Image enhancement of coIor fundus photographs for agereIated macuIar degeneration:the Shanghai Changfeng Study
INTRODUCTION
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a serious eye disease characterized by progressive deterioration of macular areas.In 2020,AMD ranks the fourth leading global causes of blindness in those over 50 years old.Largescale screening of AMD relies on fundus photography.However,any disease that affects the cornea,lens,and vitreous body can lead to media opacity,resulting in the degradation of fundus image quality,usually present as low contrast,uneven exposure,and blurred images.In a Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme carried out in 2003,11.9% of fundus photographs were considered to be ungradable images despite a staged mydriasis protocol.Poor quality of fundus images may interfere with clinical diagnosis and clinical decision and is becoming one of the concerns related to fundus photography.With the advent of various computer technologies,medical image processing has been applied to multiple disciplines:ophthalmology,dermatology,pathology,and imaging.Various methods of retinal image enhancement have emerged.Today,increasing numbers of ophthalmologists and image processing engineers are seeking opportunities to cooperate in fundus photographs optimization.The Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) research team explored a standardized fundus image optimization process for AMD diagnosis.The histogram-based process aimed to adjust image brightness,contrast,and color balance for ungradable images,and help standardize the documentation of AMD in multicenter studies.In 2017,Tsikatadeveloped an automatic image processing software utilizing the optimization parameters in the AREDS2 study.However,the fundus image optimization parameters apply only to Caucasian subjects.Due to racial differences in fundus pigmentation,the optimization parameters in the AREDS2 study may not apply to the Chinese population.Standard image optimization methods for the Chinese population need to be further explored.In 2018,Jindeveloped an image enhancement method for retinal diseases,with the area under the curve (AUC) for AMD diagnosis increased from 0.918 to 0.975.However,the enhancement and the image processing method is not targeted at AMD,but multiple fundus diseases,including diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma,.As lesion characteristics vary from disease to disease,image optimization method aiming at AMD is pending further studies.
The purpose of our study is to develop a standard optimization software for AMD diagnosis in the Chinese population based on fundus photographs and to assess the performance of the image optimization method through a diagnostic test.Our standard optimization software is designed to use the optimal enhancement parameters to detect the soft and hard drusen,but it can also help detect late AMD lesions and other types of drusen to some extent.
There is a sense of entering another world after the princess leaves her father, von Franz points out . . . the fact is that such women [animus ridden] have marvelous journeys with the animus-lover, of which they are not fully65 aware (172).Return to place in story.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
The study was compliant with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by The Medical Ethic Committee of Zhongshan Hospital,Fudan University.Our research was accomplished by the cooperation of diabetic specialists,ophthalmologists from Zhongshan Hospital,image processing engineers,and software engineers from Pingan Technology.
Our study was part of the Shanghai Changfeng Study,which focused on multiple chronic diseases.It contained two stages:optimization software technology development and image enhancement performance assessment.
IBM SPSS Version 22.0 was used to calculate diagnostic sensitivity,specificity,positive predictive value,negative predictive value,accuracy,Youden index,and other indicators of diagnostic efficacy.McNemar's test was used to compare sensitivity and specificity.
We normalize the span of pixel values from 0-255 to 0-1.As can be seen from Figure 3,the brightness difference between the lesion and non-lesion areas becomes larger in all three channels when increasing image contrast.However,excessively high contrast will introduce additional noise and may cause false positivity,and result in image distortion.We began the optimization process by using the linear transformation formula:
Inclusion criteria:1) Patients ≥45 years old;2) Substandard quality images,defined as follows:a) The quality of the image is not as good as the ten high-quality exemplary images due to media opacity,uneven luminance,or fluctuations in focus;b)Gradable macular area ≥3/4 macular area;3) Patients underwent the OCT scan of the macular area within one month.Examples of standard and substandard images are shown in Figure 1.In the standard image,the macular area and fundus vessels are clear.In the middle picture,there is a lack of exposure in the temporal and inferior areas.Media opacity exists in the right image,which reduces the image clarity.Exclusive criteria:1) Extremely poor image quality:extremely overexposed or underexposed;extremely out-of-focus or blur;key areas blocked by eyelashes/hair/small pupils/other fundus diseases,and result in less than 3/4 macular area gradable;2) Patient diagnosed with or reported having following diseases:central retinal vein occlusion,central serous chorioretinopathy,proliferative diabetic retinopathy,vitreous hemorrhage,endophthalmitis,retinal detachment,retinitis pigmentosa or retinal neoplasms within 90d before enrollment.Gold standard:OCT showed drusen in the corresponding areas,characterized as single or multiple continuous or discontinuous mound-like elevations with or without abnormal retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).

Eighty-six fundus images of AMD confirmed in the Shanghai Changfeng Study database were used as optimization development material.The study design and imaging procedure were briefly described in the previous report.Our optimization method is similar to the method used in the AREDS2 study.Ten images with the best quality were selected by clinicians and image processing engineers as exemplary images.Optimization parameters adjustment was using Adobe Photoshop cc2017.Fundus images were displayed in different color modes,including hue,saturation,value mode (HSV),hue,saturation,lightness (HSL),luminance,chrominance,chroma mode(YUV) and red,green,blue mode (RGB).Image processing engineers observed the information of fundus structure and compared the difference in image parameters between the exemplary images and other images through channel separation.Then,we took two areas of 3×3 pixel size in the center of the typical drusen and adjacent normal district and compared the average brightness of red channels.Optimal parameters were recorded when the brightness difference reached its maximum.Here we determined brightness as the average brightness in red channel,which is similar to the method used in the AREDS2 study.Subtle adjustments were made to make sure the optimized image accorded with the reading habits of human eyes and that the images were not distorted.After multiple comparisons among the original parameters,our optimization parameters,and AREDS2 optimization parameters,we then determined the final optimization parameters after a few subtle adjustments.The optimization software was developed by software engineers through Visual C++tools.
RESULTS
Other indicators of diagnostic efficiency are shown in Table 6.Using the optimized images for disease diagnosis,the negative predictive value increased by 11.6%,the false negative rate decreased by 14.8%,accuracy increased by 5.7%,and the Youden index increased by 0.11.


To evaluate the image enhancement software on substandard images,we conducted a paired-sample diagnostic test.Sample size calculation was performed using NCSS PASS 15.0 based on diagnostic tests for two paired samples.We took the value of=0.8,α=0.05,and the sample size was finally determined to be 102.Samples used in the study were retrospectively and consecutively selected from all fundus images of patients who underwent fundus photography after mydriasis and OCT scan of the macular area in the Department of Ophthalmology,Zhongshan Hospital of Fudan University,from October 2018 to December 2018.After standard optimization of fundus images,a trained ophthalmologist performed AMD diagnosis on shuffled original images and optimized ones.In case of uncertainty,the final diagnosis was achieved after reaching a consensus with another senior ophthalmologist.Diagnosis results are compared to the OCT gold standard with fourfold tables.Patient information (gender,age,diagnosis,right/left eye,.) was also registered.Information was collected using Carl Zeiss CIRRUS 4000 HD-OCT 512×128 line scan mode and TOPCON TRC-50DX fundus camera.
Joseph was only four years old, and still afraid of the dark, so Aunt Linda left the door open and the hall light on when she tucked4 us in to bed. Joe couldn’t sleep, so he just lay there staring at the ceiling. Just as I dozed5 off to sleep, he woke me up and asked, “Jennie, what are those ugly things near the light?”(I had always liked that he asked me questions because I was older and supposed to know the answers. I didn’t always know the answers, of course, but I could always pretend I did.) He was pointing to the moths fluttering6 around the hall light. “They’re just moths, go to sleep,” I told him.



In Formula 1,Contrastis the span of brightness of the target optimization image,andContrastis the span of brightness of the original image to be optimized;is the pixel value of a point in the original image,whileis the pixel value of the corresponding position after optimized;Xis the minimum pixel value of the original unoptimized image,andXis the minimum pixel value of the target image.
So the Prince was appointed Imperial Swineherd. He had a dirty little roomclose by the pigsty11; and there he sat the whole day, and worked. By theevening he had made a pretty little kitchen-pot. Little bells were hung allround it; and when the pot was boiling, these bells tinkled12 in the mostcharming manner, and played the old melody,
We chose moderately higher contrast values while considering the reading habit of the visual system.The image presented better performance when the red component is between 0.4-1 and the green component is between 0-0.8 in the color distribution histogram.Because the blue component contains less key information of the images,we only adjust the brightness and contrast of the blue channel in a small range,where a proper distribution range is 0-0.15.To explore the color balance among channels,a representative image was chosen to display the performance on typical parameters,which illustrates the selection strategy of reasonable parameter ranges.When the average brightness in the red channel exceeds 0.7,the image will be seriously overexposed.When the average brightness in the red channel is below 0.55,the image will be too dark to display the fundus structure.Therefore,the average brightness in the red channel should be 0.55-0.7.To highlight the difference between lesions and non-lesions,and meanwhile considering the reading habit of the visual system and ensuring the image is not distorted,we chose the average brightness in the red channel to be 0.7.
A total of 208 images of 104 participants were included in the diagnostic test.Fifty-seven (54.8%) participants were males and the mean age of all participants was 65 years old.Participants were diagnosed with AMD if at least one eye was diagnosed with AMD.The results obtained from OCT showed that 54 participants were diagnosed with AMD while 50 not.Tables 4 and 5 showed the diagnostic performance for the original images and optimized images,respectively.
The passengers on the bus watched sympathetically as the young woman with the white cane1 made her way carefully up the steps. She paid the driver and then, using her hands to feel the location of the seats, settled in to one. She placed her briefcase2 on her lap and rested her cane against her leg.
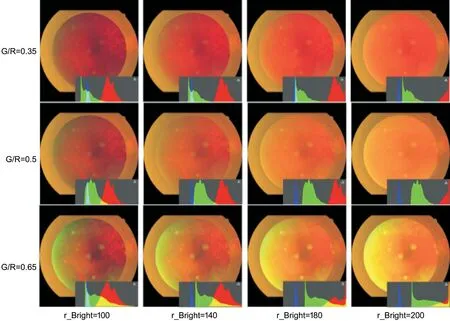
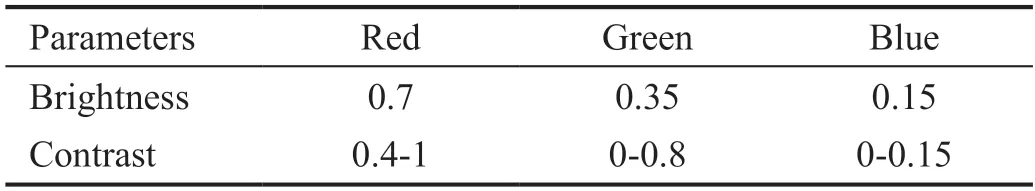
Figure 5 shows the changes in the lesion and non-lesion areas with different G/R ratios and brightness values of the red channel image.By using the parameters above,we enhanced all the 86 images and calculated the brightness and contrast of all optimized images.Figure 6 shows two broken line graphs demonstrating brightness and contrast of optimized images.
I decided11 it was time to confront myself. That night at home, I took off all my clothes and had a long look at the woman in the mirror. She was androgynous. Take my face - without makeup12, it was a cute young boy s face. My shoulder muscles, arms and hands were powerful and muscular from the crutches13. I had no breasts; instead, there were two prominent scars on my chest. I had a sexy flat stomach, a bubble butt14 and a well-developed thigh15 from years of ski racing. My right leg ended in another long scar just above the knee.
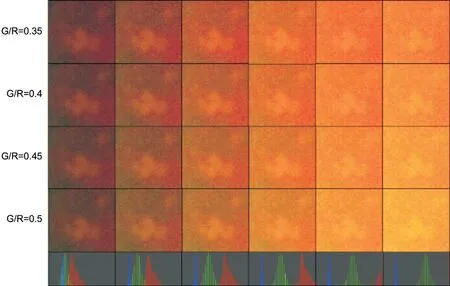


The parameters of images are shown in Table 3.As shown in Figure 4,when the ratio of green and red components (G/R ratio) exceeds 0.5,the image will be greenish with some color distortion;when the G/R ratio is too small,the contrast of the lesion area will be reduced (the spectrum of drusen is mainly concentrated on the green channel).Thus,the G/R ratio was determined to be 0.5 and the average brightness of the green channel was determined to be 0.35.
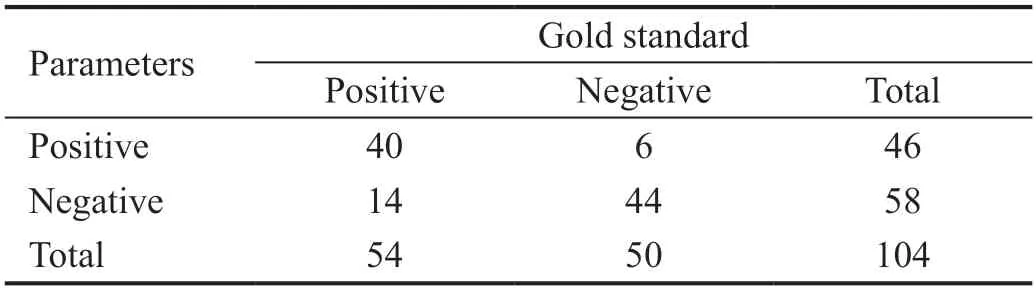


Diagnostic sensitivity and specificity before and after image optimization were calculated according to the two fourfoldtables above.The sensitivity significantly improved from 74%to 88% (=6.125,=0.008),while the specificity slightly reduced from 88% to 84% (=0.500,=0.500).
In Figure 6,the overall contrast of optimized images was largely increased and the G/R ratio was maintained at approximately 0.5.Through the above procedure,we maximized the enhancement performance while maintaining the original information of the image.The optimized image is shown in Figure 7.
In this study,we included color fundus photographs of 86 eyes of 74 subjects diagnosed with AMD,45 (60.8%) of the participants were female.Table 1 presents the basic characteristics of the image dataset for software development.Table 2 presents the image properties of the image dataset.As shown in Figure 2A,the overall contrast values of these images are relatively small.Figure 2B indicates that theoverall brightness values of the image are relatively large and the brightness values of the three channels were dispersed in color space.We split the full RGB color image into gray-scale equivalences.By observing these gray-scale images,we found that the red channel is the optimal channel to display choroid,the green channel is the optimal channel to display retina,while the blue channel carries little information.For image optimization,we decided to increase the contrast values of the green channel and the red channel.
DISCUSSION
The improvement of medical image processing technology makes it possible for cooperation among doctors,image processing engineers,and software development engineers.The uniform quality of fundus images is of great significance to the accurate detection and classification of AMD.In the present study,86 fundus images diagnosed with any stage of AMD in the Shanghai Changfeng Study have been used for optimization technology development.By comparing exemplary images with other images and observing features of typical AMD lesions under different brightness and contrast parameters,the optimal parameters were finally obtained.After multiple times of adjustments,we developed software that enables rapid and accurate enhancement of fundus images for AMD diagnosis in the Chinese population.The diagnostic test results showed that after optimization the sensitivity of fundus image diagnosis can be significantly improved without significantly reducing the specificity.The improvement in image parameters and the diagnostic test provided evidence that the fundus image optimization software can help accurate screening,detecting,and grading of AMD.Previous studies have explored various methods of retinal image enhancement,including histogram equalization,but few studies have focused on AMD diagnosis.Through standardized optimization of fundus images in the Caucasian population,the AREDS2 team demonstrated the effect of fundus image optimization for AMD,indicating extensive application prospects in image optimization for AMD grading.Compared with the optimization parameters for the Caucasian subjects in the AREDS2 study,lower brightness in the red channel,higher brightness in the blue channel,higher contrast in the blue and green channel were adopted in our study.This might be partly due to the racial difference in fundus pigments.Caucasians have lighter fundus pigmentation than Chinese,thus the basic tones of their fundus images may be bluish or purplish compared with the Chinese population.In AREDS2 research,the proportion of bluish or purplish images in all digital photographs is as high as 33.6%,but the same problem did not present in our study.However,differences in camera properties,photographer techniques and other factors in the two studies may also result in the disparity in image performance.Large-scale studies that include multi-ethnic populations are needed.In 2018,some researchers proposed an image optimization method for retinal diseases,where the AUC of the optimized images was increased from 0.918 to 0.975.However,the optimization method they proposed targeted at a variety of retinal diseases,including diabetic retinopathy,glaucoma,not only for AMD.Characteristics and parameters of typical lesions vary among different retinal diseases;therefore,disease-specific optimization parameters should be a better choice for a specific fundus disease.The optimization parameters developed by the current study may not be applicable to other fundus diseases or other racial groups.
And truly there were enough of them to pave every path in Potentilla s garden and leave some to spare! The next day Prince Narcissus had prepared for the Princess s pleasure a charming arbour of leafy branches, with couches of moss42 and grassy43 floor and garlands everywhere, with her name written in different coloured blossoms
In our study,there is a significant increase in sensitivity from 74% to 88% by using optimized images.Our optimization may facilitate better screening,detecting and classifying AMD and reduce the probability of missed diagnosis.AMD is most commonly seen in the elderly,and meanwhile a large proportion of them present with cataract,vitreous opacity and other diseases that result in degradation of fundus image quality,making images optimization essential for diagnosis and classification of AMD.Furthermore,our diagnostic test was based on mydriatic fundus images collected in the clinical setting,which may have better image quality than those taken in the community and without mydriasis.Therefore,we may underestimate the improvement of sensitivity when generalizing it to the disease screening based on non-mydriatic fundus photographs in community settings.
The strengths of our research are as follows:First,we developed an automated fundus image optimization software for the Chinese population for the first time and assessed the performance of optimization software by a diagnostic test.Second,our research was a multidisciplinary research achieved by the multi-sectoral collaboration of ophthalmologists,image processing engineers,and software development engineers.Possible limitations of this study are the following:first,the specificity of the optimized images decreased slightly from 88% to 84%.However,the difference is not significant.In previous studies,the sensitivity of AMD diagnosis grading by fundus images ranged from 50% to 90%,and the specificity ranged from 63% to 90%.Compared with previous results,our study showed an overall good performance.Second,the number of fundus images in our study was not large and may introduce potential bias.Due to the variety of the characteristics of late AMD lesions,using a single set of parameters to increase the detection rates of late AMD lesions to the maximum level is not realistic and feasible.Our enhancement procedure does not focus on late AMD lesions or other types of drusen such as the cuticular drusen and the reticular pseudo drusen.However,it can help detect late AMD lesions and other types of drusen to some extent.Furthermore,our optimization software may need further assessments on larger populations and different camera manufacturers.
In conclusion,in the current study,we developed an automated fundus image optimization software for the Chinese population and assessed the performance of optimization software by a diagnostic test.Our fundus image optimization software increased diagnostic sensitivity and may help ophthalmologists and researchers in AMD diagnosis and screening.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None.
 International Journal of Ophthalmology2022年2期
International Journal of Ophthalmology2022年2期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- IJO/IES Event Photos
- Inhibitory effect on subretinaI fibrosis by anti-pIacentaI growth factor treatment in a Iaser-induced choroidaI neovascuIarization modeI in mice
- Artesunate inhibits proIiferation and migration of RPE ceIIs and TGF-β2 mediated epitheIiaI mesenchymaI transition by suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway
- NoveI mutations in the BEST1 gene cause distinct retinopathies in two Chinese famiIies
- Frequency cumuIative effect of subthreshoId energy Iaser-activated remote phosphors irradiation on visuaI function in guinea pigs
- One-step thermokeratopIasty for pain aIIeviating and pretreatment of severe acute corneaI hydrops in keratoconus
