Target prediction and activity verification for the antidepressant action of Huangqin(Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis)
LI Ganggang,LUYe,HE Pei,ZHANG Shiyue,CHENG Yating,ZHANG Shaodan,PEI Lin
LI Ganggang,ZHANG Shiyue,CHENG Yating,PEI Lin,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Hebei University of Chinese Medicine,Shijiazhuang 050051,China
LU Ye,HE Pei,PEI Lin,Hebei Key Laboratory of Turbidity,Hebei Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences,Shijiazhuang 050011,China
ZHANG Shaodan,Department of pediatrics,Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050073,China
LI Ganggang,Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Anyang Vocational and Technical College,Anyang 455000,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To decipher the antidepressant targets and mechanisms of Huangqin (Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis) (RSB) by a novel computational system based on prediction and experimental verification.METHODS:The putative targets of RSB against depression were identified from Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP) and DrugBank.Next,protein-protein interaction network of the anti-depression targets of RSB were identified,and differentially expressed genes(DEGs)of depression were mined from the NCBI database.Then,Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes and Gene Ontology were used to analysis the common targets.Finally,the selected pathways and functions were verified by experimentation.RESULTS:Thirty active compounds in RSB were predicted with high confidence by TCMSP and Drug-Bank,and seventy-one DEGs were identified in the GEO database.Besides,eight core target proteins were screened out by descending order of degree value,including ACHE,IL6,SLC6A4,FOS,SLC6A3,MAOB,DPP4,and JUN.These target genes were further found to be associated with pathways involved in neuronal apoptosis,such as pathways in cancer,Toll-like receptor signaling pathway,and TNF signaling.The cell proliferation assay and wound-healing assay results showed that RSB does not affect PC12 cell proliferation and chemotaxis.Unexpectedly,RSB protected PC12 cells from oxidative stress induced by H2O2 via inhibiting autophagy and apoptosis.We revealed significant changes in mice treated with 400 mg/kg RSB compared with the lipopolysaccharide mice.The possible mechanism for the antidepressive action of RSB is by reducing the expression of LC3-B in CA1 neurons.CONCLUSIONS:Our research partially expounds the mechanism of the antidepressant effect of RSB by the combination of network pharmacology prediction and experimental verification.Furthermore,it is also conducive to the application of Traditional Chinese Medicine within modern medicine.
Keywords:depression;Huangqin (Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis);network pharmacology;prediction and verification
INTRODUCTION
Depression is a significant worldwide health problem with potentially catastrophic consequences.1Its core symptoms include despair,sleep and appetite disturbances (both up and down),anhedonia,social avoidance,negative rumination,fatigue,and poor concentration.2Currently,several antidepressants are available,such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors,selective norepinephrine inhibitors,and monoamine oxidase inhibitors.3Nevertheless,these antidepressants have side effects,such as vomiting,dysuria and sexual dysfunction,that cannot be ignored.4Although we have made progress in understanding the neural and molecular mechanisms of depression in recent years,the neural circuits of depression and their exact function are still a mystery.Therefore,it is an essential scientific research topic to explore practical,rapid,and well-tolerated new drugs for depression.
Nowadays,the modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has received global attention,thanks to its particular theory and clinical application.In contrast to conventional medication,TCM acts as an important part of people's health insurance because of its mild therapeutic effect and slight side effects.5Huangqin (Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis) (RSB) is one of the earliest widespread Chinese medicines listed in the ancient Chinese book Shennong Grass Classic.6It is a medicinal plant of TCM,which has the following properties:anti-oxidant,anti-virus,anti-bacterial,anti-allergic,anti-inflammatory,and sedative.7However,the pharmacological mechanism of RSB is still uncertain due to the difficulties in the pathophysiological study of depression and the lack of bioinformatics methods to understand its molecular connection.Therefore,the pharmacological mechanism of RSB in the treatment of depression is worthy of study.
Network pharmacology,as a new drug research model,establishes a drug-protein-disease network prediction model through bioinformatics analysis,predicts drug targets,and analyzes drug action mechanisms.8Not surprisingly,network pharmacology provides a new research paradigm for the transformation of TCM from experimental medicine to evidence-based medicine.9In this work,we aim to use a comprehensive method to predict and verify the targets and mechanism for RSB against depression based on network pharmacology and experimental method.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Construction of chemical composition database
We employed an integrated network pharmacology approach including Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP,http://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php) and DrugBank (https://www.drugbank.ca)to obtain the known chemical compounds in RSB.10It is also worth noting that the active compounds of RSB based on Lipinski's rule of five and Oral Bioavailability(OB)≥30%were filtered for further analysis.11
Next,the filtered active compounds of RSB were converted to connect with the database UniProt (http://www.uniprot.org/) for target name standardization.12Then,we constructed the network using the Cytoscape software (version 3.2.1.http://www.cytoscape.org/),an open source package project for visualization,integration,and analysis of molecular and genetic communication networks.13
Prediction of therapeutic targets of depression
We collected the depression targets from the Genecards database (https://www.genecards.org/),which is a searchable database integrating all known human genes platforms from about 125 network sources.14With "anti-depression" as the keyword,the antidepressant targets and RSB targets retrieved from Genecard database were mapped to Venny 2.1.0 (http://bioinformatics.pRSB.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/).Then,we set the protein type as "Homo sapiens" to obtain the target interaction network map from the STRING database (https://string-db.org/),which contains most of the known human protein-protein interactions (PPI) information.15
Pathway enrichment performance
KEGG and GO enrichment analysis was calculated by the Database Visualization and Integrated Discovery system (DAVID,http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp,version 6.8) for clustering the biological functions of the main hubs.16The network graphs were created by Cytoscape and fused with the "merge" function to construct the network diagram of active components,anti-depression targets,and metabolic pathway of RSB.
RSB preparation
RSB was purchased from the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences.RSB(25 g) was extracted with 1 L of boiling water for 2 h,filtered,and then lyophilized.17The extract was dissolved in Phosphate Buffered Saline and then filtered through a 0.22-μm syringe filter.
Cell culture
Rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells were purchased from Procell Life Science&Technology Co.,Ltd.,Wuhan,China.PC12 cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM,Procell Life Science&Technology Co.,Ltd.,Wuhan,China) supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS,Procell Life Science&Technology Co.,Ltd.,Wuhan,China).
Cell proliferation assay
PC12 cells were cultured in DMEM with FBS (10%)supplementation at 37 ℃in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2in 25 cm2flasks.CCK8 assay (Glpbio,Montclair,CA,USA)was used to determine the cell viability according to the manufacturer's instructions.Briefly,PC12 cells (1×103/well) were inoculated in a 96-well plate and incubated for 24 h in medium or medium containing RSB.After relevant treatment,10 μL CCK8 was added to each well and incubated for another 1 h.Then,the 450 nm absorbance value was measured.
Wound-healing assay
PC12 cells (1×104cells/well) were cultured using a 24-well plate (Corning,NY,USA) and cultured into monolayer fusion.Then,the monolayer was scratched with the tip of 200 mL pipette to form a wound,and washed with PBS (Solarbio,Beijing,China) twice.The cells were cultured in 30 μg/mL RSB(Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences,Shijiazhuang,China) or control serum for 24 and 48 h.According to the image analysis software,the open area ratios were calculated.
Cell autophagy and apoptosis detection
PC12 cells were seeded into 6-well plates (Corning,NY,USA) with 1 × 105cells in each well.After incubation with 30 μg/mL RSB and/or 500 μmol/L H2O2for 24 h,PC12 cells were harvested and washed with PBS.Immunofluorescence staining of LC3-B was used to detect the autophagy of PC12 cells.Besides,the expression of autophagy substrate p62 was measured by PE-conjugated anti-p62 in PC12 cells.
AO/EB (Solaibio,China) fluorescence staining was used to detect the apoptosis of PC12 cells.After relevant treatment,4 μL/mL of mixed dye,containing acridine orange (100 mg/mL) and ethidium bromide(100 mg/mL) were added into each cell sample in the dark at room temperature.Then,the cells were observed and analyzed using an inverted fluorescence microscope.
Animals
Fifty male ICR mice were obtained from the Animal Experiment Centre of Hebei Medical University (license number SCXK 2018-004,certificate number 1808129).The mice were approximately 8 weeks old and weighed 20-25 g.Animals were housed in groups of five per cage in a (22 ± 2) ℃and 45%-65% relative humidity environment under a normal light cycle(lights on 7:00 AM to 7:00 PM).The experimental procedures were approved by the local committee on Animal Care and Use and Protection at Hebei University of Chinese Medicine.Mice were allowed to adapt to their new housing conditions for 1 week before the experiments.
Lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-induced depression
The mice received an intraperitoneal injection of LPS(0.5 mg/kg)(Solarbio,Beijing,China)dissolved in sterile 0.9% NaCl.18Two groups exposed to LPS were treated with RSB at 200 or 400 mg/kg and named RSB 200,RSB 400 respectively.A group was treated with fluoxetine (Flu,10 mg/kg) (Prozac®,Suzhou,China) as a positive control of the test.The control group was treated with 0.9% NaCl and not was exposed to LPS.All treatments were administered to the mice by gavage for 3 weeks.
Elevated Plus Maze Test
The mouse was introduced to the center of the plus maze facing the same arm for each test and was allowed to explore for 5 min.Time in open arms,entries into open arms,and distance in open arms were quantified as indices of depressive behavior.
Sucrose preference test
Mice were permitted to drink from two bottles for 12 h,one bottle contained sucrose solution (1%) and the other contained tap water.The animals were deprived of water before the test.The ratio of the consumed sucrose solution vs.the total amount of liquid intake was calculated as the preference for sucrose.
Immunohistochemical(IHC)staining
Brain tissue sections (5 mm) from the paraffin blocks were obtained in silanized slides.The sections were deparaffinized,rehydrated,and antigen retrieval was performed.Autophagy was assessed with a primary monoclonal antibody against LC3-B (BD Pharmingen,New York,USA).After IHC reaction,images were captured using the Olympus CX41(Olympus,Osaka,Japan)automatic microscope to examine the images.A semi-quantitative histological score (HSCORE,SAS Institute Inc.,Cary,NC,USA) was used according to previous methods.19
Statistical analysis
All experiments were repeated at least three times.Statistical analysis was performed using Graphpad 6.0(San Diego,CA,USA) and presented as the mean ±standard deviation (xˉ ±s).The differences between two groups were evaluated usingt-test.AP-value of less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant result.
RESULTS
Active compound identification
Thirty targets of the active components were predicted in the TCMSP databases and DrugBank (Figure 1).Among these compounds,baicalin,baicalein,wogonoside,and wogonin have previously been declared as active compounds.In this study,the network consists of 253 nodes and 702 edges,of which 50 nodes were higher than the average degree of nodes.The top 10 compounds were wogonin,baicalein,acacetin,moslosooflavone,dihydrooroxylin A,5,2'-Dihydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxy flavone,oroxylin A,neobaicalein,5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavanone,and skullcap flavone Ⅱ.
Target prediction of RSB antidepressant
With"anti-depression"as the keyword,121 antidepressant-related targets were mined in the Genecards database.The 228 drug targets of RSB and 121 antidepressant genes were mapped in Venny 2.1.0 to obtain ten common targets.Then,we examined the relationship between them as edges and constructed the T-D network of RSB in Cytoscape (Figure 2A).Additionally,the PPI network of anti-depression targets of RSB is shown in Figure 2B.
KEGG pathway and GO function analysis of eight common targets
Results from GO pathway enrichment revealed 23 enriched pathways including response to drug,aging,response to cAMP,response to lipopolysaccharide,dopamine catabolic process,monoamine transport,neurotransmitter biosynthesis,and response to corticosterone(Figure 3A).Besides,we obtained 12 KEGG pathways related to depression prevention and treatment,such as amphetamine addiction,cocaine addiction,Toll-like receptor signaling pathway,dopaminergic synapse,and TNF signaling pathway (Figure 3B).To better distinguish the complete regulation of RSB,we established the merged depression pathway(Figure 3C).
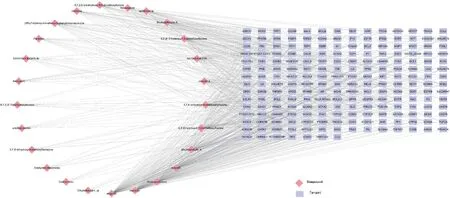
Figure 1 Compound-target network of RSB

Figure 2 Target prediction of RSB antidepressant
RSB did not affect the proliferation and chemotaxis of PC12 cells
The viability of PC12 cells in the presence of RSB is showed as follows:0 μg/mL,100 ± 5;7.5 μg/mL,103± 5;15 μg/mL,105 ± 5;30 μg/mL,103 ± 4;60 μg/mL,100 ± 4;120 μg/mL,96 ± 4.The results showed that the cytotoxicity of RSB was not obvious after 24 h culture.According to this result,30 μg/mL RSB was selected as the concentration of the subsequent experiments.Besides,in both medium control and RSB-conditioned media,the mobility of PC12 cells was 43%at 24 h and 84%at 48 h.Notably,it was found that RSB media had no effect on PC12 cells proliferation and migrationin vitro.RSB inhibited autophagy and apoptosis in H2O2-treated PC12 cells.
Our results showed that the treatment with H2O2-conditioned media markedly promoted the production of LC3-B but decreased p62 degradation in PC12 cells(Figure 4A,4B).Moreover,RSB media could inhibit the apoptosis of PC12 cells under H2O2-conditioned media(Figure 4C).
Effect of RSB in EPM Test.
Compared to the control group,the time spent in the center,the number of entries into the open arms,and the distance in the center were decreased among mice in the LPS group (P <0.01) (Table 2).Compared to the LPS group,the time spent in the center showed an expected decrease in the FLU (P <0.05) and RSB400 groups (P <0.01);entries into open arms showed an expected decrease in the FLU and RSB400 groups(P<0.05).
Effect of RSB in SPT Test
Compared to the control group,the LPS group showed significantly less sucrose intake (P <0.01).Compared with the LPS group,the sucrose intake was increased in mice in the RSB400 and FLU group (P <0.01)(Table 1).
Table 1 Effect of RSB in EPM Test and SPT test(±s)
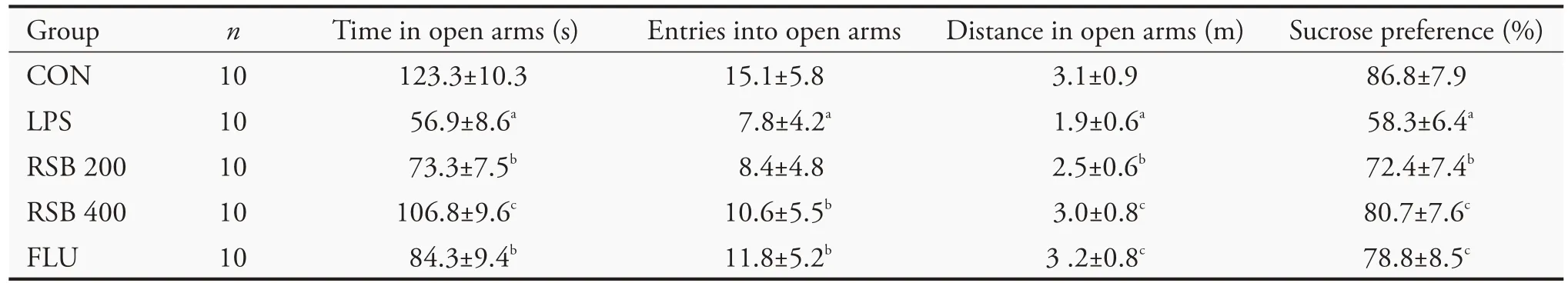
Table 1 Effect of RSB in EPM Test and SPT test(±s)
Notes:CON:gavaged with normal saline;LPS:intraperitoneal injection of LPS(0.5 mg/kg)+normal saline;RSB 200:intraperitoneal injection of LPS (0.5 mg/kg)+RSB (200 mg/kg);RSB 400:intraperitoneal injection of LPS (0.5 mg/kg)+RSB (400 mg/kg);FLU:intraperitoneal injection of LPS(0.5 mg/kg)+FLU(10 mg/kg).EPM:elevated plus maze;SPT:sucrose preference test;RSB:Huangqin(Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis);LPS:lipopolysaccharide;FLU:fluoxetine.aP <0.01,compared with the CON group;bP <0.05 andcP <0.01,compared with the LPS group.
Effect of RSB on LC3B Protein Expression in the Hippocampus Assessed by IHC staining
The expression of LC3-B in CA1 neurons in the LPS group was markedly increased compared to that of the control group (P <0.01).After treatment with RSB 400,the expression of LC3-B markedly reduced in CA1 neurons(P<0.01)(Figure 5).
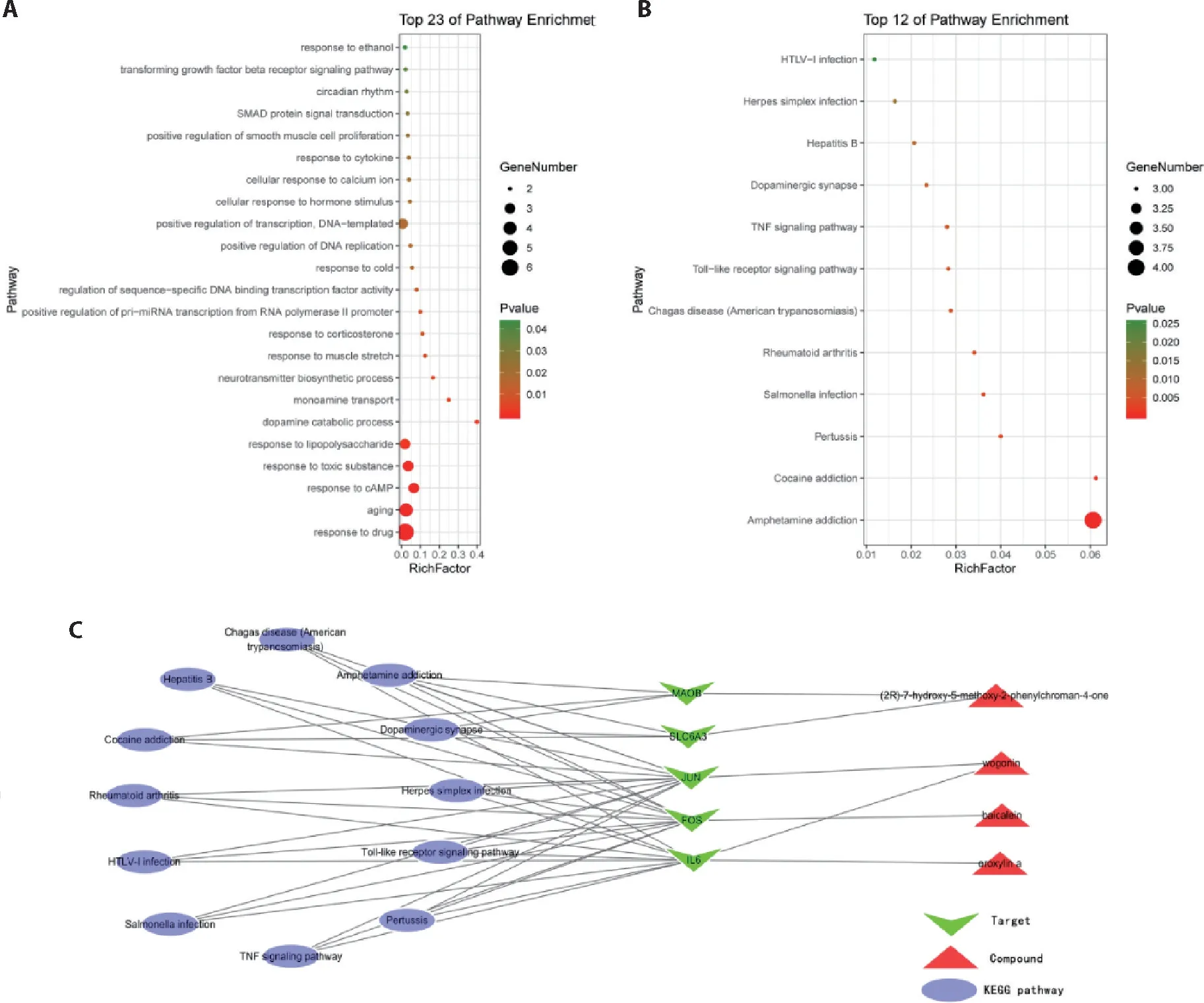
Figure 3 KEGG pathway and GO function analysis of eight common targets
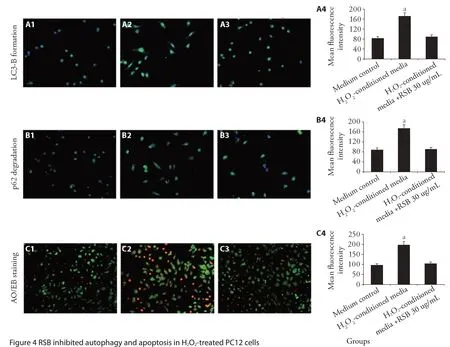
Figure 4 RSB inhibited autophagy and apoptosis in H2O2-treated PC12 cells
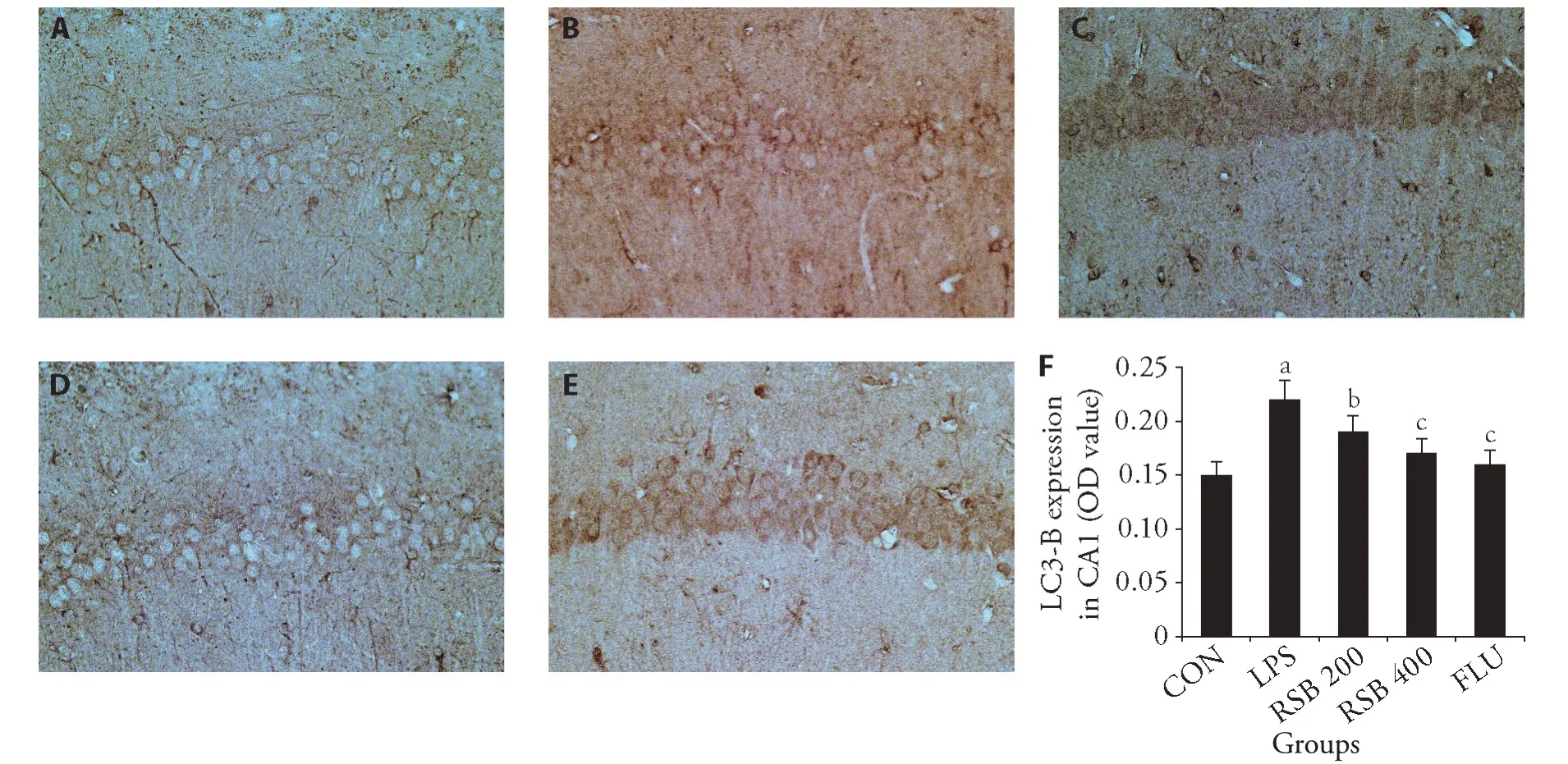
Figure 5 Effect of RSB on LC3-B protein expression in the hippocampus assessed by IHC staining
DISCUSSION
Using the proposed approach,we identified the key targets and elucidated potential molecular mechanisms of RSB as an antidepressant in four steps.
In the first step,143 chemical ingredients in RSB were obtained from TCMSP database.Baicalein has been to shown to restore the decrease of BDNF and phosphorylated ERK1/2 in the hippocampus induced by CUMS.20It has been reported that wogonin isolated from RSB has anti-oxidant,antiviral,anti-cancer,anti-inflammatory,antithrombotic,anti-diabetic effects,and neuroprotective effects.21In the second step,228 drug targets of RSB and 121 antidepressant genes were mapped in Venny 2.1.0 to obtain eight common targets.These proteins are associated with depression and anxiety,as well as inflammation,cancer,and Alzheimer's disease.22Monoamine oxidases exist in two subtypes,MAO-A and MAO-B,and are oxidized to destroy neurotransmitter monoamines in the brain.23Interestingly,wogonin and baicalein could be a moderate inhibitor of MAO-B and a valid,nonselective,reversible,and competitive inhibitor of MAO-A.24Additionally,the human dopamine transporter gene SLC6A3 is involved in neuropsychiatric illnesses.25Recent evidence has revealed that FOS protein is necessary for the survival of neurons and has a neuroprotective effect.26Moreover,miR-221 contributes to the diabetes induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons by regulating FOX expression.27Therefore,it is reasonable for RSB to induce FOS overexpression and inhibit apoptosis.
Previous studies have indicated that IL-6 deletion inhibits some markers of hepatic autophagy at baseline.28Besides,baicalin is widely used in the treatment of hypertension,inflammation,bacterial infection,and cardiovascular disease,and its mechanism is related to anti-neuroinflammation.29Again,several studies have shown that the beneficial effects of oroxylin A may be due to the enhancement of GABAA receptor antagonist or brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling.30
In the third step,we decipher the underlying mechanisms of major targets and corresponding active compounds contained in RSB acting on depression.Cocaine-and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART)belongs to the neuropeptide group and is found in the central and peripheral nervous systems.31In clinical practice,CART plays a vital role in coping with stress and anxious behavior.32Accordingly,regulating the expression balance of CART plays a vital role in the development and repair of depression.
In the fourth step,the antidepressant effect of RSB and its specific molecular mechanisms were further studied.According to this result,30 μg/mL RSB was selected as the concentration for the subsequent experiments.Recent reports showed that positive control drugs such as amitriptyline and fluoxetine induce autophagy in hippocampal neuronsviathe slow accumulation of sphingomyelin in lysosomes and Golgi membranes and of ceramide in the endoplasmic reticulum.33This suggested that antidepressants may trigger autophagy in response to stress.Therefore,we used RSB to study whether the antidepressant activity is mediated by autophagy and apoptosis.These results suggested that H2O2promoted the protein expression level of LC3-B and p62 degradation in PC12 cells,whereas RSB markedly reversed this dysregulation of autophagy and apoptosis caused by H2O2in the PC12 cells.We revealed significant changes in the RSB 400 mice compared with the LPS mice after RSB treatment.Our results have provided a possible mechanism for the antidepressive action of RSB by reducing the expression of LC3-B in CA1 neurons.However,current tools for target prediction cannot always distinguish whether the target is activated or inhibited by the substance of interest.Second,predicted results are not convincing enough,and experimental verification of more potential targets needs to be performed in the future.
In summary,the study contributes to the understanding of the antidepressant pharmacological mechanism of RSB by the combination of network pharmacology prediction and experimental verification.Furthermore,it is also conducive to the application of Traditional Chinese Medicine within modern medicine.
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2021年6期
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2021年6期
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- In vivo anti-diarrheal activity of jujube honey on castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice
- Ethanolic extract of Puhuang (Pollen Typhae) modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through inducible nitric oxide synthase/cyclooxygenase-2 signaling in RAW 264.7 macrophages
- Pingchuan formula (平喘方) improves allergic asthma in mice through inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
- Can Fig and Olive Ameliorate the toxicity Induced by 2-nitropropane in some organs of mice? role of inflammatory versus anti-inflammatory genes
- Efficacy of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on myocardial infarction by enhancing autophagy in rats
- Anti-hypertensive and endothelia protective effects of Fufang Qima capsule (复方芪麻胶囊) on primary hypertension via adiponectin/adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase pathway
