddy became very ill and was hospitalized. This time, he was fighting a different kind of war. A new prescription13 for arthritis14 had been introduced to his system, and it had almost killed him. He was scheduled for kidney dialysis when I decided to fly down to West Virginia to visit him. As I sat by his bedside, we discussed the letters. He told me how much receiving those lipstick-kissed letters had meant to him when he had been so far from home.As I left, the thought raced through my mind that tomorrow was Valentine s Day. But I quickly dismissed this thought. My father wasn t in any kind of shape to shop for a valentine. My parents had been married for fifty-six years. My mother would understand that her valentine would just have to be skipped this year.
No obvious abnormality was noted in the laboratory examination results.
Imaging examinations
Surgical treatment was performed with local infiltration anaesthesia.The solid,welldefined,2-cm tumour was located in the subcutaneous soft tissue of the armpit and seemed to lack a defined capsule.After complete removal of the tumour and complete haemostasis,the incision was sutured.
NTK,mixed subtype(left hallux).
Histopathological examination
They rode for three days-whether by a near or a far road, or on highland15 or lowland, the tale is soon told, but the journey is not done quickly-till they came to a green plain from whose center three roads started, and there a great stone was set with these words carved upon it:
The patient was diagnosed with tuberculous pleurisy 20 years previously and was cured,and she underwent uterine fibroid surgery 1 year previously.


FlNAL DlAGNOSlS
Case 1
An ultrasound from the local hospital showed a round,well-demarcated soft tissue mass in the left armpit with nosignificant alterations in the surrounding tissue.
Case 2
Cellular NTK(left axilla).
TREATMENT
Case 1
Laboratory tests revealed signs of inflammation in the urinary system,and the percentage of neutrophils(73.9%)in blood and white blood cell(99.6/μL)and bacterial(1014.5/μL)counts in urine were slightly elevated.
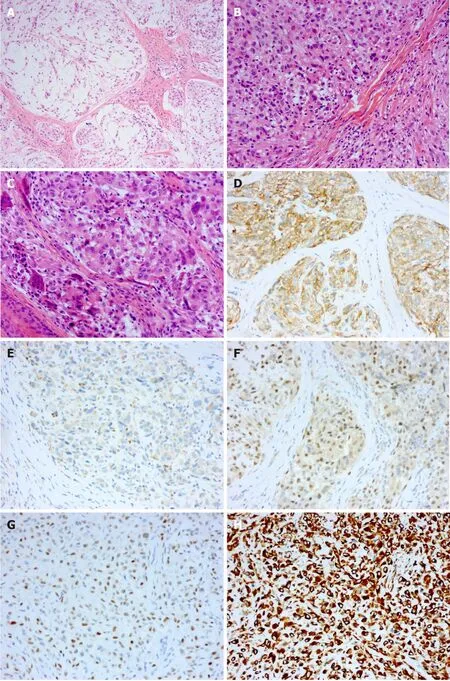
In general,the red,solid,verrucous mass was approximately 0.8 cm in diameter and had a tough texture(Figure 1A).Histopathological examination of the specimen showed that the tumour tissue was in the form of multiple small nodules or clusters.The nodules,which were composed of oval and spindle tumour cells,were abundant in some areas and sparse in other areas.In the cellular area,oval cells were relatively uniform in size with a rich and eosinophilic cytoplasm,a visible nucleolus,and a mild to moderate degree of mitotic activity.In the intermediate area,spindle cells were arranged in bundles and exhibited a benign morphology.Myxoid matrix could be observed in the nodules or interstitium(approximately 40%)(Figure 1B-D).Immunohistochemical examination revealed positive staining for CD10,CD99,transcription factor binding to IGHM enhancer-3(TFE3)and CD163,indicating NTK(Figure 1E-H).Negative staining for S-100,cytokeratin(CK),epithelial membrane antigen,smooth muscle actin(SMA),desmin,Stat6,anaplastic lymphoma kinase(ALK),and neuron-specific enolase(NSE)can be helpful in differential diagnosis,as this profile distinguishes NTKs from other soft tissue tumours such as dermal nerve sheath myxomas(DNSMs),smooth muscle cell-derived tumours,solitary fibrous tumours,epithelioid fibrous histiocytomas(EFHs),and neuroblastomas(Figure 1I-N).CD34 staining suggested vascular hyperplasia,and the Ki-67 proliferation index was approximately 20%(Figure 1O and P).
Case 2
An ultrasound from the local hospital showed a solid nodule on the plantar side of the left hallux with abundant blood supply.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
At the 12-mo follow-up,both patients had maintained a favourable postoperative clinical evolution without local pain or motion limitation.The surgical incisions had healed well,and neither patient showed signs of recurrence or metastasis.
DlSCUSSlON
NTKs are rare,benign soft tissue tumours that were first described by Gallager and Helwig in 1980[5].NTKs were initially considered to be neurogenic tumours originating from Schwann cells,and NTKs were diagnosed and reported for many years as one of the subtypes of dermal nerve sheath myxomas[6].Recently,studies have shown that,unlike DNSMs,NTKs do not express the S-100 protein[7].Further analysis of gene expression profiles shows that DNSMs are similar to schwannomas,while NTKs show evidence of myofibroblastic differentiation and possible relation to dermatofibromas[8].Therefore,NTK was classified as an independent disease for diagnosis.NTKs clinically manifest primarily as painless,slow-growing subcutaneous nodules with good mobility.Clinical diagnosis of these rare neoplasms is challenging because NTKs are not distinctive in physical examinations and imaging examinations.NTK is often mistaken for a sebaceous cyst,a Spitz naevus,a fibrous histiocytoma,a basal cell carcinoma,or a skin adnexal tumour(mainly pilomatricoma)[9,10],and an accurate diagnosis depends on histopathological and immunohistochemical examination.
Society has changed, people have changed , he murmured to himself. Years ago, if somebody picked up something lost, they would give it back. Not any more!
Histopathologically,NTK is a poorly circumscribed nodule typically composed of fascicles of spindle-shaped and epithelioid tumour cells with a sparse or no mucinous matrix[10].Epithelioid cells,which present as oval or polygonal eosinophilic cells,arerich in the cytoplasm and arranged in a nodular or plexiform pattern;spindle-shaped cells are arranged in bunches or swirls and have a benign morphology.The stroma is composed of hyalinized collagen fibres often accompanied by mucoid degeneration.Depending on the amount of myxoid matrix,NTKs have been subclassified into three types:myxoid(myxoid matrix > 50%),mixed(10% < myxoid matrix ≤ 50%)and cellular(myxoid matrix < 10%).The myxoid matrix can occasionally superficially infiltrate skin or muscle tissue.The nuclei can show mild to moderate atypia,and approximately 0-25 mitotic nuclei per high power field can be observed.
They set to work with all their might, and by dawn next day, the dress of moonbeams was laid across her bed. The girl, though she could not help admiring its beauty, began to cry, till the fairy, who heard her, came to her help.
Immunohistochemical examination demonstrates that tumour cells express CD10,CD63(NKI/C3),and mitf.Most tumours also express CD99.A few tumours express SMA and are negative for S-100,cytokeratin,Melan-A,and SOX-10 staining[11,12],indicating that NTKs are associated with scattered histiocytes.
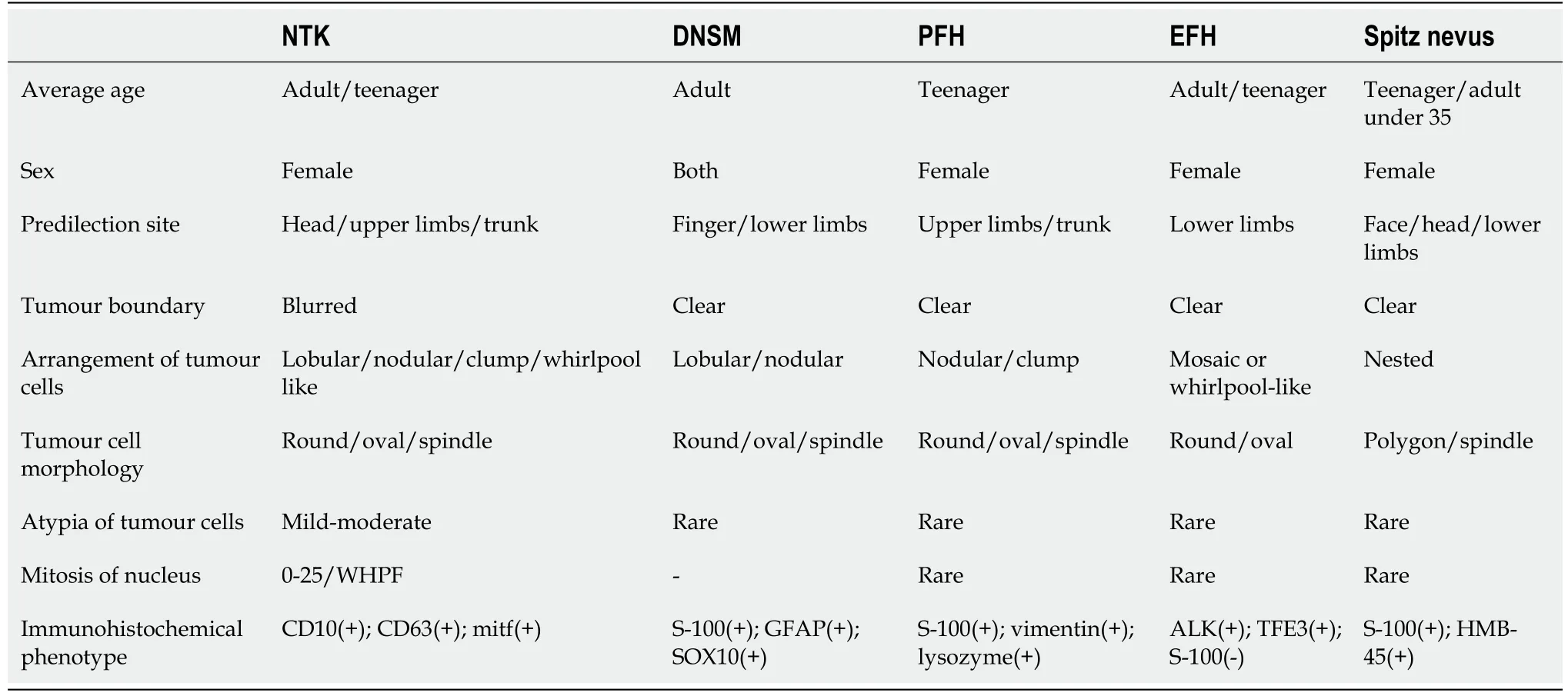
Accurate diagnosis of NTKs is essential given that these lesions can be mistaken for malignancies,leading to unnecessary treatment.The differential diagnosis includes mainly various types of cysts,DNSMs,plexiform fibrous histiocytomas(PFHs),EFHs,Spitz nevi,The clinical manifestations of these diseases are similar,but the pathological characteristics are different:subcutaneous cysts contain keratinized or necrotic material without tumour cells;DNSMs express S-100,GFAP and SOX10,as assessed by immunohistochemistry[13];PFHs have spindle-shaped fibroblasts around the nodular-arranged tumour cells[14];EFH tumour cells are mostly diffusely arranged and do not express CD63[15];and Spitz nevi are composed of epithelioid or spindle-shaped pigment cells and express S-100[16].The differential diagnosis of these diseases is shown in Table 1.
CONCLUSlON
Herein,we report two rare NTKs;both were completely resected after clinical evaluation,and an accurate diagnosis was obtained after the histopathological and immunohistochemical examination.In addition,we provide a summary of the differential diagnosis and the possible diagnostic pitfalls.The diagnostic and therapeutic experience reported here can be used as a reference for other surgeons and pathologists.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年5期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年5期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Management of procedural pain in the intensive care unit
- Effect of prior malignancy on the prognosis of gastric cancer and somatic mutation
- Elemene-containing hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy combined with chemotherapy for elderly patients with peritoneal metastatic advanced gastric cancer
- Timing theory continuous nursing,resistance training:Rehabilitation and mental health of caregivers and stroke patients with traumatic fractures
- Significance of serum glucagon-like peptide-1 and matrix Gla protein levels in patients with diabetes and osteoporosis
- Effect of precise nursing service mode on postoperative urinary incontinence prevention in patients with prostate disease
