Identification of microRNA-21 as a valuable diagnostic marker of oral squamous cell carcinoma and potential target*
Hua Yang,Yuxue Wei,Gangli Liu
1 Department of Stomatology,People's Hospital of Lanling County,Linyi 276000,China
2 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,Hospital of Stomatology,School of Stomatology,Qilu Medical College,Shandong University,Jinan 250012,China
Abstract Objective The aim of the study was to summarize the diagnostic value of miR-21 as a biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) using a review of the literature and data from the cancer genome atlas(TCGA) database.Methods Data from TCGA database was sorted and analyzed by bioinformatics to determine the expression level of miR-21 in OSCC.Further,we searched for relevant articles in Embase,PubMed/Medline,Scopus,and Web of Science published before March 2021,extracted the data,and conducted quality assessment.The bivariate meta-analysis model with Stata 16.0 was used to analyze the diagnostic value of miR-21 for OSCC.Results A total of 304 related articles were identified,and seven were selected for meta-analysis.The diagnostic results after analysis were as follows:sensitivity 0.76 [95% confidence interval (CI),0.57-0.88];specificity 0.77 (95% CI,0.58-0.89);positive likelihood ratio 3.34 (95% CI,1.58-7.08);negative likelihood ratio 0.31 (95% CI,0.15-0.63);diagnostic odds ratio 10.75 (95% CI,2.85-40.51);and area under the curve 0.83 (95% CI,0.80-0.86).The Deeks’ funnel chart showed that there was no potential bias (P=0.54).Prediction analysis of the potential target genes of miR-21 was performed via the biological website,and DAVID was used to cross target genes for gene ontology (GO) annotation function analysis.Conclusion The results showed that miR-21-3p and miR-21-5p were significantly more highly expressed in OSCC tissues than in normal tissues (P < 0.05),and the results of the meta-analysis indicated that they could be used as potential biomarkers in the diagnosis of OSCC.In addition,58 potential target genes of miR-21 were significantly enriched in 28 GO annotation functional pathways,which provided a biological basis for further clinical diagnostic value research.
Key words:miR-21;oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC);diagnostic meta-analysis;target gene prediction
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) accounts for 90% of oral and maxillofacial tumors and is the sixth most common type of malignant tumor worldwide[1].Its incidence and mortality have not been affected by the improvement of surgical techniques,which is recognized as a serious problem.Traditional detection methods have several limitations,including expensive inspection fees and low specificity.Thus far,early detection and treatment are the best the rapeutic strategies.Therefore,identification of new diagnostic markers for the early detection of OSCC is a potential treatment option.MicroRNAs (miRNAs),endogenous non-coding small RNAs with a length of 18–25 nucleotides,are considered as potential cancer biomarkers for early detection and diagnosis.Increasing evidence have shown that miRNA can be used as a new and non-invasive biomarker for the early diagnosis of various types of cancer[2–3].miR-21 is located on chromosome 17p23.1,which is an oncogenic miRNA that promotes carcinogenesis through anti-apoptotic effects.miR-21 is highly expressed in many cancers,including gastric,esophageal,ovarian,and breast cancer.Inhibition of its expression can lead to tumor shrinkage and has a significant impact on the chemoresistance of tumors[4–5].Gombos and other studies have shown that miR-21 is highly expressed in oral cancer tissues,and miR-21 can be used as a non-invasive biomarker for the diagnosis and detection of other cancers[6].However,the diagnostic value of miR-21 in OSCC requires further confirmation.Therefore,in this metaanalysis,we screened and summarized the diagnostic value of miR-21 as a biomarker in OSCC and analyzed its potential target genes and related enrichment pathways,which are necessary for effective diagnosis and treatment of OSCC patients.
Materials and methods
Download and organization of the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) database
We downloaded all of the miRNA-related transcriptome data of OSCC from the TCGA database(https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/) and drew pictures using the“beeswarm”package in the R software.
Literature search
We searched the Embase,PubMed/Medline,Scopus,and Web of Science databases,for articles published before March 2021.We searched for synonyms of OSCC and miR-21 as keywords through the keyword MeSH function in PubMed,and relevant documents were collected comprehensively and systematically.
Literature inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion and exclusion of the literature were completed separately and integrated by two individuals.The inclusion criteria were as follows:miR-21 diagnosis data–sensitivity or specificity,the control group information of healthy patients can be obtained from the literature or by contacting the author;the exclusion criteria included:inability to provide valid data such as sensitivity and specificity,non-human studies,nonclinical studies,reviews,conference abstracts,case reports,and repeated published studies.
Literature quality evaluation and data extraction
The quality of the literature was evaluated using QUADAS-2;the items in the QUADAS list were applied to each article,and the answer was determined to be“yes,”“no,”or“unclear.”Two researchers rated the literature according to the scoring criteria,and articles with inconsistent scores were re-scored by group discussion.The data extraction information included the name of the first author,publication,year,country/region,ethnicity,sample size,specimen and cancer type,detection method,true positive,false positive,true negative,and false negative numbers.
Statistical processing
Statistical analysis was performed using Stata version 16.0;the bivariate meta-analysis model was used to calculate the relevant values,the comprehensive sensitivity and specificity,diagnostic odds ratio (DOR),positive likelihood ratio (PLR),and negative likelihood ratio (NLR).Analysis of the summary receiver operating characteristic curve (SROC) and the calculation of the area under the curve (AUC) were carried out to evaluate the value of the overall diagnosis of miR-21 in cancer detection and diagnosis;the data used the hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic model(HSROC) model for further confirmation.Spearman’s correlation coefficient and ROC plane analysis evaluated the heterogeneity of threshold effects.The heterogeneity of non-threshold effects was detected by Q test and discordance index (I2),whereP< 0.10 orI2> 50%indicates that there is obvious heterogeneity between studies.Fagan nomograms verified pre-test probability,likelihood ratio,and post-test probability;Deeks’ funnel chart was used to test bias.
miR-21 target gene analysis
Three online target gene prediction tools,namely TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org/vert_71/),miRDB(http://mirdb.org/),and PicTar (https://pictar.mdc-berlin.de/),were used to predict the potential target genes of miR-21 (including miR-21-3p and miR-21-5p).Further,we used the VennDiagram package in the R software to draw a Venn diagram of the three databases to take the intersection for subsequent analysis.
Functional enrichment analysis of target genes
The online tool DAVID (http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/) was used to perform gene ontology functional enrichment analysis (GO analysis) on the intersecting target genes,andP< 0.01 was set as the significance threshold to obtain the top 28 statistically significant GO annotation analyses.
Results
Expression level of miR-21 in different tissues
Through the download and analysis of TCGA database,the expression levels of miR-21-3p and miR-21-5p in OSCC and normal tissues were sorted out,and the results showed that both were significantly highly expressed in OSCC (P=0.021 andP=0.04;Fig.1),which further illustrated that the study of miR-21 is of great significance for OSCC patients.
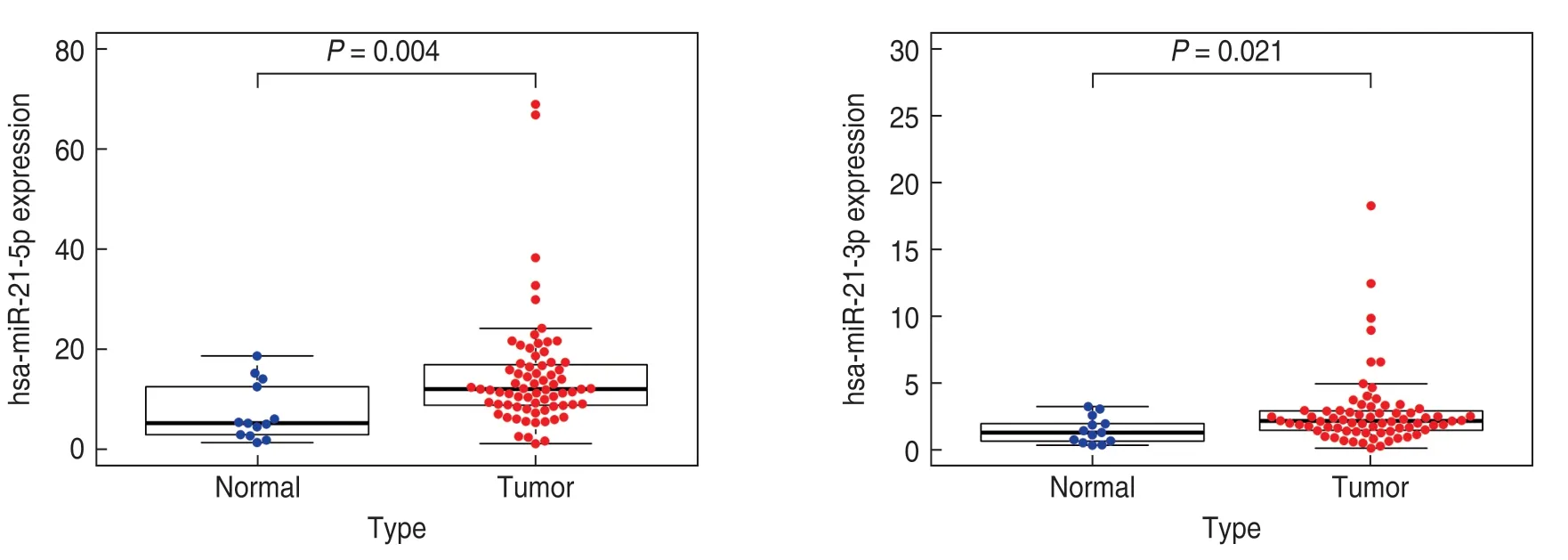
Fig.1 The expression levels of miR-21-3p and miR-21-5p.The gene expression profiling data of OSCC tissues and normal samples in TCGA database were chosen to analyze the mRNA levels of miRNA-21-5p (P=0.04) and miRNA-21-3p (P=0.021)
Literature review
A total of 304 documents were obtained from the online database.A total of 88 duplicate documents were removed by two authors,leaving 216 documents;168 articles were initially screened by reading document titles,keywords,and abstracts,and 136 documents were retained;41 documents were eliminated by reading the full text and following the exclusion rules.Finally,a total of seven articles,including 609 studies (359 OSCC patient groups and 250 control groups) were included in the metaanalysis.A flow chart of the literature selection is shown in Fig.2.The basic information of the seven included meta-analysis documents and the results of QUADAS-2.The results of the literature quality evaluation are shown in Table 1.
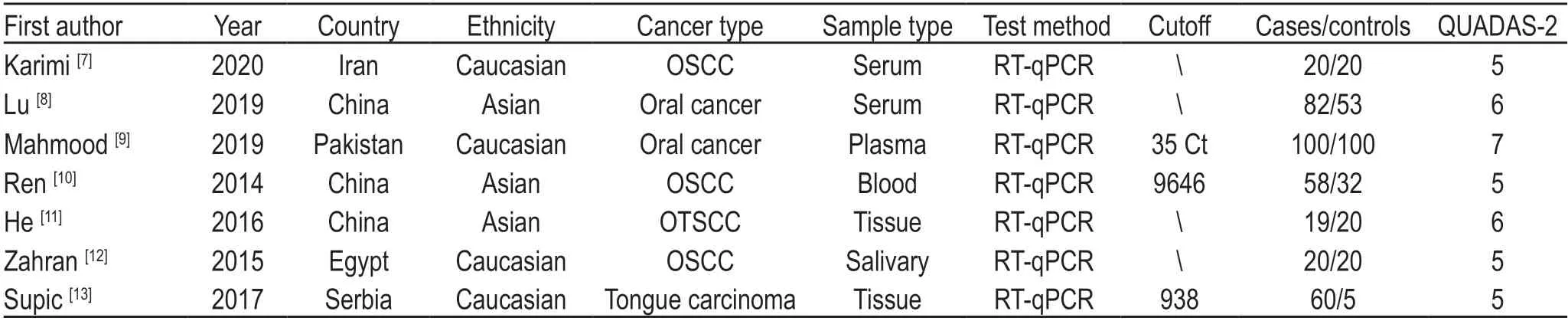
Table 1 Characteristics of publications included in the meta-analysis
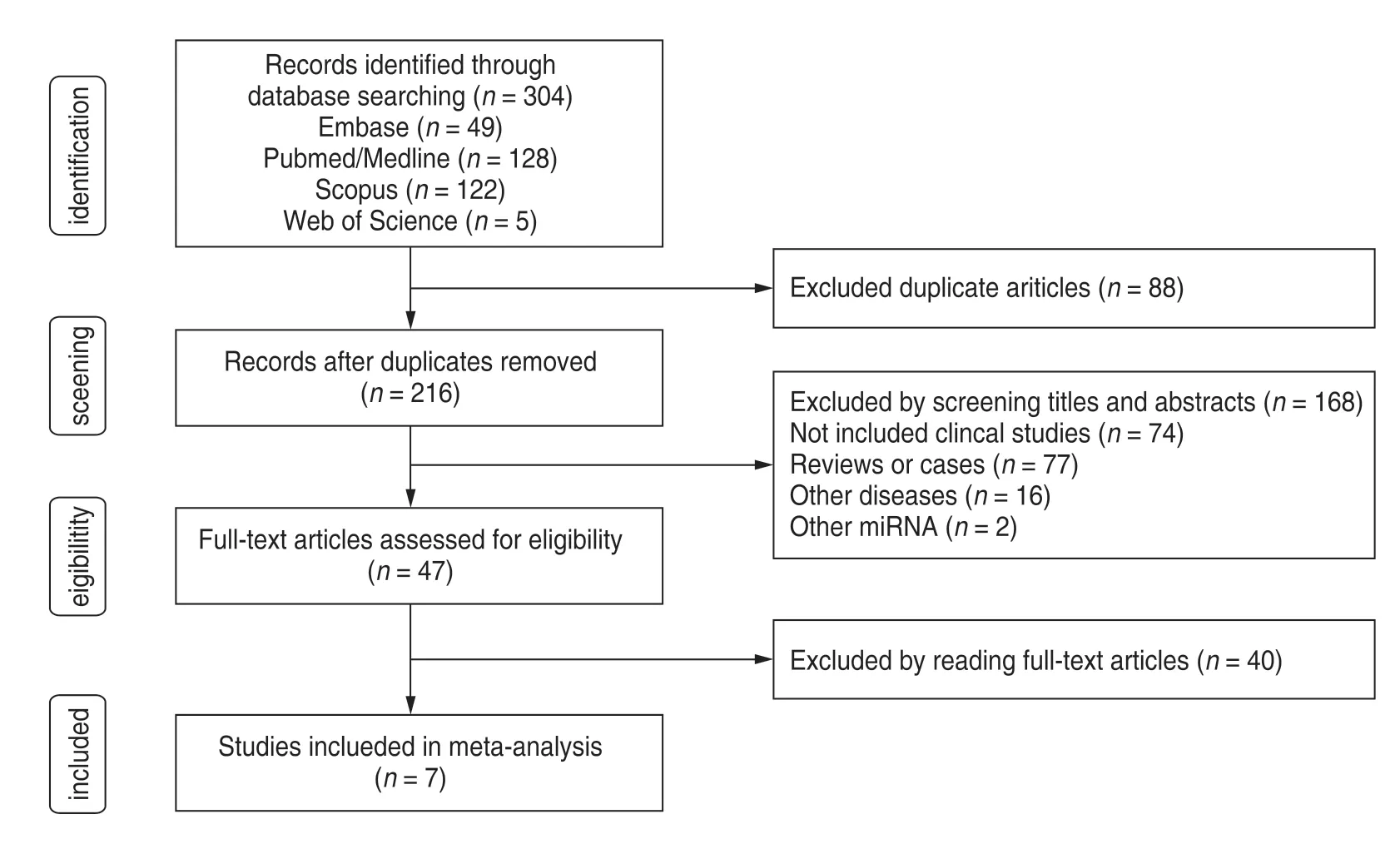
Fig.2 Flow chart of articles selection
Threshold effect and heterogeneity analysis
This study examined the threshold effect by drawing the ROC curve and calculating the Spearman correlation coefficient between the logarithm of sensitivity and the logarithm of (1-specificity).The results showed that the ROC curve did not reveal a shoulder-arm-like distribution(Fig.3);Spearman’s correlation coefficient was 0.19,and thePvalue was 0.04,both of which indicate no threshold effect;I2=94% indicated heterogeneity,and the metaanalysis revealed heterogeneity caused by non-threshold effects.Since only seven studies were included in this meta-analysis,meta-regression analysis could not be performed to investigate the source of heterogeneity.

Fig.3 ROC curve of miR-21
Analysis of meta consolidated statistics
The pooled sensitivity and specificity of miR-21 for the diagnosis of OSCC were 0.77 (95% CI,0.58–0.89) and 0.76 (95% CI,0.57–0.88;Fig.4),and the PLR was 3.34(95% CI,1.58–7.08),NLR was 0.31 (95% CI,0.15–0.63;Fig.5),and DOR was 10.75 (95% CI,2.85–40.51;Fig.6).The AUC of miR-21 was 0.83 (95% CI,0.80–0.86;Fig.7).These results indicated that miR-21 was highly accurate at differentiating OSCC patients from controls.To assess the clinical utility of the index test,Fagan nomograms were used to predict the increasing inerrability of a positive diagnosis using the value of the test.As shown in Fig.8,the pre-test probability was 50%,and a positive result of post-test probability was raised to 77%,whereas a negative result of post-test probability decreased to 24%.All pooled estimates indicated that miR-21 had a relatively moderate to high accuracy in distinguishing OSCC patients from healthy individuals in this analysis.
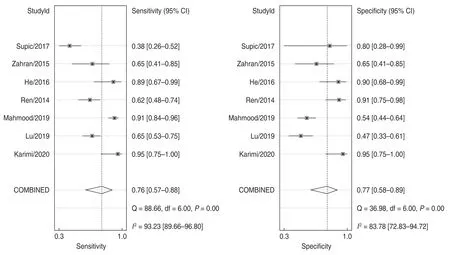
Fig.4 The sensitivity and specificity of miR-21
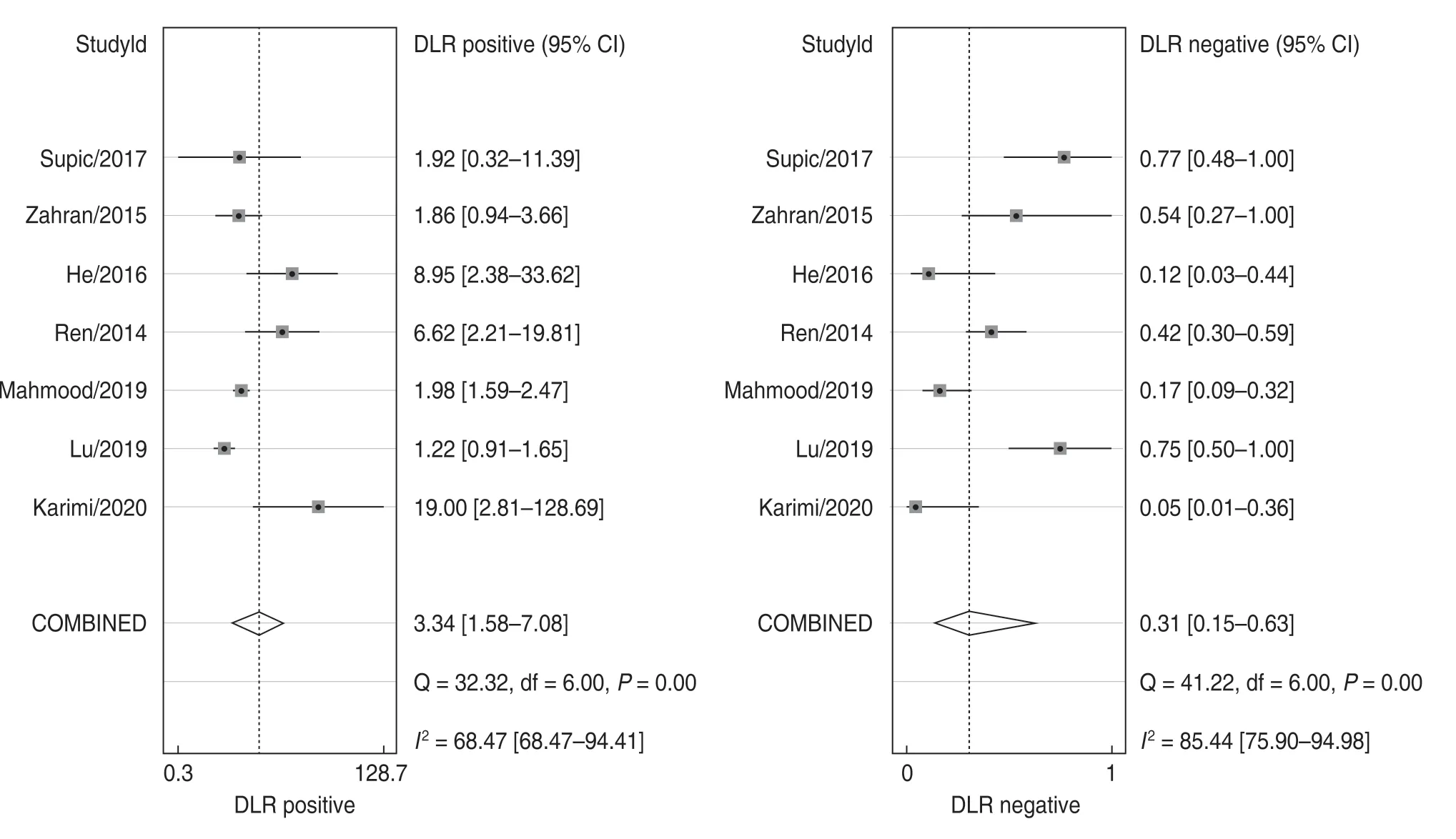
Fig.5 The PLR and NLR values of miR-21

Fig.6 The DOR value of miR-21

Fig.7 SROC curve of miR-21
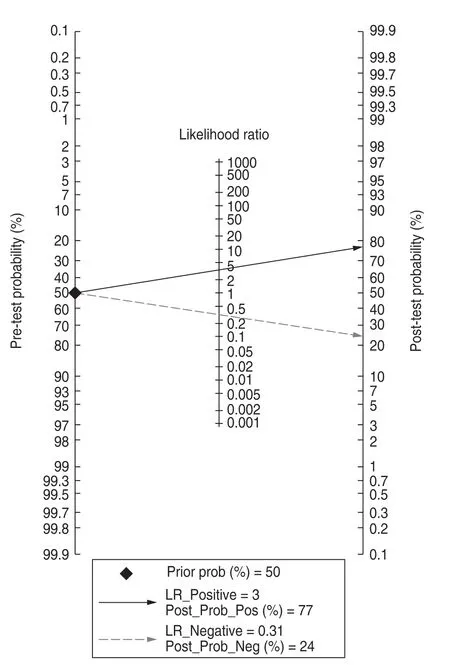
Fig.8 Fagen nomogram of miR-21
Assessment of publication bias
The results of Deeks’ funnel chart analysis using Stata are shown in Fig.9.The results showed that the slope coefficient wasP=0.54,suggesting no significant publication bias among the documents included in the meta-analysis.
MiR-21 target gene prediction analysis
The number of potential miR-21 target genes predicted by the three online databases,TargetScan,miRDB,and PicTar,were 4048,1064,and 137,respectively,and a Venn diagram was drawn to take the intersection of the above results,and 58 predicted target genes were obtained(Fig.10).
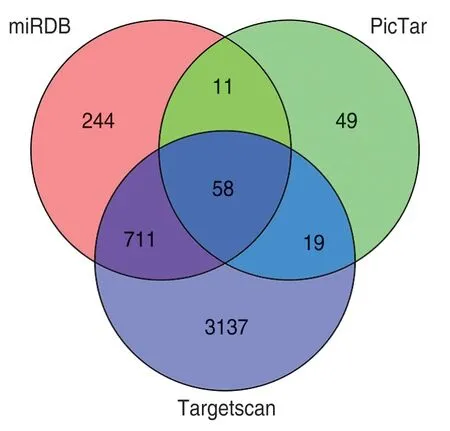
Fig.10 Venn diagram of predicted target genes
Prediction of the GO function annotation for the potential target gene
GO analysis was performed on 58 target genes,and biological pathway enrichment analysis was performed using functional annotation in the DAVID database.Based on analysis of the whole human genome,we identified that the target genes of miR-21 were significantly enriched in 28 functional pathways (P< 0.01),of which 47 intersection target genes were enriched in protein binding functional pathways,and 30 were enriched in the nucleus functional pathway (Fig.11).
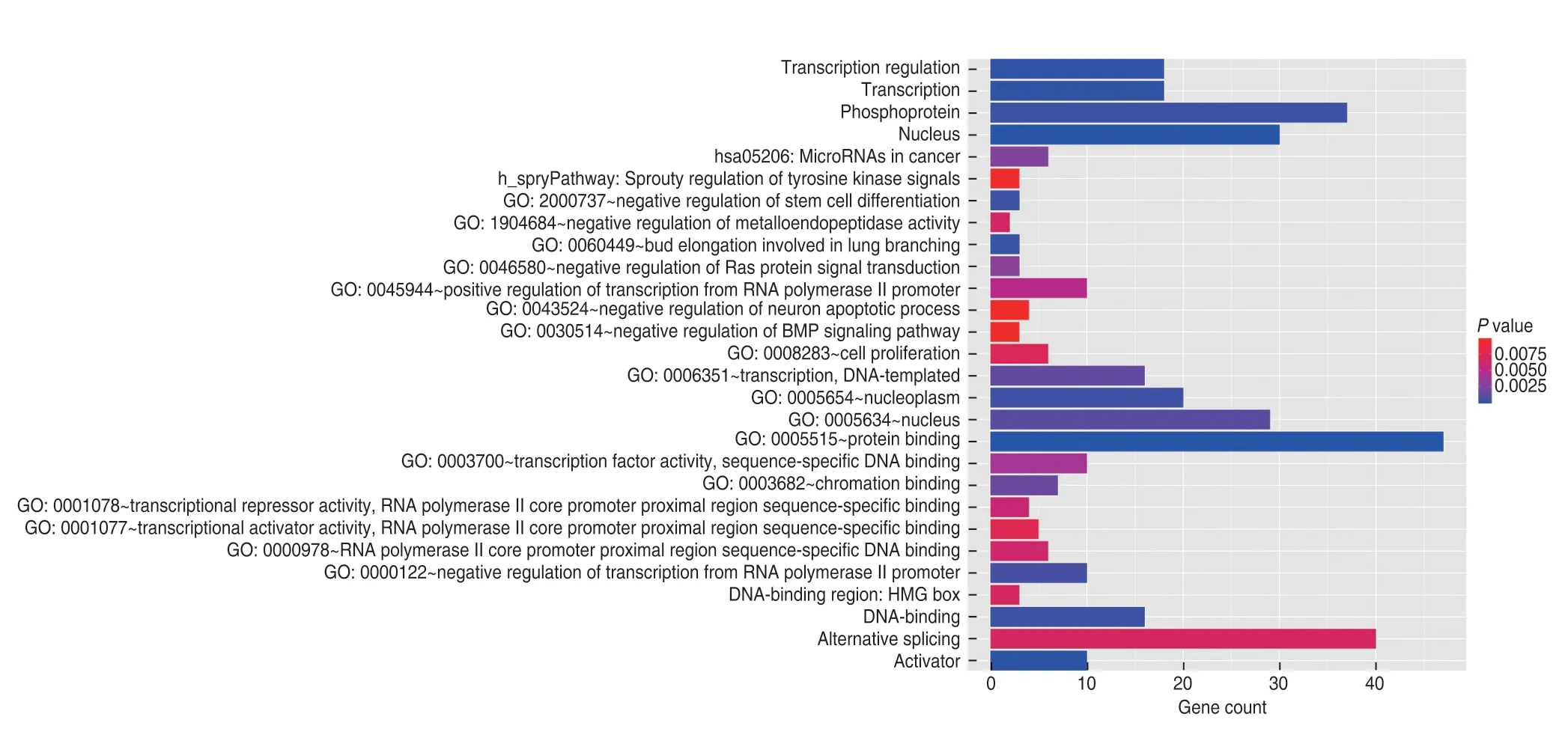
Fig.11 GO function annotation diagram of potential target genes
Discussion
OSCC has a high morbidity and fatality rate;therefore,early diagnosis of the disease and effective prognosis of patients are particularly important[14].Traditional diagnostic examinations are expensive and have poor sensitivity and specificity;therefore,a new approach is required.As a new OSCC biomarker,miRNAs are involved in cell growth,development,differentiation,and apoptosis,and their expression is closely related to the diagnosis,staging,progression,prognosis,and response to treatment[15].This is expected to become a therapeutic target for most diseases and is an important step towards gene therapy for human diseases[16].Among them,miR-21 is a dysregulated miRNA that has been studied in OSCC,and its overexpression in serum or tissue is related to tumor size and distant metastasis.Studies have shown that miR-21 can regulate a variety of cancer-related target genes,and the serum miR-21 of OSCC patients is upregulated significantly,which could be used as a biomarker of OSCC prognosis[9,17].In this study,the expression of miR-21-3p and miR-21-5p was first analyzed in OSCC and normal tissues,which illustrated the importance of miR-21 in OSCC patients.
The meta-analysis in this study was used to evaluate the diagnostic value of miR-21 in OSCC testing.The combined PLR was 3.34 (95% CI,1.58–7.08),NLR was 0.31 (95% CI,0.15–0.63),and the positive rate of miR-21 in the OSCC case group was 3.3 times compared to that of the control group;the negative rate of miR-21 was 31% of that in the control group;and the DOR was 10.75 (95% CI,2.85–40.51).The above results indicated that miR-21 as a biomarker for the diagnosis of OSCC is highly reliable and accurate,and its clinical value is considerable.Fagan’s nomogram revealed that if the pretest probability was 50%,the positive probability after the test increased to 77% when the PLR was 3.3,and the negative probability after the test decreased to 24% when the NLR was 0.31,indicating miR -21 is relatively reliable for cancer detection and treatment.
The discussion of heterogeneity in this study may be restricted by several limitations,as follows:(1) The number of available studies and the number of participants were small;(2) The data are mainly from Asian and Caucasian participants,which may lead to incomplete ethnic coverage;(3) Sample collection was performed via various methods,including blood,saliva,and tissues,which may cause differences in the results;(4) The cutoff value of miR-21 could not be determined as a whole,because each study used different cut-off values:(5) The analysis of this study was retrospective,and selective bias can reduce the credibility of the results;(6) Published research only contained English,which may lead to the neglect of research published in other languages.
Furthermore,prediction analysis revealed that miR-21 has 58 potential target genes,which are mostly enriched in protein binding and nuclear function pathways,according to the results of the GO function annotation.In addition,six potential target genes (STAT3,PDCD4,TIMP3,SPRY2,RECK,andCDC25A) were enriched in pathway–hsa05206:microRNAs in cancer,and OSCC is a type of malignant tumor,indicating that there is a strong correlation between miR-21 and OSCC.
In summary,the results of this meta-analysis revealed that miR-21 can effectively distinguish OSCC patients from healthy controls and could potentially be used as a supplement to improve the accuracy of existing diagnostic methods.Future research should focus on the combined use of miR-21 and other biomarkers to further improve the accuracy of OSCC diagnosis.
Conflicts of interest
The authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
 Oncology and Translational Medicine2021年5期
Oncology and Translational Medicine2021年5期
- Oncology and Translational Medicine的其它文章
- Special IgD-λ type multiple myeloma based on bone marrow cell morphology:A case report
- Evaluation of endocrine therapy combined with intensity modulated radiation therapy in patients with advanced prostate cancer
- CircBAGE2 (hsa_circ_0061259) regulates CCND1 and PDCD10 expression by functioning as an miR-103a-3p ‘sponge’ to alter the proliferation and apoptosis of prostate cancer cells*
- SMARCC1 copy number variation is related to metastatic colon cancer:an investigation based on TCGA data*
- Ultrasound-guided No Touch liver pedicle microwave ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment
- Cone beam computed tomography-guided differences among registration methods for lung cancer and the effects of tumor position,treatment model,and tumor size on positioning errors*
