A comparative study on the anti-bacterial effect of Echinops persicus, Cardamine uliginosa and Vaccaria oxyodontha Boiss on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli bacteria in vitro
Background
Today, bacterial resistance to antibiotics has become a global problem in the treatment of diseases.Therefore,in recent years, medicinal plants have been considered due to their lesser side effects.The problem of resistance to antibiotics, occurs for various reasons,including their improper and inappropriate use.Due to the beneficial effects of medicinal plants in the treatment of diseases and their availability and greater compatibility with the human immune system, the use of plants and their active ingredients is increasing in the against of side effects caused by the use of chemical drugs [1].Among the rich flora of Iran, there are more than 7,500 species of plants, many of which are plants that are called medicinal for various reasons and are known by the local names of the places where they grow.One of the uses of medicinal plants is the use of their essential oils, which have many effects such as anti-bacterial, antiviral, antifungal, repellent of insects, and they can also be used today in aromatherapy.These properties determine chemical compounds in essential oils and extracts and their quality and effectiveness [2].Plants with a wide variety of chemicals are a possible source of anti-bacterial agents.There have been reports of anti-bacterial and antioxidant compounds in various plant components [3].The antimicrobial activity of extracts and essential oils of plants is based on applications such as food spoilage prevention,pharmacy, medicine, and natural treatment [4].Chemicals in plants with antimicrobial activity can be divided into several groups, including phenols and polyphenols, quinones, flavonoids and flavonols,tannins, terpenoids, coumarins, alkaloids, lectins and polypeptides, and compounds such as polyamines(especially spermidine),isothiocyanates, thiosulfinates,and glucosides [5].The clinical efficacy of many available antibiotics is at risk with the emergence of multidrug-resistant pathogens.Many infectious diseases have been treated with herbal medicines throughout human history, and herbs have remained the most common source of anti-bacterial agents.The use of traditional medicines is the most popular treatment in 80% of the world’s population in Asia,Latin America, and Africa and has been reported to have minimal side effects.Nearly 20% of the world’s plants have been evaluated for biological and pharmacological tests.The experiment of plant extracts reveals ongoing efforts to find new compounds that have the potential effect to act against multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria and fungi [6,7].
belongs to the sunflower (or chicory)family.So far,120 species have been reported worldwide, which according to the flora of Iranica, 54 species of
are distributed in different parts of Iran.Species of this genus are found in many parts of Iran,including Khuzestan,Azerbaijan,Hamedan,around Tehran,Fars, etc.[8].In Eastern and Southern Europe, Asia, and North Africa,
plants are also distributed [9].This plant is a valuable medicinal plant, some of which have long been used to treat skin diseases, abscesses, blood clotting, seizures, colds, cough relievers, and soothing esophageal irritation and eye infections[8].
(
) is a plant of the genus Caryophyllaceae.This order includes 70 genus and 2,000 species, and their highest distribution is in the Mediterranean region.Their origin is attributed to the Pliocene period.The plants of this genus are herbaceous, perennial, or in the form of woody shrubs.Some of the genus plants are grown due to their beautiful and fragrant flowers, and others are used in traditional medicine.
and
species are widely used in medicine due to their anti-cancer, analgesic, and other properties [10].From the plants of this family, various studies on the antibacterial properties of this plant family are available.Such as checking the properties of the
L.(cow cockle)plant from Falih et al.[11] or
seeds plant in the study of mao et al.[12].
belongs to the order Brassicaceae and the genus Cardamineae, which is one of the largest genera of the Cruciferae family and is one of the genera that have a global distribution.Seven species of this genus have been reported in Iran,which grows in the lowlands to the highlands of humid areas.This genus shows a great variety of karyology and morphology [13].in the study of Cilic et al.The antibacterial activity of
.essential oil was tested,
antibacterial activity againt of
and
and other bacterias the shiwed antibacterial effects[14].
This study aimed to compare the antibacterial effect of
,
, and
on
and
in vitro.
Methods
Preparation and extraction of plants
,
and
plants were prepared from the medicinal plant’s Nahavand Agriculture Jihad Education Center Section.After collecting medicinal plants, they were approved by Dr.Bostan Rudi,Professor of Botany, Damghan Azad University.
,
and
have with herbarium codes 14,605,16,862, and 23,140, respectively, transferred to the laboratory for further study.The plants were dried at room temperature and pulverized by a mill.
50 gr of plant powders were weighed and poured into sealed glass containers for extraction.Then they were mixed with 85% methanol in a ratio of 1 to 10 and placed on the heater for 24 hours.
RTCC 1885 and
PTCC 1330 were used in this study, which was lyophilized from the Faculty of Pharmacy’s Microbial Collection Tehran University of Medical Sciences.Sterile lyophilized ampoules (
and
) were transferred to nutrient broth (made by Merck, Berlin, Germany) and incubated for 24 hours at 37 °C.Broth nutrient culture medium was used to ensuring the purity of the bacteria.It was cultured linearly on differential culture medium overnight and incubated for 48 hours at 37 °C.Then a loop was taken from the bacterial colony and to prepare the new sample of culture medium, the bacteria were inoculated with broth nutrients, 24 hours before each test.Similarly, new 24-hour culture was prepared for each test to evaluate the antimicrobial effects.Finally, a microbial suspension with a concentration equal to 0.5 McFarland was prepared.
Then, to test the antibacterial properties, sterile blank paper disks were placed at a certain distance from each other and the edge of the plate on the agar.The discs were placed in concentrations made from the extract.The culture media containing the bacteria were then incubated at 37 °C for 24 hours.The diameter of the growth disk diffusion around the disks was measured with a digital caliper.The results were compared with the Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute tables [15].This experiment was performed three times for each bacterial strain in different concentrations.Standard discs of gentamicin (10 mg)and vancomycin (30 mg) antibiotics were used for positive control and dimethyl sulfoxide for negative control.
Concentrations of 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32, and 1/64 of the extract were prepared using sterile distilled water to ensure the anti-bacterial properties.Each experiment was repeated three times.
Preparation of microbial strains
The prepared extracts were then refined using Whatman filter paper (No.1).The extract was filtered using a vacuum pump in the second stage.In the next step, the extract was placed in a rotary apparatus at a temperature of 44 °C.The refined extracts were dried in sterile glass plates under absolute darkness at 37 °C for 24 hours.500 mg of dry extract of each plant was dissolved in 1 mL of sterile distilled water and considered concentration 1.Then dilution was performed from a concentration of 500 mg/mL, and concentrations of 1.2, 1.4, 1.8, 1.16, 1.32 and 1.64 were prepared with sterile distilled water.
Determination of microbial susceptibility
According to Table 1,
,
,
extracts a stronger effect than vancomycin in three concentrations 500,250,125 mg/mL.The effect of the
extract against
at a concentration of 500 mg/mL was close to gentamicin’s effect on this bacterium.
9. Sunshine: Olderr s symbolic meanings for the sun include: potential good, the will, the hero, the eye of God, sovereignty, the active power of nature, the male, guiding light, heaven, and domination (Olderr 1986).Return to place in story.
When at last the right fish came swimming along she gave him a nudge, and he seized it at once, drove his knife into it, and split it up, took the heart out of it, and cut it through the middle
Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of methanolic extracts of Echinops persicus,Cardamine uliginosa and Vaccaria oxyodontha Boiss by minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC)method
The MIC test was performed by dilution in a liquid medium (micro broth dilution).One-tenth and one-hundredth dilutions of the 0.5-McFarland suspension prepared from the 24-hour culture of microorganisms were prepared to give an approximate number of 10
microorganisms per milliliter of suspension.To each successive dilution of 500 to 7.8 mg/mL of the prepared extracts was added 2 mL of Müller-Hinton broth medium (prepared by the company Merck, Berlin, German ).To each tube was added 20 μL of microbial suspension, and finally, all tubes were transferred to an incubator at 37 °C and evaluated for MIC after 24 hours.The test was repeated three times.To determine the extracts’MIC,a 5 mg/mL solution of triphenyl tetrazolium chloride was used.After adding tetrazolium dye, the plates were incubated for one hour.After one hour, the color of the solution in the tubes indicates the growth of bacteria.Bacteria had grown in tubes with red color,and bacteria had not grown in tubes with green and yellow color.The positive control tube contained a culture medium and bacterial suspension, and the negative control tube contained a culture medium and extract.SPSS software was used to analyze the obtained data.
For MBC testing, all turbid tubes from the previous step were cultured separately on Müller-Hinton agar medium samples were kept in a 37°C incubator for 24 hours.The lowest concentration of the extract in which the bacteria did not grow was reported as the lethal concentration.
Results
The disk diffusion method and kerby-Bauer protocol used for testing the ability of different concentrations of plant extracts in inhibitory of bacteria growth and detect the percentage of anti-bacterial properties.According to Figure 1,
extract has the strongest effect against
and
than
and
.The high inhibitory effect of
extract on
can also be expressed.

One of these blocks had been placed by loving hands on a child s grave, and one of the women who had come out of the church walked up to it; she stood there, her eyes resting on the weather-beaten memorial, and a few moments afterwards her husband joined her
Disk diffusion method was used to determine microbial strain’s susceptibility to methanolic extracts of
,
and
, Respectively.A concentration of 0.5 McFarland was prepared from all microbial strains in Müller-Hinton broth medium and then cultured on the surface of Müller-Hinton agar medium evenly.
But as he did this he had plenty of time to read them as well, and he read away at them until at last he was just as wise as his master--who was a great wizard4--and could perform all kinds of magic
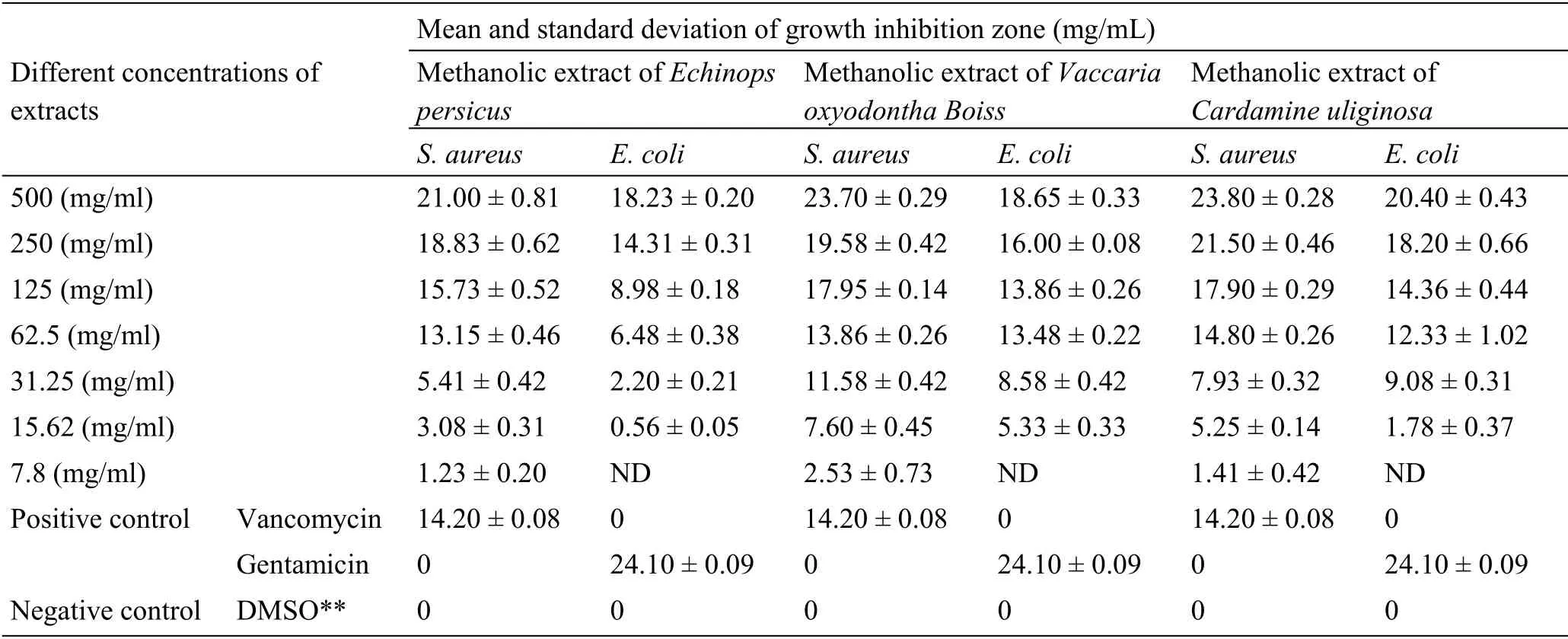
Table 2 shows the MIC and the MBC in extracts.The MICs against
strains were 125 mg/mL,31.25 mg/mL, and 15.65 mg/mL, respectively, for
,
and
.The MICs in
,
extracts and
were 31.25 mg/mL, 62.5 mg/mL and 15.62 mg/mL, respectively against
strain details MBC testing are shown in Table 2.

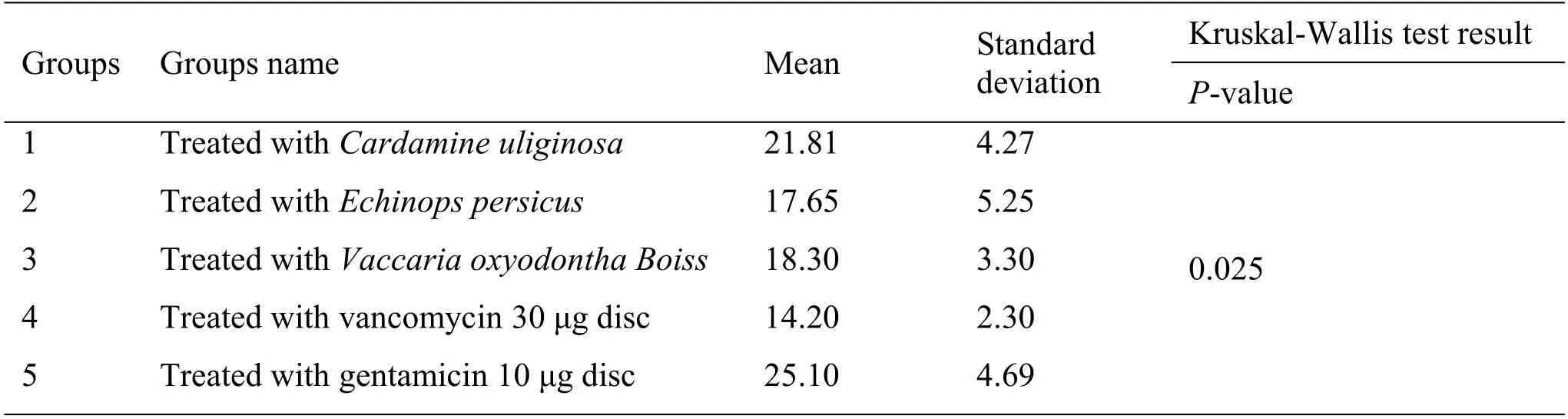
According to the results of Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute tables, the minimum growth inhibition zone for gentamicin antibiotic (10 μg disc)against
strain has an inhibition growth zone diameter of 19-26 mm.In the minimum growth inhibition zone for the antibiotic vancomycin (30 μg disc), the growth inhibition zone’s diameter against
strain is 14-15 mm.In Table 3, the intergroup comparison with the Kruskal-Wallis test showed that these extracts had antimicrobial properties equal to gentamicin and vancomycin antibiotics(
<0.05).
When the kids came in, he took them for walks along the pier21 near their office. Often she went along and watched Eric, who was becoming a master of sign language, talk and laugh with her boys as no one else had before.
Discussion
Considering the widely distributed medicinal plants in Iran, studies on these plants provide a good background for medicinal and food purposes.The results of this study showed that methanolic extracts of
,
and
in the tested concentrations had anti-bacterial effects on
and
.the most effective methanolic extract was of
against of
with inhibition growth zone 23.7 ± 0.29 mm.The minimum lethal concentration was 31.25 mg/mL in the this extract.This plant also had a significant effect on
.
extract had stronger antimicrobial properties on gram-positive bacteria compared to gram-negative bacteria in the present study,which was consistent with the study by Sancholi et al.[16].In study Al-Sorchee et al.in 2010, the antimicrobial effects of ethanolic and aqueous extracts of
were investigated on four
serotypes.The results showed that the
extract had antimicrobial properties that were consistent with the results of the present study[17].In another study by Maoz et al.,the MIC of aqueous extracts of the upper parts of the
was obtained 5% (w/v) by agar dilution method for
.These findings from the above studies show that
different extracts have an effect on gram-positive and negative bacteria.And these results prove the antimicrobial effects of this plant [18].The
has a MIC of 31.25 mg/mL and a MBC (62.5 mg/mL), which showed higher anti-bacterial activity than
.Cai et al.showed effect of
inhibitory activity against oral pathogens [19].Also in the study of Hosseini et al.were investigated the anti-bacterial properties of clove essential oil against
and coliforms in raw hamburger.This study showed that with increasing the concentration of essential oil and progression of storage time, the amount of microorganisms decreased and some concentrations showed a better effect.In general, time and high concentrations of clove essential oil (at least 0.1%)were both equally effective in reducing microbial load[20].Finally, it can be noted that similar results of anti-bacterial properties were observed in the plant extract of the
as well as clove.In a report by Iranbakhsh is expressed the reason for the difference between the MIC and MBC values of different studies on different bacteria,differences in the method of extraction of medicinal plants, different methods of studying antimicrobial activity, genetic differences of plants, differences in chemical composition between species and geographical environment[21].
Another plant whose antimicrobial effects were evaluated in this study is
,a genus of perennial plants.This plant is distributed in most Iran provinces,especially Khorasan,Fars, Isfahan,Kerman,Kermanshah, Hamedan, Lorestan, Semnan,Mazandaran,and Tehran at an altitude of 1,800 meters above sea level [22].Numerous studies on the effects of
have shown that this plant has many alkaloid compounds,flavonoids,terpenoids,fats,steroids and polystylenes.Studies have shown that
has strong anti-bacterial activity,which in the present study was clearly seen on gram-positive and negative bacteria [23].The study by Hymete et al.proved the anti-bacterial effects of castor sugar in the treatment of intestinal infections caused by Enterobacteriaceae, especially
.The anti-bacterial effects of this plant can be due to the presence of flavonoid compounds [24].
had a MIC and a minimum lethal concentration of 125 mg/mL and had a lower MIC against gentamicin and vancomycin antibiotics.Plants of this family are
and
and
can be mentioned that these plants also have anti-bacterial properties.As Soltian et al.,in evaluating the antimicrobial properties of
extract observed that this plant has strong anti-bacterial properties due to the presence of phenic acid,phenol,biphenyl,thymol compounds[7,25].
In the methanolic extract of
,like
extract, the MIC was 31.25 mg/mL, and the MBC was 62.5 mg/mL.However, compared to gentamicin and vancomycin antibiotics, in the against of bacteria, it showed a stronger inhibitory effect with an inhibition growth zone of 23.8 ± 0.28 mm.A study of the antibacterial effect of different extracts of seeds
by Naderi et al.showed that aqueous, methanolic, and hydroalcoholic extracts of
seeds with different concentrations had bactericidal or at least bacteriostatic effect [26].
and
are classified in one plant family.However, according to the study,
had a higher antibacterial effect than its
seeds.
It seemed like I d been through this before, but I patiently explained, once again, that you don t just go out and throw around an all-leather, NFL regulation, 1963 Chicago Bears-inscribed football
In general, according to Table 1, methanolic extract of
, at a concentration of 500(mg/mL) showed a stronger inhibitory effect than
,
and vancomycin and gentamicin antibiotics against
and
.
extract also had a stronger inhibitory effect than
extract.
Conclusion
In general, according to the results of the antibacterial activity of different medicinal plants in this study,methanolic extract of
,
and
extract had the highest antibacterial properties, respectively.The high anti-bacterial properties of
and
require more scientific studies.
1.Karamolah KS, Mousavi F, Mahmoudi H.Antimicrobial inhibitory activity of aqueous,hydroalcoholic and alcoholic extracts of leaves and stem of
on growth of oral bacteria.
.2017;12:Doc16.
2.Zakizadeh M, Nabavi S, Nabavi S, Ebrahimzadeh M.In vitro antioxidant activity of flower, seed and leaves of
.
.2011;15(4):406-412.
3.Doss A, Vijayasanthi M, Parivuguna V, Anand S.Evaluation of anti-bacterial properties of ethanol and flavonoids from
Linn.and
Jacq.
.2011;1:39-44.
4.Hammer KA, Carson CF, Riley TV.Antimicrobial activity of essential oils and other plant extracts.
.1999;86(6):985-990.
5.Cowan MM.Plant products as antimicrobial agents.
.1999;12(4):564-582.
6.Doss A, Parivuguna V, Vijayasanthi M,Surendran S.Anti-bacterial evaluation and phytochemical analysis of
L.against some microbial pathogens.
.2011;4(5):550-552.
7.Nascimento GG,Locatelli J,Freitas PC,Silva GL.Anti-bacterial activity of plant extracts and phytochemicals on antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
.2000;31(4):247-256.
8.Nasirzadeh A, Javidtash I, Riasat M.Identification of
species and study on some biological characteristics of larinus vulpes ouv.As manna producer in Fars Province.2005.
9.Shukla Y.Chemical, botanical and pharmacological studies on the genus
: a review.
.2003;25(3):720-732.
10.Ahmady-Asbchin S,Nasrolahi Omran A,Jafari N,Mostafapour M, Kia S.Anti-bacterial effects of
essential oil, on Gram positive and negative bacteria.
.2012;6(2):35-41.
11.Falih HY, Abed SY, Shaker ZF.Chemical constituents and descriptive properties of
plant: a review.
.2020;20(2):2411-2414.
12.Mao X, Yao R, Guo H, et al.Polysaccharides extract from
seeds inhibits kidney infection by regulating cathelicidin expression.
.2021;267:113505.
13.Engler A.Cruciferae-Sisymbrieae.
IV 105 (Heft 86) ed.Berlin:Wilhelm Engelmann;1924.
14.Kiliç Ö, Özdemir FA.Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of
Bieb.growing wild in eastern region of Turkey.
.2017;19(3):1-7.
15.Wayne P.Clinical and laboratory standards institute;2007.Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing CLSI document M100-S27;2018.
16.Sanchooli N, Rigi M.The effect of plant extracts
,
and
against three species of fish pathogenic bacteria.
.2015;70(4).
17.Al-Sorchee SMA, Rabat AAK, Juma IM.The effect of extract plant on the causative agent of diarrhoae in children of Erbil Kurdistan Iraq.
.2010;8(395):1-9.
18.Maoz M, Neeman I.Antimicrobial effects of aqueous plant extracts on the fungi
and
and on three bacterial species.
.1998;26(1):61-63.
19.Cai L, Wu CD.Compounds from
possessing growth inhibitory activity against oral pathogens.
.1996;59(10):987-990.
20.Hoseini SE, Shabani SH, Delfan AF.Antimicrobial properties of clove essential oil on hamburger during storage in freezer.
.2015;5(17):67-76.
21.Iranbakhsh A, Ebadi M, Bayat M.The inhibitory effects of plant methanolic extract of
L.and leaf explant callus against bacteria and fungi.
.2010;4(2):149-155.
22.Mozaffarian V.
:
,
,
:
;1996.
23.Khadim EJ, Abdulrasool AA, Awad ZJ.Phytochemical investigation of alkaloids in the Iraqi
(Compositae).
.2014;23(1):26-34.
24.Hymete A, Kidane A.Screening for anthelmintic activity in two
.
.1991;9(1):67-71.
25.Narimani R, Moghaddam M.Investigation of anti-bacterial properties of ethanolic extracts of four native medicinal plants of Ardebil Province by two methods of disk and well diffusion.
.2016;40(3):149-154.
26.Naderi RB.Anti-bacterial activity of various extracts of
on human pathogenic bacteria.
.2015;2(2):10-13.
