Study on traditional Chinese medicine syndrome of esophageal cancer based on Delphi method
Yu-Ling Zheng, Hong-Xin Sun, Ya-Ling Zhang, Xue-Kun Song, Jun-Tao Wang, Ya-Qi Meng
1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China; 2Henan Province hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhegzhou, China
Abstract Esophageal cancer is one of the common malignant tumors in humans.Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)has unique advantages in the treatment of esophageal cancer.However, the TCM syndrome classification of esophageal cancer is not standardized.This Delphi survey aimed to explore the TCM syndrome classification and symptom characteristics of esophageal cancer.Methods: Based on literature research, an expert consultation questionnaire was developed for the study of the TCM syndrome rules of esophageal cancer.Two rounds of questionnaire surveys were conducted among 62 experts across the country.Statistical description and statistical analysis of the mean, coefficient of variation, grade sum, and unimportant percentage of the retrieved data.TCM syndrome rules and diagnostic indicators for esophageal cancer after screening and sorting out the questionnaire items, convening experts to demonstrate.Results:62 valid questionnaires were collected, and the expert positive coefficient was 100%.The Kendall's coefficient of concordance W of the first and second rounds are 0.232 and 0.2334 respectively.In addition, the Kendall's coefficient of concordance W of the second round has been improved compared with the first round, suggesting that experts have a better degree of coordination on the importance of indicators.The common TCM syndromes of esophageal cancer are obtained:"liver-stomach disharmony, phlegm and qi obstruction syndrome", "liver and spleen disorders, phlegm accumulating with stagnation syndrome", "deficiency of liver and kidney yin, stubborn blood syndrome", " deficiency of spleen and kidney yang, stubborn blood syndrome ".Conclusion: The TCM syndrome indicators of esophageal cancer has been established.It provides a basis for the standardized research of TCM syndrome diagnosis of esophageal cancer, which is of positive significance for improving the level of clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Esophageal cancer; syndrome; Delphi method; expert questionnaire; traditional Chinese medicine
Introduction
Esophageal cancer (EC) is one of the common malignant tumors in humans.TCM provides unique advantage for the treatment of EC.TCM inhibited the growth of esophageal cancer cells, reduced symptoms of dysphagia, improved quality of life in patients and prolonged survival [1-2].In the process of in-depth research on the rule of TCM syndromes of esophageal cancer, Professor Yuling Zheng’s research group consulted ancient Chinese medical books from the Han Dynasty to the Qing Dynasty, carefully combed the relevant TCM diagnosis and treatment of the esophagus published in the Chinese Academic Journal Full-text Database (CNKI) from 1972 to 2018 Modern literature on cancer, found that the interpretation of the relationship between early, middle and late stages of esophageal cancer in ancient literature is not clear.This problem found by the research group makes TCM syndrome differentiation and diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer complicated, which is not conducive to clinical differentiation and treatment.Based on TCM syndrome research methods [3-9], by referring to the existing "Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Cancer in Traditional Chinese Medicine".Professor Zheng Yuling's research group combined TCM syndrome differentiation treatment of esophageal cancer with long-term clinical practice experience [10-14], so that they finally conducted systematic research on the TCM syndrome classification and diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer and putted forward hypotheses.With internationally accepted Delphi method, they solicited opinions from peer experts and verified the hypothesis [5].In this way, there search group preliminarily clarified the diagnostic indicators for the TCM syndrome classification of esophageal cancer, expecting to provide a theoretical basis for the standardized research of TCM syndromes.
Methods
There are problems such as non-standard TCM syndrome classification of esophageal cancer and limited clinical application, which are not conducive to syndrome differentiation and treatment of esophageal cancer and the establishment of clinical pathways.To overcome this challenge, we have used the Delphi technique, which is increasingly used in healthcare research [15-17].A survey-based method of consensus building, the Delphi technique is based on fundamental principles of purposive sampling of experts in the field of interest, panelist anonymity, iterative questionnaire presentation and feedback of statistical analysis[18,19,20-22].
Survey object
Based on the characteristics and requirements of the Delphi method, the task force follows the principles of authority, representativeness and extensiveness,and takes into account regional factors.The selection criteria for experts in this survey: 1)Professional titles of associate professor and above; 2)Involved in Chinese medicine, Chinese and Western medicine oncology clinical work for more than 15 years; 3)It is geographically representative.
Questionnaire content
The first round of questionnaire s mainly included experts' recognition of the types of TCM syndromes and diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer; the second round of questionnaires was formed based on the statistical results of the first round of surveys and some expert opinions.Experts can list supplementary or revised opinions in the two rounds of questionnaires.
Basis of indicator assignment
The importance or performance degree of each indicator is assigned with 0, 1, 2, and 3 points, that is, 0,1, 2, and 3 represent unseen, rare, common, and most common respectively.
Statistical methods
The data administrator is responsible for data review and sorting, using SPSS 21.0 statistical software to review and sort the collected data, and establish a database.Use the mean, coefficient of variation,grade sum, and percentage of insignificance for statistical description, andP< 0.05 as the difference is statistically significant [5,23].
Results
Basic situation of experts
A total of 62 experts participated in the two rounds of questionnaire surveys.In both rounds of surveys, 62 expert consultation questionnaires were returned.The experts were from18 different provinces, including Beijing, Guangzhou, Tianjin, Shanxi, Hebei, Chengdu,Xinjiang, Chongqing, Fujian, Jiangsu, Anhui, Gansu,and Sichuan, Guangdong, Shandong, Hubei, Ningxia,Henan, which are geographically representative.All experts engaged in Chinese medicine or Chinese and Western medicine oncology, have an average working life of 27 years.Among them, 44 have senior titles and 18 have deputy senior titles.They have good professional representation and authority.
Expert positive coefficient
The positive coefficient of experts reflects the degree of attention and understanding of the experts in this research.It is expressed in the questionnaire response rate.It is generally considered that a recovery rate of>60% is better [5].Each of the two rounds of surveys retrieved 62 expert questionnaires, the recovery rate was 100%, and the expert positive coefficient was 100%.Among them, in the first round of the survey, 4 experts (6.45%) gave their opinions, suggesting that the experts are highly active and have good feedback.
Degree of concentration of expert opinions
Refers to the concentration of opinions of experts on the relative importance of each indicator, expressed by means (x̅), grade sum (S), and unimportant percentage(R).The mean refers to the average value assigned by experts to an indicator.The grade sum refers to the total score of an expert after assigning a value to an indicator.The larger the mean, level and value, the higher the importance of the index.The unimportant percentage refers to the proportion of the indicator’s unnecessity.The number of experts with a score of 0 is usually calculated as the proportion of the total number of experts participating in the evaluation.The higher the value, the higher the unimportance.All indicators in this study meet the deletion criteria of low concentration of expert opinions (mean <1.5, grade sum < 93, unimportant percentage>50%) and poor coordination of expert opinions (CV>0.7) [23].
Degree of coordination of expert opinions
It is evaluated by the coefficient of variation CV and the Kendall's coefficient of concordance (W).The coefficient of variation indicates the degree of fluctuation or coordination of the importance of each indicator by experts.The smaller the coefficient of variation, the higher the consistency of the evaluation of the importance of the index by experts, the higher the degree of coordination and the smaller the differences.When the CV value is greater than or equal to 70%, it indicates that the expert opinions of this indicator are quite different, which can be used as the basis for deleting the indicator [9].
Kendall's coefficient of concordance (W) is the degree of coordination of all experts' evaluation of all indicators, and its value is 0-1.It is generally believed that the greater the value, the higher the degree of coordination.The expert consultation of this research was conducted in 2 rounds.Kendall's coefficient of concordance (W) of the first-round was 0.232 as well as that of the second-round0.234.In addition, the W in the second round has been improved compared with the first round, suggesting that experts have a better degree of coordination on the importance of indicators.See Tab.1.
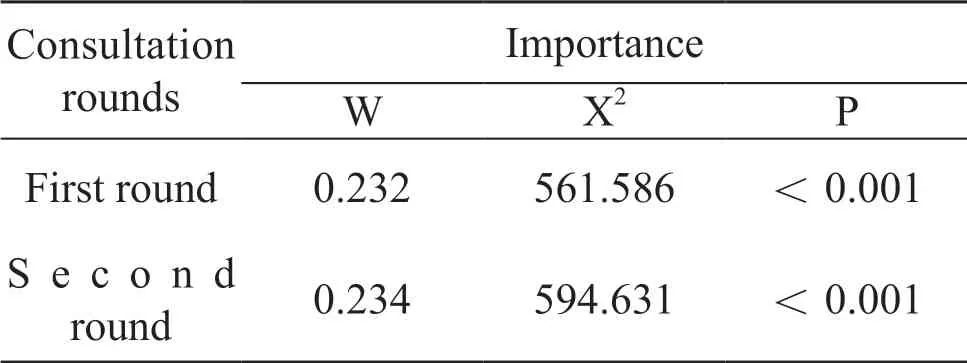
Table 1 Degree of coordination of expert opinions Characteristics of common TCM syndromes of esophageal cancer and evaluation of indicators importance liver-stomach disharmony, phlegm and qi obstruction syndrome
It can be seen from Tab.2 that, except for the thin and greasy coating, wiry and slippery pulse in the first round, dry mouth and throat, and irregular bowel movements in the second round, the R was 1.61%(<50%), and the other index R values were all 0.In the first round of questionnaire survey: liver-stomach disharmony, phlegm and qi obstruction syndrome for the diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer mainly include 10 indicators.Among the indicators,X is between 1.87 and 2.87,S is between 116178, and experts’ opinions are highly concentrated.From the degree of coordination of experts’ opinions, the CV value of the remaining indicators fluctuates between 13.40%and 40.50%.Itimplies expert opinions are more consistent.The expert added the symptom items of "inappetence " to the next round of expert the questionnaires.In the second round of questionnaire survey, the diagnostic indicators of liver-stomach disharmony, phlegm and qi obstruction syndrome included 11indicators.Various diagnostic indicators X is between 1.86and 2.90, S is between 115 and 180.Expert opinions have a high degree of concentration.From the point of view of the degree of coordination of expert opinions, the CV value fluctuates between10.03%and 37.60%, suggesting that experts’ opinions are more consistent.
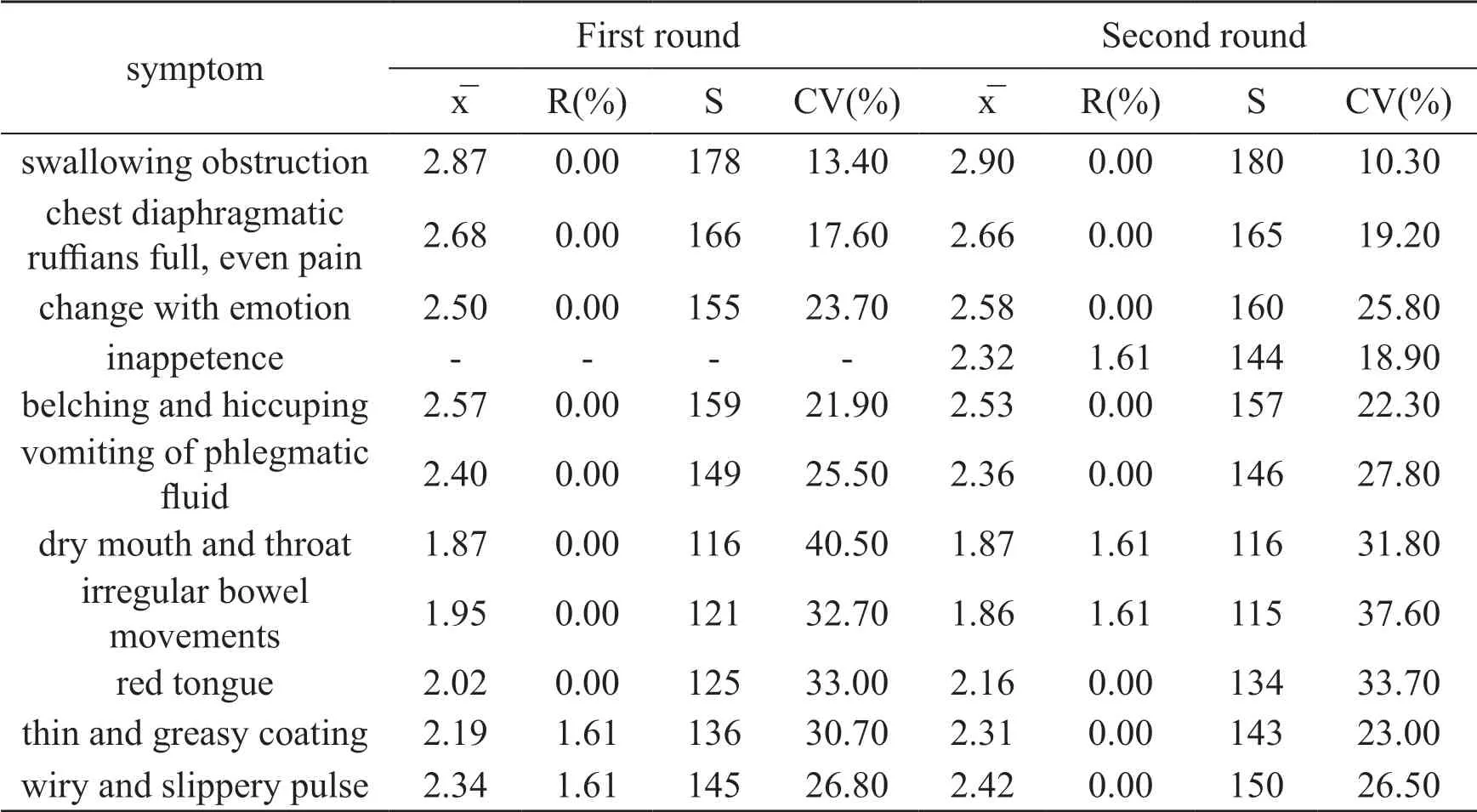
Table 2 Analysis of various diagnostic indicators of liver-stomach disharmony, phlegm and qi obstruction syndrome
liver and spleen disorders, phlegm accumulating with stagnation syndrome
It can be seen from Tab.3 that, except for the dry skin in the first round, the R was 1.61% (<50%), and the other index R values were all 0.In the first round of questionnaire survey: liver and spleen disorders,phlegm accumulating with stagnation syndrome for the diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer mainly include 10 indicators.Among the indicators,x̅ is between 2.00and 2.86,S is between 124177,and experts' opinions are highly concentrated.From the degree of coordination of experts’ opinions,the CV value of the remaining indicators fluctuates between14.00%and 32.70%.It implies expert opinions are more consistent.The expert added the symptom items of "sleepy night, dreaminess" to the next round of expert questionnaires.In the second round of questionnaire survey, the diagnostic indicators of liver and spleen disorders, phlegm accumulating with stagnation syndrome included 11indicators.Various diagnostic indicators x̅ is between 1.98 and 2.84, S is between 123 and 176.Expert opinions have a high degree of concentration.From the point of view of the degree of coordination of expert opinions, the CV value fluctuates between14.50% and 34.00%, suggesting that experts’ opinions are more consistent.
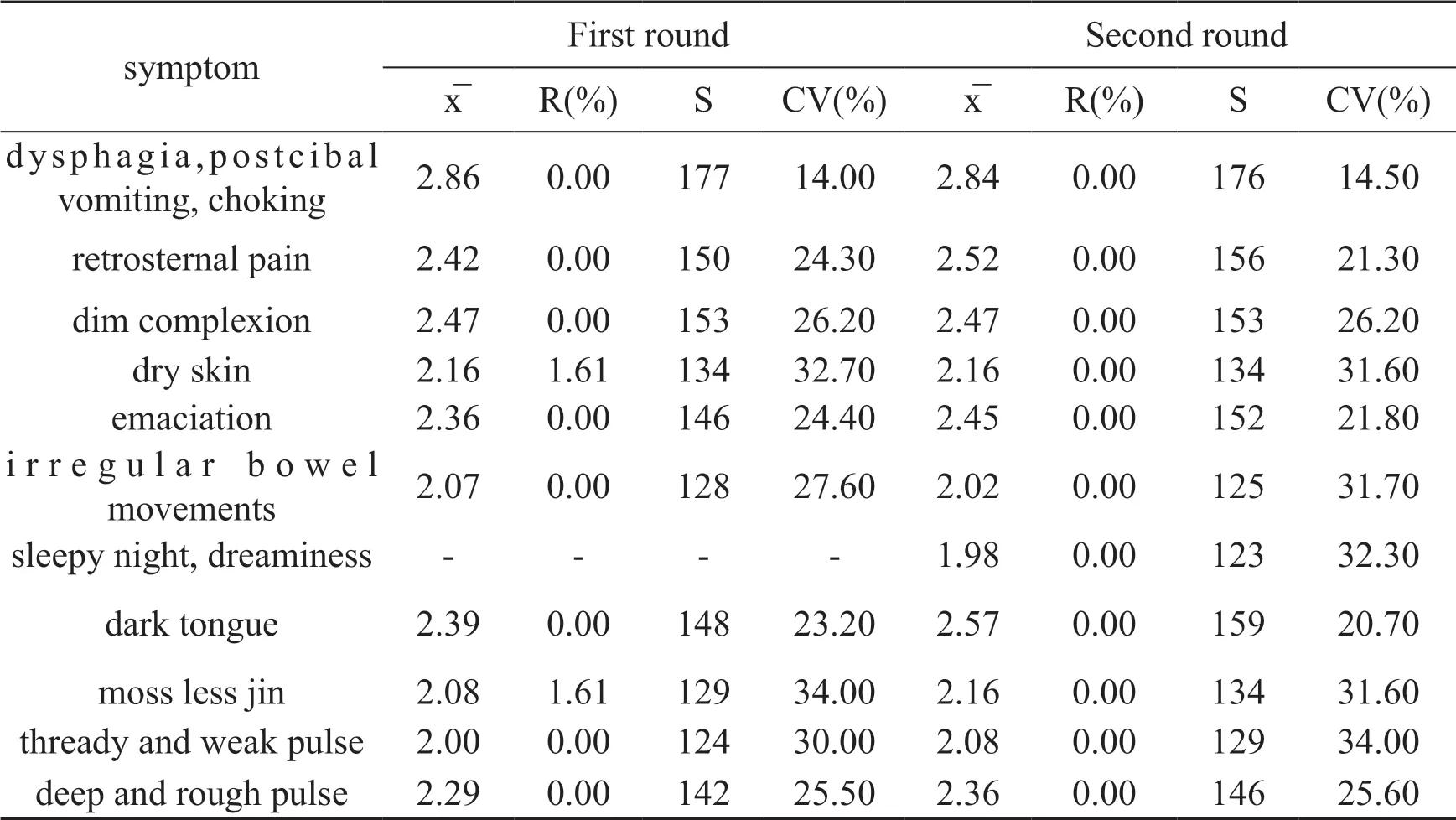
Table 3 Analysis of various diagnostic indicators of liver and spleen disorders, phlegm accumulating with stagnation syndrome
Deficiency of liver and kidney yin ,stubborn blood syndrome
It can be seen from Tab.4that the R-value in the two rounds of questionnaire surveys are 0.In the first round of questionnaire survey: deficiency of liver and kidney yin, stubborn blood syndrome for the diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer mainly include 9 indicators.Among the indicators, x̅ is between 2.34 and 2.86,S is between 145177, and experts’ opinions are highly concentrated.From the degree of coordination of experts' opinions, the CV value of the remaining indicators fluctuates between 12.40% and 25.00%.

Table 4 Analysis of various diagnostic indicators of deficiency of liver and kidney yin , stubborn blood syndrome
Deficiency of spleen and kidney yang, stubborn blood syndrome
It can be seen from Tab.5 that, except for the irregular bowel movements in the first round, irregular bowel movements and deep and thready pulse in the second round, the R was 1.61% (<50%), and the other index R values were all 0.In the first round of questionnaire survey: deficiency of spleen and kidney yang, stubborn blood syndrome for the diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer mainly include 11 indicators.Among the indicators, x̅ is between 1.94 and 2.77, S is between 120172, and experts’ opinions are highly concentrated.From the degree of coordination of experts' opinions,the CV value of the remaining indicators fluctuates between 15.20% and 36.10%.In the second round of questionnaire survey, the diagnostic indicators x̅ is between 2.00and 2.79, S is between 124 and 173 of deficiency of spleen and kidney yang, stubborn blood syndrome.Expert opinions have a high degree of concentration.From the point of view of the degree of coordination of expert opinions, the CV value fluctuates between 17.30% and 37.30%, suggesting that experts’'opinions are more consistent.
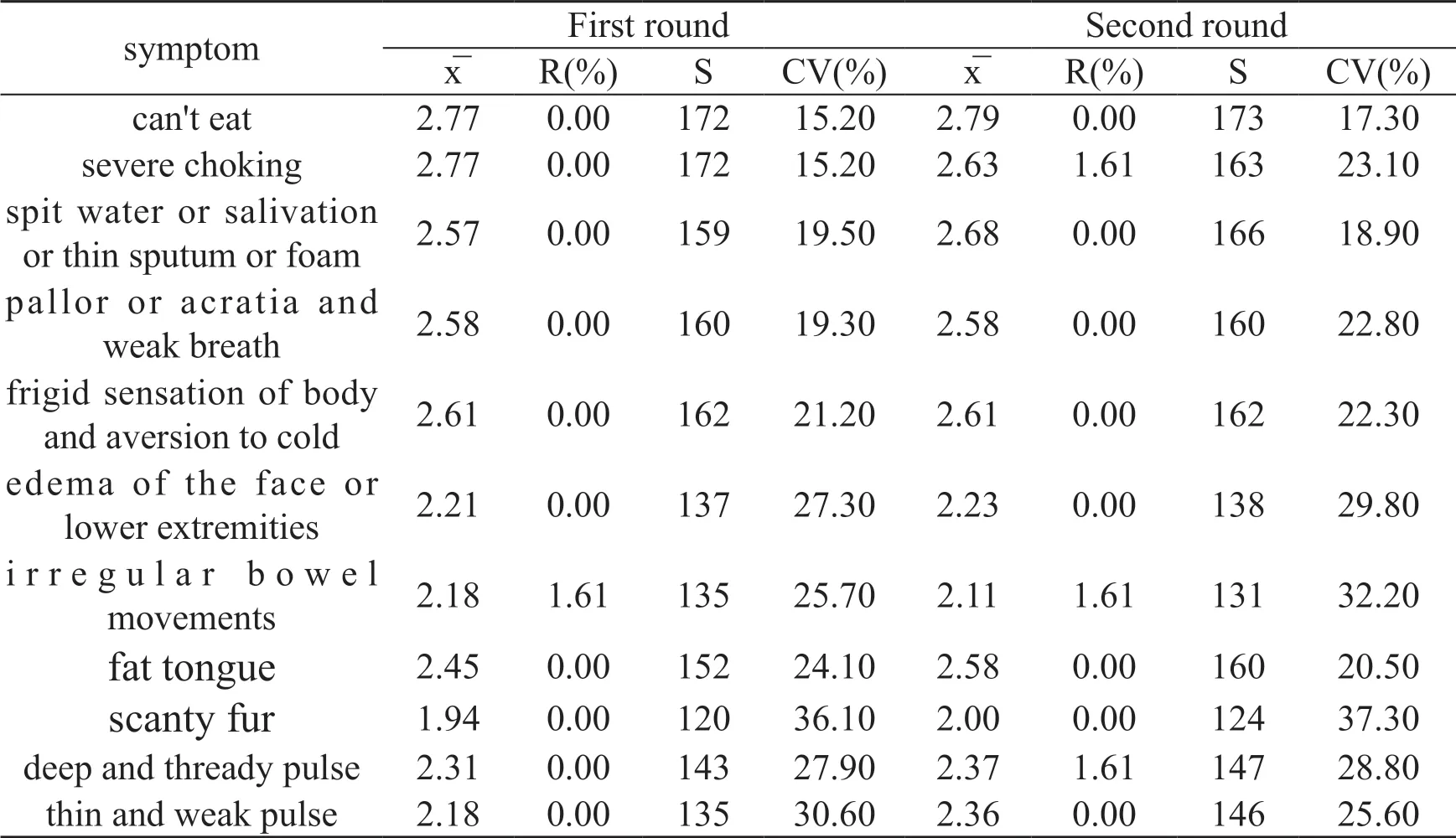
Table 5 Analysis of various diagnostic indicators of deficiency of deficiency of spleen and kidney yang,stubborn blood syndrome
Expert meeting argumentation
After summarizing the previous two rounds of statistical results, 15 authoritative experts put forward specific amendments and supplementary opinions, laid the foundation for the expert discussion meeting.In the demonstration of the expert meeting, the participating experts conducted full exchanges and discussions on the TCM syndromes of esophageal cancer and its diagnostic indicators, summarized and revised the results of the two rounds of Delphi surveys, and finally reached a unified opinion to determine the TCM syndromes of esophageal cancer and its diagnostic indicators.See in Tab.6

Table 6 TCM Syndrome and Symptom Table of esophageal cancer
Discussion
In this study, we sought consensus on the diagnostic indicators of TCM syndromes of esophageal cancer.These issues should be judged by TCM physicians in the clinical treatment of Chinese clinical practice.To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to achieve consensus on such list of standardization of TCM syndrome diagnosis of esophageal cancer in using formal consensus techniques.
Professor Zheng Yuling combined the theoretical research of TCM and long-term clinical observations,and proposed for the first time the direct and indirect positions of esophageal cancer.She believed that the direct and indirect positions of esophageal cancer were in the esophagus in the early, middle and late stages, and the indirect positions involved the spleen and stomach depending on the stage liver and kidney.On the basis of the academic point of view of double disease location of esophageal cancer, the hypothesis of TCM syndrome differentiation of esophageal cancer is first proposed, which divided esophageal cancer into4 types and established its diagnostic indicators: liver-stomach disharmony, phlegm and qi obstruction syndrome; liver and spleen disorders,phlegm accumulating with stagnation syndrome;deficiency of liver and kidney yin, stubborn blood syndrome; deficiency of spleen and kidney yang,stubborn blood syndrome.In the previous literature excavation and retrospective study of clinical cases,the research team summarized the common TCM syndrome types and characteristic diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer, which served as an important reference for this expert questionnaire.Taking into account factors such as region, title, unit, working years, etc., this study selected 62 experts nationwide.The positive coefficients of experts in the two rounds of surveys were both 100%, prompting experts to actively cooperate and provide timely feedback on research opinions.This study uses the Delphi method to investigate and demonstrate the hypothesis, and the conclusions drawn from this study have formed a basically unanimous opinion among peer experts.
Based on the results of the Delphi method, experts recognize that common TCM syndromes of esophageal cancer are 4types:liver-stomach disharmony, phlegm and qi obstruction syndrome; liver and spleen disorders, phlegm accumulating with stagnation syndrome; deficiency of liver and kidney yin, stubborn blood syndrome; deficiency of spleen and kidney yang,stubborn blood syndrome.In terms of the diagnostic index items of syndromes, the mean, grade sum,unimportant percentage and coefficient of variation are used to investigate the concentration and coordination of expert opinions.In the results of the two rounds of questionnaires, x̅ value < 1.5, S < 93 (S total score is 186), unimportant percentage > 50%, and poor coordination of expert opinions (CV > 0.7) are used as the criteria for item deletion, which is used as the standard for selection diagnostic indicators of common TCM syndromes in esophageal cancer.The research results show that the average number of diagnostic index items for each syndrome type is higher, and the coefficient of variation is smaller.It can be seen that experts have a more unified understanding of better representative symptom items, and the second round of investigation is compared with the first round.The coefficient of variation of most items has been reduced,showing that the opinions of experts tend to be more consistent.The Kendall's coefficient of concordance(Kendall's W) scored by the experts in the first round of questionnaire survey was 0.232, and in the second round was 0.234.The degree of expert coordination has improved.Therefore, after the results of the two rounds of questionnaires are summarized, authoritative experts propose specific amendments.With supplementary opinions, an expert discussion meeting was held to conduct full exchanges and discussions on the diagnosis of TCM syndromes of esophageal cancer.The two rounds of Delphi survey results were summarized and revised, which was widely recognized by experts, and finally reached a unified conclusion.
Conclusion
The current research aims to solve the problem of unclear symptoms of esophageal cancer.Based on the Delphi method, through two rounds of expert questionnaire surveys and expert demonstration meetings, the research group combined with open-ended opinions, fully absorbed the opinions of experts in the field on the TCM syndromes and diagnostic indicators of esophageal cancer, and better improved the previous research.As a result, the diagnostic indicators of TCM syndrome classification of esophageal cancer were clarified, and the long-standing problem of complicated TCM syndrome classification of esophageal cancer was clarified, which laid a preliminary foundation for standardizing TCM clinical diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer.
Although the Delphi method can give full play to the collective effects of experts and play an important role in the quantitative diagnosis of TCM syndromes,it is after all a research method based on the subjective opinions of experts, and it has disadvantages such as inability to strictly research.Therefore, the results of this expert questionnaire survey need to be combined with clinical investigation and research.On the basis of clinical research, further clinical verification,assessment, and improvement will be necessary, in order to provide guidance for standardizing the clinical diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All study participants gave consent before taking part in the study.This study is divided into two rounds of questionnaire surveys.The first is to invite 62 Chinese experts from Beijing, Guangzhou, Tianjin, Shanxi,Hebei, Chengdu, Xinjiang, Chongqing, Fujian, Jiangsu,Anhui, Gansu, Sichuan, Guangdong, Shandong, etal.18 different provinces, including Hubei, Ningxia,Henan, etc., are geographically representative.All experts are engaged in TCM or TCM oncology clinical work with an average working life of 27 years.Among them, 44 have senior titles and 18 have deputy senior titles.They have good professional representativeness and authority.The first round of questionnaire survey was conducted through WeChat, and the questionnaire was revised and supplemented according to the opinions of experts, and then the second round of questionnaire survey was conducted to finally complete the survey.
According to the requirement of exemption from ethical review by Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (IRB SQ/02.01/03.0),research involving education, training tests (cognition,judgment, attitude, effectiveness), interview survey, or public behavior observation can be exempt from ethical review.Compliance with the study’s risk to the subject is not greater than the minimum risk, and if it is out of the “research” background, the behavior or procedure under the same circumstances does not require written informed consent.For example, interview research,email/phone survey.This study can exempt participants from signing their informed consent.
Authors' contributions
All authors participated in the conception and design of this study and the recruitment of team members.YL Z conducted this research and drafted the manuscript.HX S, YL Z, XK S JT W and YQ M contributed to data analysis and survey development.All authors participated in the revision of the manuscript, read and approved the final manuscript.
 Medical Theory and Hypothesis2021年2期
Medical Theory and Hypothesis2021年2期
- Medical Theory and Hypothesis的其它文章
- Comparison of serum ALT levels in mice with autoimmune hepatitis induced by ConA: a meta-analyses
