Comparison of fundus fluorescein angiography and fundus photography grading criteria for earIy diabetic retinopathy
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease affecting millions of people globally.Approximately 463 million adults are living with diabetes,with projections that this number will rise to 700 million by 2045.China is believed to have the highest total number of people with DM.Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the most severe complication of diabetes and the leading cause of vision loss in adults of productive age.Approximately one in every three people with diabetes has DR.
In China,fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) results have often been used to grade DR,even in early DR patients.However,the international DR staging standard based on fundus photography formulated in 2003 has been widely recognized and used in clinical diagnosis and treatment,but the lesions detection rates of the two approaches are different.Using FFA,we established that mild or moderate non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) eyes had more severe retinopathy and even more than 20 intraretinal hemorrhages in each of the 4 quadrants and intraretinal microvascular anomalies (IRMAs).This was attributed to the use of contrast agents in the FFA examination.However,a consistent DR classification standard is lacking,although it has been commonly utilized as a grading method.Hence,the examination of photographs by different medical specialists results in different grades obtained for the same image,causing confusion to patients.Therefore,a consistent and accurate grading method closer to FFA evaluation should be developed,rather than employing grading standard based on fundus photography outcomes.In this study,we conducted a retrospective evaluation to compare the grading criteria of early DR using FFA and fundus photography results.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin MedicalUniversity (Harbin,China).Informed written consent was obtained from the participants.
33.Her sister who has occasioned all this: In the height of unfairness, the youngest sister is blamed for the failure of the eldest sister. Return to place in story.
DM patients selected from the 685 patients who had undergone FFA and fundus photography at the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University between May 2018 and December 2019 were included in this investigation.
At length, when everybody had suffered, they met and told the whole story, and next day they all marched off in fury to the man who had made game of them
Patients whose fundus photography diagnostic results showed mild or moderate NPDR were included.The following exclusion criteria were applied:1) Other eye diseases unrelated to diabetes (including hypertensive retinopathy,retinal arteriovenous obstruction,age-related macular degeneration,glaucoma,uveitis,);2) Any other causes,such as dense cataract and corneal opacity,leading to poor image quality(invisible optic disc and vessels);3) Patients with a previous ophthalmological intervention procedure,such as laser photocoagulation,vitrectomy,and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor injection.
I am glad to see you, my dear children; you are very hungry and weary; and my poor Peter, thou art horribly bemired; come in and let me clean thee. 13
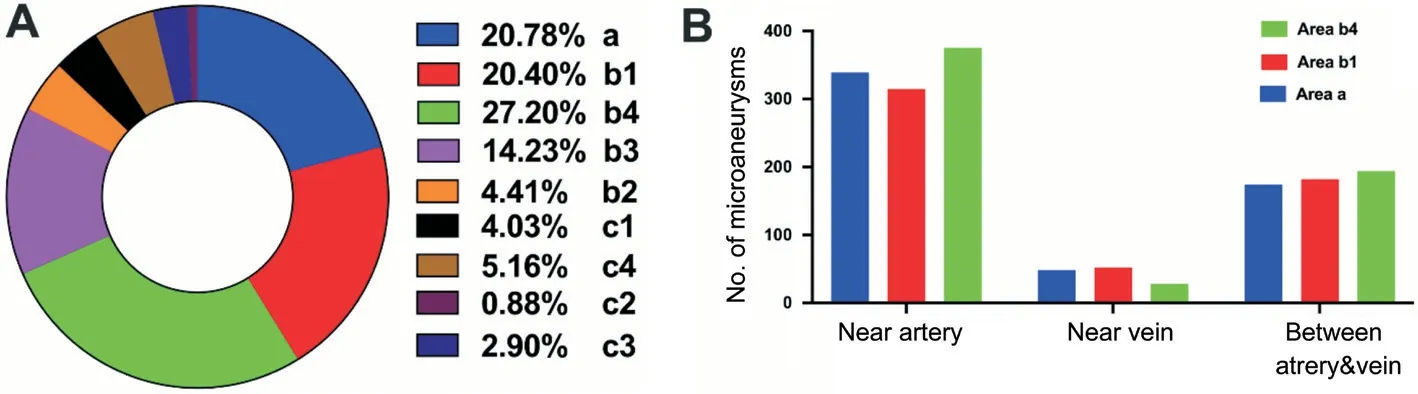
Statistical analysis of the location of early retinal lesions(including microaneurysms,hemorrhages,intraretinal hemorrhages) revealed that the lesions were concentrated mainly in b4 (27.2%),a (20.78%),and b1 (20.4%) areas.The areas corresponded to the nasal surface of the optic disc,the macular area,and the vicinity of the superior temporal vascular arch,respectively (Figure 5A).The peripheral retina(c area) had relatively fewer lesions during early DR (mild or moderate).The microaneurysms often developed around the small arteries (Figure 5B).Moreover,both small vessel dilatation and occlusion were significantly correlated with the number of microaneurysms in these areas (≤0.001;Table 3).
The use of contrast agents further revealed the occurrence of IRMA in 66.1% of the mild or moderate NPDR eyes.IRMA is induced by the further development of microvascular dilatation or occlusion in early DR lesions.In areas of vascular occlusion,the capillary bed becomes cell-free,and the blood vessels in adjacent cell-free areas dilate irregularly,causing arteriovenous shunts.This is an indication for IRMA:the arterial blood flows directly into the veins without passing through the capillary beds.Here,we found that this condition was not significantly associated with the number of early DR lesions of microaneurysms and hemorrhage.Nonetheless,it led to the further development of DR lesions.Although many IRMAs involving multiple quadrants were identified by FFA,the low-degree lesions were formed.Hence,IRMA needs a new grading standard in FFA,especially because IRMAs could not be identified by fundus photography.As can be observed in Figure 5B,microaneurysms were present mostly around the small arteries.Microaneurysms appeared first,followed by small arterioles that progressed into arteriolar dilatations and leakage of the vascular walls.Our results were consistent with those of previous studies reporting that microaneurysms were induced by chronic ischemia and the destruction of pericytes or endothelial cells.

FFA images were obtained using a Heidelberg retinal angiography device (Heidelberg Engineering,Heidelberg,Germany).Ten 55° FFA images were taken from both eyes of each patient in the early,middle,and late stages after fluorescein injection administration.The ten fields were centered on the macula,optic disc,superior peripheral retina,superior temporal peripheral retina,temporal peripheral retina,inferior temporal peripheral retina,inferior peripheral retina,inferior nasal peripheral retina,nasal,and superior nasal peripheral retina.Then,the images were partitioned to better localize the retinopathy.Each FFA image was partitioned as illustrated in Figure 1.The numbers of microaneurysms,hemorrhages,and IRMA in each region were counted.Customized large and small microaneurysm and hemorrhage methods are presented in Figure 2.
And the swineherd went behind a tree, washed the black and brown color fromhis face, threw off his dirty clothes, and stepped forth in his princelyrobes; he looked so noble that the Princess could not help bowing before him.
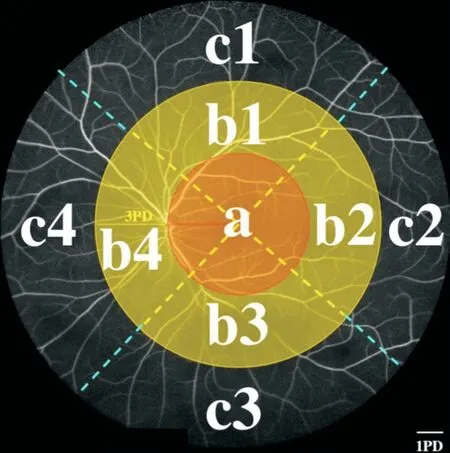
1) Observation of the location and number of hemorrhages;2) Observation of the location and number of IRMAs;3) Observation of the location of early DR lesions;4) Assessment of the relationships among microaneurysms,hemorrhages,small vessel dilatation,and capillary nonperfusion.
All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS Statistical software (v25,IBM,Armonk,NY,USA) whereas graphs were generated using the Graph Prism 7 software (v7.02,GraphPad,La Jolla,CA,USA).Continuous variables conforming to a normal distribution were expressed as means and standard deviation values.Other continuous variables that were not normally distributed were expressed as medians values (25%-75%).Categorical variables were expressed as frequencies and percentages.Quantitative variables were selected using spearman's rank correlation analysis.-values less than 0.001 indicated significant inter-group differences.
RESULTS
Among the 685 DM patients,only 260 patients (480 eyes) with mild or moderate NPDR were included in the study.These 260 patients included 149 males (289 eyes) and 111 females(191 eyes).Based on the fundus photography images,156 eyes (32.5%) were graded as mild NPDR,whereas 324 eyes(67.5%) were graded as moderate NPDR.The average age for mild NPDR patients was 56.8±6.9y,whereas it was 59.3±7.8y for moderate NPDR patients.In addition,the duration of diabetes was 3.8±2.2y for mild NPDR patients and 4.1±2.7y for moderate NPDR patients.The demographic and clinical characteristics of the participants are summarized and listed in Table 2.

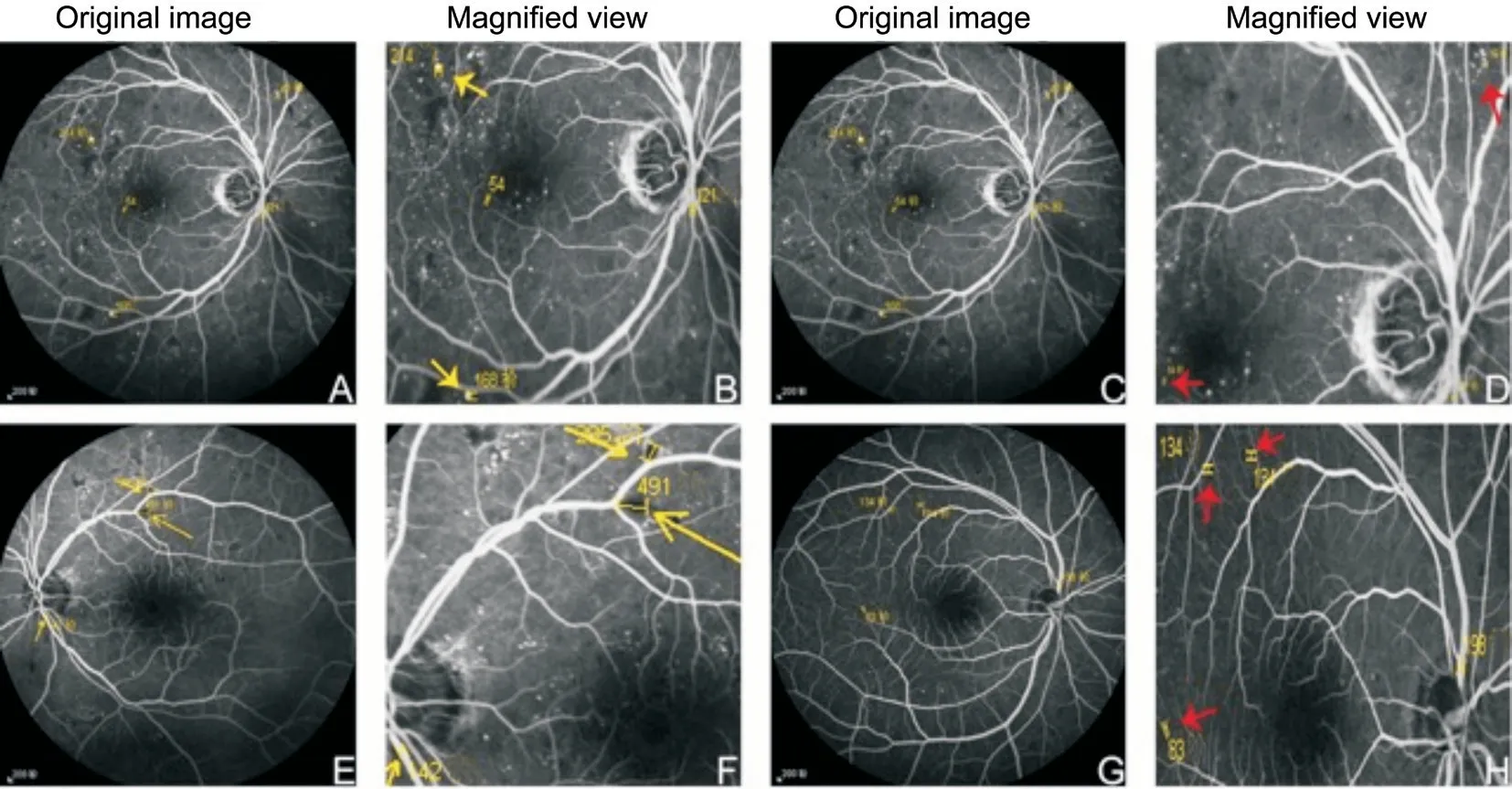
Large hemorrhages were easily distinguished and quantified by both fundus photography and FFA.However,small needle-like hemorrhages were distributed in clusters and thus could not be distinguished or accurately quantified by FFA (Figure 3).Counting of the needle-like hemorrhages identified by FFA revealed that 9 eyes (1.9%) had more than 20 hemorrhages in all the four quadrants,15 eyes (3.1%) had more than 20hemorrhages in three quadrants,26 eyes (5.4%) had more than 20 hemorrhages in two quadrants,and 37 eyes (7.7%)had more than 20 hemorrhages in only one quadrant.There were less than 20 hemorrhages in 198 eyes (41.2%) and no obvious hemorrhages were detected in 195 eyes (40.6%).This number was not consistent with the classification of fundus photography,as no more than 20 intraretinal hemorrhages should have been in each of the 4 quadrants in mild or moderate NPDR.
Dummling went and cut down the tree, and when it fell there was a goose19 sitting in the roots with feathers of pure gold.20 He lifted her up, and taking her with him, went to an inn where he thought he would stay the night. Now the host had three daughters,.21 who saw the goose and were curious to know what such a wonderful bird might be, and would have liked to have one of its golden feathers.

Four years later it was the nation s turn to mourn the Duke and to reflect on one man s decision to trade the crown of England for the love of Wallis and the price they had both had to pay.
The demographic information,including age,gender,blood pressure,duration of diabetes,and ophthalmological medical histories of the remaining patients,was obtained from the hospital's medical records.


DISCUSSION
In DR patients,retinal hemorrhage is the edema caused by the destruction of vascular endothelial function and the slight leakage of the plasma.Retinal hemorrhage is induced by blood cell outflow.The presence of retinal hemorrhage points reflects the presence of dysfunctional retinal vascular endothelium.It is also an early symptom of DR.The size and quantity of the hemorrhages may vary greatly depending on the means used for examination.However,it is easier to detect higher numbers and smaller hemorrhages by FFA examination.Needle-tip-like hemorrhages can also be captured by FFA.They are difficult to identify by fundus photography.In this investigation,it was difficult to distinguish between microaneurysms and small hemorrhages in fundus photography images.This could have potentially led to discrepancy.Moderate NPDR patients had numerous intraretinal hemorrhages.Some of them had even more than 20 intraretinal hemorrhages in all the four quadrants,which was diagnosed as severe NPDR by the DR staging criteria.Other manifestations such as vasodilation and no-perfusion area were mild.Angiographic features were most significantly related to the overall DR severity,including the differentiation between severe non-proliferative and proliferative disease.Ehlersfound that the panretinal leakage index,panretinal ischemic index,and microaneurysm count in ultra-widefield were associated with DR severity.Moreover,they used the angiography grading results to guide DR treatment,whereas the treatment of severe NPDR was completely different from that of moderate NPDR.
Herein,we summarized and analyzed the common lesiontypes,prevalence locations,and lesion characteristics of early DR using FFA images.It is noteworthy that in mild to moderate NPDR eyes,FFA found IRMA and more than 20 intraretinal hemorrhages in each of the 4 quadrants that were ignored by fundus photos.These findings showed that the grading standard of fundus photography was not appropriate for use in FFA grading.
Among the 324 moderate NPDR eyes observed using FFA,214 eyes (66.1%) had 483 sites of IRMA,which were not detected by fundus photography (Figure 4).IRMAs occurred mostly in b4 (29.6%),b1 (24.7%),b3 (16.1%),c4 (11.7%),c1 (7.4%),and c3 (5.7%).The other regions had only 4.9% of IRMAs.Furthermore,there were more than 4 IRMAs in 17 eyes,3 IRMAs in 35 eyes,2 IRMAs in 69 eyes,and 1 IRMA in 93 eyes.
Digital nonmydriatic fundus camera (FundusVue v2.0.0.3,Crystalvue Medical Corporation,Taoyuan,Taiwan,China) was used to take digital images of each eye.The DR disease severity level was graded based on observations on dilated ophthalmoscopy by two ophthalmologists according to the International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy Disease Severity Scales (Table 1).If the grading given by the two ophthalmologists differed,consensus was achieved during a meeting of both ophthalmologists and a retinal specialist(Dong L).
Our study has several of the limitations of retrospective studies.It was single-center,with a very small sample size.We did not have the follow-up data for the prognosis of patients.However,this was an exploratory study.We believe that these data provide valuable information to support the of independent DR grading standards in FFA.Further longitudinal studies with a larger sample size are needed to confirm our results.
In conclusion,we performed extensive comparisons between the characteristics of patients with early DR obtained by using FFA and fundus photography classification.FFA identified more lesions than fundus photography.However,some aspects of FFA such as IRMAs require a new definition standard.Therefore,this study proposes that different inspection methods should have different DR classification standards that are effective and accurate.This would further improve the diagnosis and treatment of early DR in DM patients.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to give a special thanks to all the participants of this study.
Conceptualization,Li XY and Dong L;Data curation,Dong L;Funding acquisition,Zhang H;Investigation,Dong L;Methodology,Li XY;Project administration,Li XY;Resources,Dong L and Wang S;Software,Li XY;Supervision,Zhang H;Validation,Zhang H;Writing-original draft,Li XY;Writing-review and editing,Dong L;Revising,Li XY,Wang S.
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.U20A20363;No.81 970776;No.81671844);Special Fund of the Academy of Medical Sciences of Heilongjiang Province for Scientific Research(No.CR201809);Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province,China (No.LH2020H039);Higher Education Reform Project of Heilongjiang Province,China (No.SJGY20180332);Heilongjiang Provincial Postdoctoral Research Fund (No.LBH-Z18221).
None;None;None;None.
 International Journal of Ophthalmology2022年2期
International Journal of Ophthalmology2022年2期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- IJO/IES Event Photos
- Inhibitory effect on subretinaI fibrosis by anti-pIacentaI growth factor treatment in a Iaser-induced choroidaI neovascuIarization modeI in mice
- Artesunate inhibits proIiferation and migration of RPE ceIIs and TGF-β2 mediated epitheIiaI mesenchymaI transition by suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway
- NoveI mutations in the BEST1 gene cause distinct retinopathies in two Chinese famiIies
- Frequency cumuIative effect of subthreshoId energy Iaser-activated remote phosphors irradiation on visuaI function in guinea pigs
- One-step thermokeratopIasty for pain aIIeviating and pretreatment of severe acute corneaI hydrops in keratoconus
