Observation of the clinical effects of catgut implantation at acupoints on postpartum obesity with insulin resistance
Zi-jiao Guan, Rui Li, Dong-li Yu, Xiao-feng Sui*
1Qingdao Women and Children’s Hospital, No.217 Liaoyang West Road, Shi Bei District, Qingdao, Shandong, 266034, China.
Abstract: To observe the effect of catgut implantation at acupoints on the treatment of patients with postpartum obesity and insulin resistance.Methods: A total of 120 patients with postpartum obesity and insulin resistance were randomly divided into treatment and control groups (60 patients per group).The treatment group was administered catgut implantation at acupoints while the control group received acupuncture alone for 12 weeks.The patients’ body parameters, including body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), fat percentage (FP),fasting blood glucose (FPG), fasting insulin (FINS), insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR), total cholesterol (TC),triglycerides (T), high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C), and other biochemical indexes of blood lipids, were compared before and after treatment to investigate the efficacy of catgut implantation and acupuncture on postpartum obesity with insulin resistance.Results: The overall response rates were 93.33%and 85% in the treatment and control groups, respectively.After treatment, BMI, WHR, FP, FINS, HOMA-IR,TC, TG, and LDL-C decreased, HDL-C increased (P < 0.05), and FPG did not change significantly (P > 0.05) in both groups; however, the changes in the treatment group were superior to those in the control group (P < 0.05).Conclusion: Both catgut implantation and acupuncture therapy showed good effects on improving postpartum obesity with insulin resistance.The therapeutic effect of catgut implantation on postpartum obesity was better than that of acupuncture therapy, and was therefore worthy of clinical application.
Keywords: catgut implantation; postpartum obesity; insulin resistance; acupuncture
Introduction
Obesity is a pathological state that impairs human health through the excessive accumulation or abnormal distribution of fats in the body, abnormal weight gain, and metabolic disorders [1].Women experience endocrine, nutritional intake, and lifestyle changes after childbirth, often resulting in increased body mass (BM)and obesity.Nearly 88% of women meet the criteria for postpartum obesity (PO) [2].Moreover, many patients with PO are abdominally obese.
Adipose tissue is the center of energy storage and has a powerful endocrine function of secreting adipocytokines in paracrine, autocrine, and telecrine forms [3].Resistin, a recently discovered hormone of adipocyte origin, inhibits the insulin signaling pathway, leading to insulin resistance (Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance, HPMA-IR)[4], which is the pathological basis for diseases such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis (AS), and hypertension [5].
In recent years, postpartum obese patients have accounted for an increasing proportion of postpartum women and obese people, greatly increasing their risks of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, and other diseases [6].How to treat PO scientifically and effectively has become a hotspot of medical attention.From January 2019 to March 2021,the author used catgut implantation at acupoints to treat 120 cases of PO with insulin resistance in the Adult TCM Department of Qingdao Women and Children’s Hospital, with good efficacy.The report is as follows.
1 Data and methods
1.1 General data
This study included 120 non-lactating postpartum obese patients, aged 22-40 years, who attended the Adult TCM Department of Qingdao Women and Children’s Hospital between January 2019 and March 2021.These included 26 women who were 3-6 months postpartum;58, 6 months-1 year postpartum; 25, 1-3 years postpartum; and 11, more than 3 years postpartum.The women were classified as overweight (27 cases), class 1 obesity (54 cases), and class 2 or above obesity (39 cases).
1.2 Diagnostic criteria [7, 8]
The diagnostic criteria were based on the recommended diagnostic criteria for obesity from the Expert Consensus on Medical and Nutritional Treatment of Overweight/Obesity in China (2016 version) and the Redefinition and Treatment of Obesity in the Asia-Pacific Region issued by the World Health Organization(WHO) in February 2000.(Table 1)

Table 1 Relevant indicators and judgment standards
1.3 Inclusion criteria
(1) Participants who met the diagnostic criteria for obesity; (2) postpartum non-lactating women with obesity; (3) women with no treatments for obesity in the last 3 months; (4) those with a clear mind,and voluntary agreement for catgut implantation at acupoints and acupuncture treatment and who signed the informed consent form.
1.4 Exclusion criteria
(1) Women with secondary obesity during pregnancy or lactation; (2) women with primary diseases such as endocrine and metabolic diseases and mental disorders;(3) women who used other therapies (including the addition of other drugs) by themselves or who were unable to adhere to the treatment during the study period; (4) women who were allergic to or did not absorb the foreign protein catgut.
1.5 Treatment methods
1.5.1 Acupoint selection
Main acupoints: Qihai, Guanyuan, Zhongwan, Tianshu,Daheng, Xuehai, Zusanli.Matching acupoints:Yinlingquan, Fenglong, and Sanyinjiao.
1.5.2 Treatment group (catgut implantation at acupoints)
Operation method: The women were placed in a supine position and the skin at the desired acupoints was fully exposed.A 0.9 mm × 62 mm disposable catgut implantation needle (Zhenjiang Gaoguan Medical Instrument Co., Ltd.) and a 2-0 absorbable surgical suture (Shandong Boda Medical Products Co.,Ltd.) were used.After routine skin disinfection, the catgut was loaded into the catgut implantation needle using sterilized forceps and the needle was quickly inserted.After the patient felt the needle, the needle core was pushed and the catgut was implanted in the subcutaneous layer or muscle layer of the acupoint;simultaneously, the right hand slowly withdrew the needle to keep the catgut in the acupoint.A cotton ball was pressed against the pinhole to prevent bleeding and a 3M infusion patch was used to cover and protect from infection.After 1 week, a follow-up was performed to confirm that the patient had no rejection of the catgut.A single treatment course comprised six series of injections performed once every 14 days,with treatment suspended during menstruation.The treatment lasted for a total of 3 months [9].
Precautions: Several patients experienced slight rejection of the catgut; therefore, they were directed to not expose the needle eye to water within 24 h after the implantation to prevent infection.
1.5.3 Control group (acupuncture)
The same acupoints were used as in the treatment group.
Operation method: Each woman was placed in a supine position and the skin at the desired acupoints was fully exposed.The acupoints were disinfected and Huatuo 0.25 mm × 40 mm disposable sterile acupuncture needles were used.All acupoints were directly punctured and the needles were quickly inserted until the desired sensation was achieved.The needles were twisted once every 10 min and left for a total of 30 min, once daily, with 10 repetitions defined as a course of treatment.The treatment was stopped during menstruation.The treatment lasted for a total of 3 months [10].
Precautions: The abdominal acupoints were not punctured too deeply to avoid damage to the internal organs.
1.6 Observation indexes
1.6.1 Objective indexes
BM, waist circumference (WC), hip circumference(HC), and fat percentage (FP) were measured, and body mass index (BMI) and waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) were calculated before and after treatment in both groups.Fasting blood glucose (FPG) and fasting insulin level(FINS) were measured before and after measuring the BM, and the insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) was calculated.Thecalculation formulas are as follows:
1.6.2 Efficacy index [11]
The treatment efficacy was categorized according to the standard formulated by the Fifth National Academic Conference on Obesity Research in Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, as follows:
Cured: The BM decreased to the standard BM range(BMI < 24 kg/m2) and the WHR reached the normal standard.
Significantly responsive: BMI loss of ≥ 4 kg/m2 or a BM loss of 30-70% of the difference between the actual weight and the standard.
Responsive: BMI loss of 2-4 kg/m2 or BM loss of 25%-30% of the difference between the actual BM and the standard.
Non-responsive: BMI loss <2 kg/m2 or BM loss of<25% of the difference between the actual BM and the standard.
1.7 Statistical methods
SPSS 19.0 was used for statistical analysis.All measurement data are expressed as means ± standard deviation (Mean±Standard).t- and x2 tests were used for measurement and count data, respectively.Differences with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
2 Results
2.1 Comparisons of general data
No significant differences in age or postpartum time(P> 0.05) were observed between the two groups;therefore, the two groups were comparable (Table 2).

Table 2 Comparisons of general data between the two treatment groups ( Mean±Standard)
2.2 Comparisons of treatment efficacy between the two treatment groups
The women in both groups showed good results before and after treatment, although the treatment group had better results than the control group (P< 0.05) (Table 3).

Table 3 Comparisons of treatment efficacy between the two groups (cases, %)
2.3 Comparisons of body parameters between the two groups before and after treatment
Compared to before treatment, the BMI, WHR, and FP were significantly lower in both groups after treatment(P< 0.05).At the end of treatment, the changes in the body parameters of patients in the treatment group were greater than those in the control group, and the efficacy in the treatment group was better than that in the control group (P< 0.05) (Table 4).
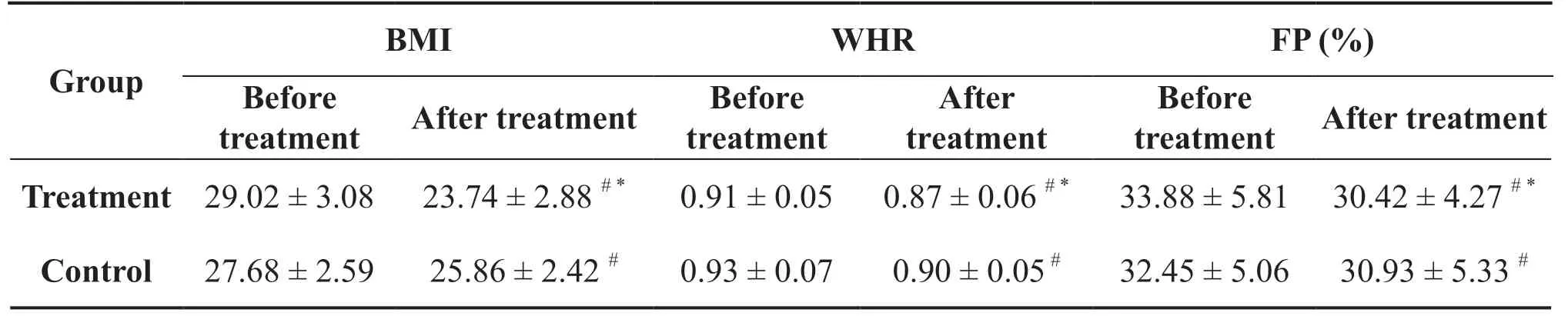
Table 4 Comparisons of BMI, WHE, and FP before and after treatment between the two groups of patients (Mean±Standard)
2.4 Comparisons of insulin resistance-related indexes before and after treatment between the two groups
Compared to before treatment, the FPG of patients in both groups did not change significantly after treatment(P > 0.05), while FINS and HOMA-IR decreased significantly (P < 0.05).At the end of treatment, the changes in insulin resistance-related indexes in the treatment group were greater than those in the control group, and the efficacy of the treatment group was better than that of the control group (P < 0.05) (Table 5).
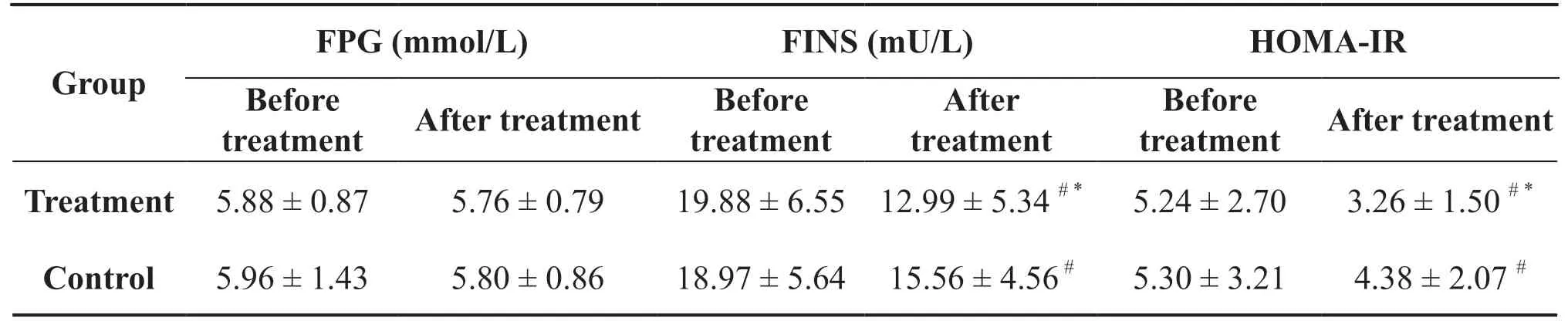
Table 5 Comparisons of FPG, FINS, and HOMA-IR before and after treatment between the two groups (Mean±Standard)
2.5 Comparisons of lipid-related indexes before and after treatment between the two groups
Compared to before treatment, total cholesterol (TC),triglyceride (TG), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C)levels were significantly lower, while high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) levels increased significantly in both groups after treatment (P < 0.05).At the end of treatment, the changes in lipid-related parameters of patients in the treatment group were greater than those in the control group, and the efficacy of the treatmentgroup was better than that of the control group (P<0.05) (Table 6).
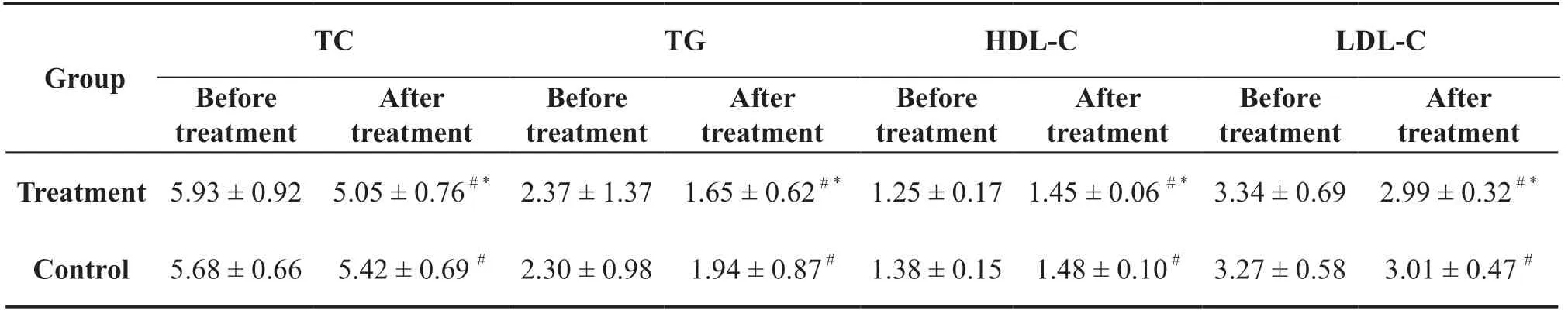
Table 6 Comparisons of TC, TG, HDL-C, and LDL-C levels before and after treatment between the two groups (Mean±Standard)
Overall, both catgut implantation at the acupoints and acupuncture for PO showed good efficacy and significant effects on improving insulin resistance and reducing blood lipid indexes; in addition,catgut implantation at the acupoints was superior to acupuncture in the treatment of PO.
3 Discussion
With improved living standards and changes in the dietary structure, the number of patients with PO is increasing annually in China, and the treatment of this disease has become a hotspot of medical research.PO is not only closely related to the temporary disorder of hypothalamic-gonadal function caused by pregnancy[12] but is also closely related to the traditional Chinese culture of “confinement.” During the period of confinement, a large amount of tonic products are consumed and the diet structure is single, fatty, sweet,and greasy, resulting in an excessive intake of calories.In China, most postnatal women sit in bed and do not exercise; this sleep-oriented lifestyle results in abdominal muscle relaxation and excessive abdominal fat deposition.PO undermines daily work and life and also increases the risk of diabetes, hypertension,atherosclerosis, and other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases [13].
The various methods to treat obesity include Western medicine, surgery, acupuncture, decoction, and massage.Based on a summary of recent literature reports, acupuncture has the advantage of remarkable effects and no side effects [14]; while Western medicine has a clear target for treatment, it is ineffective and has toxic side effects [15].While surgery has obvious efficacy, it is risky and has serious postoperative reactions [16].Thus, in comparison, acupuncture offers advantages in the treatment of obesity.Catgut implantation at the acupoints is a modified acupuncture therapy with the same root and mechanism.This treatment method not only retains the advantages of acupuncture but also makes up for the shortcomings of a long course of acupuncture and is generally performed once every 2 weeks, providing convenience for many people in today’s fast-paced society who have stressful lives, do not have enough time, and are also troubled by diseases.The mechanism of the effect of acupuncture on weight loss has not been fully clarified.Most studies have shown that acupuncture achieves weight loss through its effects on the central nervous system, peripheral nerves and their transmitters,endocrine and glucose metabolism, energy metabolism,lipid metabolism, and kidney and digestive functions.Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believes that postpartum diseases have multiple blood stasis and deficiencies [17].Following birth, most parturients have deficiencies in qi, blood, yin, and yang.Therefore,the basic causes of PO are insufficient qi and blood,spleen and kidney yang deficiency, liver qi stagnation,improper diet, and gastrointestinal dysfunction, which leads to the accumulation of phlegm and dampness,turning into fat, which accumulates over time to result in obesity.Acupuncture treatment primarily starts from the Large Intestine Meridian of the Hand-Yangming,Stomach Meridian of Foot-Yangming, Spleen Meridian of Foot-Taiyin, Kidney Meridian of Foot-Shaoyin,Liver Meridian of Foot-Jueyin, and the Ren meridian[18].
Qihai, Guanyuan, and Zhongyin are all important acupoints for health care.Guanyuan is the junction point of Front-Mu Point of Small Intestine, Ren meridian, and Three Yin Meridians of Foot.“Leijing Tuyi” says, “This point is in the middle of the four sides of the human body, so it is also known as the Great Central Pole, which is where men stores up essence and women blood.” [19] Qihai, as its name implies, is the sea of vital energy and can be used for all related diseases.Zhongwan is the Front-Mu Point of Stomach Meridian, the Influential Point of Fu-organs, and the rendezvous for the Ren meridian, Hand-Taiyang, and Foot-Yangming, which can harmonize the stomach and invigorate the spleen, warm dampness, and promote gastrointestinal peristalsis.Postpartum “multiple deficiencies” manifest in many aspects such as qi,blood, and five internal organs.These three acupoints can well consolidate the body, nourish the kidney,warm the yang, invigorate the spleen and stomach.
Daheng, Xuehai, Sanyinjiao, and Yinlingquan belong to the Spleen Meridian of Foot-Taiyin.The Daheng acupoint regulates stomach and qi and invigorates the spleen.It is the junction of Foot-Taiyin and Yinwei Meridian, which has a two-way regulating effect; i.e.,it strengthens weak gastrointestinal peristalsis and weakens excessive gastrointestinal peristalsis.Xuehai is also known as the “Sea of the Twelve Meridians”and regulates the meridians and blood, strengthens the spleen and resolves dampness, and treats all syndromes related to qi and blood.Sanyinjiao is a meeting point of the Three Yin Meridians of Foot, which invigorates the spleen and stomach, benefits the liver and kidneys, regulates the menstrual belt, and can be used for diseases related to the liver, spleen, kidneys,and gynecology.Yinlingquan is a joint point of the spleen meridian useful for regulating qi flow, clearing dampness and heat, and benefiting the kidneys to regulate menstruation.Zusanli, Tianshu, and Fenglong belong to the Stomach Meridian of Foot-Yangming.Zusanli is a joint point of the Stomach meridian and can be used for all symptoms of asthenia and to invigorate the spleen and stomach, support and cultivate the vital energy, open and activate the meridians, and increase qi flow.Fenglong is a stomach meridian point that can be used for all symptoms related to phlegm and dampness and is a common point for dispelling dampness.Tianshu is a Front-Mu Point of the Large Intestine that regulates the middle and stomach, regulates qi,and strengthens the spleen, and also has a two-way regulatory effect.Tianshu, Daheng, Xuehai, Sanyinjiao,Zusanli, and Fenglong are all important acupoints on the spleen and stomach meridians.The two organs of the spleen and stomach are the sources of qi and blood in the postnatal period, while the two meridians of the spleen and stomach are the path of qi and blood prosperity.Taking these points can make moderate qi and blood in patients with PO.
The acupoints in this study strengthen the body, warm the kidney and yang, and regulate qi and blood for their metabolism.Furthermore, they harmonize the stomach and the spleen, promote qi moisturization, and accelerate spleen and stomach movement.They not only eliminate PO and fatigue and help women exercise on their own to treat PO but also regulate postpartum physique and promote a good physiological state.This enhances the happiness quotient and helps to prepare for a second child, thus demonstrating many benefits.
Both catgut implantation at acupoints and acupuncture enhanced physical fitness, regulated endocrine,and promoted fat metabolism.However, catgut implantation at acupoints was more effective than acupuncture in treating PO, reducing blood lipid levels,and regulating insulin resistance.Catgut implantation at the acupoints continuously stimulated acupoints to balance yin and yang, harmonize qi and blood, and regulate viscera, providing unique advantages for PO.Catgut implantation at acupoints is the inheritance and further application of acupuncture and has a wide range of indications.Thus, it is worthy of promotion.
 Medical Theory and Hypothesis2021年4期
Medical Theory and Hypothesis2021年4期
- Medical Theory and Hypothesis的其它文章
- Hypothesis on how Distance External Qi Therapy works
- Study on the Mechanism of Shimian Granules (SMG) against Depression via Regulating Circadian Rhythms
- SARS-CoV-2 And The Gastrointestinal Disorders
- CiteSpace-based Knowledge Graph Analysis of the Current Status and Trends of Chinese Medicine Research in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy
