全球特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育特征及其控制因素
屈 童,黄志龙,王 瑞,谭思哲,李志远,郭小波,赵 静,潘永帅
全球特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育特征及其控制因素
屈 童1,2,黄志龙1,2,王 瑞1,2,谭思哲3,李志远1,2,郭小波4,赵 静1,2,潘永帅1,2
(1. 中国石油大学(北京) 油气资源与探测国家重点实验室,北京 102249;2. 中国石油大学(北京) 地球科学学院,北京 102249;3. 中海石油(中国)有限公司上海分公司,上海 200335;4. 西安石油大学 地球科学与工程学院,陕西 西安 710065)
特提斯域构造活动背景控制下发育一系列煤系烃源岩发育盆地,且环太平洋带古近纪和新近纪煤多以“富氢”为特征,生烃潜力巨大,这一类煤系是我国东南沿海含油气盆地重要的烃源岩,因此,对特提斯背景下的煤系烃源岩发育特征及其控制因素进行系统总结尤为重要。通过系统分析特提斯域煤系烃源岩的发育时代、环境、地球化学特征及生物标志化合物特征,归纳总结影响煤系烃源岩发育的控制因素,明确煤系烃源岩的有利发育条件及优质源岩形成的控制因素。结果表明:特提斯域控制下的煤系烃源岩主要发育于东南亚沿海地区拉张背景下的盆地,多发育于断陷时期的海陆过渡相沉积环境,发育年代与特提斯构造活动时期吻合;煤系烃源岩发育受古植物、古环境、岩相古地理、陆源有机质供给、构造活动强度、沉积–沉降速率等多因素共同控制,各因素相互联系,相互影响,将其归纳为母源因素、构造–沉积因素及保存因素3类;富含壳质组和富氢镜质体的植物类型是富氢煤形成的必要母源条件,有利的聚煤环境及稳定构造背景是煤系烃源岩大规模发育的关键因素,合适的水体条件和还原环境是有机质得以保存的重要因素;我国东南沿海盆地煤系烃源岩生烃潜力巨大,东海盆地西湖凹陷煤系富含树脂体,珠江口盆地煤系富含孢子及花粉,琼东南盆地发育广泛的煤系泥岩,勘探前景巨大。
特提斯域;煤系烃源岩;分布特征;发育特征;控制因素
特提斯域演化对重建岩相古地理与油气勘探具有重要意义,前人关于特提斯域含油气盆地分布、油气成藏特征、烃源岩形成环境与发育特征及其影响因素已有大量研究[6-7,9,13-18],主要认为煤系烃源岩发育受控于沉积–沉降速率、边界断层规模、陆源有机质供给、有机质保存条件、构造活动强度、岩相古地理条件等因素[16-20]。不同盆地煤系烃源岩发育的控制因素也有所差异,田杨等[21](2019)在对东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖组煤系烃源岩发育模式的研究中认为,煤系烃源岩主要受沉积–沉降速率、母质来源及有机质保存条件的控制,而沈文超[22](2018)则认为西湖凹陷平湖组煤系烃源岩主要受古气候、古植物、古构造及古地理因素控制;周宝昌[20](1983)研究鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪煤系源岩发育规律时认为,其发育主要受构造、岩相古地理及古河道控制;刘玉虎等[23](2012)认为吐哈盆地侏罗纪煤系烃源岩主要受沉积古地理和古气候控制;任佳宇等[24](2015)认为琼东南盆地北部坳陷带崖城组煤系烃源岩主要受构造活动强度及沉降速率控制,吴飘等[19](2019)认为琼东南盆地崖城组烃源岩也受陆源有机质输入的控制;杨婷等[16](2017)在对北卡那封盆地(North Carnarvon Basin)煤系烃源岩发育特征的研究中认为,煤系烃源岩发育主要受沉积环境的影响。煤系烃源岩发育的影响因素较多,不同学者考虑的因素错综复杂,且诸多因素相互重叠,如边界断层规模与沉积–沉降速率有直接关系,边界断层规模越大,沉积–沉降速率也越大,两者所表达的含义是相同的。近年来随着我国东南沿海盆地油气勘探开发的推进,海上钻井较少制约烃源岩的研究,因此,对特提斯背景控制下的煤系烃源岩特征及其控制因素的系统梳理与总结尤为重要。笔者通过大量调研,分析特提斯背景下的煤系烃源岩发育规律,总结梳理煤系烃源岩发育的控制因素,进而明确优质烃源岩的发育背景及有利因素,以期促进我国沿海盆地烃源岩评价、优质烃源岩精准预测及煤系资源开发。
1 煤系烃源岩内涵
20世纪60年代末期,煤成烃理论的提出引起了学者们对煤系烃源岩的关注[25-26],之后煤源岩、煤系烃源岩等术语频繁出现。煤系烃源岩是指成煤环境下形成的具有生烃能力、已经生成并排出了或者正在生成和排出石油和天然气的含煤地层,主要包括煤、炭质泥岩和泥岩3种岩性,同一套煤系烃源岩通常包括这3种岩性中的几种或一种[27-28]。在海陆过渡环境中,煤系烃源岩向海的方向通常过渡为富含陆源有机质的泥岩,也可作为有效的烃源岩。
2 煤系烃源岩发育盆地的分布
在板块运动过程中,特提斯域的范围也在随之演变。中生代时华北板块、哈萨克板块与欧洲板块之间的大洋体系及劳亚大陆与冈瓦纳大陆之间的大洋体系共同构成了古特提斯域[6,11],这一时期形成了一系列的煤系烃源岩发育盆地,如我国西部的塔里木盆地和准噶尔盆地,土库曼斯坦的卡拉库姆盆地(Kalakumu Basin)及澳大利亚西北大陆架的北卡那封盆地(North Carnarvon Basin)等。之后华北板块、哈萨克板块与欧洲板块闭合形成欧亚板块,欧亚板块、北美洲板块与南部非洲板块、南美洲板块之间的大洋体系形成了现今的新特提斯域,这一时期现代深水含油气盆地大量发育于这一构造域内[29-30],而煤系烃源岩多发育于我国东南沿海、马来西亚及新加坡以东及环印度尼西亚地区,如我国东海盆地、琼东南盆地、马来西亚东部马来盆地(Malay Basin)、泰国湾盆地(Gulf of Thailand Basin)、印度尼西亚打拉根盆地(Tarakan Basin)、库泰盆地(Kutai Basin)等。总的来说,煤系烃源岩主要发育于东南亚沿海地区,沿大陆边缘呈带状分布(图1)。本次研究共调研特提斯域内煤系烃源岩发育的盆地33个、42套煤系,煤系烃源岩主要发育于弧后盆地、被动大陆边缘裂谷盆地及陆内裂陷盆地等区域拉张应力场控制下的盆地,多发育于断陷时期的海陆过渡相沉积环境(图2)。
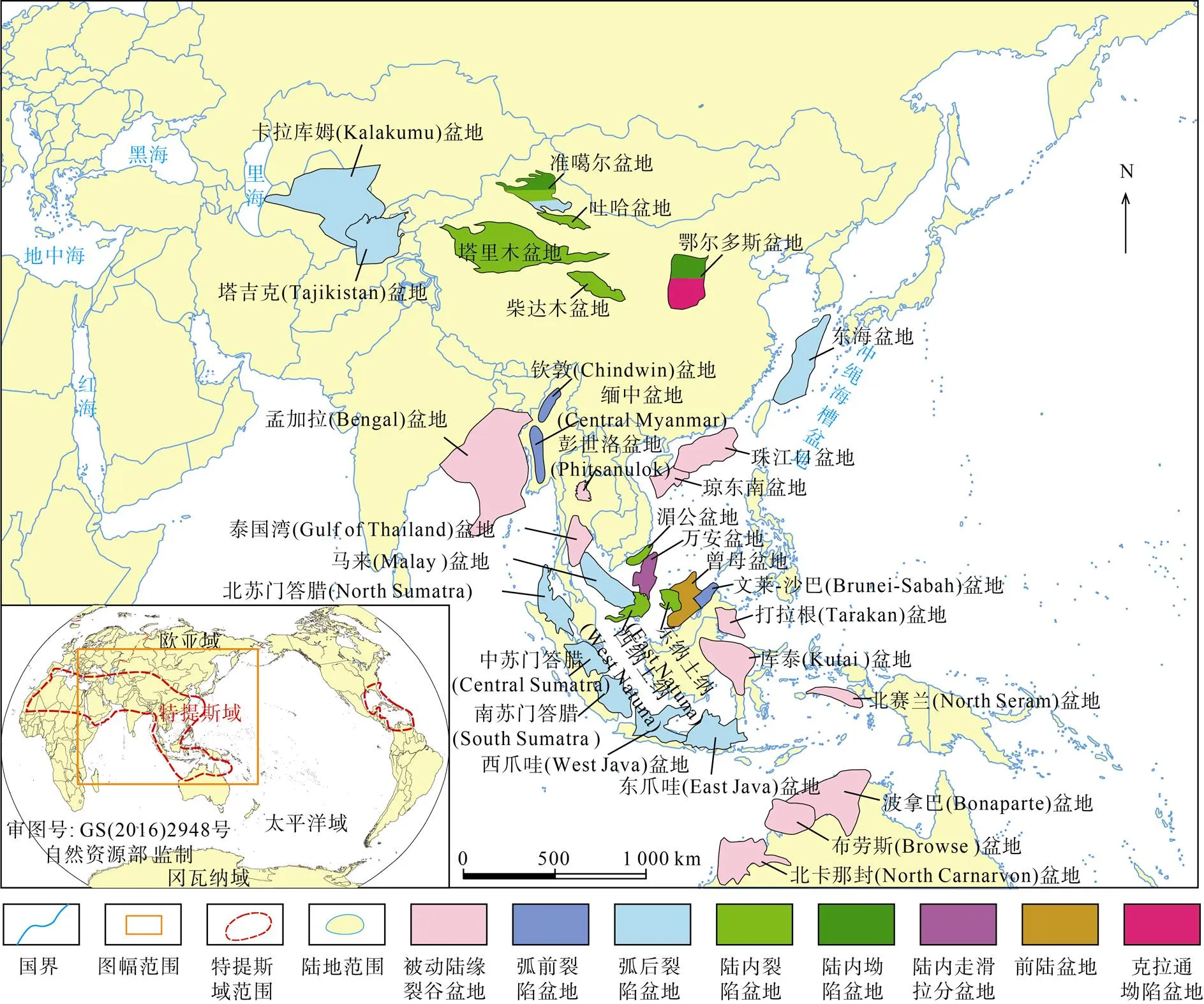
图1 特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育盆地分布

图2 煤系烃源岩发育的盆地类型、构造和沉积环境统计直方图
3 煤系烃源岩特征
3.1 煤系烃源岩发育时代与环境
煤系烃源岩是重要的生烃源岩,煤系烃源岩发育盆地资源量巨大,如中苏门答腊盆地(Central Sumatra Basin)、文莱–沙巴盆地(Brunei-Sabah Basin)、库泰盆地等均为世界级富油气盆地[31-33]。煤系烃源岩在特提斯域广泛分布,发育时代为石炭系–新近系,主要发育于侏罗系、始新统–中新统(图3),其发育时代与特提斯域活动时期相吻合,晚古生代至中生代古特提斯活动时期,煤系烃源岩主要发育于侏罗系,晚中生代至新生代新特提斯活动时期,煤系烃源岩主要发育于始新统–中新统(表1)。区域上,由西北向东南方向,煤系烃源岩发育时代逐渐变新,这与板块活动的先后顺序有关,石炭–二叠纪煤系烃源岩主要发育于华北板块和哈萨克板块交汇处,如准噶尔盆地;三叠–侏罗纪煤系烃源岩主要发育于华北板块中西部、欧洲板块东部及澳大利亚西北缘,如塔里木、卡拉库姆、北卡那封盆地等;新生代煤系烃源岩则主要发育于东南沿海及环印度尼西亚伸展区内,如琼东南、珠江口、库泰盆地等。由于煤系烃源岩的发育与陆源物质的供应息息相关,因此,其主要发育于陆相及海陆过渡相沉积环境,陆相沉积环境中多发育于低能静水的湖泊沼泽,而海陆过渡相主要发育于潮坪、潟湖、三角洲平原–前缘等环境,向浅海方向发育受限(表1)。
3.2 煤系烃源岩地球化学特征
煤系烃源岩岩性多样,通常包括煤、炭质泥岩及泥岩,因此其有机碳含量也变化较大,泥岩TOC最低小于0.1%,煤TOC可高达83.09%(表2),煤和炭质泥岩通常有机碳含量较高,是盆地内重要的生烃源岩,在我国东海盆地西湖凹陷、南海文莱–沙巴盆地均已证实煤和炭质泥岩是主要的生油源岩[33,62],煤系泥岩由于富含陆源有机质也可作为有效的生烃源岩,如琼东南盆地崖南凹陷、澳大利亚北卡那封盆地、布劳斯盆地(Browse Basin)均已证实富含陆源有机质的泥岩是盆地内的有效生气源岩[58,86,89]。

图3 煤系烃源岩发育时代地层统计直方图
煤系烃源岩干酪根类型多样,以Ⅱ–Ⅲ型干酪根为主,部分盆地可发育Ⅰ型干酪根,如彭世洛(Phitsanulok)、中苏门答腊、西纳土纳(West Natuna)等盆地,这些盆地主要位于南海及环印度尼西亚海域等利于浮游藻类输入的地区。值得注意的是,近海盆地煤系烃源岩以Ⅱ2、Ⅲ型为主,但也有部分煤和煤系泥岩质量较好,可达Ⅱ1型(图4),部分盆地的煤甚至可达Ⅰ型,如东海盆地西湖凹陷、马来盆地、文莱–沙巴盆地[62,68,90],这类煤系烃源岩是盆地内重要油气来源。煤在低成熟–成熟阶段通常可生成原油或凝析油,且煤活化能通常更低,生烃时间更早,可为盆地提供大量的原油来源,如东海盆地西湖凹陷、中苏门答腊盆地、东纳土纳盆地(East Natuna Basin)内低熟–成熟阶段的煤及炭质泥岩是盆地内石油的重要来源[32,62,73],煤系泥岩有机质多为Ⅱ2、Ⅲ型,有机质丰度取决于陆源物质的供给程度,是各个含油气盆地重要的源岩(表2)。
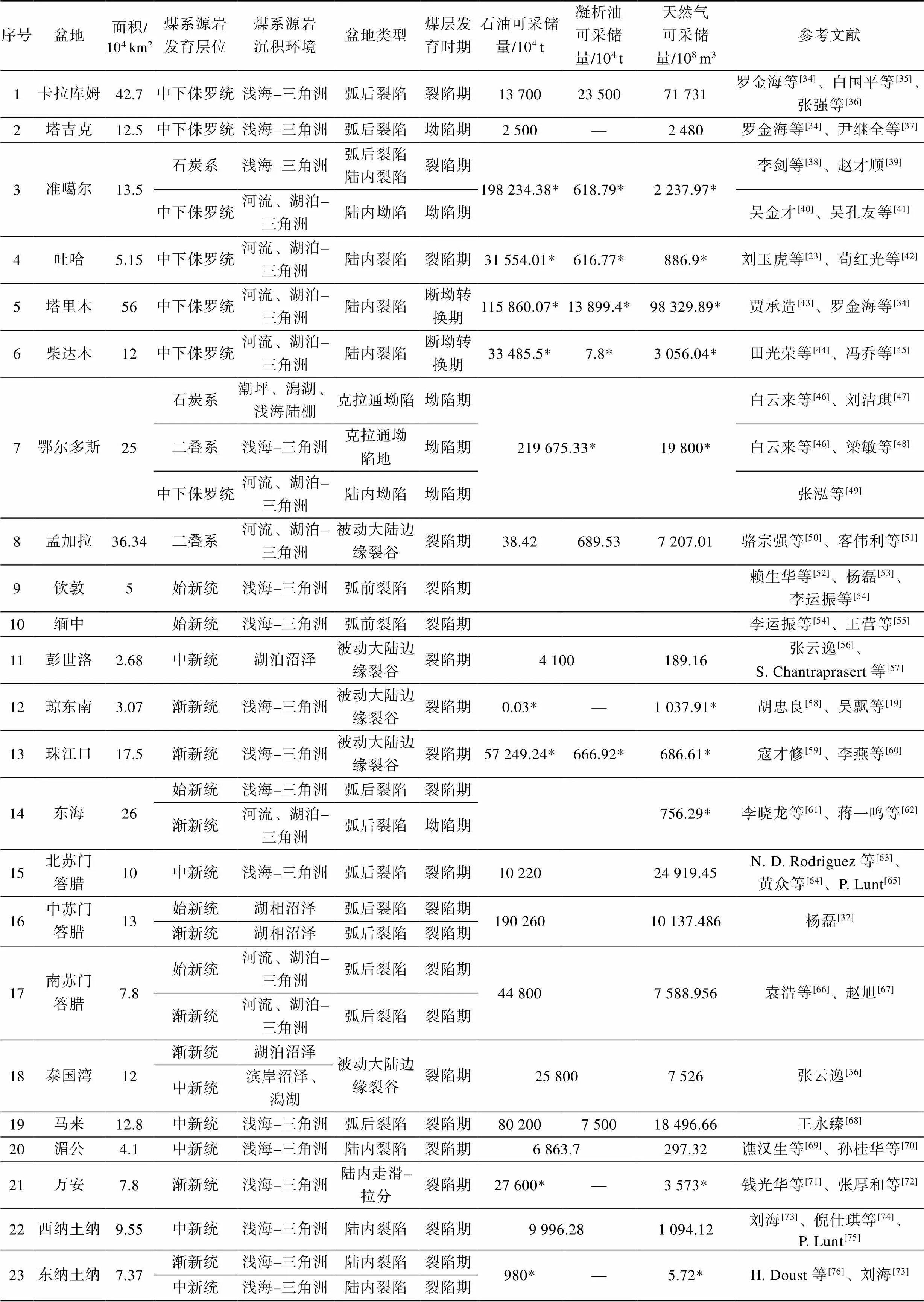
表1 特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育盆地及层位特征统计结果
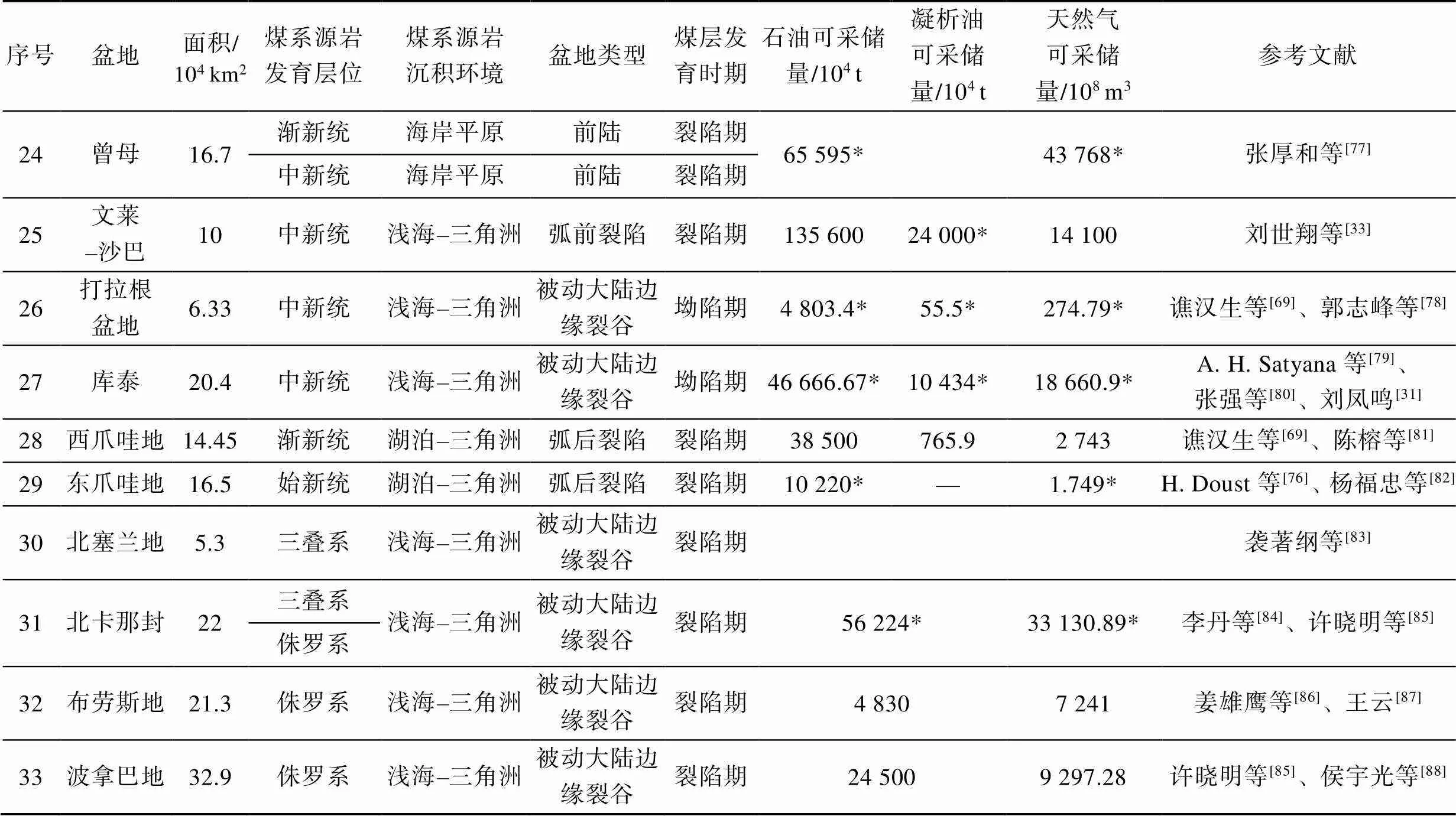
续表
注:*表示探明地质储量。
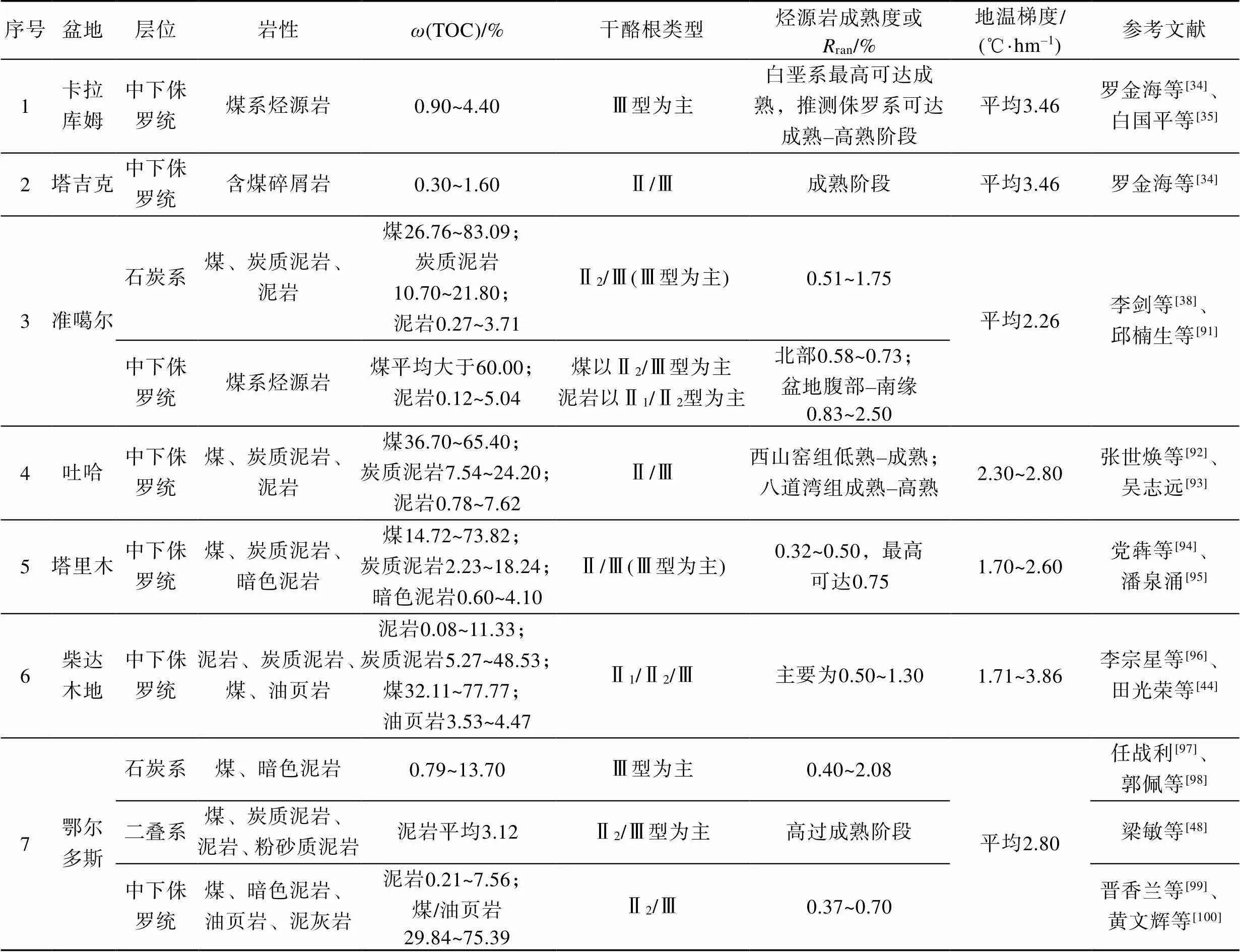
表2 特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育特征

续表

续表
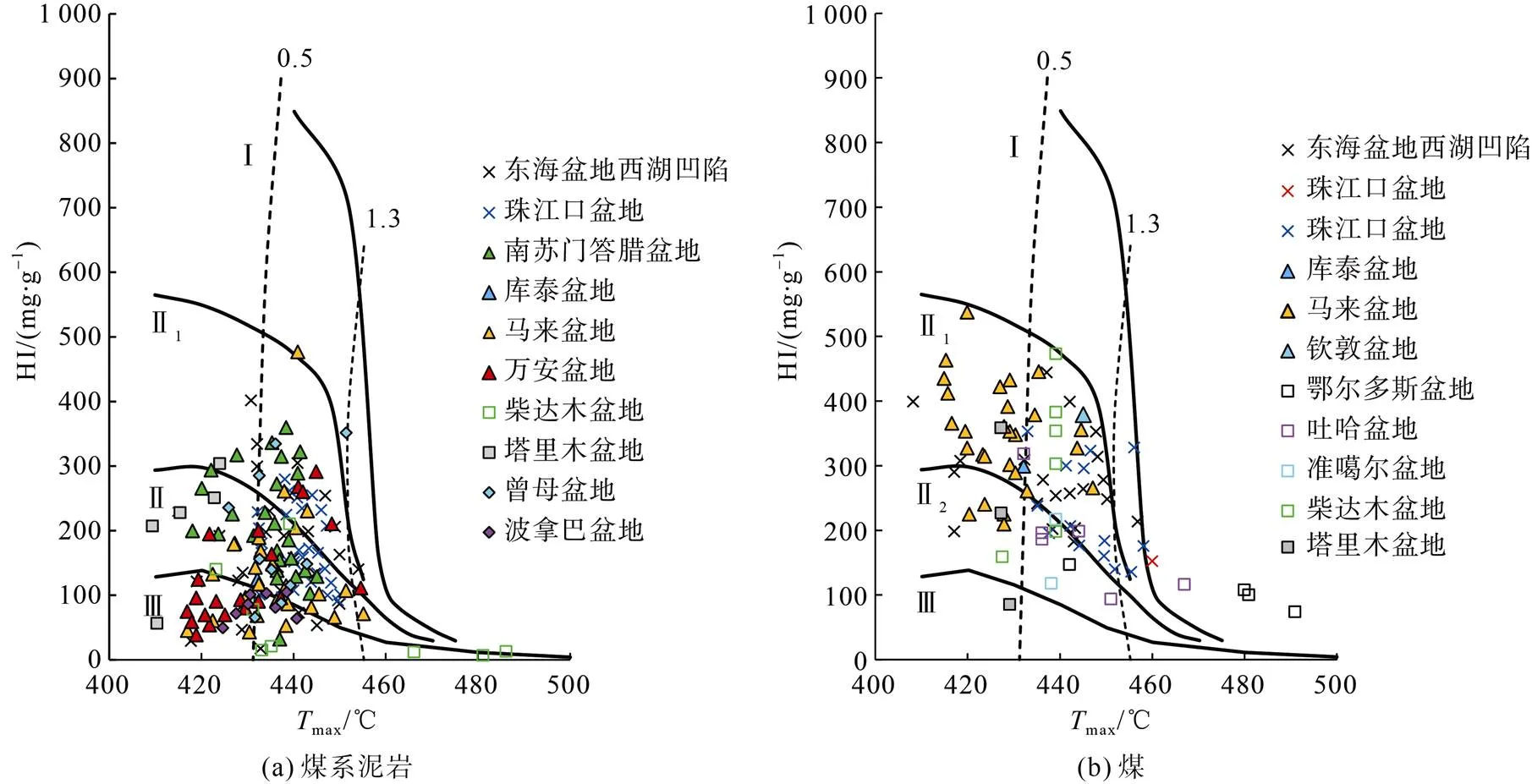
图4 特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育盆地的煤系泥岩和煤有机质类型判别(数据自文献[31,53,58,60,62,66,68,72,77,93-94,110,116-118])
3.3 煤系烃源岩生物标志化合物特征
煤系烃源岩的发育与陆源植物的输入密切相关,因此常具有高姥/植比(姥鲛烷/植烷)、C29甾烷优势及大量奥利烷、杜松烷等陆源指示化合物。高姥/植比反映氧化条件下的陆相有机质输入,琼东南、珠江口、东海西湖凹陷、钦敦(Chindwin)、北卡那封、文莱–沙巴、曾母等盆地煤系均具有高姥/植比的特征[16,22,77,119-121],钦敦盆地、琼东南盆地、东海西湖凹陷煤系烃源岩姥植比普遍大于3.0[19,22,120],珠江口盆地恩平组煤系源岩姥植比最高甚至可达9.07[119]。煤系源岩多具C29甾烷优势,反映陆源有机质的输入,在诸多盆地该特征普遍较为明显(图5)。此外,煤系烃源岩通常具有较高的奥利烷、8β-补身烷、扁枝烷、海松烷及五环三萜烷等化合物,这些化合物均可作为陆源植物输入的标志[122],在钦敦盆地、珠江口盆地珠二坳陷、琼东南盆地、曾母盆地、北苏门答腊盆地、马来盆地等均以奥利烷优势为特征[19,63,68,77,119-120],在琼东南盆地、曾母盆地、马来盆地煤系烃源岩中也富含双杜松烷[19,68,77],在东海盆地西湖凹陷煤系中存在着高含量的8β(H)-半日花烷、4β(H)-19-降异海松烷、朽松木烷、异海松烷、16β(H)-贝壳杉烷、松香烷等二萜类化合物及五环三萜烷,这些化合物均指示了陆源沉积有机质的赋存[22]。
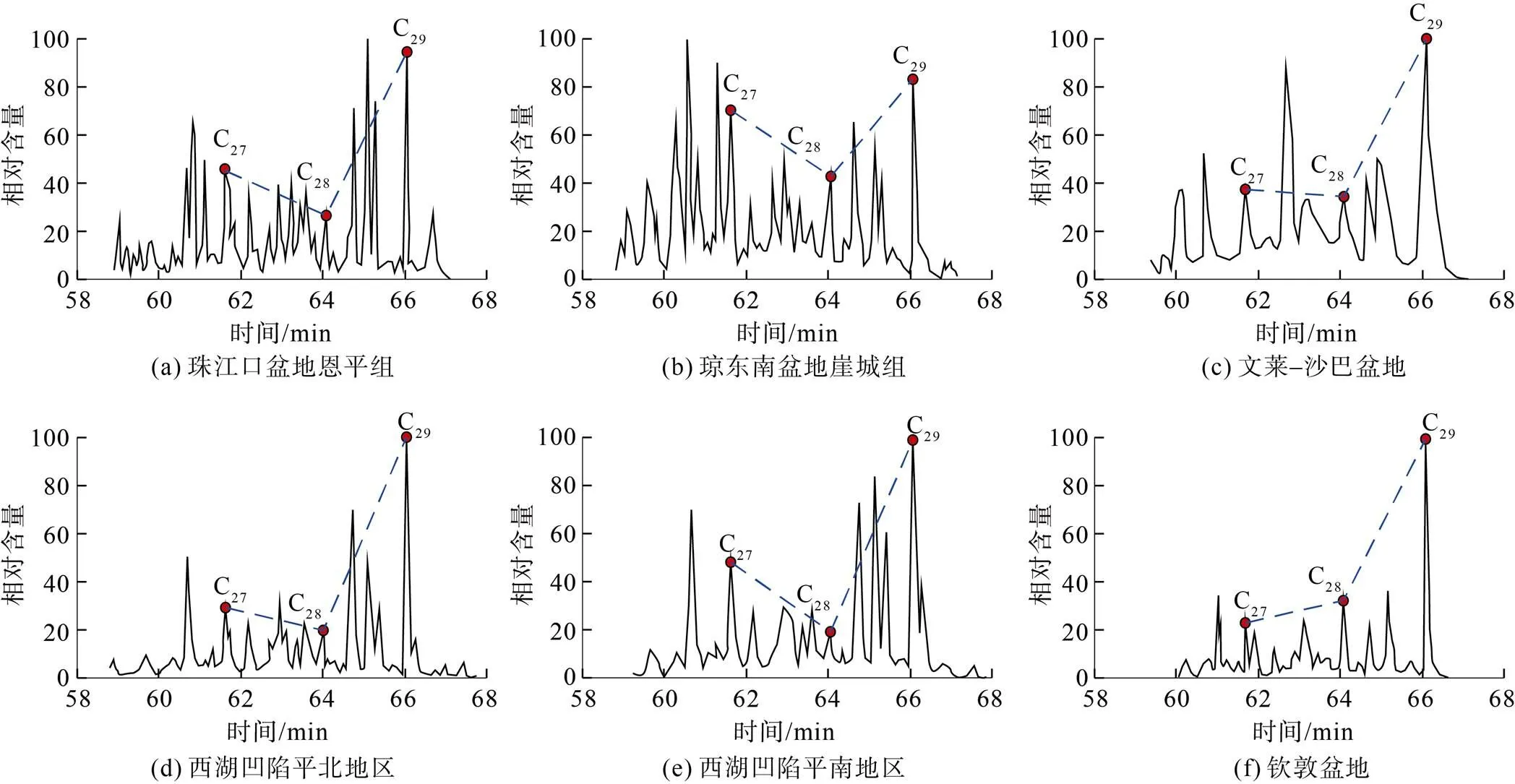
图5 典型煤系烃源岩生物标志化合物饱和烃质谱m/z 217图(自文献[62,119-121])
4 煤系烃源岩发育控制因素
在整理分析前人研究认识的基础上,笔者认为煤系烃源岩发育的控制因素可分为母源因素、构造与沉积因素、保存因素三大类。母源因素主要包括古植物、陆源碎屑及陆源有机质供给等,构造与沉积因素主要包括岩相古地理、构造活动强度、沉积–沉降速率等因素,保存因素主要包括古环境条件和成岩作用。各因素相互联系、相互影响,其他因素通过对以上因素的控制而影响煤系烃源岩的发育。
4.1 母源因素
古植物及陆源物质供给主要决定煤系烃源岩的有机质丰度及类型。古植被的繁盛程度很大程度上决定煤系烃源岩是否发育,而古植被与古气候直接相关,通常湿热气候带植被利于煤系烃源岩的形成[123]。北卡那封盆地三叠系时期处于中高纬度潮湿气候带,草本沼泽逐渐发展为森林沼泽,使得煤系烃源岩大量发育[16];东海盆地西湖凹陷孢粉相显示,从平湖组至花港组湿热气候带植物逐渐减少,从而导致平湖组聚煤好于花港组[22];琼东南盆地崖城期气候湿热,大型植被发育使得陆源有机质输入充足,促使煤系烃源岩较为发育[19]。同时古植被的类型决定了煤系烃源岩的类型及生烃潜力,曾母盆地及文莱–沙巴盆地煤系烃源岩的母质来源是红树林[121],红树林来源的有机质具有富壳质组和富氢镜质体的特征,因此曾母盆地和文莱–沙巴盆地煤系烃源岩有机质类型较好,含大量Ⅱ型干酪根,有些煤干酪根甚至为Ⅰ型(表2),生油能力强,使得这两个盆地十分富油。
综上所述,我国在林下套种中草药的栽培方面重视程度较高,很多区域工作的开展,都能够取得较好的效果。日后,应继续在林下套种中草药的栽培方面深入研究,不断的提高工作的可靠性、可行性,减少错误的操作。与此同时,林下套种中草药的栽培多项内容必须保持较高的协调性,争取创造出更高的价值。
陆源碎屑及陆源有机质的供给量直接决定了煤系泥岩及富陆源有机质泥岩的有机质丰度,陆源物质的供应又受水动力强度、类型及搬运距离等因素影响[124]。孟加拉盆地(Bengal Basin)远离陆架区,陆源有机质供应不足使得有机质含量降低[125],北卡那封盆地近物源处由于冲刷作用过强使得煤系泥岩有机质丰度低,在远端三角洲有机质丰度达到高值,之后由于水动力逐渐减弱,陆源有机质含量呈减少趋势,且在河流与海水交锋区不利于陆源有机质的沉积(图6)[84];在曾母盆地由于陆源物质呈近岸富集的特征,富陆源有机质泥岩有机质丰度较低[121],在鄂尔多斯盆地、琼东南盆地、马来盆地等均有同种现象[19-20,77]。
综上可知,古植物、陆源碎屑及陆源有机质供给等母源因素控制着煤系烃源岩有机质的性质,包括有机质类型及丰度,湿热气候条件下广泛分布大型植被有利于煤系烃源岩的形成,红树林等富含壳质组和富氢镜质体的植物类型有利于倾油型富氢煤的形成,充足的陆源有机质供给是高丰度煤系泥岩及富陆源有机质泥岩发育的关键条件。
4.2 构造与沉积因素
岩相古地理条件包括古地理单元分布及岩相分布,控制着煤系烃源岩的差异发育。古地理单元受古地貌的控制,由于地势的不均一性,通常存在多个聚煤中心,如东海西湖凹陷、鄂尔多斯盆地、吐哈盆地、北卡那封盆地[16,20,22-23]。煤系烃源岩通常发育于湖泊、三角洲、河流河道间、潮坪、潟湖等低能静水环境[23,99,126],而相对动荡水体、不利于泥炭化的环境中则形成煤系泥岩[22,99],因此,沉积环境的差异造成煤系烃源岩的岩性差异,如鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪由湖区向盆地边缘呈浅湖–湖沼–河沼的冲积平原地貌,浅湖相发育煤系泥岩,煤层欠发育,由湖沼相向河沼相煤层逐渐发育[20],在岩相古地理条件控制下,岩性的有序分布决定了其生烃潜力的差异。
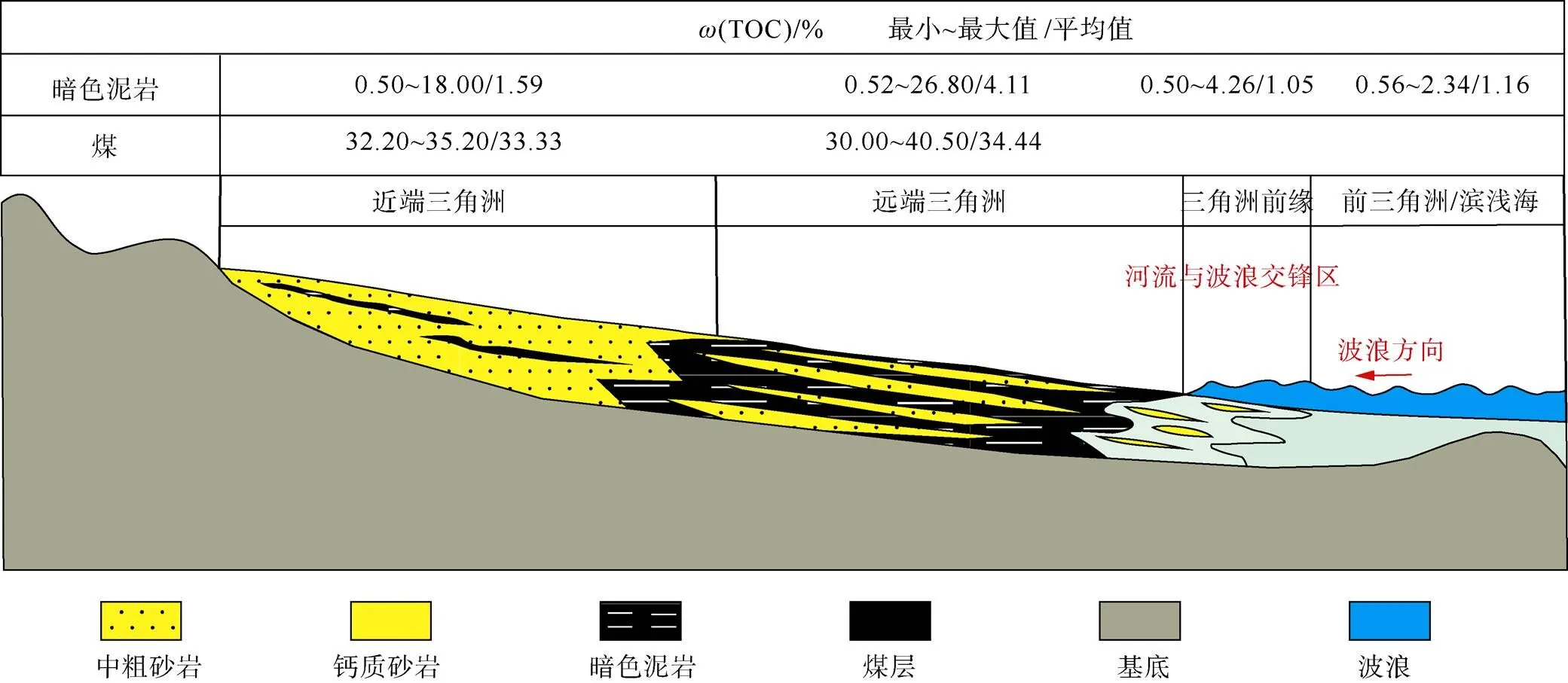
图6 北卡那封盆地Mungaroo组三角洲陆源有机质分布模式(据李丹等[84],2014改)
构造活动弱有利于煤层的发育,通常构造活动相对较弱、地层稳定沉降有利于厚层连续煤层的形成,构造活动频繁、地层沉降不稳定条件下形成的煤层多具薄、多、散(单层厚度薄、层数多、横向连续性差)的特征。珠江口盆地白云凹陷构造活动比琼东南盆地北部坳陷带弱,地层沉降更为稳定,因此白云凹陷煤层具有厚层连续的特征,而琼东南盆地煤层具有横向连续性差、厚度薄、层数多的特征[24];北卡那封盆地三叠系受盆地持续性构造沉降的影响使得煤层平面分布面积广、厚度大[16];准噶尔盆地、柴达木盆地、吐哈盆地等陆内盆地相对稳定,发育厚层稳定煤层[23,39],而陆缘盆地受板块运动影响构造频繁,多具薄、多、散的特征[127-129]。
合适的沉积–沉降速率有利于煤系烃源岩的发育。沉降速率控制可容纳空间的增加速率,进一步控制烃源岩的发育,沉降速率过大导致水体深度大,不利于泥炭的发育,沉降速率过小暴露环境氧化性强容易破坏烃源岩的发育,因此合适的沉积–沉降速率利于煤系烃源岩的发育。缅甸盆地群煤系烃源岩发育于始新统中期,为持续水进的中期,合适的水体深度使得煤系烃源岩普遍发育[54];东亚特提斯域煤系烃源岩均发育于裂谷2幕及后裂谷期(图7)[17,130],裂谷2幕为裂陷鼎盛时期,沉积–沉降速率较大,煤系烃源岩发育范围相对较局限,多发育于近物源斜坡带水深合适的地区,如我国琼东南盆地崖南凹陷崖城组、东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖组、澳大利亚西北大陆架北卡那封盆地三叠世Mungaroo组,煤系源岩均发育于近物源斜坡带或三角洲平原地区[19,22,84];后裂谷时期多为裂陷向坳陷转换的阶段,裂陷作用相对较弱,主要发育三角洲平原沼泽或滨岸平原煤系烃源岩,如文莱–沙巴盆地中新统煤系烃源岩[130]。
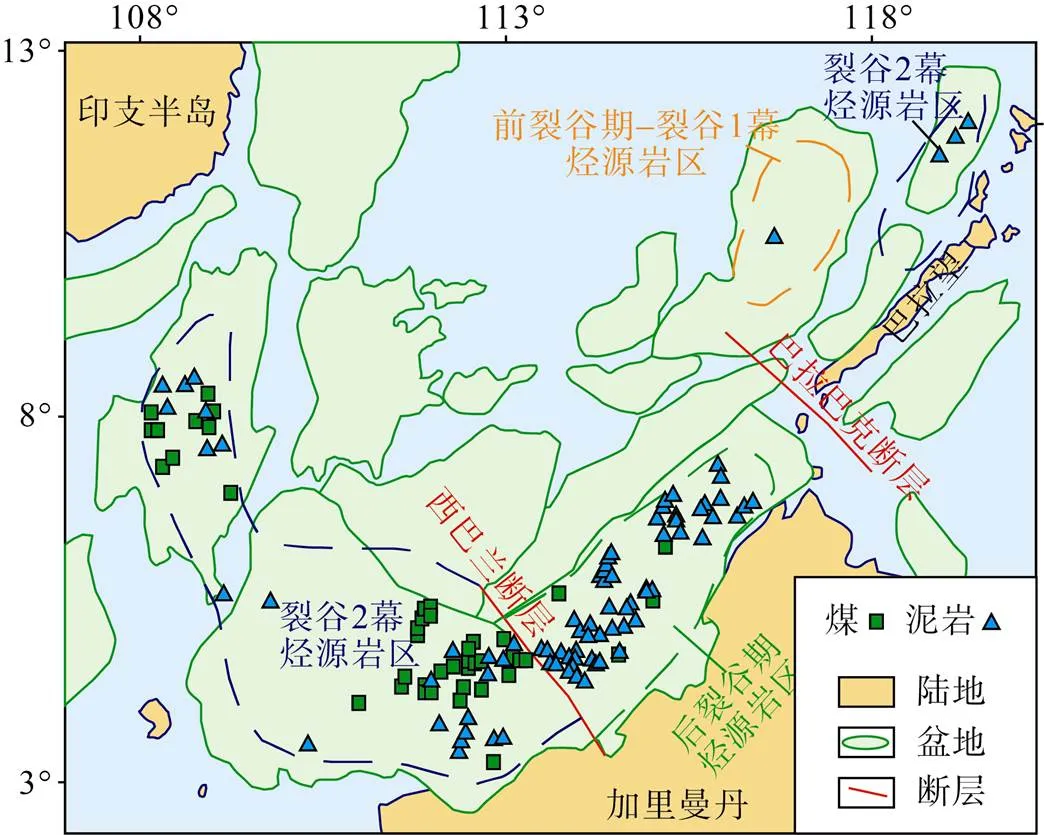
图7 东亚特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育构造区及时期分布(据杨明慧等[130],修改)
综上可知,岩相古地理、构造活动强度、沉积–沉降速率等构造–沉积因素控制着煤系烃源岩的发育特征。湖泊沼泽、三角洲平原沼泽、潟湖沼泽等环境是有利的聚煤环境,常常形成聚煤中心;构造活动相对较弱、地层稳定沉降有利于厚层连续煤层的形成,合适的沉积–沉降速率及合适的水深是煤系烃源岩发育的必要条件。
4.3 保存因素
古环境条件和成岩作用决定了煤系烃源岩是否能够保存,古环境条件包括古水体盐度、pH、Eh、氧化还原条件等,同样也受控于古气候。水体盐度、pH值及Eh值可通过对沉积物及有机质本身的改造进而影响有机质的赋存,水体盐度降低、pH的适度增加和Eh的降低有利于有机质的保存[124],卢双舫等[131](2008)认为只有在Eh值小于0的还原环境中有机质才能得以保存。成岩作用同样可以对有机质进行改造,张成君等[132](2012)、A. L. Lamb等[133](2004)认为成岩作用能降低沉积物的C/N比,使得有机质发生降解,但针对成岩作用对有机质保存的控制作用的具体研究目前仍然较少。因此,低盐度、低Eh及合适pH的水体条件及还原环境是煤系烃源岩得以保存的有利环境。
5 我国沿海盆地煤系烃源岩生烃潜力分析
我国近海特提斯域聚煤盆地主要位于东南沿海地区,包括东海陆架盆地、珠江口盆地、琼东南盆地等(图1)。我国东南沿海盆地聚煤层系相对较为发育,煤的有机质类型整体以Ⅱ1、Ⅱ2型为主(图4b),可作为主要的生油源岩,东海盆地西湖凹陷西部斜坡带已有相关油田的发现[134-135],煤系泥岩以Ⅱ2、Ⅲ型为主(图4a),可作为有效的气源岩,琼东南盆地崖城组已证实富陆源有机质泥岩,对崖13-1气田也有一定的贡献[58]。特提斯域背景下的煤系烃源岩发育盆地油气资源量丰富,中苏门答腊、库泰盆地更有世界级大油气田的发现,而我国东南沿海琼东南盆地、珠江口盆地及西湖凹陷煤系烃源岩生烃潜力较其他盆地并不差(图8),且西湖凹陷煤及炭质泥岩树脂体含量较高[62],珠江口盆地煤系源岩富含孢子及花粉[60],致使西湖凹陷及珠江口盆地煤生油潜力相对较大。因此,我国东南沿海盆地烃源岩条件十分可观,勘探前景巨大。
6 结论
a. 全球特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育的盆地主要位于东南亚沿海地区,煤系烃源岩主要发育于弧后盆地、被动大陆边缘裂谷盆地及陆内裂陷盆地等区域拉张应力场控制下的盆地,多发育于断陷时期的海陆过渡相沉积环境,主要发育于侏罗系、始新统–中新统。煤系烃源岩以Ⅱ2、Ⅲ型为主,部分可达Ⅱ1型,甚至I型,常具有高姥植比、C29甾烷优势特征,富含奥利烷、海松烷、杜松烷等陆源指示化合物。
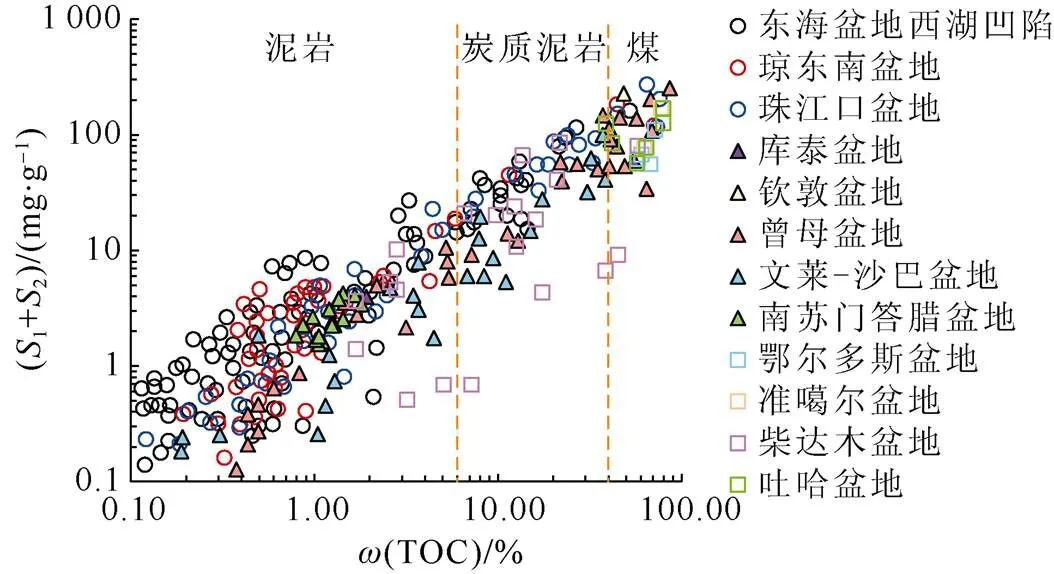
图8 煤系烃源岩TOC含量与S1+S2关系(数据自文献[19,31-32,58,60,62,66,75,93,110,116-117,121])
b. 煤系烃源岩发育受母源因素、构造与沉积因素和保存因素控制,母源因素控制着煤系烃源岩的质量,湿热气候条件下广泛分布大型植被有利于煤系烃源岩的形成,红树林等富含壳质组和富氢镜质组的植物类型有利于倾油型富氢煤的形成,充足的陆源有机质供给是高丰度煤系泥岩及富陆源有机质泥岩发育的关键条件;构造–沉积因素控制着煤系烃源岩的发育程度,湖泊沼泽、三角洲平原沼泽、潟湖沼泽等环境常形成聚煤中心,构造活动相对较弱、地层稳定沉降、合适的沉积–沉降速率及合适的水深是煤系烃源岩发育的必要条件;低盐度、低Eh及合适pH的水体条件及还原环境是煤系烃源岩得以保存的有利环境。这对钻井较少的海上盆地的烃源岩评价及烃源岩预测有重要意义。
c. 我国东南沿海琼东南盆地、珠江口盆地及西湖凹陷煤系烃源岩生烃潜力巨大,但不同盆地煤系烃源岩仍各具特色,如西湖凹陷煤系烃源岩富树脂体,珠江口盆地富孢子及花粉,不同的母质特征其生烃潜力及倾油/倾气性皆有差异,这一方面需结合不同盆地背景特征进一步深入研究。
[1] 陈智梁. 特提斯地质一百年[J]. 特提斯地质,1994,18:1–22.
CHEN Zhiliang. One hundred years of Tethys geology[J]. Tethyan geology,1994,18:1–22.
[2] 潘桂棠. 全球洋-陆转换中的特提斯演化[J]. 特提斯地质,1994,18:23–40.
PAN Guitang. The evolution of Tethys in the global ocean continent transition[J]. Tethyan geology,1994,18:23–40.
[3] MEULENKAMP J E,SISSINGH W. Tertiary palaeogeography and tectonostratigraphic evolution of the Northern and Southern Peri-Tethys platforms and the intermediate domains of the African-Eurasian convergent plate boundary zone[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2003,196(1/2):209–228.
[4] WANG Zhongwei,WANG Jian,FU Xiugen,et al. Sedimentary successions and onset of the Mesozoic Qiangtang rift basin(Northern Tibet),Southwest China:Insights on the Paleo- and Meso-Tethys evolution[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,102:657–679.
[5] BORRUEL-ABADíA V,LóPEZ-GóMEZ J,DE LA HORRA R,et al. Climate changes during the Early-Middle Triassic transition in the E. Iberian plate and their palaeogeographic significance in the western Tethys continental domain[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2015,440:671–689.
[6] 甘克文. 特提斯域的演化和油气分布[J]. 海相油气地质,2000,5(3/4):21–29.
GAN Kewen. Evolution and hydrocarbon distribution of Tethys domain[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2000,5(3/4):21–29.
[7] 丘东洲,谢渊,李晓清,等. 亚洲特提斯域岩相古地理与油气聚集地质特征[J]. 海相油气地质,2009,14(2):41–51.
QIU Dongzhou,XIE Yuan,LI Xiaoqing,et al. Geological characteristics of lithofacies paleogeography and hydrocarbon accumulation in Asian Tethyan tectonic domain[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2009,14(2):41–51.
[8] 吴福元,万博,赵亮,等. 特提斯地球动力学[J]. 岩石学报,2020,36(6):1627–1674.
WU Fuyuan,WAN Bo,ZHAO Liang,et al. Tethys geodynamics[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2020,36(6):1627–1674.
[9] 丘东洲. 亚洲特提斯域油气聚集地质特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2007,27(2):1–8.
QIU Dongzhou. Geological characteristics of the hydrocarbon accumulation in the Tethyan tectonic domain[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2007,27(2):1–8.
[10] KLEMME H D,ULMISHEK G F. Effective petroleum source rocks of the world:Stratigraphic distribution and controlling depositional factors[J]. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletion,1991,75(12):1809–1851.
[11] 叶和飞,罗建宁,李永铁,等. 特提斯构造域与油气勘探[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2000,20(1):1–27.
YE Hefei,LUO Jianning,LI Yongtie,et al. Tethyan tectonic domain and petroleum exploration[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2000,20(1):1–27.
[12] 李思田,路凤香,林畅松,等. 中国东部及其邻区中、新生代盆地演化及地球动力学背景[M]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,1997.
LI Sitian,LU Fengxiang,LIN Changsong,et al. Mesozoic Cenozoic basin evolution and geodynamic background in eastern China and its adjacent areas[M]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press,1997.
[13] LI Sanzhong,ZHAO Shujuan,LIU Xin,et al. Closure of the Proto-Tethys ocean and Early Paleozoic amalgamation of microcontinental blocks in East Asia[J]. Earth Science Reviews,2018,186:37–75.
[14] 赫鹏飞,曹华. 北非地区特提斯洋演化特征及对油气成藏的控制[J]. 内蒙古石油化工,2018,1(5):120–124.
HE Pengfei,CAO Hua. Evolution characteristics of Tethys ocean and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation in North Africa[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry,2018,1(5):120–124.
[15] 赫鹏飞,周航辉. 北非特提斯域油气地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 石油化工应用,2018,37(8):73–77.
HE Pengfei,ZHOU Hanghui. Petroleum geology characteristics and exploration prospect in the North Africa Tethyan tectonic domain[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application,2018,37(8):73–77.
[16] 杨婷,康洪全,刘东旭,等. 北卡那封盆地沉积演化规律与烃源岩发育特征[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2017,39(5):81–91.
YANG Ting,KANG Hongquan,LIU Dongxu,et al. The sedimentary facies evolution and the development characteristics of source rocks’ in North Carnarvon Basin,Australia[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition),2017,39(5):81–91.
[17] 刘志峰,杨东升,王升兰,等. 中国近海盆地三幕裂陷有序性及其油气勘探意义[J]. 海洋工程装备与技术,2019,6(增刊1):283–292.
LIU Zhifeng,YANG Dongsheng,WANG Shenglan,et al. Sequence of rifting in three episodes of offshore basins in China and its significance for oil and gas exploration[J]. Ocean Engineering Equipment and Technology,2019,6(Sup.1):283–292.
[18] LI Yang,ZHANG Jinliang,LIU Yang,et al. Organic geochemistry,distribution and hydrocarbon potential of source rocks in the Paleocene,Lishui Sag,East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,107:382–396.
[19] 吴飘,侯读杰,甘军,等. 琼东南盆地深水东区渐新统烃源岩发育模式[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(3):633–647.
WU Piao,HOU Dujie,GAN Jun,et al. Developmental model of Oligocene source rock in the Eastern deep-water area of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2019,37(3):633–647.
[20] 周宝昌. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪聚煤规律[J]. 陕西地质,1983,1(1):38–46.
ZHOU Baochang. Jurassic coal accumulation rule in Ordos Basin[J]. Geology of Shaanxi,1983,1(1):38–46.
[21] 田杨,叶加仁,雷闯,等. 断陷盆地海陆过渡相烃源岩发育模式:以西湖凹陷平湖组为例[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(3):898–908.
TIAN Yang,YE Jiaren,LEI Chuang,et al. Hydrocarbon source rock development model of marine terrestrial transitional facies in fault basin:A case study of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag[J]. Editorial Committee of Earth Science,2019,44(3):898–908.
[22] 沈文超. 西湖凹陷古近系煤的聚集模式及沉积有机相研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2018.
SHEN Wenchao. The coal accumulation model and sedimentary organic facies of Paleogene coal in the Xihu Depression[D]. Beijing:China University of Mining and Technology(Beijing),2018.
[23] 刘玉虎,赵丹丹,刘兴旺,等. 吐哈侏罗纪原型盆地演化对烃源岩分布的控制[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2012,34(4):29–39.
LIU Yuhu,ZHAO Dandan,LIU Xingwang,et al. The control of the evolution of Turpan Hami Jurassic prototype basin on the distribution of source rocks[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Natural Science Edition),2012,34(4):29–39.
[24] 任佳宇,姜波,屈争辉,等. 东海与南海北部盆地构造演化及其构造控煤特征[J]. 煤炭技术,2015,34(5):99–102.
REN Jiayu,JIANG Bo,QU Zhenghui,et al. Tectonic evolution and control of coal with contrast of East China Sea and Northern South China Sea[J]. Coal Technology,2015,34(5):99–102.
[25] 李荣西. 九十年代煤系烃源岩研究新进展[J]. 地质科技情报,2000,19(4):55–59.
LI Rongxi. Achievements of the coal source rock research in last ten years[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2000,19(4):55–59.
[26] 黄第藩. 成烃理论的发展:(Ⅱ)煤成油及其初次运移模式[J]. 地球科学进展,1996,11(5):432–438.
HUANG Difan. Advances in hydrocarbon generation theory:(Ⅱ)Oils from coal and its primary migration model[J]. Advances in Earth Science,1996,11(5):432–438.
[27] 柳广弟. 石油地质学[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2009.
LIU Guangdi. Petroleum geology[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2009.
[28] 孙金山,刘国宏,孙明安,等. 库车坳陷侏罗系煤系烃源岩评价[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2003,25(6):1–4.
SUN Jinshan,LIU Guohong,SUN Ming’an,et al. Source rock evaluation of coal-measures strata in Kuqa Depression of Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition),2003,25(6):1–4.
[29] 张功成,米立军,屈红军,等. 全球深水盆地群分布格局与油气特征[J]. 石油学报,2011,32(3):369–378.
ZHANG Gongcheng,MI Lijun,QU Hongjun,et al. A basic distributional framework of global deepwater basins and hydrocarbon characteristics[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2011,32(3):369–378.
[30] 屈红军,张功成. 全球深水富油气盆地分布格局及成藏主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学,2017,28(10):1478–1487.
QU Hongjun,ZHANG Gongcheng. Distribution framework and main factors controlling hydrocarbon accumulation of global oil and gas-rich deepwater basins[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2017,28(10):1478–1487.
[31] 刘凤鸣. 库泰盆地石油地质特征与油气资源评价[D]. 北京:中国石油大学(北京),2017:7–36.
LIU Fengming. Petroleum geological characteristics and evaluation of oil and gas resources in Kutai Basin[D]. Beijing:China University of Petroleum(Beijing),2017:7–36.
[32] 杨磊. 中苏门答腊盆地石油地质特征与油气勘探潜力[J]. 新疆石油地质,2011,32(3):329–331.
YANG Lei. Petroleum geology and exploration potential analysis in Central Sumatra Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2011,32(3):329–331.
[33] 刘世翔,赵志刚,谢晓军,等. 文莱–沙巴盆地油气地质特征及勘探前景[J]. 科学技术与工程,2018,18(4):29–34.
LIU Shixiang,ZHAO Zhigang,XIE Xiaojun,et al. Petroleum geology and exploration prospects of Wenlai-Shaba Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2018,18(4):29–34.
[34] 罗金海,周新源,邱斌,等. 塔里木–卡拉库姆地区的油气地质特征与区域地质演化[J]. 地质论评,2005,51(4):409–415.
LUO Jinhai,ZHOU Xinyuan,QIU Bin,et al. Petroleum geology and geological evolution of the Tarim-Karakum and Adjacent Areas[J]. Geological Review,2005,51(4):409–415.
[35] 白国平,殷进垠. 中亚卡拉库姆盆地油气分布特征与成藏模式[J].古地理学报,2007,9(3):293–301.
BAI Guoping,YIN Jinyin. Distribution characteristics and accumulation model for oil and gas in Karakum Basin,Central Asia[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2007,9(3):293–301.
[36] 张强,张光亚,李曰俊,等. 卡拉库姆盆地晚二叠世—三叠纪的构造属性讨论[J]. 地质科学,2016,51(1):157–164.
ZHANG Qiang,ZHANG Guangya,LI Yuejun,et al. Discussion on structural attributes of Late Permian Triassic in Karakum Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,2016,51(1):157–164.
[37] 尹继全,贾承造,王春生,等. 阿富汗–塔吉克盆地油气地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质,2015,20(4):43–48.
YIN Jiquan,JIA Chengzao,WANG Chunsheng,et al. Petroleum geological characteristics and exploration direction of Afghanistan Tajik Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2015,20(4):43–48.
[38] 李剑,姜正龙,罗霞,等. 准噶尔盆地煤系烃源岩及煤成气地球化学特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2009,36(3):365–374.
LI Jian,JIANG Zhenglong,LUO Xia,et al. Geochemical characteristics of coal-measure source rocks and coal-derived gas in Junggar Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2009,36(3):365–374.
[39] 赵才顺. 准噶尔盆地腹部及周缘地区石炭系构造特征[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2010.
ZHAO caishun. Structural characteristics of carboniferous system in the hinterland and periphery of Junggar Basin[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2010.
[40] 吴金才. 准噶尔盆地腹部侏罗系层序地层学研究与隐蔽圈闭识别[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2005.
WU Jincai. Jurassic sequence stratigraphy and subtle trap identification in the hinterland of Junggar Basin[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2005.
[41] 吴孔友,查明,王绪龙,等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化与动力学背景再认识[J]. 地球学报,2005,26(3):217–222.
WU kongyou,ZHA Ming,WANG Xulong,et al. Further researches on the tectonic evolution and dynamic setting of the Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica,2005,26(3):217–222.
[42] 苟红光,张品,佘家朝,等. 吐哈盆地石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质,2019,24(2):85–96.
GOU Hongguang,ZHANG Pin,SHE Jiachao,et al. Petroleum geological conditions,resource potential and exploration direction in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2019,24(2):85–96.
[43] 贾承造. 塔里木盆地构造特征与油气聚集规律[J]. 新疆石油地质,1999,20(3):3–9.
JIA Chengzao. Structural characteristics and oil/gas accumulative regularity in Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,1999,20(3):3–9.
[44] 田光荣,李红哲,白亚东,等. 柴达木盆地侏罗系煤系烃源岩生烃潜力分类评价[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2018,46(5):73–80.
TIAN Guangrong,LI Hongzhe,BAI Yadong,et al. Classification and evaluation of the hydrocarbon generation potential of Jurassic coal measures of Qaidam Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2018,46(5):73–80.
[45] 冯乔,付锁堂,张小莉,等. 柴达木盆地及邻区侏罗纪原型盆地恢复及油气勘探前景[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(1):44–58.
FENG Qiao,FU Suotang,ZHANG Xiaoli,et al. Jurassic prototype basin restoration and hydrocarbon exploration prospect in the Qaidam Basin and its adjacent area[J]. Earth & Science Frontiers,2019,26(1):44–58.
[46] 白云来,王新民,刘化清,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部边界的确定及其地球动力学背景[J]. 地质学报,2006,80(6):792–813.
BAI Yunlai,WANG Xinmin,LIU Huaqing,et al. Determination of the borderline of the Western Ordos Basin and its geodynamics background[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2006,80(6):792–813.
[47] 刘洁琪. 煤系烃源岩天然气成藏过程研究:以鄂尔多斯盆地东部山西组为例[D]. 西安:西安石油大学,2017.
LIU Jieqi. Study on natural gas accumulation process of coal measure source rocks:A case study of Shanxi Formation in Eastern Ordos Basin[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Petroleum,2017.
[48] 梁敏,王辉,梁辉,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地山西组煤系烃源岩特征研究[J]. 地下水,2018,40(2):93–95.
LIANG Min,WANG Hui,LIANG Hui,et al. Coalbed gas and shale gas resource prospect study of Heyang-Hancheng Area[J]. Ground Water,2018,40(2):93–95.
[49] 张泓,晋香兰,李贵红,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪–白垩纪原始面貌与古地理演化[J]. 古地理学报,2008,10(1):1–11.
ZHANG Hong,JIN Xianglan,LI Guihong,et al. Original features and palaeogeographic evolution during the Jurassic-Cretaceous in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2008,10(1):1–11.
[50] 骆宗强,刘铁树,袭著纲. 孟加拉国孟加拉盆地油气勘探潜力分析[J]. 中国石油勘探,2012,17(2):67–73.
LUO Zongqiang,LIU Tieshu,WANG Zhugang. Analysis of oil and gas exploration potential in Bengal Basin,Bangladesh[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2012,17(2):67–73.
[51] 客伟利,童晓光. 孟加拉盆地油气地质特征与勘探潜力[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2013,28(5):15–20.
KE Weili,TONG Xiaoguang. Petroleum geological characteristics and exploration potential of Bengal Basin[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University(Natural Science),2013,28(5):15–20.
[52] 赖生华,麻建明,廖林. 缅甸中央沉降带Chindwin盆地油气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业,2005,25(11):21–24.
LAI Shenghua,MA Jianming,LIAO Lin. The oil-gas exploration potential of Chindwin sag in the central basin in Burma[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2005,25(11):21–24.
[53] 杨磊. 缅甸D区块油气成藏条件分析[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2011.
YANG Lei. Analysis of hydrocarbon accumulation conditions in Block D of Myanmar[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2011.
[54] 李运振,吕明,白海强,等. 缅甸钦敦–睡宝盆地火山岛弧带沉积环境分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2013,33(3):48–55.
LI Yunzhen,LYU Ming,BAI Haiqiang,et al. Sedimentary environments of the volcanic island arc zone in the Chindwin-Shwebo Basin,Myanmar[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2013,33(3):48–55.
[55] 王营,辛仁臣. 缅甸含油气盆地群形成演化及其地球动力学背景[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(1):27–35.
WANG Ying,XIN Renchen. Formation and evolution of petroliferous basins in Myanmar and their geodynamic background[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(1):27–35.
[56] 张云逸. 泰国彭世洛盆地与泰国湾盆地油气地质特征对比[D]. 北京:中国石油大学(北京),2016:7–29.
ZHANG Yunyi. Comparison of petroleum geological characteristics between Pengshiluo Basin and Gulf of Thailand Basin in Thailand[D]. Beijing:China University of Petroleum(Beijing),2016.
[57] CHANTRAPRASERT S,UTITSAN S. Origin of synchronous extension and inversion in a rift basin:The Phitsanulok Basin,central Thailand[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2021:104774.
[58] 胡忠良. 琼东南盆地崖南凹陷烃源岩生烃动力学和油气成藏研究[D]. 广州:中国科学院研究生院(广州地球化学研究所),2005.
HU Zhongliang. Hydrocarbon generation dynamics and hydrocarbon accumulation of source rocks in Yannan sag,Qiongdongnan Basin[D]. Guangzhou:Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry),2005.
[59] 寇才修. 南海北部海区珠江口盆地前渐新统找油的新领域[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1984,4(2):41–47.
KOU Caixiu. A new field for oil exploration in the pre Oligocene of the Pearl River Mouth Basin in the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Quaternary Geology,1984,4(2):41–47.
[60] 李燕,邓运华,李友川,等. 珠江口盆地河流—三角洲体系煤系烃源岩发育特征及有利相带[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2016,40(1):62–71.
LI Yan,DENG Yunhua,LI Youchuan,et al. Development characteristics and favorable facies zones of coal measure source rocks in river delta system of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University,2016,40(1):62–71.
[61] 李晓龙,许长海,高顺莉,等. 东海晚中生代岩浆弧与陆缘汇聚作用:碎屑锆石U-Pb年代约束[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(2):480–490.
LI Xiaolong,XU Changhai,GAO Shunli,et al. Late Mesozoic magmatic arc of continental margin:Constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb data,East China Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(2):480–490.
[62] 蒋一鸣,刁慧,曾文倩. 东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖组煤系烃源岩条件及成烃模式[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(3):30–39.
JIANG Yiming,DIAO Hui,ZENG Wenqian. Source rock conditions and hydrocarbon generation model of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag,Donghai Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(3):30–39.
[63] RODRIGUEZ N D,PAUL PHILP R. Productivity and paleoclimatic controls on source rock character in the Aman Trough,north central Sumatra,Indonesia[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2012,45:18–28.
[64] 黄众,胡孝林,郭刚,等. 苏门答腊裂谷盆地带构造分带及其成藏模式[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2018,34(8):61–67.
HUANG Zhong,HU Xiaolin,GUO Gang,et al. Structural zonation and hydrocarbon accumulation model of the Sumatra back arc rift basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2018,34(8):61–67.
[65] LUNT P. Partitioned transtensional Cenozoic stratigraphic development of North Sumatra[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,106:1–16.
[66] 袁浩,张廷山,王海峰,等. 南苏门答腊盆地M区块古近系烃源岩特征及评价[J]. 天然气地球科学,2012,23(4):646–653.
YUAN Hao,ZHANG Tingshan,WANG Haifeng,et al. Characteristics and evaluation of Paleogene source rocks in block m of South Sumatra Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2012,23(4):646–653.
[67] 赵旭. 南苏门答腊盆地WJ区裂陷期沉积层序及古构造控制[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2020.
ZHAO Xu. Sedimentary sequence and paleotectonic control during rifting in WJ area of South Sumatra Basin[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2020.
[68] 王永臻. 马来盆地石油地质条件及成藏主控因素分析[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2011.
WANG Yongzhen. Petroleum geological conditions and main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in Malay Basin[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2011.
[69] 谯汉生,于兴河. 裂谷盆地石油地质[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2004.
QIAO Hansheng,YU Xinghe. Petroleum geology of rift basin[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2004.
[70] 孙桂华,高红芳,彭学超,等. 越南南部湄公盆地地质构造与沉积特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010,30(6):25–33.
SUN Guihua,GAO Hongfang,PENG Xuechao,et al. Geological structure and sedimentary characteristics of Mekong Basin in southern Vietnam[J]. Marine Geology Quaternary Geology,2010,30(6):25–33.
[71] 钱光华,樊开意. 万安盆地地质构造及演化特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质),1997,11(2):1–7.
QIAN Guanghua,FAN Kaiyi. The geological tectonic and it's evolution in Wan’an Basin[J]. Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology) of China,1997,11(2):1–7.
[72] 张厚和,赫栓柱,刘鹏,等. 万安盆地油气地质特征及其资源潜力新认识[J]. 石油实验地质,2017,39(5):625–632.
ZHANG Houhe,HE Shuanzhu,LIU Peng,et al. New understanding of oil and gas geological characteristics and resource potential in Wan’an Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment,2017,39(5):625–632.
[73] 刘海. 东、西纳土纳盆地石油地质特征及对比研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2012.
LIU Hai. Petroleum geological characteristics and comparative study of East and West Natuna Basins[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2012.
[74] 倪仕琪,王志欣,刘凤鸣,等. 印度尼西亚西纳土纳盆地油气地质特征与分布规律[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2017,33(2):26–34.
NI Shiqi,WANG Zhixin,LIU Fengming,et al. Geological characteristics and distribution pattern of petroleum in West Natuna Basin,Indonesia[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2017,33(2):26–34.
[75] LUNT P. A reappraisal of the Cenozoic stratigraphy of the Malay and West Natuna Basins[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences:X,2021,5:100044.
[76] DOUST H,NOBLE R A. Petroleum systems of Indonesia[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2008,25:103–129.
[77] 张厚和,赫栓柱,刘鹏,等. 曾母盆地烃源岩评价及油源探讨[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2017,36(3):466–475.
ZHANG Houhe,HE Shuanzhu,LIU Peng,et al. Evaluation of source rocks and oil-source correlation of Zengmu Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2017,36(3):466–475.
[78] 郭志峰,胡孝林,郭刚,等. 印尼打拉根盆地油气成藏特征与主控因素[J]. 海相油气地质,2018,23(2):83–89.
GUO Zhifeng,HU Xiaolin,GUO Gang,et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and main controlling factors in Dalagan Basin,Indonesia[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2018,23(2):83–89.
[79] SATYANA A H,NUGROHO D,SURANTOKO I. Tectonic controls on the hydrocarbon habitats of the Barito,Kutei,and Tarakan Basins,Eastern Kalimantan,Indonesia:Major dissimilarities in adjoining basins[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,1999,17(1-2):99–122.
[80] 张强,吕福亮,毛超林,等. 印度尼西亚库泰盆地油气地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质,2012,17(4):8–15.
ZHANG Qiang,LYU Fuliang,MAO Chaolin,et al. Petroleum geology and exploration prospect in Kutai Basin,Indonesia[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2012,17(4):8–15.
[81] 陈榕,贺敬博. 印度尼西亚富有机质页岩分布情况与页岩气资源潜力[J]. 中国矿业,2018,27(S1):164–168.
CHEN Rong,HE Jingbo. Distribution of organic shale and shale gas resource potential in Indonesia[J]. China Mining Magazine,2018,27(S1):164–168.
[82] 杨福忠,罗良,贾东,等. 印尼东爪哇盆地新生代构造演化[J]. 高校地质学报,2011,17(2):240–248.
YANG Fuzhong,LUO Liang,JIA Dong,et al. Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of the East Java Basin,Indonesia[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2011,17(2):240–248.
[83] 袭著纲,胡孝林,方勇,等. 印度尼西亚北塞兰盆地构造演化及其对油气成藏条件的控制[J]. 中国石油勘探,2016,21(6):91–97.
XI Zhugang,HU Xiaolin,FANG Yong,et al. Tectonic evolution of North Seram Basin,Indonesia,and its control over hydrocarbon accumulation conditions[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2016,21(6):91–97.
[84] 李丹,杨香华,常吟善,等. 澳大利亚北卡那封盆地中上三叠统Mungaroo三角洲陆源有机质分布特征[J]. 古地理学报,2014,16(2):193–204.
LI Dan,YANG Xianghua,CHANG Yinshan,et al. Distribution characteristics of terrigenous organic matter in the middle upper Triassic Mungaroo delta of North Carnarvon basin,Australia[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2014,16(2):193–204.
[85] 许晓明,于水,骆宗强,等. 北卡那封盆地与波拿巴盆地大气田形成条件对比研究[J]. 石油天然气学报,2014,36(2):6–11.
XU Xiaoming,YU Shui,LUO Zongqiang,et al. Comparative study on formation conditions of large gas fields in North Carnarvon basin and Bonaparte Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology,2014,36(2):6–11.
[86] 姜雄鹰,傅志飞. 澳大利亚布劳斯盆地构造地质特征及勘探潜力[J]. 石油天然气学报,2010,32(2):54–57.
JIANG Xiongying,FU Zhifei. Petroleum geological features and exploration potential of Browse Basin in Australia[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology,2010,32(2):54–57.
[87] 王云. 澳大利亚西北陆架深水区布劳斯盆地油气地质特征研究[J]. 地下水,2018,40(1):121–123.
WANG Yun. Oil and gas geological characteristics of Braus basin in deep water area of northwest shelf,Australia[J]. Ground Water,2018,40(1):121–123.
[88] 侯宇光,何生,杨香华,等. 澳大利亚波拿巴盆地大陆边缘裂陷期海陆过渡相烃源岩地球化学特征与发育模式[J]. 石油实验地质,2015,37(3):374–382.
HOU Yuguang,HE Sheng,YANG Xianghua,et al. Geochemical characteristics and development model of transitional source rocks during the continental margin rifting stage,Bonaparte Basin,Australia[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment,2015,37(3):374–382.
[89] 白国平,殷进垠. 澳大利亚北卡那封盆地油气地质特征及勘探潜力分析[J]. 石油实验地质,2007,29(3):253–258.
BAI Guoping,YIN Jinyin. Petroleum geological features and exploration potential analyses of north Carnavon Basin,Australia[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment,2007,29(3):253–258.
[90] 姚永坚,吕彩丽,康永尚,等. 东南亚地区烃源岩特征与主控因素[J]. 地球科学,2013,38(2):367–378.
YAO Yongjian,LYU Caili,KANG Yongshang,et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon source rocks and their main controlling factors in Southeast Asia[J]. Earth Science,2013,38(2):367–378.
[91] 邱楠生,王绪龙,杨海波,等. 准噶尔盆地地温分布特征[J]. 地质科学,2001,36(3):350–358.
QIU Nansheng,WANG Xulong,YANG Haibo,et al. The characteristics of temperature distribution in the Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,2001,36 (3):350–358.
[92] 张世焕,王志勇,张朝富. 吐哈盆地煤系烃源岩特征与油气分布关系初探[J]. 新疆石油地质,1996,17(1):29–33.
ZHANG Shihuan,WANG Zhiyong,ZHANG Chaofu. Preliminery study on the relation between the coal source rock characteristics and oilgas distribution in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,1996,17(1):29–33.
[93] 吴志远. 十三间房及周围地区煤系烃源岩评价及油气成藏机制研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2017.
WU Zhiyuan. Evaluation of coal measure source rocks and Study on hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism in Shisanjianfang and surrounding areas[D]. Beijing:China University of Mining and Technology(Beijing),2017.
[94] 党犇,赵虹,姜常义. 塔里木盆地东北部侏罗系烃源岩特征及初步评价[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2004,26(1):1–5.
DANG Ben,ZHAO Hong,JIANG Changyi. Preliminary studies and characteristics of the Jurassic hydrocarbon source rocks in the northern Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Earch Sciences and Environment,2004,26(1):1–5.
[95] 潘泉涌. 塔里木盆地台盆区地温梯度分布特征[J]. 内蒙古石油化工,2018,44(10):52–55.
PAN Quanyong. Geotemperature gradient distribution of Tarim Basin,Northwest,China[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry,2018,44(10):52–55.
[96] 李宗星,高俊,李文飞,等. 柴达木盆地地温场分布特征及控制因素[J]. 地学前缘,2016,23(5):23–32.
LI Zongxing,GAO Jun,LI Wenfei,et al. The characteristics of geothermal field and controlling factors in Qaidam Basin,Northwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2016,23(5):23–32.
[97] 任战利. 利用磷灰石裂变径迹法研究鄂尔多斯盆地地热史[J]. 地球物理学报,1995,38(3):339–349.
REN Zhanli. Study on geothermal history of Ordos Basin by apatite fission track method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,1995,38(3):339–349.
[98] 郭佩,刘池洋,王建强,等. 宁南地区石炭系沉积演化及烃源岩评价[J]. 地质科技情报,2015,34(3):15–23.
GUO Pei,LIU Chiyang,WANG Jianqiang,et al. Carboniferous sedimentary evolution of southern Ningxia and its source rock evaluation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2015,34(3):15–23.
[99] 晋香兰,张慧. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部侏罗纪煤系烃源岩的分布特征[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2010,22(1):15–19.
JIN Xianglan,ZHANG Hui. Distributing features of Jurassic coal measures hydrocarbon source rock in Northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology of China,2010,22(1):15–19.
[100] 黄文辉,敖卫华,肖秀玲,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪含煤岩系生烃潜力评价[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(3):461–467.
HUANG Wenhui,AO Weihua,XIAO Xiuling,et al. Hydrocarbon generation potential evaluation of Jurassic coal bearing strata in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2011,36(3):461–467.
[101] 客伟利,童晓光,温志新,等. 孟加拉湾西侧盆地群油气地质特征与勘探潜力[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2014,36(6):9–17.
KE Weili,TONG Xiaoguang,WEN Zhixin,et al. Petroleum geological characteristics and exploration potential of West Bengal Basin Group[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Natural Science Edition),2014,36(6):9–17.
[102] 胡圣标,龙祖烈,朱俊章,等. 珠江口盆地地温场特征及构造–热演化[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(增刊1):178–187.
HU shengbiao,LONG Zulie,ZHU Junzhang,et al. Characteristics of geothermal field and tectonic thermal evolution of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2019,40(Sup.1):178–187.
[103] 朱明,张向涛,黄玉平,等. 珠江口盆地烃源岩特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(增刊1):53–68.
ZHU Ming,ZHANG Xiangtao,HUANG Yuping,et al. Characteristics and resource potential of source rocks in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2019,40(Sup.1):53–68.
[104] YANG Shuchun,HU Shengbiao,CAI Dongsheng,et al. Present-day heat flow,thermal history and tectonic subsidence of the East China Sea Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2004,21:1095–1105.
[105] 冯晓杰,蔡东升. 东海陆架盆地中新生代构造演化对烃源岩分布的控制作用[J]. 中国海上油气,2006,18(6):372–375.
FENG Xiaojie,CAI Dongsheng. Controls of Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution on source rock distribution in East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2006,18(6):372–375.
[106] 曹冰. 西湖凹陷中央反转构造带花港组致密砂岩储层埋藏史–热史[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,43(4):405–414.
CAO Bing. Study of burial and thermal history of Huagang Formation tight sandstone reservoir in central reversal structural belt,Xihu Depression,East China Sea[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition),2016,43(4):405–414.
[107] 田鑫. 印尼南苏门答腊盆地油气成藏规律研究及油气藏精细勘探[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2016.
TIAN Xin. Study on hydrocarbon accumulation and fine exploration in South Sumatra Basin,Indonesia[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2016.
[108] 刘振湖,吴进民. 南海万安盆地油气地质特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质),1997,11(3):1–8.
LIU Zhenhu,WU Jinmin. Petroleum geology of Wan’an Basin,South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,1997,11(3):1–8.
[109] CURIALE J,LIN R,DECKER J. Isotopic and molecular characteristics of Miocene-reservoired oils of the Kutei Basin,Indonesia[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2005,36:405–424.
[110] 鲁银涛,栾锡武,史卜庆,等. 加里曼丹岛库泰盆地海相成藏组合特征及油气富集区分带性分析[J]. 海洋科学,2019,43(1):38–49.
LU Yintao,LUAN Xiwu,SHI Buqing,et al. Characteristics of Lower Miocene marine petroleum play and prospective petroleum accumulation region in the Kutei Basin,the Kalimantan Island[J]. Marine Science,2019,43(1):38–49.
[111] TODD S,DUNN M,BARWISE A. Characterizing petroleum charge systems in the tertiary of SE Asia[J]. Petroleum Geology of Southeast Asia,1997,126:25–47.
[112] 张家青. 澳大利亚西北大陆架油气地质特征及勘探潜力:以北卡那封盆地为例[J]. 内蒙古石油化工,2011,37(9):186–190.
ZHUANG Jiaqing. Petroleum geological characteristics and exploration potential of Northwest continental shelf in Australia:A case study of North Carnarvon Basin[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry,2011,37(9):186–190.
[113] 李燕. 澳大利亚北卡那封盆地含油气系统分析与资源评价[D]. 北京:中国石油大学(北京),2018.
LI Yan. Petroleum system analysis and resource evaluation of North Carnarvon basin,Australia[D]. Beijing:China University of Petroleum(Beijing),2018.
[114] 龚承林,王英民,崔刚,等. 北波拿巴盆地构造演化与层序地层学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010,30(2):103–109.
GONG Chenglin,WANG Yingmin,CUI Gang,et al. Structural evolution and sequence stratigraphy of North Bonaparte Basin[J]. Marine Geology Quaternary Geology,2010,30(2):103–109.
[115] 段威,侯宇光,何生,等. 澳大利亚波拿巴盆地Petrel次盆古生界页岩有机质热演化的差异及其地质意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2013,37(6):17–23.
DUAN Wei,HOU Yuguang,HE Sheng,et al. Thermal evolution differences and its geological significances of organic matter of Paleozoic shale in Petrel subbasin,Bonaparte Basin,Australia[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science),2013,37(6):17–23.
[116] 于会娟,妥进才,刘洛夫,等. 柴达木盆地东部地区侏罗系烃源岩地球化学特征及生烃潜力评价[J]. 沉积学报,2000,18(1):132–138.
YU Huijuan,TUO Jincai,LIU Luofu,et al. Geochemical characteristics and evaluation on hydrocarbon generation potentials of source rocks in Jurassic Eastern Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2000,18(1):132–138.
[117] 肖贤明,刘德汉,傅家谟. 我国聚煤盆地煤系烃源岩生烃评价与成烃模式[J]. 沉积学报,1996,14(增刊1):10–17.
XIAO Xianming,LIU Dehan,FU Jiamo. The evaluation of coal-measure source rocks of coal-bearing basins in China and their hydrocarbon-generating models[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,1996,14(Sup.1):10–17.
[118] 雷闯,叶加仁,王修平,等. 澳大利亚北波拿巴盆地Plover组烃源岩特征及热演化[J]. 地质科技情报,2011,30(1):108–113.
LEI Chuang,YE Jiaren,WANG Xiuping,et al. Characteristics and thermal evolution of source rocks of Plover Formation in the Northern Bonaparte Basin,Australia[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2011,30(1):108–113.
[119] 李劭杰. 南海北部盆地煤系烃源岩形成模式研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学,2015.
LI Shaojie. Study on the formation model of coal measure source rocks in the northern basin of South China Sea[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences,2015.
[120] 鲜志尧. 缅甸D区块烃源岩有机地球化学特征及油气源对比[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2012.
XIAN Zhiyao. Organic geochemical characteristics and oil-gas source correlation of source rocks in Block D of Myanmar[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2012.
[121] 兰蕾. 南海南部盆地烃源岩特征及其对含油气性的影响[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(4):23–29.
LAN Lei. Characteristics of source rocks in the southern basin of the South China Sea and their influence on petroliferous properties[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2019,38(4):23–29.
[122] 彼得斯 K E,沃尔特斯 C C,莫尔多万 J M. 生物标志化合物指南第二版–下册[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,1995.
PETERS K E,WALTERS C C,MORWAN J M. Guide to biomarkers,Second Edition-Volume Ⅱ[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1995.
[123] 薛沛霖. 山西晚古生代的聚煤历程[J]. 化石,2018(3):28–30.
XUE Peilin. Coal accumulation process of Late Paleozoic in Shanxi[J]. Fossil,2018(3):28–30.
[124] 屈童,高岗,徐新德,等. 三角洲—浅海沉积体系陆源有机质分布控制因素[J]. 沉积学报,2020,38(3):648–660.
QU Tong,GAO Gang,XU Xinde,et al. Control factors of terrestrial organic matter distribution in delta-shallow sea sedimentary system[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2020,38(3):648–660.
[125] 韩冰,李学杰,吕建荣,等. 孟加拉湾深水盆地油气勘探潜力[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2012,28(4):50–56.
HAN Bing,LI Xuejie,LYU Jianrong,et al. Petroleum exploration potential of bay of Bengal deep water basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2012,28(4):50–56.
[126] 蒋一鸣,邵龙义,李帅,等. 西湖凹陷平湖构造带平湖组沉积体系及层序地层研究[J]. 现代地质,2020,34(1):141–153.
JIANG Yiming,SHAO Longyi,LI Shuai,et al. Deposition system and stratigraphy of Pinghu formation in Pinghu Tectonic Belt,Xihu Sag[J]. Geoscience,2020,34(1):141–153.
[127] 李居云,姜波,屈争辉,等. 东海西湖凹陷构造演化及控煤作用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2016,44(5):22–27.
LI juyun,JIANG Bo,QU Zhenghui,et al. Tectonic evolution and control of coal in Donghai Xihu sag[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2016,44(5):22–27.
[128] 宫贺晏. 珠江口盆地珠三坳陷构造演化及其对煤系烃源岩的控制[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2014.
GONG Heyan. Tectonic evolution of Zhusan depression in Pearl River Mouth Basin and its control on coal measures source rocks[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2014.
[129] 熊斌辉,王春红,张锦伟,等. 西湖凹陷古近系平湖组煤层分布及油气意义[J]. 海洋石油,2007,27(3):27–33.
XIONG Binhui,WANG Chunhong,ZHANG Jinwei,et al. The distribution and exploration implications of coal beds of Pinghu Formation,Paleologene in Xihu Sag[J]. Offshore Oil,2007,27(3):27–33.
[130] 杨明慧,张厚和,廖宗宝,等. 南海南沙海域沉积盆地构造演化与油气成藏规律[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2017,41(4):710–720.
YANG Minghui,ZHANG Houhe,LIAO Zongbao,et al. Tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of the sedimentary basins in Nansha Sea Waters(South China Sea)[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2017,41(4):710–720.
[131] 卢双舫,张敏. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2008.
LU Shuangfang,ZHANG Min. Petroleum geochemistry[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2008.
[132] 张成君,张菀漪,樊荣,等. 湖泊环境早期成岩作用对沉积物中有机质C/N和碳同位素组成的影响[J]. 地球环境学报,2012,3(4):1005–1012.
ZHANG Chengjun,ZHANG Wanyi,FAN Rong,et al. Effect of early diagenesis in lake environment on C/N and carbon isotope composition of organic matter in sediments[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2012,3(4):1005–1012.
[133] LAMB A L,LENG M J,UMER MOHAMMED M,et al. Holocene climate and vegetation change in the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley,inferred from the composition(C/N and δ13C) of lacustrine organic matter[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2004,23:881–891.
[134] 仝志刚,贺清,赵志刚,等. 从油气赋存状态分析油气充注能力:以东海西湖凹陷平湖油气田为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2011,23(3):154–157.
TONG Zhigang,HE Qing,ZHAO Zhigang,et al. Analyzing hydrocarbon charges from hydrocarbon occurrences:a case of Pinghu oil and gas field in Xihu sag,East China sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2011,23(3):154–157.
[135] 单超,叶加仁,曹强,等. 西湖凹陷孔雀亭气田成藏主控因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2015,35(1):135–144.
SHAN Chao,YE Jiaren,CAO Qiang,et al. Controlling factors for gas accumulation in Kongqueting Gas Field of Xihu Sag[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2015,35(1):135–144.
Development characteristics and controlling factors of coal-measure source rocks in the global Tethys region
QU Tong1,2, HUANG Zhilong1,2, WANG Rui1,2, TAN Sizhe3, LI Zhiyuan1,2,GUO Xiaobo4, ZHAO Jing1,2, PAN Yongshuai1,2
(1. State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources and Prospecting, China University of Petroleum(Beijing), Beijing 102249, China; 2. College of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum(Beijing), Beijing 102249, China; 3. Shanghai Branch, CNOOC(China) Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200335, China; 4. School of Earth Science and Engineering, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an 710065, China)
Under the control of tectonic activity in the Tethys region, a series of basins with coal measure source rocks developed, and the Tertiary coal in the circum Pacific belt is characterized by "hydrogen-rich" and has great hydrocarbon generation potential.This type of coal measure strata is an important source rock in petroliferous basins along the southeast coast of China.Therefore, it is particularly important to systematically analyze the development characteristics and controlling factors of coal measure source rocks under the Tethys background. Based on the systematic analysis of the development age, environments, geochemical characteristics and biomarker characteristics of the coal measure source rocks in the Tethys region, the controlling factors affecting the development of the coal-measure source rocks are summarized, and the favorable development conditions and controlling factors of high-quality coal-measure source rocks are clarified. The research results show that the coal-measure source rocks under the control of the Tethyan region are mainly developed in the basins under the extensional background of the coastal areas of Southeast Asia, mostly in the marine-terrestrial transitional facies sedimentary environment during the rifting period, and the development age is consistent with the period of Tethys tectonic activity.The development of coal-measures source rocks is controlled by many factors, such as paleovegetation, paleoenvironment, lithofacies paleogeography, terrigenous organic matter supply, tectonic activity intensity, sedimentation rate and so on. The factors are interrelated and influence each other, which can be divided into three types: parent source factor, tectonic-sedimentation factor and preservation factor.The plant types rich in the chitinous and hydrogen-rich vitrinites are the necessary parent source conditions for the formation of hydrogen-rich coal. The favorable coal accumulation environment and stable tectonic background are the key factors for the large-scale development of coal measure source rocks. Appropriate water conditions and reduction environment are important factors for the preservation of organic matter. The coal measure source rocks in the southeast coastal basins of China have great hydrocarbon generation potential. The coal measure source rocks are rich in resin in the Xihu Sag of the East China Sea basin, the coal measure source rocks are rich in spores and pollen in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, and the coal measure mudstone is widely developed in Qiongdongnan Basin, which has great exploration prospect.
Tethys region; coal-measure source rock; distribution characteristics; development characteristics; controlling factors

移动阅读
语音讲解
P618.13
A
1001-1986(2021)05-0114-18
2021-06-16;
2021-08-15
国家自然科学基金面上项目(41472111)
屈童,1994年生,男,陕西咸阳人,博士研究生,研究方向为油气成藏与分布规律. E-mail:qutong1994@sina.com
黄志龙,1962年生,男,浙江诸暨人,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事油气藏形成与分布等方面的教学和研究工作. E-mail:huang5288@163.com
屈童,黄志龙,王瑞,等. 全球特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育特征及其控制因素[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(5):114–131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.05.013
QU Tong,HUANG Zhilong,WANG Rui,et al. Development characteristics and controlling factors of coal-measure source rocks in the global Tethys region[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(5):114–131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn. 1001-1986.2021.05.013
(责任编辑 范章群)

