Improvement of the annotation of Antheraea pernyi (Lepidoptera:Saturniidae)genome using full-length transcripts
LI Ying,LEI Yu-Yu,LIANG Shi-Mei,ZHANG Xian,DU Jie, YANG Xin-Feng,LI Shan-Shan,DUAN Jian-Ping,*
(1.Henan Key Laboratory of Insect Biology in Funiu Mountain,Henan Provincial Engineering Laboratory of Insects Bio-reactor, Nanyang Normal University,Nanyang,Henan 473061,China;2.Henan Institute of Sericulture Science, Zhengzhou 450008,China)
Abstract:【Aim】 This study aims to improve the annotation of the genome of the Chinese oak silkworm,Antheraea pernyi,so as to expand its application to comparative genomics and breed improvement.【Methods】 The full-length transcriptome of A. pernyi was sequenced and analyzed,and compared with the reference genome to identify novel genes and transcripts with functional annotation and to predict long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs).The gene models in the genome of A. pernyi were modified by thousands of novel protein-coding transcripts and lncRNAs.Finally,the corrected and merged annotation of the genome of A. pernyi was created.【Results】 A total of 1 997 novel protein-coding genes and 3 399 novel lncRNA genes were discovered and supported by 2 402 and 3 574 full-length transcripts,respectively.The genome of A. pernyi contains 25 021 genes,including 19 825 protein-coding genes,from which seven juvenile hormone acid O-methyltransferase genes were identified.【Conclusion】 This study improves our knowledge of the known genes in the genome of A. pernyi and provides valuable resources for comparative and functional genomic studies in A. pernyi and its relatives.
Key words:Antheraea pernyi;genome annotation;full-length transcriptome;protein-coding genes;lncRNA;juvenile hormone acid O-methyltransferase genes
1 INTRODUCTION
Accurate gene annotation is an essential feature of a highly-qualified reference genome.An obtained genome usually needs to be reannotated several times to achieve this goal (Xiaetal.,2004;Kawamotoetal.,2019).Any updated annotation is an aspect tied to the genome,such as a coding gene model,a fused transcript,or a non-coding RNA gene,which is a prerequisite for the efficient use of the genome in the fields of functional genomics and breed improvement.
Along with the other two silkworm species,Bombyxmori(Xiaetal.,2004;Kawamotoetal.,2019)andAntheraeayamamai(Kimetal.,2018),Antheraeapernyiis also an important insect valuable to the silk industry,food industry,tissue engineering and regenerative medicine (Yang Metal.,2014;Wang Jetal.,2019;Yang Ketal.,2019).Considering its economic importance,comparative transcriptome analyses have been carried out to identify the key genes controlling important traits inA.pernyi,especially those mediating the response to nucleopolyhedrovirus infection (Wang GBetal.,2019),determining silk properties (Dongetal.,2015),and regulating molting and metamorphosis (Bianetal.,2019).However,these studies were not based on a highly-qualified reference genome because of the lack ofA.pernyigenome data for a long time,thereby limiting the excavation of important gene resources,such as the juvenile hormone acidO-methyltransferase gene (JHAMT),which encodes a rate-limiting enzyme controlling the transformation of juvenile hormone (JH)acid into JH in the presence of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM)(Shinoda and Itoyama,2003).ApJHAMThad not yet been completely identified using second-generation transcriptome sequencing data (Bianetal.,2019).Although the genome ofA.pernyiwas initially assembled one year ago using long subreads generated by Pacific Biosciences (PacBio),producing a 720.67-Mb genome with 21 431 predicted genes (Duanetal.,2020),its gene structure annotation was based on a less complete catalog of transcripts from the mixture of the 5th instar larval tissues,which might influence the completion of gene models and consequently limit the progress of research onA.pernyi.
Considering the advantage of the complete structure of full-length transcripts in improving genome structure annotation (Wangetal.,2016),the objective of this study is to modify the gene models for the genome ofA.pernyiwith thousands of novel protein-coding transcripts and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs)from full-length transcriptome sequencing,so as to promote comparative and functional genomic studies inA.pernyiand its relatives.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Oak silkworm samples
Jiaolan,a univoltineA.pernyistrain,was reared on the oak trees on the mountain at the Chinese oak silkworm base of Henan Institute of Sericulture Science,Zhengzhou,China.Five types of whole individuals (larvae,female pupae,male pupae,virgin moths with unfertilized eggs,and male moths)were prepared for full-length transcriptome sequencing.
2.2 PacBio Iso-Seq library preparation and sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from the five types of samples (section 2.1)using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen,USA)and further purified using RNeasy Mini Kits (Qiagen,Australia).RNA concentration was measured using a Qubit 2.0 Flurometer (Invirogen,USA).PolyA(+)RNAs were purified using mRNA Capture Beads (Vazyme,China),and then the purified polyA(+)RNAs were pooled in equal amounts,and 1 μg was used to synthesize cDNA using the SMARTer PCR cDNA Synthesis Kit (Clontech,USA).Two Iso-Seq libraries without size selection were constructed using the SMRTbell Template Prep Kit (Pacific Biosciences,USA),which were run on the PacBio Sequel II platform (Pacific Biosciences,USA).The collected dataset has been deposited in China National Center for Bioinformation,National Genomics Data Center (CNCB-NGDC)with the accession number CRA003642 that is publicly accessible at https:∥bigd.big.ac.cn/.
2.3 Full-length transcriptome processing
Effective subreads were obtained using SMRT Link software v8.0.0.79519 (https:∥www.pacb.com/support/software-downloads/).According to the presence of the 3′ primer,5′ primer,and poly(A),the circular consensus sequence (CCS)were extracted and divided into three types of sequences:full-length sequence,full-length non-concatemer sequence (FLNC),and full-length non-concatemer sequence with poly(A).The FLNC reads with poly(A)were mapped to the genome ofA.pernyiusing GMAP software (Wu and Watanabe,2005).The high-quality maps were constructed under the condition that an FLNC read could only be aligned to one gene with the highest percentage of identity (PID),in addition to local PID>97% and overall PID>95%.These high PID FLNC reads were finally used to annotate genes and transcripts.Two FLNC reads that overlapped by more than 20% in sequence and had one overlapping exon to at least 20% were designated as a transcript from the same genes.For transcript mapping,the FLNC reads were removed when the 5′ ends were missing.A transcript was maintained when all of the splicing sites of the multiple-exon FLNC reads were identical,or single-exon FLNC reads with overlap were identified as the same transcript.
2.4 Identification and functional annotation of novel genes and their transcripts
After the full-length transcripts were compared with the annotation of the reference genome ofA.pernyi(CNCB-NGDC accession number:GWHABGR00000000),the criteria that the neighbor genes had no overlap or overlapped by less than 20% in sequence,or that they overlapped by more than 20% in sequence but had different directions,were used to identify new genes (Lietal.,2018).In addition,changes in the 5′ or 3′ end and the emergence of new exons or introns were used to distinguish novel transcripts.Furthermore,functional annotation was carried out using Diamond v 0.8.33 (Buchfinketal.,2015)with public databases,including National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI),Non-Redundant Protein Sequence Database (NR),Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)(Kanehisaetal.,2004),Gene Ontology (GO)(Ashburneretal.,2000),KOG (Tatusovetal.,2003),and Swiss-Prot (Gasteigeretal.,2001),with an E-value threshold of 1e-5.
2.5 LncRNA prediction
Novel transcripts of ≥200 bp in length,which could not be aligned against the NR,KOG,KO,and Swiss-Prot databases,were used to predict their protein-coding potential using CNCI (Sunetal.,2013),CPC2 (Kongetal.,2007),CPAT (Wangetal.,2013),and PLEK (Lietal.,2014)software tools,which have the power to distinguish non-coding RNAs from protein-coding RNAs,with default parameters.The transcripts without protein-coding potential made up the candidate set of lncRNAs.The remaining transcripts,whose protein-coding potential could not be determined,were used to detect the putative coding sequences (CDSs)using TransDecoder with default parameters (http:∥transdecoder.github.io/).
2.6 Identification of the JHAMT family in A. pernyi
The improved annotation of the genome ofA.pernyiwas used to predict the members of the JHAMT family.TheB.moriJHAMT protein sequence (GenBank accession number:NP_001036901.1)was downloaded from NCBI (https:∥www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/).BmJHAMT was used as a query to the BLAST alignment tool against the corrected protein set of the genome ofA.pernyiwith an E-value threshold of 1e-10.Subsequently,all of the targeted proteins were aligned to determine the consensus SAM-binding domains in the JHAMT family inA.pernyi.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Evaluation of full-length transcripts of the genome of A. pernyi
In total,361 120 polymerase reads representing more than 34 Gb were collected with a mean length of ~95 kb (Table 1),indicating that a single transcript was sequenced several times.After removing adapters,the mutual correction of errors,and the filtering of low-quality reads,263 195 high-quality CCS reads with a mean length of 2 348 bp were obtained (Fig.1:A),including the full-length transcript,FLNC,and FLNC with poly(A)sequences (Table 1).The average accuracy of the CCS reads was 99.93%.Alignment of the FLNCs with poly(A)to the genome ofA.pernyiby GMAP showed that 102 284 (75.05%)FLNCs were perfectly mapped.These effective FLNCs,with an accuracy of 99.93%,could be used for further study.

Table 1 Summary of PacBio Iso-Seq data of the transcriptome of Antheraea pernyi

Fig.1 Analysis of the PacBio Iso-Seq data of the transcriptome of Antheraea pernyiA:Mean length of the circular consensus sequence reads.B:Comparison of the transcript length between reference annotation and PacBio Iso-Seq data.
To optimize the annotation of the genome ofA.pernyi,we first compared the gene coverage of the full-length transcripts and reference annotations.In the PacBio Iso-Seq dataset,a total of 102 284 high-quality FLNCs covered 14 803 transcripts and were allocated to 11 253 genes.Approximately 83.21% of the gene transcripts were ≥1 kb in length.However,in the reference annotation,only 42.25% of gene transcripts were ≥1 kb in length.The length of transcripts was obviously increased in full-length transcripts (Fig.1:B),indicating that the integrality and quality of gene transcripts from PacBio Iso-Seq full-length sequencing were better than those of the reference annotation.These identified transcripts could be used further to promote the annotation of the genome ofA.pernyi.
3.2 Improvement of gene annotation in the genome of A. pernyi
We identified 5 396 novel genes in the geneome ofA.pernyi,which were supported by 5 976 novel full-length transcripts (Fig.2:A).Furthermore,we identified 7 328 novel transcripts covering 4 652 reference genes.In particular,we discovered 707 gene spans,which might result from the wrong reference annotation of 1 028 genes,and 521 gene-split events,which might be derived from the wrong designation of adjoining genes as a single gene.Functional analysis showed that 1 993 novel genes could be functionally annotated (Fig.2:B),and these genes were designated as protein-coding genes.These newly identified protein-coding genes were mainly enriched in 37 GO terms,including 17 biological process,11 cellular component,and 9 molecular function terms (Fig.3).

Fig.2 Identification of novel genes and transcripts in the genome of Antheraea pernyiA:Details of novel genes;B:Functional annotation of novel protein-coding genes in databases NR,KEGG,GO,KOG,and Swiss-Prot;C:Assessment of novel lncRNAs using CPC2,CPAT,PLEK and CNCI softwares;D:Details of novel lncRNAs.

Fig.3 Enriched GO terms of the newly identified protein-coding genes from the genome of Antheraea pernyi
In addition,4 010 full-length transcripts were successfully assessed as lncRNAs (Fig.2:C),3 574 of which were derived from the transcription of 3 399 novel lncRNA genes (Fig.2:D).Four novel genes were unsuccessfully annotated.However,they were predicted to have CDSs.Therefore,we designated these four genes as protein-coding genes,using the standard that the putative protein encoded by a gene was at least 100 amino acids in length or it could be functionally annotated.Finally,the corrected annotation of the genome ofA.pernyiwas created,showing that the genome ofA.pernyicontains 25 021 genes,including 1 997 novel protein-coding genes and 3 399 novel lncRNA genes.Moreover,the gene count of the protein-coding genes forA.pernyiis 19 825.
3.3 The JHAMT family in A. pernyi
In total,sevenJHAMTgenes were identified in the improved annotation of the genome ofA.pernyi(Fig.4).All of these genes were located on chromosome 21.All of the ApJHAMTs contain the consensus SAM-binding domain.ApJHAMT4_1 and ApJHAMT4_2 are encoded by two transcripts,which were transcribed from the same gene (ApJHAMT4 with the accession number GWHGABGR006483),indicating alternative splicing.ApJHAMT4_2 represents a protein encoded by a novel full-length transcript from a known gene model,andApJHAMT6 represents a new gene found in the improved annotation of the genome ofA.pernyi.
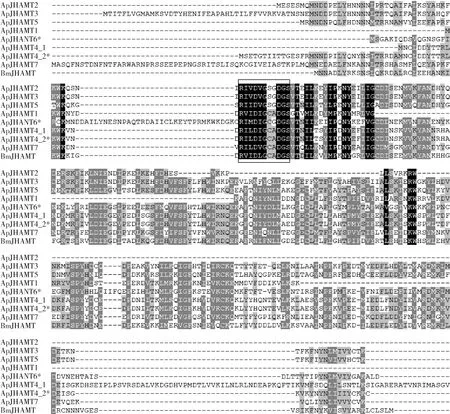
Fig.4 Alignment of all members of the JHAMT family in the genome of Antheraea pernyiAsterisk shows the two members of the JHAMT family identified in the improved annotation of the genome of A. pernyi.The putative SAM-binding motif is boxed.BmJHAMT is the juvenile hormone acid O-methytranscerase gene (GenBank accession no.:NP_001036901.1)of B. mori.The accession numbers of juvenile hormone acid O-methytranscerases of A. pernyi are as follows:ApJHAMT1,GWHGABGR006474;ApJHAMT2,GWHGABGR006476;ApJHAMT3,GWHGABGR006477;ApJHAMT4,GWHGABGR006483;ApJHAMT5,GWHGABGR006484;ApJHAMT6,GWHABGR00000014.178;ApJHAMT7,GWHGABGR006529.ApJHAMT4_1 and ApJHAMT4_2 represent two putative proteins encoded by two alternative splice forms of ApJHAMT4.
4 DISCUSSION
Mapping full-length data to a genome is a very efficient method for accurately detecting gene structure.Additionally,data from large-scale tissues and developmental stages can improve the discovery of almost all genes in a genome (Suetsuguetal.,2013;Kawamotoetal.,2019).Previously,we created gene models of the genome ofA.pernyiusing a less complete catalog of transcripts from a mixture of the 5th instar larval tissues (Duanetal.,2020).To identify as many transcripts as possible,we pooled different types of whole individuals from different developmental stages and then processed poly(A)-selected PacBio Iso-Seq to improve the gene models of the genome ofA.pernyi.As a result,we obtained 263 195 high-quality CCS reads (Table 1),with 7 328 novel transcripts covering 4 652 reference genes,5 976 novel transcripts corresponding to 1 997 novel protein-coding genes,and 3 399 novel lncRNA genes (Fig.2:A),all of which were not previously annotated in the genome ofA.pernyi.Finally,the improved annotation for the genome ofA.pernyicomprises 25 021 genes,including 19 825 protein-coding genes.From the improved annotation,we first identified almost all members of the JHAMT family in the genome ofA.pernyi(Fig.4),including a new gene,ApJHAMT6,and a novel transcript ofApJHAMT4.This novel transcript was very difficult to be accurately identified using second-generation transcriptome sequencing data (Bianetal.,2019).Therefore,our study improves our knowledge of the known gene models in the genome ofA.pernyi,and provides valuable resources for further comparative and functional studies inA.pernyiand its relatives.
It is clear that the gene coverage of full-length transcripts was not saturated.The reason for this might be that tissue-pooled library sequencing makes it impossible to trace all of the transcripts back.Thus,the current gene annotation of the genome ofA.pernyiis still incomplete.Yet,the improved annotation of the genome ofA.pernyiis another important step forward,and will help researchers better explore the heredity and molecular control mechanisms of silk properties,metamorphic development,immune response,pigmental metabolism,and other biological traits of interest inA.pernyi.

