Redefining the concept of professionalism in nursing: an integrative review
Azdeh Azemin, Abbs Ebdi, Leil Afshr*
aDepartment of Medical Education, Virtual School of Medical Education and Management, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
bBehavioral Sciences Research Center, Life Style Institute, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
cFaculty of Nursing, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Science, Tehran, Iran
dDepartment of Medical Ethics, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences,Tehran, Iran
Abstract: Objective: In today’s world with sweeping changes, nurses are responsible for providing high-quality and cost-benefit care, which would almost be impossible unless they achieve their high professional status. To date, no precise and comprehensive definition of professionalism in nursing has been evidently proposed. In fact, many of the previously proposed definitions are either complicated or ambiguous. Moreover, there is no consensus in the literature on an exhaustive definition for “a professional nurse.” The present study aimed to illustrate the concept of professionalism in nursing and identify its defining characteristics.
Keywords: Nursing • Professionalism • Professional prerequisite • Individual prerequisite • Appropriate structure • Socio-individual factors
1. Introduction
Numerous attempts have been made to define nursing professionalism (NP). In fact, although it might seem easy to propose a clear definition, offering a comprehensive one has been very difficult. In fact, several researchers of different disciplines have provided many definitions for professionalism.
Flexner (1910) described professionals as individuals with a specific career, knowledge beyond their basic education, and high levels of intellectual performance,responsibility, scientific and specialized knowledge,a desire to learn and expand their education and knowledge, self-governance, and altruism.1,2Freidson (1983,2001) and Hall (1982), two prominent sociologists, maintained that professionalism and its features might be differently defined and described in different professions.3,4According to Merriam-Webster Dictionary (11th ed.),professionalism is “the skill, good judgment, and polite behavior that is expected from a person who is trained to do a job well.” This definition is slightly different from those provided by researchers who consider professionalism as “having a unique or special knowledge.”5,6
In the health care system, nurses are the largest group of health care providers with numerous pivotal roles and the highest number of contacts with patients.Thus, due to the multiplicity and complexity of nurses’roles, nursing is viewed as aprofessionalactivity requiring enormous responsibility and considerable attention and vigilance.7
In today’s rapidly changing world, nurses are responsible for providing health care for patients, which requires up-to-date knowledge and expertise, professional performance, essential management skills, and the ability to provide safe and appropriate legal and ethical services.8Therefore, as in many other fields, achieving a professional status is an important goal in nursing.
Although international associations have consistently emphasized the importance of professionalism as one of the most significant foundations of nursing practice, it has largely been neglected in research.9,10According to the Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario, the professional standard provides a guide to the “knowledge,spirit of inquiry, accountability, autonomy, advocacy,innovation and visionary, collaboration and collegiality,and ethics” that are needed to practice safely.11
Miller developed a model called “Wheel of Professionalism in Nursing” in which the center of the wheel symbolizes education at university and scientific nursing background. The spokes indicate eight other defining characteristics: (1) research development, use, and evaluation; (2) publication and communication; (3) participation in professional organizations; (4) competence and continuing education; (5) theory development, use,and evaluation; (6) community service orientation; (7)self-regulation and autonomy, and (8) adherence to the American National Association (ANA) Code of Ethics.12
Although various definitions for professionalism have been proposed, many of them are either complex or ambiguous. So, we can say that there is no consensus on what professionalism means in nursing.9In Ottawa International Conference, Hodges et al. (2010)recommended defining and explaining the components of professional behavior in various disciplines of medical sciences and comparing them with medical definitions. They maintained that professional behavior is a significant issue in the medical sciences, which has recently become a major source of concern in medical education. Nevertheless, it is not easy to define the components of professionalism and evaluate them.13
Furthermore, in recent years, nursing in Iran and some other countries has been criticized for the poor quality of care.14–20And the increase in nursing errors has led to direct and indirect complications in patients.21,22But adhering to professional behavior can reduce professional errors and increase the quality of patient care.23,24
Several researchers have emphasized that the culture-bound nature of professionalism requires specialized knowledge in different professions.4,25Therefore, the current study examined various definitions and characteristics of professionalism through the integrated review, which is an important method for concept analysis. According to Whittemore et al., this method permits the contemporary insertion of various methods to attain a better perception of a phenomenon.26The current study is aimed to explore the concept of professionalism and its characteristics in nursing.
2. Methods
In this study, concept analysis was carried out using integrative review proposed by Whittemore R et al.This method allows combining diverse methodologies and can potentially play a more important role in evidence-based practices for nursing.26The integrated review consists of diverse perspectives on a significant phenomenon in nursing science and nursing practice.26This method consists of a five-step process, which significantly enhances its credibility.
2.1. Problem identification
First, a clear definition of the given subject and the purpose of the study are explained.26The present study aimed to redefine the concept of professionalism in nursing, which is the first step for developing a diagnostic framework. Three questions are designed to guide the study:
• What is the definition of NP in literature?
• What are the attributes of professionalism in nursing?
• Which factors influence the development of professionalism in nursing?
2.2. Literature review
To find related articles and sources on professionalism, a comprehensive search was performed in several electronic, scientific databases including Eric, PubMed,Scopus, Web of Science, EBSCO, PsychoINFO,Embass, MagIran, IranDoc, SID, and IRANMEDEX.Seven keywords namelyprofessionalism,professional behavior,NP,professional attribute,nursing, nurse,and nurseswere searched among articles written in both English and Persian until 2019. All of the retrieved articles were entered in Endnote X8. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses(PRISMA) statement and guidelines recommended by Moher D et al. were used in the review process to reduce potential errors.27
2.3. Data evaluation
The articles were reviewed based on the following criteria:
• Language (English & Persian)
• Full-text availability
• Articles with qualitative, quantitative, and mixedmethod designs as well as review papers
• Peer-reviewed journals
• Articles offering insights on different definitions and dimensions of professionalism in medical sciences and nursing as well as guidelines for its assessment
The quality of the articles with qualitative designs was assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP 2014) by paying special attention to the purpose, methodology, design, strategy, data collection,data analysis, reflexivity, ethical considerations, findings, and study value. The studies were divided into three main categories: high quality, medium quality, and low quality.28
As to quantitative articles, Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE)was used to evaluate the quality of the articles.29Finally,the quality of systematic review articles was measured by PRISMA software.30
To increase the reliability of the findings, two other authors cross-checked the papers and the corresponding persons completed appraisal forms.
2.4. Data analysis and validation
The content analysis and classification approach were used to examine the data obtained from various studies. Finally, the papers were classified based on their main themes and categories. Data validation was carried out according to the integrative review stages proposed by Whittemore et al. Further, to achieve and confirm the reliability, an expert, external observer in qualitative researches was used so that the data collection and analysis processes would be investigated.All the research stages, including the initial intention of the study, the search for studies, the analyzed data,the study findings, the extracted meanings, the codes,the themes classifications, and the details of the study process were given to two external observers who were requested to review the reports and report their results.
3. Results
The present comprehensive search initially yielded 5738 articles. After removing the duplicate articles, 2837 were selected for further investigation. Based on the primary screening of the titles and abstracts, 1517 articles were excluded. In addition, 137 articles lacking scientific rigor were excluded. Finally, 52 papers remained and were selected for analysis as shown in Figure 1.
3.1. Characteristics of the articles included
The articles entered in this paper are summarized in Table 1.
The meticulous analysis of the papers led to the extraction of four major themes, which are as follows:
Theme 1: Individual prerequisite
Personal characteristics:Personal characteristics such as self-confidence,34,36,38,48,69,71,72innovation and acuity,59self-image,38and emotional intelligence40were found to play a significant role in shaping professionalism.
Self-directed personality:Several studies placed emphasis on self-control and selfregulation,2,7,10,12,32,37,40,46,53,54,59,63,72–74lifelong learning,7,37,72and reflection11,12,40, which are major factors affecting professionalism and its development. In addition, others acknowledged the importance of technical up-todate knowledge11,37,73as well as the ability to manage conflicts40and balance professional and private life.48
Theme 2: Professional prerequisite
Professional expertise:Several studies highlighted the significance of academic knowledge and specialized skills as an essential requirement for the nursing profession.2,7,8,32,34,36,37,53,69,72,73
Professional communication:The retrieved studies reflected the importance of the relationship between nurses and patients in NP, emphasizing the undeniable role of effective interactions and interpersonal communication in the workplace.59In fact, nurses who established and maintained good communication with patients and members of the health care team reported higher levels of professionalism.

Figure 1. PRISMA diagram. PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
Professional ethics and human values:Literature underscores the importance of ethics in professionalism.7Some inherent personal values for nurses include altruism, commitment to compassion, caring, and honesty.One of the fundamental values of professional nursing practice is advocacy that requires nurses to empower patients to make informed choices by supporting their rights, values, and beliefs and by maintaining confidentiality.4,48,54,72In addition, prioritizing patients’ preferences and independence as well as promoting social justice have been identified as basic principles for professionalism.7,31,59
Professional and social responsibility: Nursing is a health-related profession and should be responsible for the health care needs of society.43,54Nurses should devote considerable effort to provide high-quality care for earning and fostering society’s trust.7,8,25
Professional commitment: Professionalism has also been considered as having a sense of belonging to the profession.7,45In fact, nurses are responsible for their own professional development and sharing of knowledge with their colleagues.12,25,43
Theme 3: Appropriate structure
Appropriate educational structure: It is very essential to pay special attention to the role of the educational curriculum in the development of the nursing profession. In fact, the educational curriculum should promote awareness about professionalism among nursing students.Moreover, nurses should have a mentor as their role model and exhibit professional behavior while caring for the patients. Furthermore, nurses should generally rely on their applied education based on philosophy, theory,and knowledge, and their actual experiences.7,34,36,69
Appropriate organizational structure: Appropriate organizational culture and structure to support NP areof utmost importance. On the other hand, factors such as the hierarchical structures of the hospitals, intense workload, requirement system failure, and inadequacy of the personnel and equipment could negatively influence NP.38,55,59,60,63,72
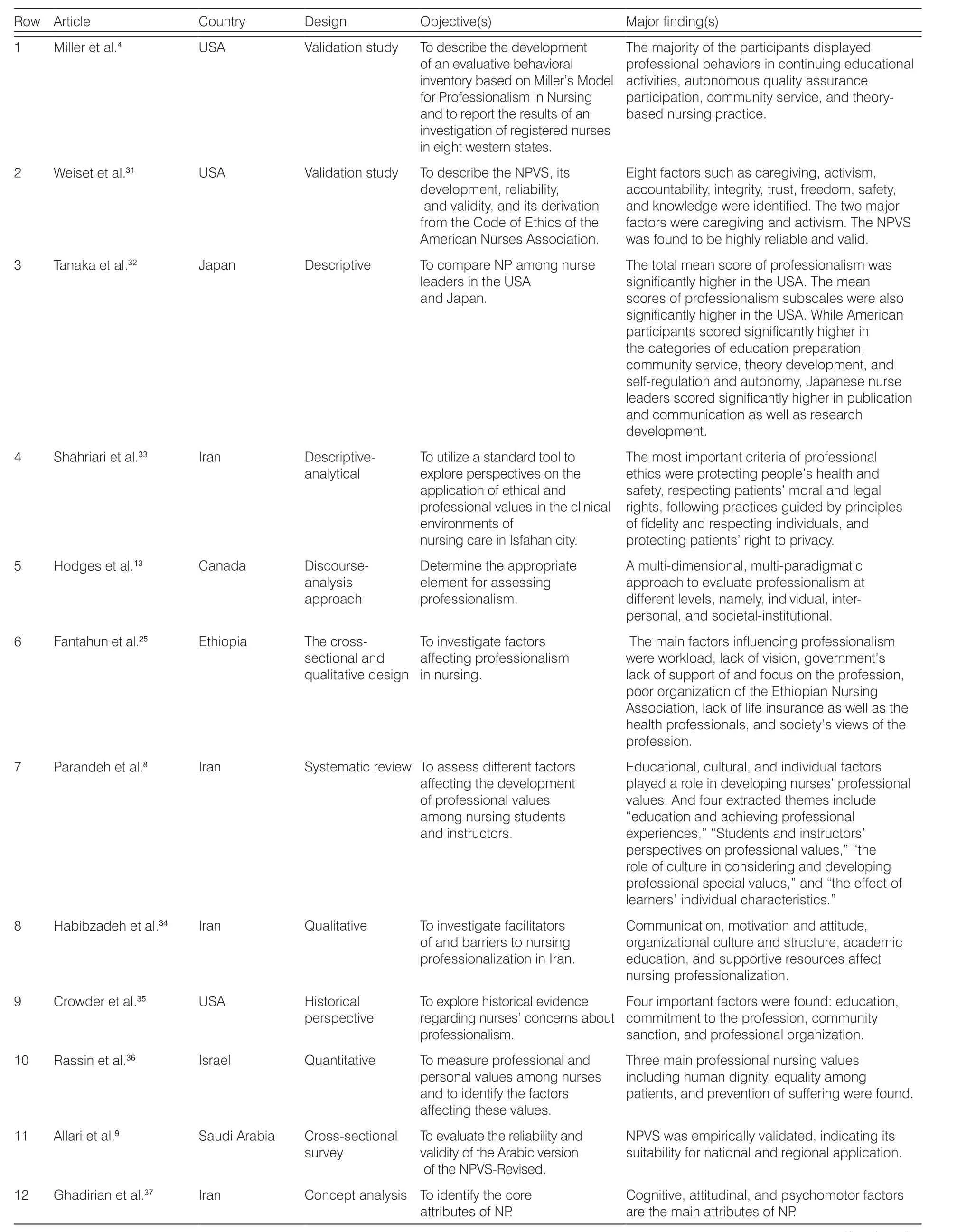
Row ArticleCountryDesignObjective(s)Major finding(s)1Miller et al.4USAValidation studyTo describe the development of an evaluative behavioral inventory based on Miller’s Model for Professionalism in Nursing and to report the results of an investigation of registered nurses in eight western states.The majority of the participants displayed professional behaviors in continuing educational activities, autonomous quality assurance participation, community service, and theorybased nursing practice.2Weiset et al.31USAValidation studyTo describe the NPVS, its development, reliability,and validity, and its derivation from the Code of Ethics of the American Nurses Association.Eight factors such as caregiving, activism,accountability, integrity, trust, freedom, safety,and knowledge were identified. The two major factors were caregiving and activism. The NPVS was found to be highly reliable and valid.3Tanaka et al.32JapanDescriptiveTo compare NP among nurse leaders in the USA and Japan.The total mean score of professionalism was significantly higher in the USA. The mean scores of professionalism subscales were also significantly higher in the USA. While American participants scored significantly higher in the categories of education preparation,community service, theory development, and self-regulation and autonomy, Japanese nurse leaders scored significantly higher in publication and communication as well as research development.4Shahriari et al.33IranDescriptiveanalytical To utilize a standard tool to explore perspectives on the application of ethical and professional values in the clinical environments of nursing care in Isfahan city.The most important criteria of professional ethics were protecting people’s health and safety, respecting patients’ moral and legal rights, following practices guided by principles of fidelity and respecting individuals, and protecting patients’ right to privacy.5Hodges et al.13CanadaDiscourseanalysis approach 6Fantahun et al.25EthiopiaThe crosssectional and qualitative design Determine the appropriate element for assessing professionalism.To investigate factors affecting professionalism in nursing.A multi-dimensional, multi-paradigmatic approach to evaluate professionalism at different levels, namely, individual, interpersonal, and societal-institutional.The main factors influencing professionalism were workload, lack of vision, government’s lack of support of and focus on the profession,poor organization of the Ethiopian Nursing Association, lack of life insurance as well as the health professionals, and society’s views of the profession.7Parandeh et al.8IranSystematic review To assess different factors affecting the development of professional values among nursing students and instructors.Educational, cultural, and individual factors played a role in developing nurses’ professional values. And four extracted themes include“education and achieving professional experiences,” “Students and instructors’perspectives on professional values,” “the role of culture in considering and developing professional special values,” and “the effect of learners’ individual characteristics.”8Habibzadeh et al.34IranQualitativeTo investigate facilitators of and barriers to nursing professionalization in Iran.Communication, motivation and attitude,organizational culture and structure, academic education, and supportive resources affect nursing professionalization.9Crowder et al.35USAHistorical perspective To explore historical evidence regarding nurses’ concerns about professionalism.Four important factors were found: education,commitment to the profession, community sanction, and professional organization.10Rassin et al.36IsraelQuantitativeTo measure professional and personal values among nurses and to identify the factors affecting these values.Three main professional nursing values including human dignity, equality among patients, and prevention of suffering were found.11Allari et al.9Saudi ArabiaCross-sectional survey To evaluate the reliability and validity of the Arabic version of the NPVS-Revised.NPVS was empirically validated, indicating its suitability for national and regional application.12Ghadirian et al.37IranConcept analysis To identify the core attributes of NP.Cognitive, attitudinal, and psychomotor factors are the main attributes of NP.
(Continued)

Row ArticleCountryDesignObjective(s)Major finding(s)13Primm et al.38USADescriptiveTo describe eight as pects of NP.Nurses can use the wheel of professionalism to iden tify their behaviors and set goals for change or improve their professionalism in practice.14Hershberger et al.39 USASurveyTo examine self-control as a component of resident professionalism through exploring residents’ and their program directors’ views.There was no correlation between residents’self-reported professionalism and their program directors’ ratings, indicating the difficulty in understanding and measuring this competency.15Ali Dehghani et al.7IranConcept analysis To clarify and reduce the semantic ambiguities related to the concept of professionalism.NP comprises three main factors: principles of care, communication, and ethics. NP can positively affect nurses, the nursing profession,and the health care system.16College of Nurses of Ontario11 Guidelines on the knowledge, skills, judgment,and attitudes necessary for safe practices were suggested.17Finnbakk et al.SwedenCross-sectional survey CanadaGuidelines for nursing standards To provide guidelines for professional standards.To examine the reliability and construct validity of the new Professional Nurse Self-Assessment Scale(ProffNurse SAS) in Norway.The instrument has acceptable reliability and construct validity, and can be used for assessing practicing nurses’ clinical competence.18Lesser et al.40USAReviewTo provide a practical approach for physicians and the organizations in which they work.19Wilkinson et al.12New ZealandLiterature review To match assessment tools to definable elements of professionalism and to identify gaps where professionalism elements are not well-addressed by existing assessment tools.Professional behaviors could be affected by the organizational and environmental context of contemporary medical practice.These external factors should be controlled to foster professionalism in practice, providing opportunities to improve health care services via reforms in education and the whole system.Professionalism consists of the following elements: adherence to ethical practice principles, effective interactions with patients and with people who are important to them,effective interactions with people working within the health system, reliability, and commitment to autonomous maintenance/improvement of competence in oneself, others, and systems.Several assessment tools were identified:observed clinical encounters collated views of coworkers, records of incidents of unprofessionalism, critical incident reports,simulations, paper-based tests, patients’opinions, global views of the supervisor, and self-administered rating scales.20Fisher41USADescriptiveTo compare the development of professionalism in pre-licensure nursing students in associate degree, diploma, and BA programs.The amount of time spent in nursing programs does not affect professionalism. Educators should use strategies to foster these values.The quantity and quality of pre-licensure education should be re-evaluated. Personal and professional values should be integrated into the ethical standards of the nursing profession while students advance along the continuum of professionalism.21Li et al.42ChinaSystematic search To systematically evaluate the psychometric properties of NP instruments and the methodological quality of the studies they were used in.Content validity, cross-cultural validity, and criterion-related validity were either unreported or received negative ratings in most studies.Based on the best-evidence synthesis, three instruments such as Hisser’s instrument for nursing students, nurse practitioners’ roles and competencies scale, and perceived faculty competency inventory were recommended.22Wynd2USADescriptive comparative/correlational To explore registered nurses’attitudes toward professionalism and to examine differences and relationships among degrees of professionalism, levels of education and experience,membership in professional organizations, and specialty certification in nursing.The findings indicated that professionalism was significantly associated with years of experience as a registered nurse, higher educational degrees in nursing, membership in organizations, service as an officer in the organization, and specialty certification.
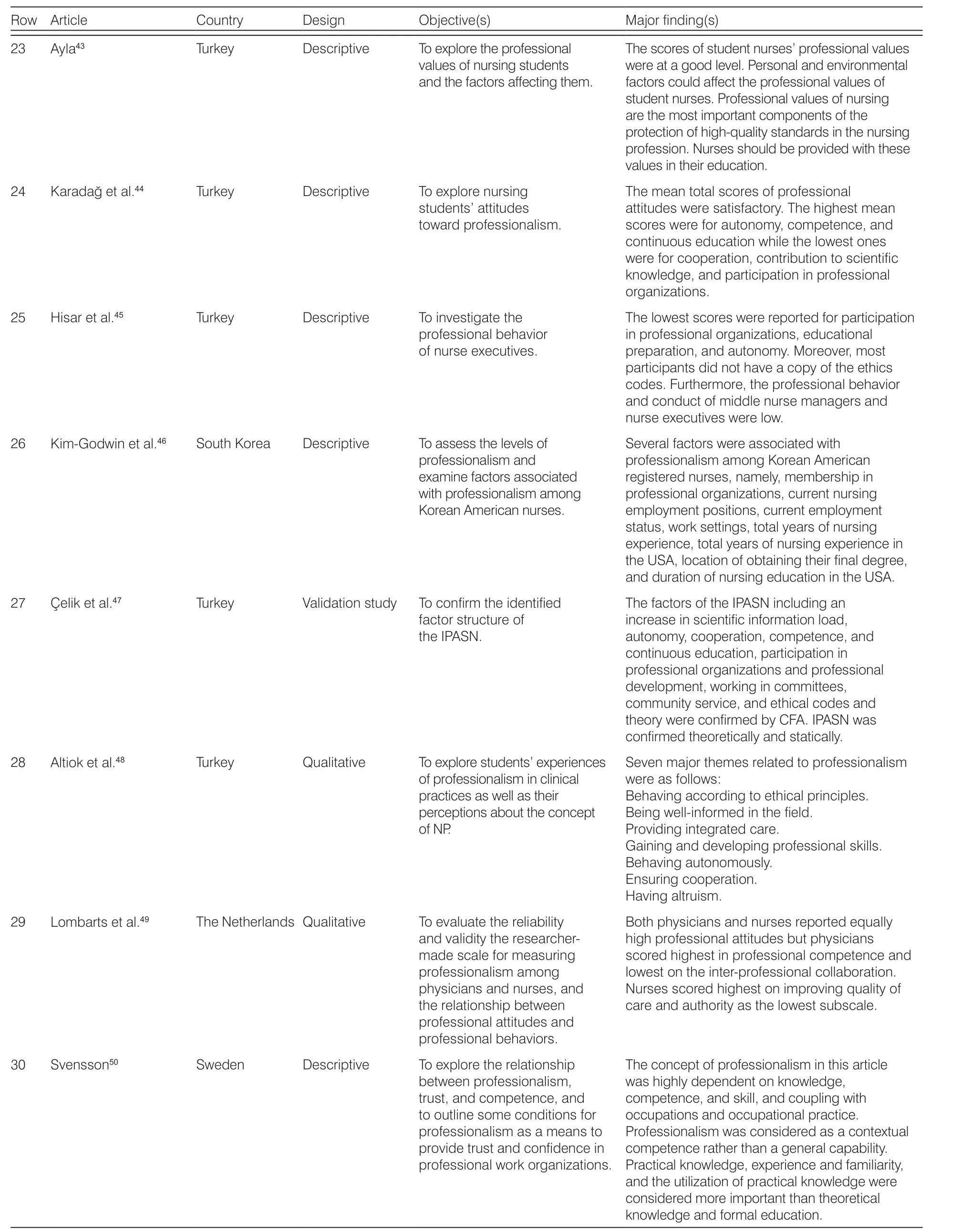
Row ArticleCountryDesignObjective(s)Major finding(s)23Ayla43TurkeyDescriptiveTo explore the professional values of nursing students and the factors affecting them.The scores of student nurses’ professional values were at a good level. Personal and environmental factors could affect the professional values of student nurses. Professional values of nursing are the most important components of the protection of high-quality standards in the nursing profession. Nurses should be provided with these values in their education.24Karadağ et al.44 TurkeyDescriptiveTo explore nursing students’ attitudes toward professionalism.25Hisar et al.45 TurkeyDescriptiveTo investigate the professional behavior of nurse executives.26Kim-Godwin et al.46South KoreaDescriptiveTo assess the levels of professionalism and examine factors associated with professionalism among Korean American nurses.27Çelik et al.47TurkeyValidation studyTo confirm the identified factor structure of the IPASN.28Altiok et al.48TurkeyQualitativeTo explore students’ experiences of professionalism in clinical practices as well as their perceptions about the concept of NP.29Lombarts et al.49The Netherlands QualitativeTo evaluate the reliability and validity the researchermade scale for measuring professionalism among physicians and nurses, and the relationship between professional attitudes and professional behaviors.The mean total scores of professional attitudes were satisfactory. The highest mean scores were for autonomy, competence, and continuous education while the lowest ones were for cooperation, contribution to scientific knowledge, and participation in professional organizations.The lowest scores were reported for participation in professional organizations, educational preparation, and autonomy. Moreover, most participants did not have a copy of the ethics codes. Furthermore, the professional behavior and conduct of middle nurse managers and nurse executives were low.Several factors were associated with professionalism among Korean American registered nurses, namely, membership in professional organizations, current nursing employment positions, current employment status, work settings, total years of nursing experience, total years of nursing experience in the USA, location of obtaining their final degree,and duration of nursing education in the USA.The factors of the IPASN including an increase in scientific information load,autonomy, cooperation, competence, and continuous education, participation in professional organizations and professional development, working in committees,community service, and ethical codes and theory were confirmed by CFA. IPASN was confirmed theoretically and statically.Seven major themes related to professionalism were as follows:Behaving according to ethical principles.Being well-informed in the field.Providing integrated care.Gaining and developing professional skills.Behaving autonomously.Ensuring cooperation.Having altruism.Both physicians and nurses reported equally high professional attitudes but physicians scored highest in professional competence and lowest on the inter-professional collaboration.Nurses scored highest on improving quality of care and authority as the lowest subscale.30Svensson50SwedenDescriptiveTo explore the relationship between professionalism,trust, and competence, and to outline some conditions for professionalism as a means to provide trust and confidence in professional work organizations.The concept of professionalism in this article was highly dependent on knowledge,competence, and skill, and coupling with occupations and occupational practice.Professionalism was considered as a contextual competence rather than a general capability.Practical knowledge, experience and familiarity,and the utilization of practical knowledge were considered more important than theoretical knowledge and formal education.
(Continued)

Row ArticleCountryDesignObjective(s)Major finding(s)31Lehna et al.51USAQualitativeTo investigate the effect of current nursing attire on the image of the nursing profession.Professionalism is a total package consisting of attire, mannerisms, and a certain attitude.The sub-themes were role identification and competency.32Tanaka et al.52 JapanDescriptiveTo examine nurse managers’perceptions of professional behaviors and the contributing factors.33Rhodes53Literature review To review the related literature on professionalism, comment on professionalism in health services professions, present a model of reaction to professionalization and draw conclusions about the results of this trend.34Bragancaa54GOAQualitativeTo explore the factors influencing professionalism among nurses.The highest and lowest scores for professional behaviors were obtained in “competence and continuing education” and “publication and communication,” respectively. Higher NP was significantly related to the increased length of nursing experience, higher levels of educational preparation, and the current position as a nurse administrator.to propose a model for professionalism in the health service professions based on ten characteristics of “professionalism” that include a full-time occupation, a strong motivation or calling for the career, a specialized body of knowledge and skills acquired during a prolonged period of education and training,decision-making on behalf of the client in terms of principles, theories or propositions,service orientation, service based on the objective needs of the client and mutual trust,autonomy of judgment for performance,formation of professional associations and other professional credentials, a specific set of knowledge, not allowing professionals to seek out clients,and internal factors such as communication challenges, individual characters, and responsibility as well as external factors like educational and cultural development,organizational preconditions, and support systems affecting professional ethics in nursing practice. Findings imply that knowledge of professional ethics and the contributing factors may help nurses and other healthcare professionals to provide better patient services.35Hintistan et al.55TurkeyDescriptiveTo identify professionalism characteristics among nurses working in the internal medicine clinics of a university hospital.Nurses believed the most important characteristics were “taking individual responsibility in nursing practices” and “paying attention to using a simple and clear language by establishing a good communication with patients and team members.” The characteristics included “becoming a member of a nursing association,” and “feeling the necessity” to use the titles of a specialist nurse.36Balang et al.56TurkeyLiterature review Describing the professionalism among Malaysian nurses.Promoting and maintaining professional behavior from the individual level to the organization level. Through mandatory regulations for nurses to participate in CPD programs for the renewal of certificates, mentor and mentee programs, and the allocation of postgraduates for nurses in the health care system.37Konukbay et al.57TurkeyDescriptiveCompressive assessment of nurses’ professional behavior.The lowest scores were reported in autonomy,publishing, and professional organization educational preparation while the highest scores were obtained in continued education,use of theory, education, research, nursing codes, and social services.38Mahmoud Salem et al.58 Saudi ArabiaAnalytic crosssectional Investing the nature of the relationship between conflict and nurses’ perceptions of their professionalism.Findings show that most nurses had a low-level perception of their professionalism. Factors that were effective in the low-level perception of nurses of professionalism include the personal interest in the nursing profession and view of family, society, and consumers to the profession.
(Continued)
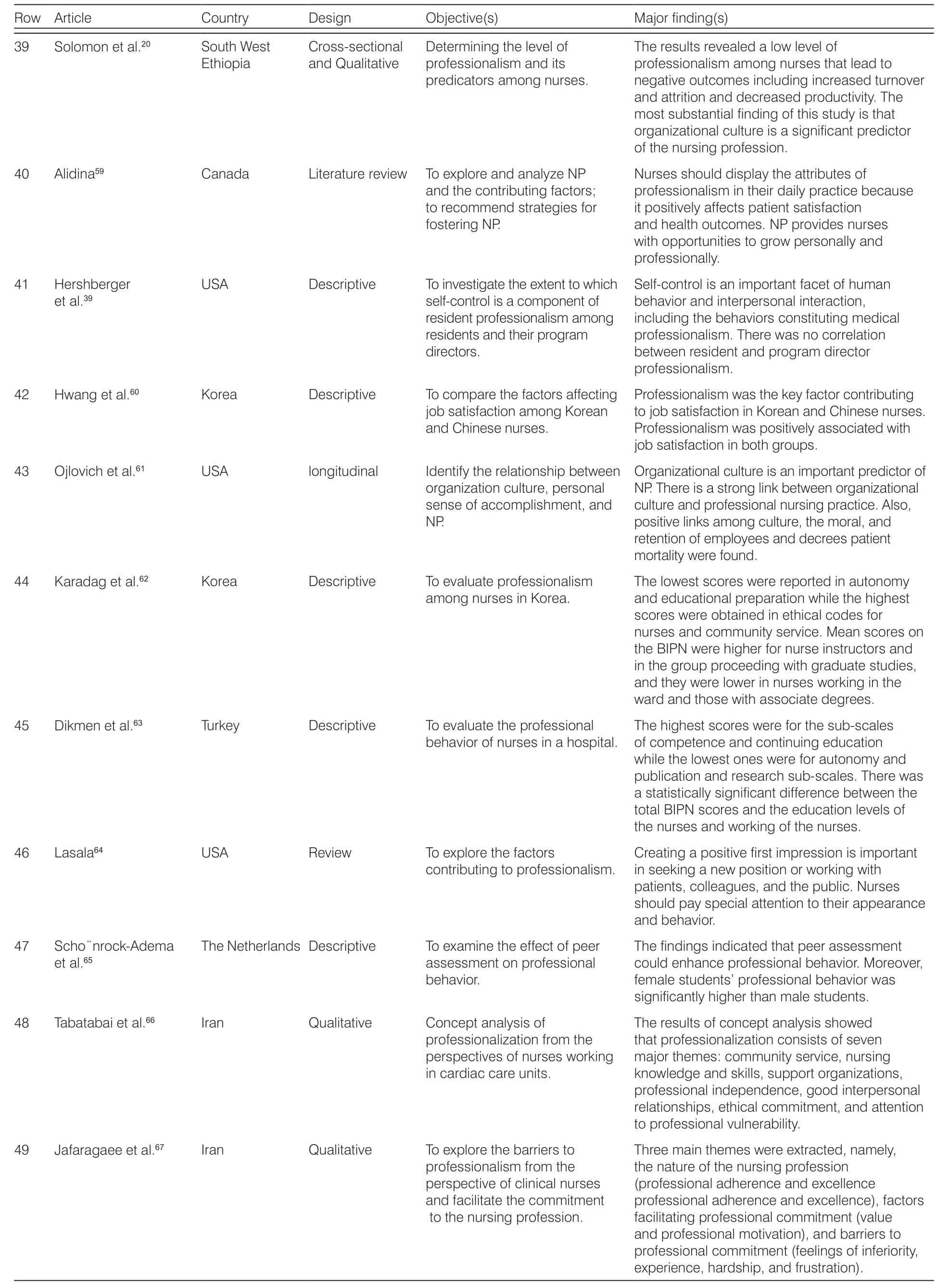
Row ArticleCountryDesignObjective(s)Major finding(s)39Solomon et al.20South West Ethiopia Cross-sectional and Qualitative Determining the level of professionalism and its predicators among nurses.The results revealed a low level of professionalism among nurses that lead to negative outcomes including increased turnover and attrition and decreased productivity. The most substantial finding of this study is that organizational culture is a significant predictor of the nursing profession.40Alidina59CanadaLiterature review To explore and analyze NP and the contributing factors;to recommend strategies for fostering NP.Nurses should display the attributes of professionalism in their daily practice because it positively affects patient satisfaction and health outcomes. NP provides nurses with opportunities to grow personally and professionally.41Hershberger et al.39 USADescriptiveTo investigate the extent to which self-control is a component of resident professionalism among residents and their program directors.Self-control is an important facet of human behavior and interpersonal interaction,including the behaviors constituting medical professionalism. There was no correlation between resident and program director professionalism.42Hwang et al.60KoreaDescriptiveTo compare the factors affecting job satisfaction among Korean and Chinese nurses.Professionalism was the key factor contributing to job satisfaction in Korean and Chinese nurses.Professionalism was positively associated with job satisfaction in both groups.43Ojlovich et al.61USAlongitudinalIdentify the relationship between organization culture, personal sense of accomplishment, and NP.Organizational culture is an important predictor of NP. There is a strong link between organizational culture and professional nursing practice. Also,positive links among culture, the moral, and retention of employees and decrees patient mortality were found.44Karadag et al.62KoreaDescriptiveTo evaluate professionalism among nurses in Korea.The lowest scores were reported in autonomy and educational preparation while the highest scores were obtained in ethical codes for nurses and community service. Mean scores on the BIPN were higher for nurse instructors and in the group proceeding with graduate studies,and they were lower in nurses working in the ward and those with associate degrees.45Dikmen et al.63TurkeyDescriptiveTo evaluate the professional behavior of nurses in a hospital.The highest scores were for the sub-scales of competence and continuing education while the lowest ones were for autonomy and publication and research sub-scales. There was a statistically significant difference between the total BIPN scores and the education levels of the nurses and working of the nurses.46Lasala64USAReviewTo explore the factors contributing to professionalism.Creating a positive first impression is important in seeking a new position or working with patients, colleagues, and the public. Nurses should pay special attention to their appearance and behavior.47Scho¨nrock-Adema et al.65 The Netherlands DescriptiveTo examine the effect of peer assessment on professional behavior.The findings indicated that peer assessment could enhance professional behavior. Moreover,female students’ professional behavior was significantly higher than male students.48Tabatabai et al.66 IranQualitativeConcept analysis of professionalization from the perspectives of nurses working in cardiac care units.The results of concept analysis showed that professionalization consists of seven major themes: community service, nursing knowledge and skills, support organizations,professional independence, good interpersonal relationships, ethical commitment, and attention to professional vulnerability.49Jafaragaee et al.67IranQualitativeTo explore the barriers to professionalism from the perspective of clinical nurses and facilitate the commitment to the nursing profession.Three main themes were extracted, namely,the nature of the nursing profession(professional adherence and excellence professional adherence and excellence), factors facilitating professional commitment (value and professional motivation), and barriers to professional commitment (feelings of inferiority,experience, hardship, and frustration).
(Continued)

Table 1. Characteristics of the included articles.
Theme 4: Socio-individual factors
Social factors: Nurses should experience a sense of confidence, self-esteem, and professional dignity in their organization and society. Society’s negative attitudes toward the nursing profession and lack of any authentic information about it in media could seriously hinder nurses’ professional development.7,37,53,68,69,75
Individual factors: A motivated and positive attitude toward the profession is an important requisite to initiate and support the professionalization of nurses.69
The present extensive review indicates that professionalism in nursing will considerably improve health care quality and enhance satisfaction among both patients and nurses.
Improving the quality of care: Many articles have emphasized about improvement in the quality of health care due to its vital role in shaping professionalism in nursing, as well as increasing patients’ safety and education, and better communication with patients and their families. Therefore, NP could play an instrumental role in improving health services.7,11,13,33,54,55,59,63,71
Patient satisfaction: Some articles in this study indicated that NP can improve the quality of care and the patients’ satisfaction.7,59,76
Nurse satisfaction: Several studies indicated that NP could possibly promote team collaboration and nurses’job satisfaction.32,40,54,55,59,60,72
4. Discussion
Professionalism in nursing is a multidimensional concept and major concept according to the literature included individual prerequisites, professional prerequisites, appropriate structures, and social and individual factors. In fact, professionalism in nursing comprises a wide range of personal characteristics, self- regulation,and professional values, striving to acquire and enhance professional expertise, professional interactions, social,professional, and legal responsibility, and the creation of a sense of belonging and professional development.
Therefore, a new definition for professionalism in nursing could be proposed based on our extensive review. Professional nurses are care providers with appropriate individual characteristics, mental excellence and creativity, professional knowledge and technical skills, ability to analyze, judge, and reason in clinical situations, up-to-date knowledge, and a sense of selfmanagement. It is very important for nurses to obtain professional certificates and become active members of professional associations. Professional nurses fulfill their legal, social, and professional responsibilities, develop a sense of belonging, professionally communicate with patients and other health professionals, effectively participate in teamwork with a patient- centered approach,and achieve ethical standards of their profession in terms of socialization and professional development.
In achieving complete professionalism by nurses in this process, a well-designed curriculum, appropriate clinical environment, and appropriate organizational structure and culture could play important roles in promoting professional values as well as change society’s attitudes toward nursing for the better. As to the social dimension, nursing professional development could result in improved quality of health care services,enhanced ability to respond to social change, increased patient-satisfaction, and a smaller number of complaints against nurses. From a professional nurse’s perspective, it results in fostering positive attitudes to work,providing job satisfaction, decreasing job burnout, and increasing full-time job retention in the profession.
5. Conclusions
The integrated review of the above articles indicated four major themes that include individual prerequisites, professional prerequisites, appropriate structure,and individual and social perspectives. In the 1990s,improving the quality of nursing services along with the cost containment of the demands started to receive considerable attention, leading to the argument that nurses should be more responsible and accountable for their services. In fact, this was an emphasis on further emphasizing the role of nurses and promoting nursing status.47Therefore, several researchers attempted to define the characteristics of the nursing profession,leading to the publication of a large amount of nursing research related to professionalism.46However, different perspectives on professionalism led to different definitions and, in turn, potential ambiguities. Hence, no clear and comprehensive definition of this concept was proposed, and accordingly, no reliable instrument was developed for its assessment. In the present study, the integrative review approach was adopted to propose a generic analytical definition of NP which can be modified based on Iranian cultural factors.
Limitation
One of the limitations of this study is the use of articles written in only English and Persian languages. In fact,selecting and analyzing articles written in other languages may provide a more comprehensive view of the concept. Finally, the use of different methodologies is considered as the main advantage of this study.
Acknowledgments
This article is based on one part of a Ph.D. dissertation on Medical Education at the School of Medical education in Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences,Iran. The authors would like to thank all the members of the Vice-Chancellor of Research for their generous support during the whole project.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Code: IR.SBMU.SME.REC.1398.120).
Conflicts of interest
All contributing authors declare no conflicts of interest.
- Frontiers of Nursing的其它文章
- Predictors of nurse’s happiness:a systematic review
- Clinical nursing competency assessment:a scoping review
- Moderating effect of psychological resilience on the perceived social support and loneliness in the left-behind elderly in rural areas†
- Effects of progressive muscular relaxation and stretching exercises combination on blood pressure among farmers in rural areas of Indonesia: a randomized study†
- Visualization analysis of research“hot spots”: self-management in breast cancer patients†
- Emotional intelligence and its impacts on the clinical performance of nurses in general public hospitals

