The Practice of Pharmacist-Driven Antimicrobial Stewardship Based on Value-Based Healthcare
Sun Yinxiang ,Xu Chunhua 2, ,Li Yong ,Huang Sichao ,Zhou Zhiling *,Cui Min
(1.Department of Clinical Pharmacy,Zhuhai People’s Hospital (Zhuhai Hospital Affiliated with Jinan University),Zhuhai 519000,China;2.School of Pharmacy,Zunyi Medical University,Zunyi 563000,China;3.Department of Hospital Affairs,Zhuhai People’s Hospital (Zhuhai Hospital Affiliated with Jinan University),Zhuhai 19000,China;4.Department of Pharmacy,Zhuhai People’s Hospital (Zhuhai Hospital Affiliated with Jinan University),Zhuhai 519000,China;5.Zhuhai People’s Hospital (Zhuhai Hospital Affiliated with Jinan University),Zhuhai 519000,China)
Abstract Objective To evaluate the effect of pharmacist-driven antimicrobial stewardship based on value-based healthcare in a tertiary hospital in China.Methods The application of plan-do-check-action (PDCA) cycle and antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) were respectively used to improve the rational use of antimicrobial agents in prophylactic and therapeutic.Data were collected and the effect was assessed during the management period (2016-2019).Results and Conclusion From 2016 (before implementation) to 2019 (after implementation),the rational use of antibiotics were obviously enhanced in outpatients,inpatients,and emergency department.For instance,the utilization rate in type I incision operation was decreased from 26.42 % to 14.60 % (P=0.000),the daily doses of antibiotic per 100 patient-days decreased from 49.34 ± 2.97 to 35.89 ± 4.96 (P=0.000),and the average antibiotic expenditures dropped from 948.53 yuan to 526.30 yuan (P=0.000).There was no significant change in infection rate,nosocomial mortality rate,and the length of hospital stay.After the implementation of clinical pharmacistdriven antimicrobial stewardship based on value-based healthcare,the consumption and cost of antibacterial have been greatly reduced.Therefore,the pharmacist-driven antimicrobial stewardship increases its value.
Keywords:pharmacist;value-based healthcare;antimicrobial stewardship;antibiotic consumption;medical quality
In pharmaceutical care,pharmacists use their knowledge of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics to provide professional support to doctors for clinical decision-making,prescription review,and medical advice review on drug treatment.Studies have shown that antimicrobial stewardship not only decreased the occurrence rate of multidrug resistance and patient mortality,but also optimized antimicrobial agents use[1].The unreasonable use of antibiotics is still a serious problem in China.Antibiotic abuse has led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant that threatens human health and safety.Antimicrobial resistance has become a global public health problem[2].If antimicrobial resistance continues to increase,the global mortality is estimated to reach 10 million by 2050[3].In response to this situation,various antimicrobial management methods have been adopted in different countries to reduce the rates of antimicrobial agents abuse and curb antimicrobial resistance.The antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) program is a management method recommended by the World Health Organization to contain antimicrobial resistance[4].Pharmacists play an important role in AMS[5].
Value-based healthcare (VBH) is a medical management model,which was firstly introduced by Porter and others in 2006.Its goal is to take patient as center and obtain the best treatment results at a certain cost[6,7].Based on the value equation proposed by Mayo Clinic [Value=Quality (Outcomes+Safety +Service)/ Cost],this study started from improving the medical quality and reducing treatment costs,which was led by clinical pharmacists to manage antimicrobial agents in a tertiary hospital in China.Data on the usage rates of antibiotics,the proportion of antibiotic prophylaxis in type I incision operations,defined daily doses (DDDs) per 100 patient-days,infection rate,nosocomial mortality rate,length of hospital stays,antimicrobial costs before and after the implementation of management (2016–2019) were collected to evaluate management effect in terms of medical treatment quality and cost.
1 Method
1.1 Study design and setting
The place where this study was performed is a tertiary hospital with 1 500 beds and more than 40 clinical specialties,including intensive care,respiratory,infectious diseases department,hematrheumatology,orthopedics,and general surgery and so on.The VBH concept was used to manage antimicrobial agents.
1.2 Data collection
The hospital information system (HIS) was used to collect medical records of outpatients and inpatients,including 3 521 124 outpatients,239 127 inpatients,476 478 emergency patients,and 28 896 patients with type I incision operations.and the data such as the usage rates of antibiotics,the proportion of antibiotic prophylaxis in type I incision operations,DDDs per 100 patient-days,infection rate,nosocomial mortality rate,length of hospital stay,and costs of antibiotics from 2016–2019 were statistically analyzed.At the same time,120 patients were randomly selected to calculate the length of hospital stay and the cost of antibiotics each year.
1.3 Management prophylactic use of antimicrobial agents during the perioperative period in patients by plan-do-check-action (PDCA)
Clinical pharmacists used PDCA cycle as the quality control method from January 2017.With administrative management as the main method,PDCA focused on regulating the application of antibiotics in surgery to avoid waste of medical resources and reduce unnecessary medical expenses of patients.PDCA cycle measures are as follows.
Baseline survey:We randomly selected medical records of 120 patients treated with antibiotics at the hospital from July 2016 to December 2016.By utilizing the method of“the 80/20 rule ”,we found that the DDDs per 100 patient-days among hospitalized patients was high due to nonstandard prophylactic medication,including long treatment course for prevention,non-indicated requisition,inappropriate usage and dosage,inappropriate selection of drugs,inadequate evaluation of infection,unreasonable combination of drugs,and unclear orders for drug change.By further applying the“fishbone analysis”(Fig.1),the main causes were that physicians did not understand preventive medicine completely.The insufficiently targeted pharmaceutical care,lack of detailed comments and interventions from pharmacists,imperfect management system and norms,and lack of performance appraisal at the hospital also led to these problems.
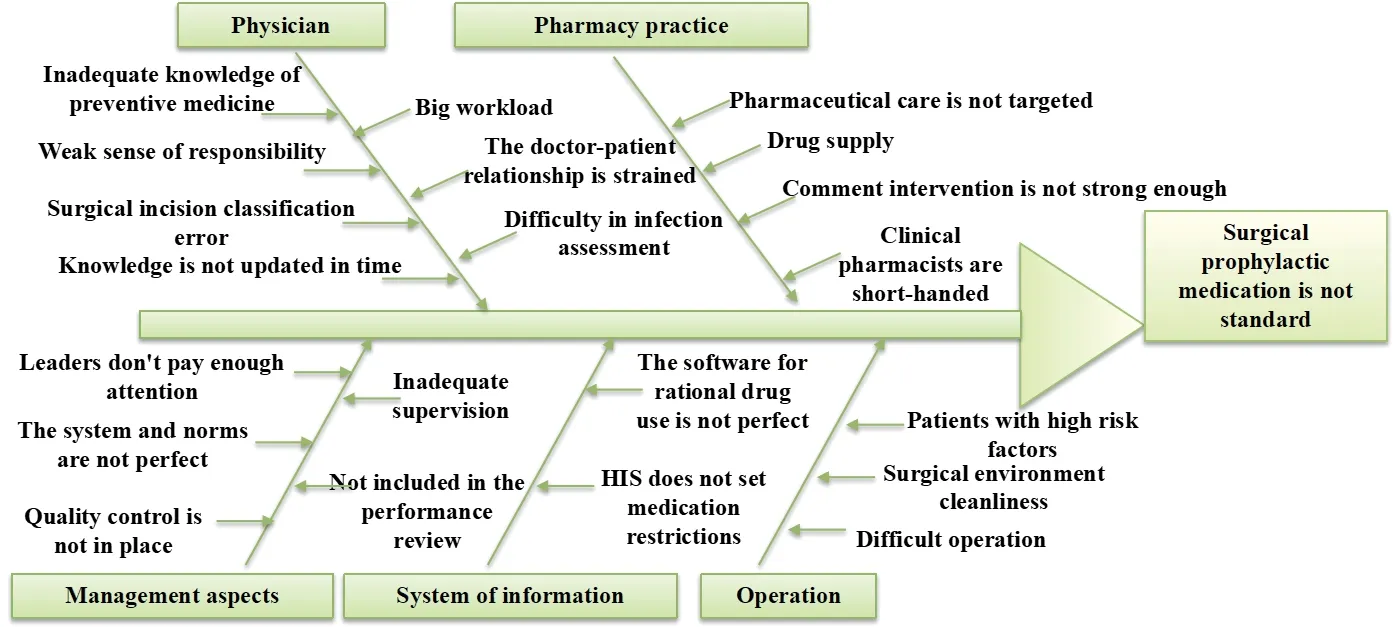
Fig.1 The cause of nonstandard surgical prophylactic medication
The following counter measures should be formulated and implemented.(1) Several antibacterial drug management systems and norms should be made and relevant rules must be set in the information system according to the system and regulations.(2) All employees should have regular training and assessment of antibacterial drugs in hospital.(3)The management guidelines of clinical application of antibacterial drugs should be revised and the physicians must sign the responsibility form to promise a rational use of antimicrobial agents.(4)Special comments and monitoring of antibiotics should be carried out.
1.4 Management of antimicrobial agents for therapeutic use by AMS
AMS program was used to manage antimicrobial agents based on“value-based healthcare”.The technical team was established mainly by clinical anti-infection experts,clinical pharmacy experts,and microbiology experts with the cooperation of hospital infection,information and other departments.The team focused on improving the rationality of therapeutic application of antibacterial agents and the quality of medical treatment by professional methods.
Specific measures are as follows.First,AMS program work meetings were convened four times per year to discuss the development of goals and plans,determine the progress and review of bacterial resistance,team building,personnel training programs,and adjust antimicrobial agent catalog in the hospital according to bacterial resistance.Second,one or two large-scale antibiotic training sessions were organized for all doctors in the hospital each year.Training contents were covered by correct specimen collection,policy propagandizing,drug sensitivity report reading,and medical treatment guidelines interpretation.Third,monitoring and publication of information on the indicator of clinical application of antimicrobial agents were made,which included the usage rate and DDDs per 100 patient-days,preventive utilization rates and variety selection of antimicrobial agents for type I incision surgery (Type I incision surgery usually does not need preventive antibiotics,because the surgical organs are sterile parts of the human body without local inflammation and they don’t involve the tract of the human body connected the outside such as the respiratory tract and digestive tract),the proportion of antibiotics prescriptions in outpatients and the emergency department,the ratio of combined application of antibiotics,inspection rate,and monitoring of blood concentration of antibiotics.Fourth,the analysis of the distribution of drug-resistance bacteria and drug warning was made every three months.Fifth,the multidisciplinary team(MDT) sessions were organized for usual discussions and learning of infectious diseases cases.
The core of AMS program is the multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of difficult infection cases and multidisciplinary casediscussion meetings.In this team,anti-infective experts were responsible for the multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of difficult or critical infection cases,including clinical experts of respiratory department,infectious department,critical care center department,clinical pharmacists,microbiologists,and iconography experts,to assist in the diagnosis,treatment,and discussion.The MDT seminar was held by clinical pharmacists once a month,including diagnostic methods,new diagnosis and treatment ideas,path management,rational use of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling,anti-infective experience,and new guides,which could help train personnel and establish the team.
1.5 Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using SPSS 21.0.Oneway ANOVA was used to analyze the continuous variables,and a chi-square test was conducted to evaluate categorical variables.Mann-Whitney U test was used for quantitative variables of nonnormal distribution.P-value <0.05 was considered significant.
Due to different prices of antimicrobial agents in each year,to make the antimicrobial expenditures from 2016 to 2019 comparable,we took 2019 as the benchmark and used the consumer price index (CPI)of medical care in our city to adjust the antimicrobial expenditures of patients.The CPI of health care from 2016 to 2019 was found through the statistics bureau of Zhuhai,and the CPI value was named asC2016,C2017,C2018,andC2019.The four CPI values were uniformly adjusted to 100 in 2016,and named successively asA2016,A2017,A2018andA2019.ThenA2016=100,A2017=(C2017×A2016)/A2016,A2018=(C2018×A2017)/A2016,A2019=(C2019×A2018)/A2016,A2016=(C2019×A2018)/A2016.The discount ratio was named asR2016,R2017,R2018,andR2019,and then after the uniform adjustment to 2019,R2019=A2019/A2019,R2018=A2019/A2018,R2017=A2019/A2017,andR2016=A2019/A2016.The discounted expense over the years was:actual expense in the current year=original expense in the current year × discount ratio in the current year (R).
2 Results
2.1 Antimicrobial utilization
The usage rates of antibiotics in outpatient,emergency,inpatient,and patients undergoing type I incision operations in 2019 were lower than that in 2016 (P=0.000).During the management period,the proportion of antibiotic prophylaxis in type I incision operations decreased significantly (P<0.01) from 2017 to 2018 (Table 1).
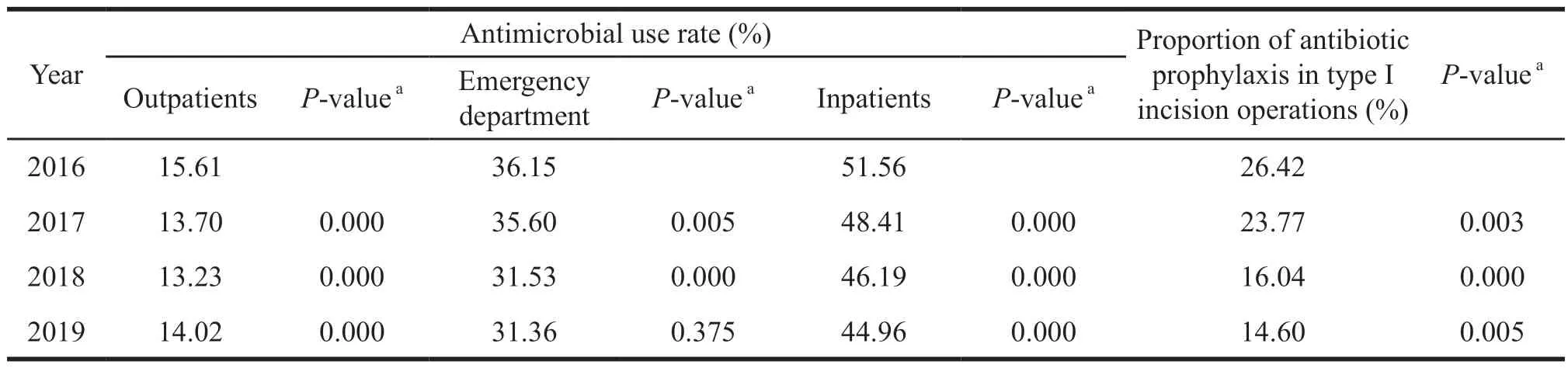
Table 1 Changes in antimicrobial usage rate from 2016 to 2019
2.2 DDDs per 100 patient-days,infection rate and infection mortality rate
The number of DDDs per 100 patient-days decreased from 49.34 ± 2.97 in 2016 to 35.89 ± 4.96 in 2019 (means ± standard deviation,P=0.000).The decrease was the most obvious between 2016 and 2017.
No significant differences were shown in the infection rate and infection mortality rate between the year 2016 and the year 2019 (P=0.259,P=0.378).Compared with 2017,the infection rate decreased significantly in 2018 (P<0.01).and the infection rate showed a downward trend during the management period.However,compared with the infection rate in 2018,there was an increase in 2019.The infection mortality rate increased in 2018 compared with that in 2017 (Table 2).

Table 2 Changes in defined daily doses per 100 patient-days,infection rate,and infection mortality rate from 2016 to 2019
2.3 Length of hospital stay and antimicrobial expenditures
We randomly selected 120 patient medical records each year from 2016 to 2019,and there was no significant difference for their length of hospital stay.The median antimicrobial expenditures decreased from ¥948.53 in 2016 to ¥526.30 in 2019 (P=0.000).Specifically,compared with 2016,in2017 the expenditures decreased significantly (P<0.01) (Table 3).
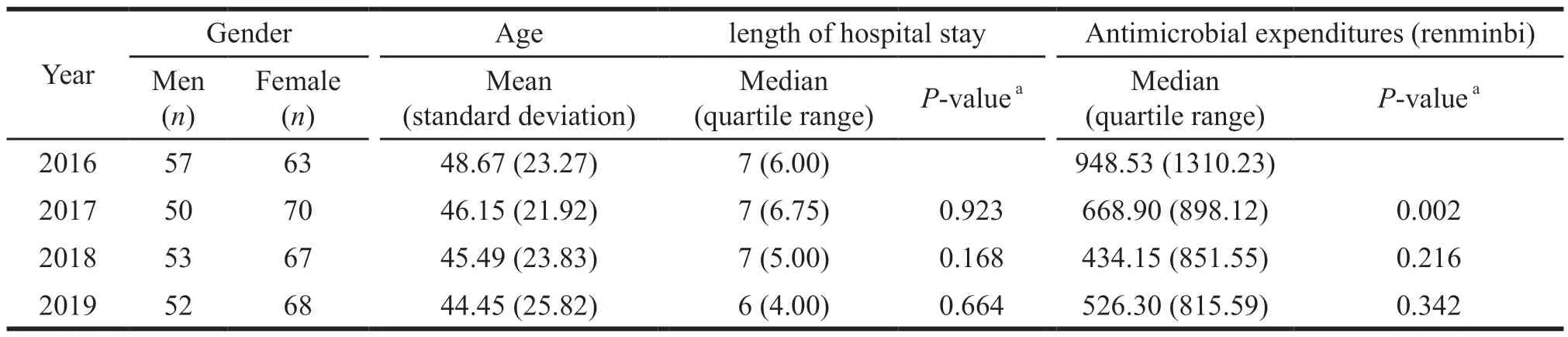
Table 3 Changes in length of hospital stay and antimicrobial expenditures of 120 patients per year from 2016 to 2019
3 Discussion
We evaluated the effectiveness of pharmacistinitiated antimicrobial management in a tertiary hospital in China in terms of both medical quality and treatment costs based on the VBH.PDCA cycle was applied in the management of the prophylactic application of antibiotics,and the AMS program focused on the management of therapeutic antimicrobial agents.We observed that after the implementation of PDCA cycle combined with AMS program,the usage rates of antibiotics in outpatient,emergency,and inpatient,the proportion of antibiotic prophylaxis in patients undergoing type I incision operations,and the number of DDDs per 100 patientdays were significantly improved.The proportion of antibiotic prophylaxis in type I incision operations decreased year by year from 2016 to 2019,with the most significant decrease in 2018,which confirmed the effectiveness of managing the prophylactic use of antimicrobial agents by using PDCA cycle.At the same time,the DDDs per 100 patient-days was decreased fast from the year 2016 to the year 2017,which indicated that the rational use of antimicrobial agents during the perioperative period in patients had a great influence on the control of the DDDs per 100 patient-days intensity of in the hospital.However,there was no significant difference between the year 2019 and 2018,which meant that PDCA method in the normalization of prophylaxis antibiotic usage in operations significantly cut DDDs in China.And the effect of AMS method on DDDs gradually declined.On the other hand,we should not expect to see the infinite declines in antimicrobial use,but the minimum amount of antimicrobial to maintain optimal clinical outcomes.
There was no significant difference in infection rate and infection mortality rate before and after the implementation of PDCA cycle combined with AMS program initiated by clinical pharmacists.It indicates that standardized antimicrobial use that reduces unnecessary antimicrobial does not increase the rate of infection and infection mortality.According to the data,the infection rate had been decreasing year by year from 2016 to 2018,and the decline in 2018 was statistically different from that in 2017.But the infection rate in 2019 was higher than that in 2018,and the infection mortality rate in 2018 was higher than that in 2017,which may be related to multiple factors such as disease epidemiology,imported infections,and people’s health level,as well as the improved treatment level of the hospital and the increase in the number of complex diseases.There was no significant difference between 2016 and 2019 in regard to the length of hospital stay.Except for slight fluctuations in 2019,the median antimicrobial expenditures decreased continuously from ¥948.53 in 2016 to ¥526.30 in 2019 (P=0.000),and the decrease rate was 44.51%.
AMS can improve patient outcomes[8],including mortality rate and length of hospital stay[9].Although our study failed to prove the effect of antimicrobial stewardship initiated by pharmacists on improving the outcomes of patients,it significantly reduced the consumption and cost of antimicrobial agents without increasing the infection rate,infection mortality rate,and the length of hospital stay of patients,which could also suggest that the intervention was beneficial to patients.Many studies have reported that the implementation of AMS plays a positive role in the rational use of antibacterial agents and saving medical expenses[10,11].However,the AMS program has not been very well established in China yet.The research of Doron et al[12]showed that the difficulties in implementing an AMS included staff constraints and insufficient funding.Therefore,more support is needed in these areas.PDCA cycle is a hot topic in antimicrobial agent management in China,and the intervention measures vary from researcher to researcher.In our study,PDCA cycle focused on reducing the proportion of antibiotic prophylaxis in type I incision operations.In the early stage of PDCA cycle,the number of DDDs per 100 patient-days was significantly reduced.However,after two rounds of the PDCA cycle to develop long-term intervention measures,the management of antimicrobial agents in the hospital was in a bottleneck period,and the DDDs per 100 patient-days had not been further improved as of the first half of 2018.The fundamental cause was that clinical pharmacists were only main members of PDCA cycle team,supplemented by the administrative personnel,which could not solve the problem of rational use of therapeutic antimicrobial agents.Therefore,we launched the AMS program and achieved good outcomes.Our study further confirmed the importance of the three technical support teams including clinical anti-infective experts,clinical pharmacists,and microbiology experts in antimicrobial stewardship.
The goal of antimicrobial stewardship is to curb antimicrobial resistance,improve patient outcomes,and reduce medical costs.Although we do not have data on the rate of antimicrobial resistance,AMS program has been reported to play an important role in curbing antimicrobial resistance[13].
4 Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that the implementation of clinical pharmacist-driven antimicrobial stewardship based on value-based healthcare can reduce the total antibacterial consumption and antibiotic expenditures.In the context of complex medical care,there is no significant change in infection rate,infection mortality rate,and length of hospital stay of patients.Therefore,the value is significant.PDCA is a quality control method to reduce the DDDs per 100 patient-days,and the effect is faster and more obvious.AMS should be carried out for a long time because the effect is relatively mild,and it will have a greater impact on the improvement of medical quality.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Problems in China’s Licensed Pharmacists System and Suggestions for Improvement
- Investigation and Analysis of the Current Situation of Online Drug Sellers
- EU Real-World Evidence Supporting Drug Regulatory Decision and Its Enlightenment to China
- Current Situation and Development Strategy of Residents’Cognition and Use of TCM in Liaoning Province
- Empirical Analysis on Performance Evaluation of A Pharmaceutical Company Based on Economic Value Added
- Research on the Status Quo and Countermeasures of Patent Application in Liaoning Biopharmaceutical Industry Based on Patent Map

