The effect of scaffolding instruction on learning among nursing students in China:a meta-analysis
Sha-Sha Jia,Yan-Yuan Lei,Chang Li,Xiang-Shu Cui*
1School of Nursing,Yanbian University,Yanji 133000,China.
Abstract Objective: To systematically evaluate the influence of scaffolding instruction on the learning effect of nursing students in China. Methods: Through the databases of CNKI,Wanfang, VIP, CBM, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase and Web of Science, the randomized controlled trials of scaffolding instruction in nursing field were collected from the establishment of the databases to the publication in March 2022. After literature screening, data extraction and quality evaluation, meta‐analysis was performed using RevMan5.3 and Stata16.0 software.Results:Nineteen articles were included,with a total of 2,340 nursing students. Meta‐analysis results showed that, compared with the traditional teaching method, the scaffolding instruction was significantly better in nursing students’theoretical examination scores (SMD = 1.37, 95% CI: 1.00 to 1.75, P <0.001), operation skill scores(SMD=1.83,95%CI:1.23 to 2.42,P <0.001),communication ability(SMD=1.51,95% CI: 0.70 to 2.32, P = 0.0003) and teaching satisfaction (P <0.05).Conclusion:Scaffolding instruction can improve the theoretical and operational scores of nursing students, and it also has a positive impact on communication ability and teaching satisfaction. This teaching method deserves to be applied and promoted in the field of nursing education.
Keywords:scaffolding instruction;Chinese nursing students;learning effect; meta‐analysis
Background
Scaffolding as a basic teaching concept and teaching strategy was first proposed by Bruner,a famous American educator and psychologist,in 1976 [1]. It is a constructivist teaching model based on the "nearest developmental zone" theory, which is now popular worldwide [2].The term "scaffolding" originally described the shelves used by construction workers to move and stack materials that would eventually be removed, but is now used as a metaphor for the framework that supports students in problem solving [3]. It emphasizes exploration learning under the guidance of the teacher,who decomposes complex learning tasks in advance, builds scaffolds for students by doing a lot of modeling and paving,and then gradually transfers the task of learning exploration to students, who must gradually disappear when they show a sense of responsibility for learning and develop their full potential [4, 5], so that they can reach independent learning and finally complete the construction of knowledge [6].
In foreign countries, scaffolding is widely used in nursing teaching.Maria scaffolds the 14 golden rules in nurse training, and the training guides nurses to explore and learn nursing knowledge and skills [7].Donna proposes that in scaffolded nursing training, the teacher‐student relationship is divided into 3 stages: imitation,collaboration, and support. Good student‐teacher interaction helps students overcome learning difficulties, and through student‐teacher interaction also allows the instructor to better understand the students' situation and to better teach. In this new teaching mode,through collaborative learning, it can promote communication among students,stimulate their learning motivation,enhance teacher‐student relationship, and promote the progress of teachers and students together [8].
In the 1990s, Professor He and others introduced scaffolded teaching in China. In recent years, scaffolded teaching has attracted more and more attention from scholars in China. Scaffolded teaching has been widely used in English, language and other subjects,and has achieved remarkable results. In nursing teaching, Zhou has reformed the teaching method of Infectious Disease Nursing based on the theory and method related to scaffolding teaching, which has enhanced students' interest and enthusiasm in independent learning [9]. Li Ling introduced scaffolding into health assessment teaching and compared it with the traditional teaching model,concluding that scaffolding can effectively improve students' operational level and resilience [10]. By constructing a scaffolding model for use in the first aid training of clinical nursing teachers, Dong Li has improved the teachers' personal first aid ability and first aid teaching ability [11].
Although scaffolding in China has been widely used in all areas of education, it is still relatively little used in nursing disciplines [12].There is no unified and clear conclusion on the teaching effectiveness of scaffolded teaching among nursing students in China,and there is a lack of quantitative and comprehensive studies to evaluate the teaching effectiveness of scaffolded teaching. Therefore, this study systematically evaluates the effect of scaffolded teaching on nursing students' learning outcomes through meta‐analysis method, and provides an evidence‐based basis for promoting the application of scaffolded teaching in nursing teaching.
Materials and methods
Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria. According to the PICOS principle of system evaluation, the inclusion criteria of articles were formulated. (1) P:Chinese full‐time nursing students, age, gender, and educational background were not limited. (2) I: Scaffolding instruction was adopted. (3) C: Traditional teaching model was adopted. (4) O:theoretical examination scores, operation skill scores, communication ability and teaching satisfaction. (5) S: studies needed to be randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that conducted in China.
Exclusion criteria. (1) Literatures for which the full text and data extraction cannot be obtained. (2) Summary of the meeting. (3) The statistical method is wrong and the intervention measures are unclear.(4) Literature review and systematic review.
Literature search strategy
The computer searches CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, CBM, PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Embase databases, and the time is set for the establishment of the database to March 2022. The keywords "护生OR 护理专业学生OR 护理教育OR 护理教学OR 护理,支架式教学OR 教学支架OR 维果斯基支架式OR 支架式教学法,随机对照试验OR 随机对照OR RCT OR 随机OR 随机对照实验OR 随机对照研究" combined with synonyms were searched in Chinese. The search was conducted in English using the subject term "Students,Nursing OR Education, Nursing OR Nursing Teaching OR Nursing,Scaffolding Instruction OR Scaffolding teaching OR Scaffolding theory OR Vygotsky Scaffolding Instruction,Randomized Controlled Trial OR Clinical Trials, Randomized OR Randomized OR Trials, Randomized Clinical OR Controlled Clinical Trials,Randomized OR RCT"combined with free words. The search language was not restricted, while in the included literature, its references were tracked and expanded to avoid omissions in order to obtain relevant literature not found.
Literature screening and data extraction
According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the two researchers independently screened the literature. After excluding the literature that was irrelevant to the theme and did not meet the inclusion criteria, the remaining literatures that might be included were read and screened in full, and then crosschecked the literature. If there is disagreement, the final literature will be determined by a third‐party researcher through discussion or arbitration.The two researchers used a pre‐designed data extraction table to extract data independently from the included literature. The extracted contents include: first author's name, publication year, teaching location, sample size,intervention measures,and outcome indicators.
Literature quality evaluation
The quality assessment of the included literature was conducted independently by two researchers, according the Cochrane Handbook(5.1.0) quality evaluation criteria. “Low‐risk bias”, “Unclear” and“High‐risk bias” were used to indicate the degree of bias risk. In case of uncertainty, a third researcher was invited to discuss it together.Quality grade A indicated that the included study's bias was low risk and all met the above criteria;quality grade B indicated the possibility of bias in the included study and partially met the above criteria;quality grade C indicated a high risk of bias in the study which can be eliminated.
Statistical analysis
RevMan5.3 software was used for meta‐analysis of data,and Stata16.0 software was used for publication bias detection and sensitivity analysis. The included studies were expressed as 95% confidence interval (CI), and inter‐study heterogeneity was determined by chi‐square test (α = 0. 05). IfP≥0.1 andI2<50%, there was no statistical heterogeneity, and the fix effect model was used for analysis. IfP<0.1 andI2≥50%, there was clinical homogeneity,then the random effect model was used for analysis, and the subgroup analysis was conducted to find the source of possible heterogeneity.In this study,only measurement data were involved, and weighted mean difference (WMD) or standardized mean difference (SMD) was used for analysis. The potential publication bias was analyzed using funnel plots, and the results were further analyzed using Begg's test and Egger's test, and a sensitivity analysis was performed using a study‐by‐study exclusion method to explore the effect of the included individual studies on the final combined effect size.
Results
Literature retrieval results
A total of 312 articles were obtained through preliminary search, 93 repetitive articles were excluded, and 142 articles were excluded after the title and abstract were read. Among them, 77 articles were likely to be included. The full‐text reading of the included articles was conducted again, 58 articles that did not meet the criteria were excluded, and 19 articles were finally included. The specific literature screening process is shown in Figure 1.
General features of included trials
A total of 19 articles were included in the study, involving 2,073 subjects, including 1,044 subjects in the experimental group and 1,029 subjects in the control group. The research types were randomized controlled trials, and the publication years were from 2013 to 2021. Inclusion studies have clear outcome indicators.Baseline data were reported as comparable between the test and control groups. The basic characteristics of the included articles are shown in Table 1.

Figure 1 Flow diagram of study selection
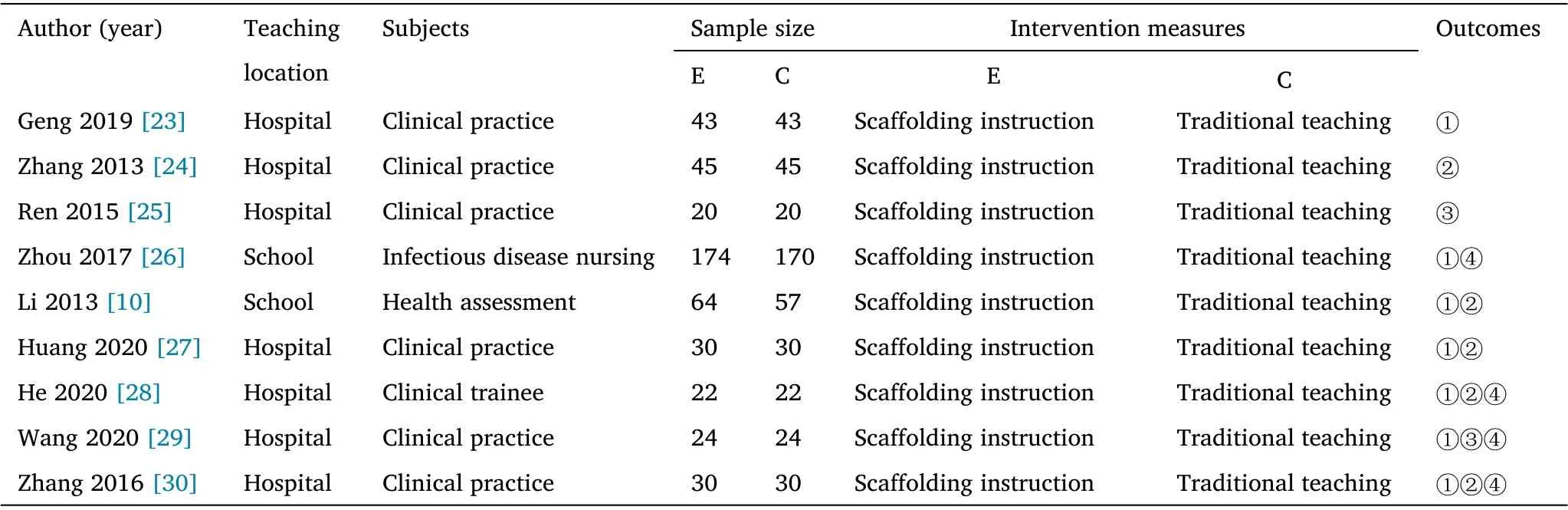
Table 1 Basic features of the included literature (Continued)
Quality evaluation of included studies
A total of 19 articles were included in this study. Three studies [13,20,24]adopted the random number table,one study[15]adopted the lottery method, two studies [23, 28] were randomly grouped according to the single and double numbers,and four articles [18, 19,21, 22] mentioned random allocation, but no specific random allocation scheme was reported, and the rest were not described in detail. All studies retained complete result data, so the probability of existence of selective reporting and other biases is considered small.The baseline data of nursing students were not compared in two of the 19 studies [19, 20], but the baseline data of nursing students were compared in the rest of the studies, which showed that the baseline data of nursing students in the experimental group and the control group were comparable (P>0.05). Only one study [29] included in the study was blinded to the subjects and implements, while none of the other studies reported or applied blinding, which might result in measurement bias. Although the outcome integrity and selective reporting of included articles were good, most studies failed to fully describe the grouping method, allocation concealment, blinding method and other risk sources, and the overall quality of the articles was low. All studies were Grade B. The specific information is shown in Table 2, and the risk of bias are summarized in Figure 2.
Meta-analysis results
Theory examination scores. Fifteen studies [10, 13, 15‐23, 26‐28,30] reported the theoretical examination scores of nursing students.There was heterogeneity between studies(I2=92%,P<0.001)and a random‐effects model was used for analysis. The result of meta‐analysis shows that the theoretical examination scores of the experimental group were higher than that of the control group (SMD=1.37,95%CI:1.00 to 1.75,Z=7.12,P<0.001,Figure 3),and the difference was statistically significant. Subgroup analysis of the 15 papers according to the teaching location showed that heterogeneity between subgroups remained large, with higher theoretical scores in the test group than in the control group in all subgroups,schools(I2=87%,P< 0.001) and hospitals (I2= 95%,P< 0.001), with statistically significant differences (P<0.05).
Operation skill scores. Nine studies [10, 13, 20‐22, 27‐30] reported the operational skill scores of nursing students. There was heterogeneity between studies (I2= 92%,P< 0.001) and a random‐effects model was used for analysis. The result of meta‐analysis shows that the operation skill scores of the experimental group were higher than that of the control group (SMD = 1.83, 95%CI: 1.23 to 2.42Z= 6.02,P<0.001, Figure 4), and the difference was statistically significant. Subgroup analysis of the 9 papers according to the teaching location showed that heterogeneity between subgroups remained large, with higher operation skill scores in the test group than in the control group in all subgroups, schools (I2=93%,P< 0.001) and hospitals (I2= 91%,P< 0.001), with statistically significant differences (P<0.05).
Communication ability. Six studies [14‐16, 24, 25, 29] reported the effect of scaffolding instruction on communication ability of nursing students, but the study of Zhang [24] did not report the total score of communication ability of nursing students, so only five studies were included for meta‐analysis. Heterogeneity between studies (I2=93%,P=0.003)was analyzed using a random effects model.The results of the meta‐analysis (SMD = 1.51, 95% CI: 0.70 to 2.32Z= 3.66,P<0.001, Figure 5) showed that the difference was statistically significant. The five articles were divided into two subgroups according to the teaching location. The analysis results in the school group [14‐16] showed great heterogeneity (I2= 93%,P<0.001),and that in the hospital group [25, 29] was (I2= 97%,P<0.001).The difference in communication ability between the experimental group and the control group in the school group was statistically significant (P<0.05), while that in the hospital group was not statistically significant (P=0.26 >0.05).
Teaching satisfaction. Eight studies [13, 16, 20, 21, 26, 28‐30]reported the evaluation of nursing students' satisfaction with scaffolding instruction. As each study mainly investigated nursing students' satisfaction evaluation on scaffolding instruction through a self‐made questionnaire, there were great differences in evaluation contents and methods. Therefore, this portion of the data was not combined quantitatively and was analyzed for descriptive purposes only. The results showed that the students in the "Scaffolding Instruction" group were more satisfied with the teaching effect,learning interests, self‐learning ability, teacher‐student interaction,problem‐solving ability,critical thinking ability,and team cooperation ability than those in the traditional teaching model group. However,in the research of Zhou [26], the students' approval for "cultivating innovative consciousness"was relatively low.
Publication bias. Since less than 10 studies included other outcome indicators, this study only tested the theoretical test scores for publication bias, the funnel plot showed the existence of publication bias, and the Egger's test was used to further test for bias. The combined effect size did not change, indicating that publication bias was not significant and the study results were relatively stable. The results are shown in Figure 6.
Sensitivity analysis.The heterogeneity test of the included literature for each outcome indicator found that there was a large heterogeneity in all studies.Sensitivity analysis of theoretical scores,skill scores,and communication skills of the included studies was performed using the piecewise exclusion method, and the results were found to have no significant changes after excluding the included literature one by one,suggesting that the results of the meta‐analysis were basically stable.
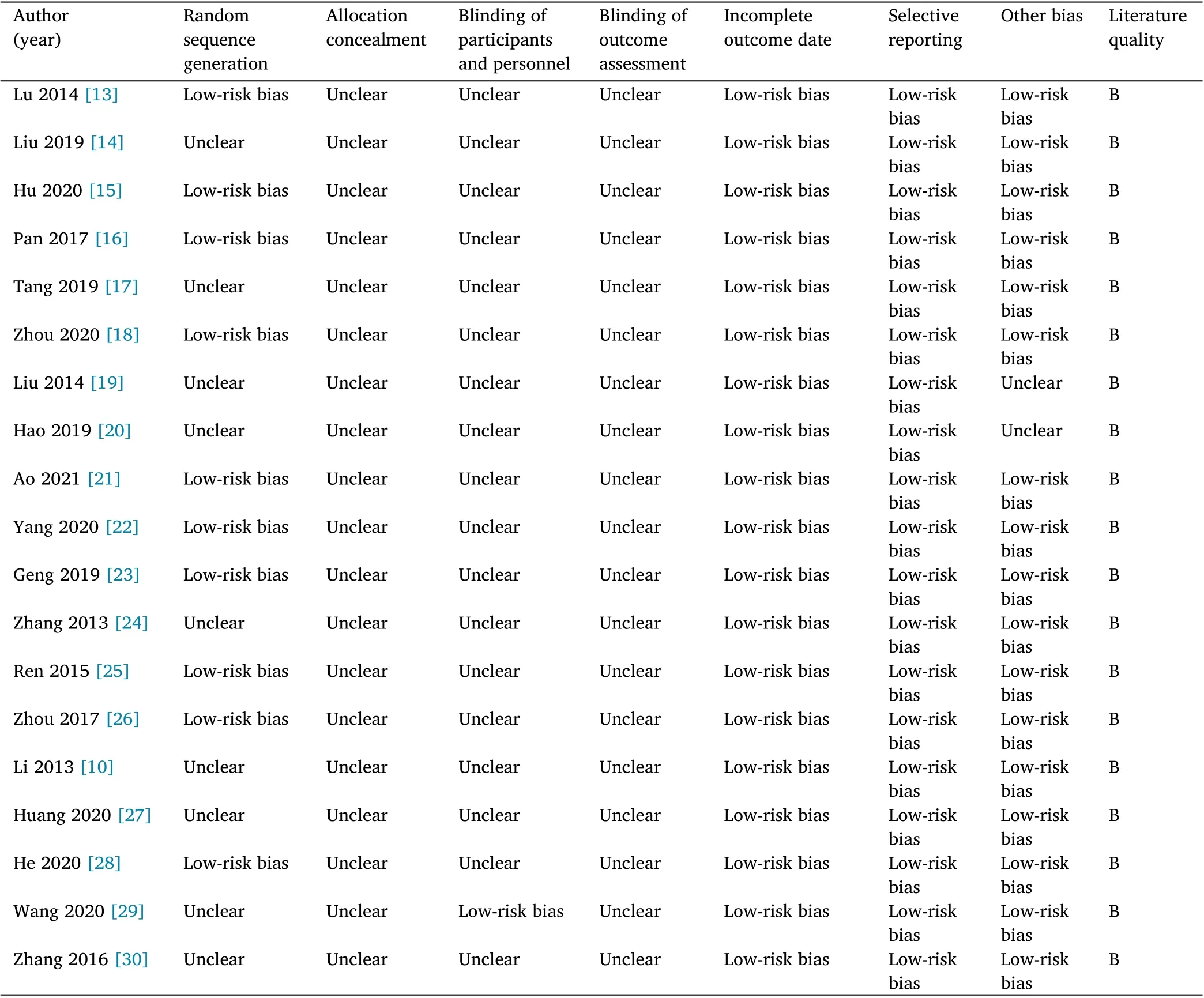
Table 2 Literature quality assessment

Figure 2 Risk of bias summary
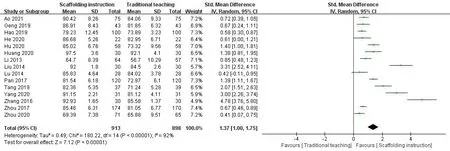
Figure 3 Forest plot of the theory examination scores

Figure 4 Forest plot of the operation skill scores
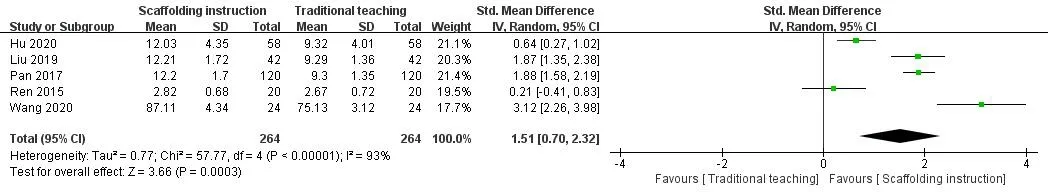
Figure 5 Forest plot of the Communication ability

Figure 6 Funnel chart of nursing students' theoretical performance
Discussion
Summary of major findings
This study found the scaffolding teaching to be conducive to nursing students' mastery of theoretical and operational knowledge, and improves students' communication ability and classroom teaching satisfaction. Therefore, the results of this study provide some theoretical support for the application of scaffolding teaching in nursing teaching in my country, and also provide a new reference model for foreign nursing education.
Meta‐analysis of 15 papers showed that the scaffolding method had positive effects on students' theoretical knowledge acquisition. In scaffolded teaching, teachers use the principle of "nearest developmental zone"to determine the"nearest developmental zone"of nursing students and set up relevant situations by building scaffolds to stimulate nursing students' desire to learn, while nursing students use the scaffolds to enhance their theoretical knowledge, The nursing students can use the scaffolding to enhance the theoretical knowledge and promote the continuous transfer of knowledge to consolidate the theoretical knowledge in the learning process [31]. Because of the high heterogeneity of the 15 papers included in the theory achievement analysis, subgroup analysis by teaching location did not reveal sources of heterogeneity, but the results of each subgroup indicated that the use of scaffolded instruction was more effective than the control group for teaching theory achievement, indicating that the results of the meta‐analysis of theory achievement were more stable and had some reference value.
The ultimate goal of nursing education is to promote the application of theoretical knowledge in clinical practice, and the results of this study showed that scaffolded instruction helped to improve the level of nursing students'operational skills compared to traditional teaching methods.This is in line with the findings of Kneusel and Tilley [7,8].For nursing students, the teachers used scaffolded teaching method to build problem scaffolds, create situations, and students explored and analyzed the problems to construct and master knowledge, and used the theoretical knowledge learned in the classroom to analyze and solve problems encountered in clinical practice, which fundamentally improved the nursing students' operational skills. The nine papers were analyzed by subgroups according to teaching location, and no source of heterogeneity was found, but the results of each subgroup indicated that the use of scaffolded instruction was more effective than the control group in teaching theoretical achievement, and the study results were more stable and had some reference value.
Communication skills are one of the core skills of nursing staff in clinical work. With the development of the nurse‐patient relationship,the clinical communication skills of nursing students have become more demanding [32]. Meta‐analysis results of five papers showed that scaffolded teaching had a positive effect on improving students'communication skills. In teaching, scaffolding inspired nursing students to think positively and to engage in discussions based on oral training of experiencing others' emotions, which honed their verbal skills. At the same time, the teacher's supportive role encouraged students who lacked confidence and were inexpressive to speak,giving each student the opportunity to express themselves and stimulating them to express their own thoughts, which is consistent with Sharon's view [33]. However, Zhang [24] found that scaffolded teaching was not effective in conveying effective information, one of the student communication skills. The reason for this may be that nursing students communicate with patients in conveying information mainly by paying attention to the tone of voice in choosing appropriate language to communicate with patients, which can be obtained in regular teaching, so scaffolded teaching is not effective in conveying effective information in communication.The 5 papers were divided into 2 subgroups according to the teaching location, and the results of the study showed that the school group had a better intervention effect on communication skills using scaffolded teaching than the control group,while the hospital group had a non‐significant intervention effect on nursing students' communication skills. The possible reasons for this are that nursing students have heavy tasks during their internship, more complicated departmental tasks, and later in their internship they are busy with matters such as thesis work and less communication with patients, and their ability is not significantly improved. Thus, it can be seen that the effect of using scaffolded teaching on nursing students' communication skills is not conclusive, and more high‐quality studies need to be conducted for verification in the future.
We found that there are certain shortcomings in the current evaluation of nursing students' satisfaction with scaffolded teaching.Since the satisfaction of nursing students with scaffolded teaching was mainly evaluated by the researcher's self‐administered questionnaire among the studies, the evaluation contents and methods were quite different, and there was no consistent and unified evaluation method about the quantitative evaluation of satisfaction, and most of them were qualitative and subjective, and the evaluation mode was single,which made it impossible to quantitatively synthesize the results for meta‐analysis. The possible reason is that there is no teaching satisfaction evaluation tool with good reliability and validity at home and abroad, and future nursing educators can further explore the construction of a teaching satisfaction evaluation index system with good reliability and validity, so that the evaluation results are comparable and referential among studies.
Limitations of this study
There may be some limitations in the included studies. First, all included studies had low methodological quality, such as inaccurate randomization methods, allocation concealment, and blinding. This can lead to selection bias and detection bias. Second, there is no standard measurement tool for assessing the effectiveness of scaffolding, potentially leading to measurement bias. Third, the sample size of some included studies is small, which may affect the intervention effect. Finally, the time and frequency of interventions among the included studies are inconsistent,the content of the courses taught, the nature and difficulty of the courses, the grades of nursing students, and the level of teachers are different, which lead to significant heterogeneity.
Conclusion
We found many advantages of scaffolded teaching compared to traditional teaching methods, which can improve nursing students'theoretical performance,operational performance,and have a positive effect in terms of communication skills and teaching satisfaction.However, there are also problems that need further improvement.Since students have different levels and learning preferences, teachers cannot prepare scaffolds for all students with different learning styles when building scaffolds, and cannot guarantee that different types of students all respond well to the scaffolds and the teaching effect does not reach expectations, so we suggest that the gap between member groups should not be too wide to avoid the psychological withdrawal and cope with the discussion. Although the scaffolded education model has been widely used in China, its use in nursing is still relatively small. It is expected that more high‐quality, large‐sample randomized controlled studies will be conducted in the future to enhance the strength of the argument, so as to obtain more rigorous results and provide a more reliable basis for the application of scaffolded teaching in the field of nursing education.
 Nursing Communications2022年13期
Nursing Communications2022年13期
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Nurses’ knowledge and skills concerning cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a descriptive study
- Surgical operation of a massive retroperitoneal tumor
- Progress in the application of Meleis transition theory in the nursing field
- Importance of teamwork communication in nursing practice
- From the perspective of traditional Chinese medicine nursing in the context of COVID-19
- Surgical first aid and nursing care of a parturient with massive hemorrhage in natural delivery
