绵阳市近60年来气候变化特征
黄雪
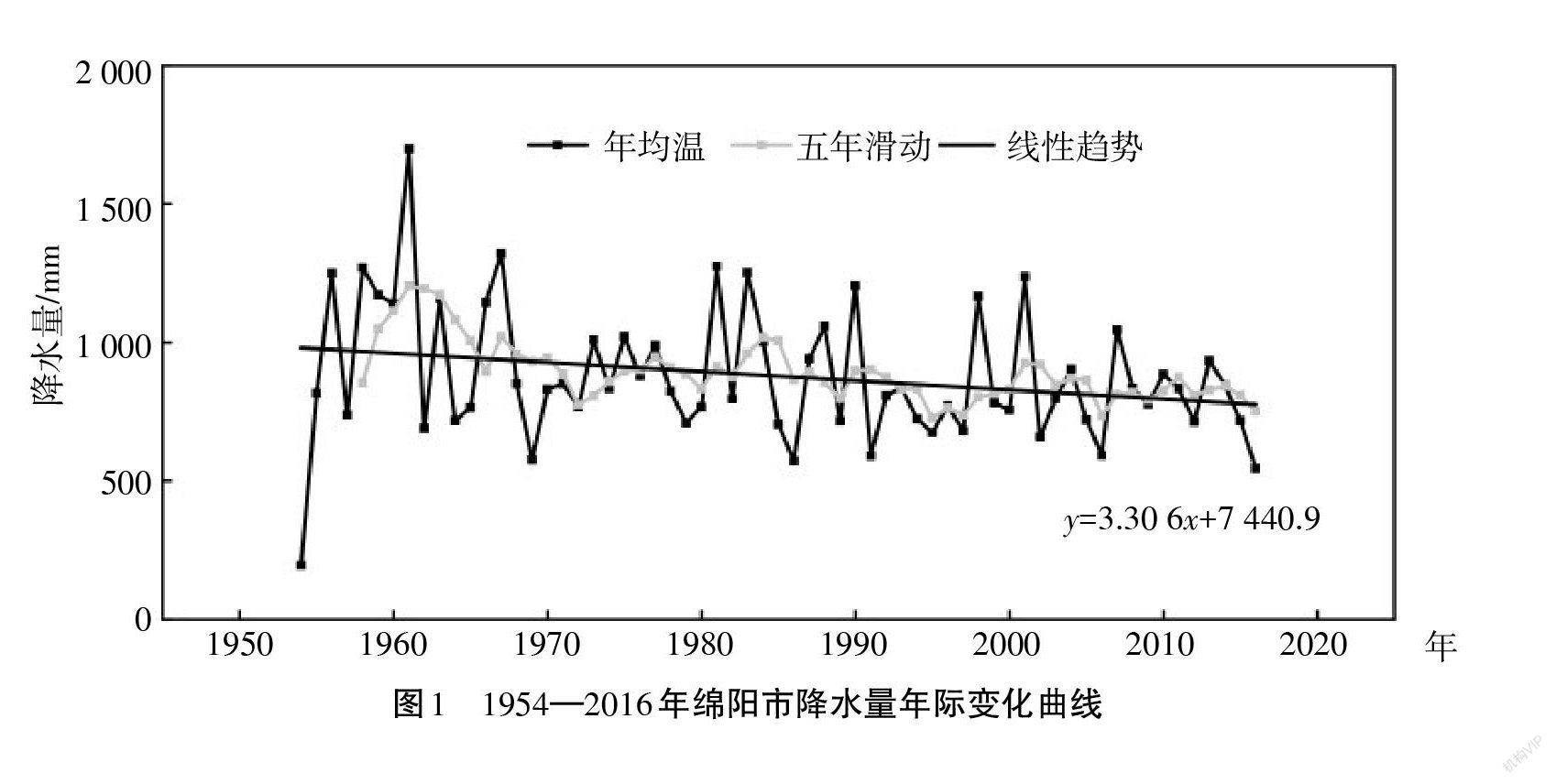
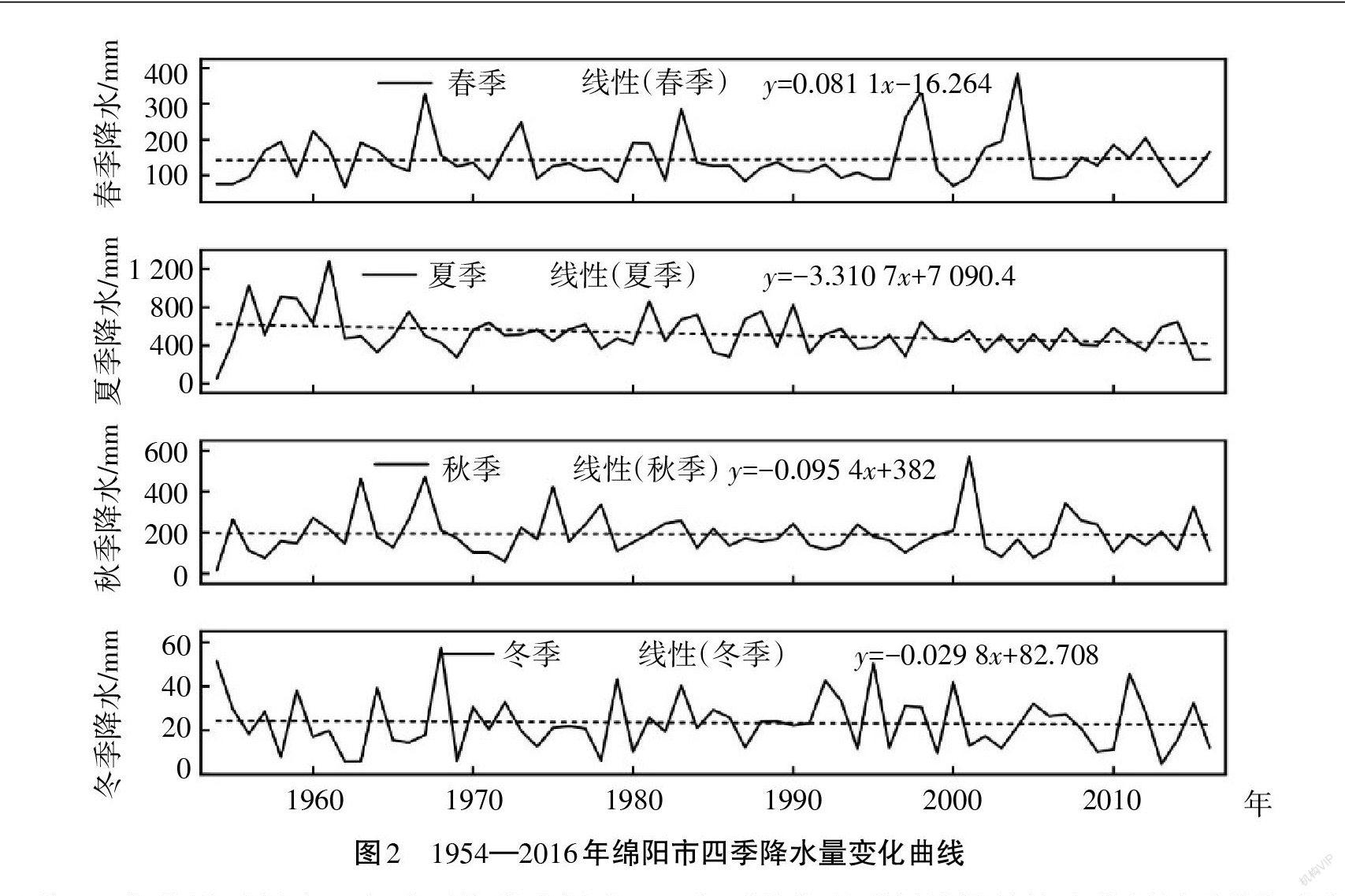

摘 要:基于綿阳市1954—2016年气象资料数据,采用线性趋势法、滑动平均法、变差系数法、累积距平法、Mann-kendall 检验法和小波分析法,分析了绵阳市近60年气候变化特征,探讨了气候变化的原因。结果表明:近60年来绵阳市年降水量处于减少趋势,下降速率为-33.06 mm/10a。绵阳市降水量季节变化趋势和幅度并不一致,春季在波动中略有上升,夏季、秋季、冬季呈波动下降趋势。年平均气温处于增长趋势,增温速率为0.168 ℃/10 a,上升速率最大的是冬季;其次为秋季,再次为春季,最小为夏季。并对气温和降水的变化趋势的原因进行了简要分析,表明绵阳市温度呈上升趋势以及降水处于下降趋势可能的原因是城市人口的增加、城市面积的扩大,以及绵阳市城市经济的发展尤其是第二产业的发展。
关键词:气候变化;趋势分析;m-k突变检验;小波分析;绵阳市
中图分类号:P467 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1003-5168(2021)24-0104-06
Analysis of Characteristics of Climate Change in Mianyang City in Recent 60 Years
HUANG Xue
(College of Geography and Environment,Baoji University of Arts and Sciences, Key Laboratory of Disaster Monitoring and Mechanism Simulating of Shaanxi Province, Baoji Shaanxi 721013 )
Abstract: Based on meteorological data from 1954 to 2016 in Mianyang City, using the least-squares method, moving average, coefficient of variation, cumulative anomaly method, Mann-Kendall test method and wavelet analysis method, the characteristics of climate change in recent 60 years were analyzed and influencing factors were discussed. The results show that the annual precipitation in a decreasing trend and the decreasing rate is -33.06mm/10a. The seasonal variation trend and amplitude of precipitation are not consistent, with a slight increase in spring and a fluctuating decrease trend in summer, autumn and winter. The annual mean temperature was on an increasing trend with a warming rate of 0.168℃/10a, and the increasing rate was the largest in winter. The second is autumn, the second is spring, and the minimum is summer. The reasons for the trend of temperature and precipitation change are analyzed briefly that the possible reasons are the increase of urban population, the expansion of urban area and the development of urban economy, especially the development of the secondary industry.
Keywords: climate change; trend analysis; mann-kendall test; wavelet analysis; Mianyang city
气候是自然地理环境的重要组成部分,与人类社会关系十分紧密,其任何变化均会对自然生态系统、社会经济系统和人类健康产生深远的影响[1]。自1988年气候系统暖化的问题一经提出便引起全球的广泛关注,联合国政府间气候变化专门委员会(IPCC)第五次评估报告(AR5)显示,1880—2012年,全球地表平均温度上升0.85 ℃。与全球气候变化趋势一致,1880年以来中国也有明显的升温,增温速率为0.05~0.08 ℃/10 a,1951—2009年,升温速率达到0.23 ℃/10 a,平均气温增加1.38 ℃[2]。近100年来,唐国利等[3]指出,我国气温上升速率为0.08 ℃/10 a,比同期全球水平高,冬春季节增温比较明显。2005年任国玉等[4]研究显示,近半个世纪来,我国地表增温速率达到0.22 ℃/10 a,增温幅度为1.1 ℃,比同期全球平均增温速率高。王绍武等[5]认为自20世纪以来我国气温以0.44 ℃/10 a的速率上升,1990年代是明显的温暖期。气候变化给全球的自然环境和社会环境造成了一系列不利的影响,如气温升高导致的冰雪融化;影响全球的水循环;粮食产量受到威胁;气候变化还会增加极端气候事件发生的频次和强度;气候变化危害生物多样性和人类的健康问题[6-10]。

