Pharmacological research progress of ursolic acid for the treatment of liver diseases
Yu Liang,Qian-Qian Niu,Yuan-Hong Zhao*
1First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 300381,China.2National Clinical Research for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion,Tianjin 300381,China.
Abstract Ursolic acid is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid with various pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory,hepatoprotective,antitumor,and hypoglycemic activity.This natural product is widely present in many common Chinese herbal medicines such as Hedyotis diffusa and Prunella vulgaris.The present review highlights the pharmacological research progress of ursolic acid in liver disease,with a focus on providing directions for future research and clinical practice of ursolic acid.Modern studies have demonstrated that ursolic acid can adjust the activities of enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and NADPH oxidase to balance oxidative stress,reduce inflammation,as well as to repair damaged liver.Research also showed that ursolic acid targeted lipid metabolic genes,activating autophagy and reducing lipid deposition in hepatocytes,further preventing the progress of fatty liver.Besides,the combination of ursolic acid with caspase-3 was able to prevent apoptosis and relieve liver injury.Furthermore,ursolic acid was showed to target the intestine by alleviating mucosal injury and restoring the balance of the intestinal microecology and protect liver through the enterohepatic axis.In terms of antitumor activity,ursolic acid targeted several tumor suppressor genes including gene of phosphate and tension homology deleted on chromsome ten and p53,and affected the expression of cyclin and apoptosis-related proteins involving Bax,Bcl-2,and Bcl-x,which acted on signal transduction pathways including phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B,extracellular regulated protein kinases and proteina fosforilata 21 wide-type actiated factorlp 1.The same compound interacted with caspases,resulting in inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis.In addition,ursolic acid also exerted anticancer activity through inhibiting angiogenesis,tumor invasion and metastasis,and improving immunity.Other studies have noted the importance of nano-preparations of ursolic acid for its clinical applications.This review provides essential information on the role of ursolic acid in liver protection.Further research on the mechanisms of action of ursolic acid would be useful for its pharmaceutical development and clinical application.
Keywords:Liver cancer,Liver fibrosis,Liver injury,Liver protection,Pharmacological mechanism,Ursolic acid
Background
In 1949,Rowe et al.in the United States isolated ursolic acid(UA),a five-ring triterpenoid compound,fromThymus mongolicus[1].In 1956,Hammouda and Men[2]in France extracted the same natural product from the leaves ofVincamajor.According to the literature,UA was first extracted in China in 1963 from Chinese herbal medicineHedyotis diffusaby Fu et al.[3].H.diffusawas first found inGuangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine Historypublished by People’s Publishing House of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region in 1959,and gradually included in herbal monographs in Chaozhou and Quanzhou of China.Fujian Chinese Herbal Medicinepublished in 1970 refers that the external application ofH.diffusasmashed and strangled juice had noticeable effects on snake bites.In 1990,Zhou[4]extracted the elements ferrum,manganese,magnesium,aluminum,silicon,calcium,and titanium fromH.diffusa,confirming that that plant may enhance immunity and treat cancer through titanium.In 1998,Jia et al.[5]confirmed the anticancer activity ofH.diffusaat the cellular level for the first time,providing a direction for the anticancer research ofH.diffusa.Xu Zhenwen[6]extracted UA fromCornus officinalis(C.officinalis)in 1981 and confirmed its effectiveness as an anti-diabetic ingredient.C.officinalisfirst appeared inShennong’s Classic of Materia Medica,a text about the Han Dynasty of China(202 B.C.E.-220 B.C.E.),and its tonic effects were recorded in works such asMaster Lei’s Discourse on Drug Processingwritten by Lei in the Southern and Northern Dynasties of China(420 B.C.E.-589 C.E.),Supplementary Records of Famous Physicianswritten by Tao(456 C.E.-536 C.E.)in the Southern and Northern Dynasties of China andMedicinal Theorywritten by Zhen(541 C.E.-643 C.E.)in the Tang Dynasty of China(618 C.E.-907 C.E.).The prescriptions created by Zhang(1563 C.E.-1640 C.E.),a physician in the Ming Dynasty of China(1368 C.E.-1644 C.E.),such as classical prescription of Chinese medicine Zuogui pill,Yougui pill,Zuogui drink,and Yougui drink,containedC.officinalis,which exerted good tonic effect.Since the 1990s,experimental studies on the single drug ofC.officinalishave been widely carried out,confirming its precise role in regulating blood sugar and improving immunity.He[7]extracted UA fromPrunella vulgarisin 1985.P.vulgariswas first published inShennong’s Classic of Materia Medicahas been widely used in inflammation-related diseases.In 1951,Zhu discovered thatP.vulgarishad a bactericidal effect in the bookScientific Folk Herbsand it could“wash wounds,treat suppurative exopathia,wash vagina,treat vagina,and uterine mucositis”.In 1983,Ma’s experiment[8]confirmed thatP.vulgariscould significantly inhibit the early inflammatory reactions.Besides,UA was also widely found in many Chinese herbal medicines such asLigustrum lucidumandChaenomeles sinensis(Table 1).
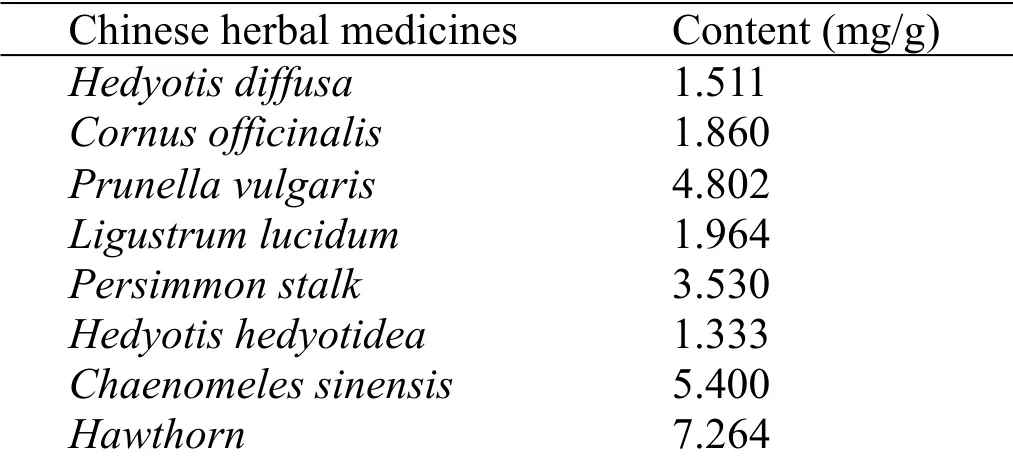
Table 1 Content of ursolic acid in different Chinese herbal medicines
With the development of modern medical technology and molecular docking techniques,the interaction between UA and the following proteins have been reported:cyclin dependent kinase 6[9],vascular endothelial growth factor A,signal transducer and transcriptional activator 3,caspase 3(CASP3),interleukin(IL)-6[10],matrix metalloproteinase(MMP)-1,MMP-3,transcription factor AP-1,tumor necrosis factor[11],and other factors.The anti-inflammatory,anti-oxidative,anti-atherosclerosis activities and the regulation of blood glucose levels and lipid metabolism are the results of the interaction between UA and targets,affecting their expression in organs such as the heart[12-14],lungs[15,16],kidneys[17,18],liver,breast[19],and others[20-22].
It is estimated that there are about 400 million people who suffer from various liver diseases in China,accounting for 1/5 of the total population.Liver disease has become a serious public health problem in China.Epidemiological investigations show that the incidence of drug-induced liver injury in the general population in China is expected to be no less than 24.2 per 100,000 people.The prevalence rate of non-alcoholic fatty liver is about 6%-27%[23].Due to hepatitis B vaccine immunization,the prevalence rate of hepatitis B virus surface antigen in China decreased from 7.18% in 2006 to 5.49% in 2014,although the reported incidence of chronic hepatitis B continues to rise.With the increased number of alcoholics,the prevalence of alcoholic liver disease in some areas has reached 8.7% and the proportion of people with liver failure caused by alcohol has increased from 0.3% in 2003 to 10.1% in 2012.GLOBOCAN[24]estimates that the incidence and mortality of liver cancer in China will be of 18.3 per 100,000 people and 17.1 per 100,000 people,respectively in 2018.The number of cases and deaths related to liver cancer in China is expected to reach 591,000 and 572,000 respectively by 2040,an increase of 50.5%and 54.9%[25].
As the main detoxification organ,liver undertakes the metabolism of most substances,including therapeutic drugs.Therefore,it is particularly crucial to prescribing drugs with low toxicity and side effects when liver function and structure are damaged.Chinese herbal medicines and theirs extracts have become focus of research in recent years due to their extensive sources,multiple pathways,and low side effects.Numerous studies have revealed that UA,as a liver protectant[26],has good potential against liver injury,liver fibrosis,and liver cancer.
This article reviews the mechanism of UA for the treatment of liver diseases,hoping to provide reference for further basic and clinical research on the hepatoprotective effect of UA.
Reversing drug-induced liver injury
Drug-induced liver injury[27]refers to liver injury caused by chemical drugs[28,29],biological agents,traditional Chinese medicine[30],natural medicines,health products,dietary supplements,and their metabolites and even excipients,which can seriously affect the treatment,prognosis,and quality of life of patients.
As a natural product found in Chinese herbal medicine extracts,UA can target liver cells,affecting the expression level of proteases,balancing the body’s oxidation and anti-oxidation,and alleviating the degree of drug-induced liver injury.Zhang et al.[31]randomly grouped patients with drug-induced liver injury.To the treatment group,it was given UA sustained-release tablets on the basis of conventional treatment,and to the control group it was given bicyclol tablets.Twenty-eight days later,the curative effect was evaluated and research found that the liver function indexes such as alanine aminotransferase,alkaline phosphatase,and aspartate aminotransferase in the treatment group were improved significantly,and serum malonaldehyde content decreased,in the group treated with UA.Additionally,superoxide dismutase content increased and necrotic hepatocytes in the central area of hepatic lobules recovered in that same group.These results indicated that UA targeted the liver and protected the biofilm system of hepatocyte membrane and organelles,reducing the degree of lipid peroxidation and repairing damaged cells by reversing the activity of superoxide dismutase and other enzymes.Gutiérrez-Rebolledo et al.[32]found that the mixture of UA and oleanolic acid could improve the liver steatosis induced by anti-tuberculosis drugs in mice.Zhou et al.[33]found that UA inhibited the expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 in rat hepatic stellate cells induced by leptin,up-regulating the expression of MMP-1 and negatively regulating the activity and expression of NADPH oxidase(NOX)4 via extracellular regulated protein kinases,PI3K/Akt and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal pathways,inhibiting the production of reactive oxygen species(ROS),reducing oxidative stress damage and the expression type I collagen gene,thereby reversing the profibrotic effect of leptin.
Improving non-alcoholic fatty liver
The liver is an important metabolic organ of the body which mainly metabolizes lipids in the body.Liver fat is mainly triggered from external food,and genetic and metabolic factors,which deregulate the function of liver lipid metabolism,leading to excessive lipid deposition in liver cells[34],and further aggravating the damage of liver function.Non-alcoholic fatty liver is a metabolic liver disease with lipid accumulation in liver cells as the main pathological feature,and closely related to insulin resistance and its genetic susceptibility.It can not only lead to liver fibrosis and liver injury,but it is also closely related to the occurrence and development of metabolic syndrome,type 2 diabetes,arteriosclerotic cardiovascular diseases,and colorectal tumors.
Ding et al.[35]established a lipid deposition model of human hepatocarcinoma cell HepG2 pretreated with different doses of UA before the treatment with oleic acid.The results showed that UA could significantly reduce the degree of lipid deposition induced by oleic acid in a dose-dependent manner.Further experiments found that the effect of UA on improving lipid deposition in hepatocytes was inhibited after the use of autophagy inhibitors.Autophagy affects important cellular processes such as inflammation,immune response,lipid metabolism and storage by decomposing damaged and excess cellular proteins,organelles and other cytoplasmic components,and recycling intracellular components[36].Autophagy plays an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of liver lipid metabolism.Enhanced autophagy can increase liver fat consumption and reduce liver lipid accumulation.Western blot analysis confirmed that UA may activate autophagy by regulating the phosphorylation of AMPK to eliminate excessive liver lipid droplets and mitochondrial damage,regulating lipid metabolism,and inhibiting lipid deposition in hepatocytes.In addition,UA was also able to act on genes related to lipid metabolism to enhance lipid excretion in hepatocytes.Lin et al.[37]found that UA could competitively bind to hepatic X receptor agonist T0901317 in the liver X receptor α ligand binding region,significantly reducing the activity of liver X receptor response elements and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 c gene promoter and the expression of liver X receptor α target gene,stimulating the phosphorylation of AMPK in hepatocytes,reducing the recruitment of steroid receptor coactivator-1 to sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 c promoter region,reversing the role of cholesterol transport related gene promoter in intestinal cells,increasing lipid excretion in intestinal cells,thereby reducing the lipid content of liver cells and inhibiting adipogenesis.
Reducing alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease relates to chronic liver disease caused by long-term excessive drinking.Its progression mechanisms may be related to the direct or indirect inflammatory reaction in the liver caused by ethanol and its derivatives within the metabolic process.Using a rat model of acute alcoholic liver injury,Ye[38]found that the therapeutic effect of UA is similar to that of bifendate,which can increase the oxidative stress level of hepatocytes,avoiding further damage and promoting the recovery of liver function while regenerating the structure of liver lobules.Ma et al.[39]clarified that CASP3 was the main target for UA as a hepatoprotector drug.The epoxy group of UA metabolite forms a covalent bond with the cysteine-163 of CASP3,which irreversibly inhibits the activity of CASP3,reducing the cleavage of poly ADP-ribose polymerase and the activity of Ca2+/Mg2+-dependent endonuclease negatively regulated by poly ADP-ribose polymerase,blocking cytotoxic T lymphocyte killing mechanism and reducing cell apoptosis.The results showed that UA mainly reduced alcoholic liver injury in mice by inhibiting CASP3 in a dose-dependent manner.
The fat solubility and toxicity of ethanol can directly destroy the intestinal mucosal barrier,increase intestinal permeability, translocate intestinal microorganisms or bacterial metabolites such as endotoxin,and make it reach the liver through the portal vein system,activating the liver immune system and leading to hepatocyte necrosis and apoptosis[40].In addition,alcohol drinking can cause an intestinal microecological imbalance[41],affecting the intestinal digestion,secretion,absorption,and metabolism.It can also lead to the decrease of reducing gastrointestinal peristalsis and increase of the pH in the stomach,further promoting the overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine and reducing the growth of beneficial intestinal microorganisms.Alcohol intake is also able to increase the number of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and to lead to the occurrence of endotoxemia[42].Ma et al.[43]found that after the UA treatment,the levels of D-lactic acid and endotoxins in blood of rats with alcoholic liver injury were significantly reduced while the contents ofBifidobacterium longumandLactobacillus acidophilusin the intestine increased;Escherichia coliandEnterococcus faecalisdecreased after the treatment with UA,indicating that this natural product could repair the intestinal mucosal barrier,reduce intestinal permeability,and the production and release of endotoxin into the blood,regulating the structure and quantity of intestinal flora,improving intestinal microecology and the degree of liver injury in rats with alcoholic liver injury.
Blocking the progression of liver fibrosis
Hepatic fibrosis[33]is a common pathological process of many chronic liver diseases,such as viral hepatitis,non-alcoholic fatty liver,and alcoholic liver disease.Various cytokines secreted by damaged hepatocytes can stimulate hepatic stellate cells to transform into myofibroblasts and induce the activation of fibrotic cells and the deposition of extracellular matrix to complete the repair of damaged hepatocytes.However,when the body is unable to balance the synthesis and degradation of extracellular matrix,the deposition of this matrix will lead to liver fibrosis[44].Without timely and effective intervention,liver fibrosis can evolve into end-stage of liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Intestinal microflora has been proved to be closely related to the process of hepatic fibrosis.Intestinal and liver[45]microflora interact with each other through various pathways such as endocrine and cell signaling pathways,promoting the development of hepatic fibrosis.It has been found that UA can improve intestinal injury and bacterial imbalance by inhibiting the expression of Ras homolog gene family member A pathway components,preventing bacteria from entering the vein,reducing intestinal immune response and the release of inflammatory factors[46],and avoiding accelerating the progression of liver fibrosis through the intestinal-liver axis.Additionally,UA was able to regulate the expression of ileal tight junction proteins claudin1 and occluding and to reduce the contents of serum lipopolysaccharide and procalcitonin by inhibiting intestinal NOX-mediated oxidative stress[47].Further experiments confirmed that after treatment with UA in mice with liver fibrosis,the expression of NOX 4 and Ras homolog gene family member A/Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase 1 decreased,the microflora imbalance,diversity,richness were improved,and the number of potentially beneficial bacteria increased[48].This indicated that UA was able to reverse liver fibrosis and reduce hepatocyte necrosis by inhibiting NOX4/ROS and RhoA/ROCK1 signal pathways.
In addition,UA also showed to reduce the expression of α-SMA and type I collagen in quiescent hepatic stellate cells[49]to inhibit the activation of quiescent hepatic stellate cell and its transformation into fibroblasts,and to block the hepatic fibrosis process.Huang et al.[50]observed that after intragastric administration of UA,the serum alanine aminotransferase levels of hepatic fibrosis rats decreased significantly,the intrahepatic fibrous septum and collagen deposition significantly improved,and the Ishak fibrosis score decreased.Further experiments found that UA could inhibit the ROS cluster produced by NOX2 and block the transcription and translation process of caspase-1 at an mRNA level,limiting its activation and release.The process resulted in reduced maturation and release of IL-1ß,thus improving the deposition of collagen in the liver.Kwon et al.[51]found that UA was an effective regulator of liver transcriptome,which could regulate the circadian rhythm of the liver by changing the expression of clock control genes and by reducing the excessive production of ROS to improve liver fibrosis.
Inhibiting the growth and migration of liver cancer
Liver cancer is one of the common malignant tumors in China,which seriously affects people’s lives and health.More than 300,000 people die of liver cancer every year[52].The therapeutic effect of existing surgery and chemotherapy for liver cancer is limited and prone to induce drug resistance.Side effects such as digestive tract reactions,liver injury,and bone marrow suppression during the treatment process also affect the patients’overall chemotherapy success.It has been found that UA can exert anticancer effects through multiple pathways and multiple targets:inhibition of cell proliferation,apoptosis induction,anti-neovascularization,regulation of immune system,metastasis production inhibitor(Figure 1).
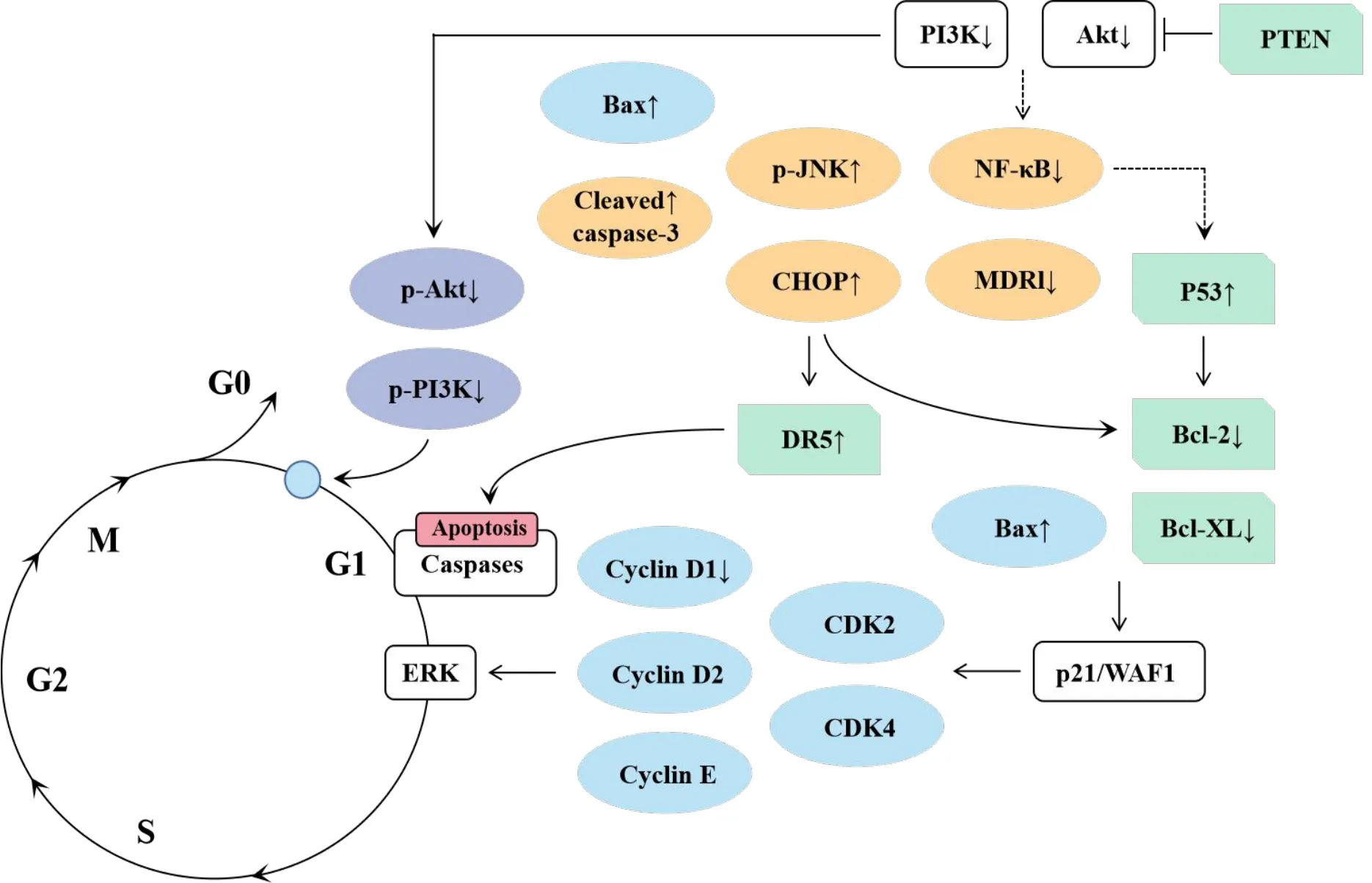
Figure 1 Mechanism of ursolic acid to block the cell cycle.PTEN,gene of phosphate and tension homology deleted on chromsome ten;Akt,protein kinase B;PI3K,phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase;JNK,jun N-terminal kinase;MDR1,multi-drug resistance gene-1;p21/WAF1,proteina fosforilata 21 wide-type actiated factorlp 1;CHOP,C/EBP homologous protein;DR5,death receptor5;CDK,cyclin dependent kinase;ERK,extracellular regulated protein kinases.
Inhibiting tumor cell proliferation
The gene of phosphate and tension homology deleted on chromsome ten(PTEN)protein is a tumor suppressor protein with dual activity on lipid phosphatase and protein phosphatase.Decreased expression of PTEN gene could activate PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and promote the production of a variety of pro-angiogenic factors,including vascular endothelial growth factor[53],resulting in the attenuation of cell apoptosis.Other studies have shown that PI3K/Akt signaling pathway inhibited p53 gene by activating the expression of nuclear factor-kappa B and multi-drug resistance gene-1,and participated in tumor resistance to cisplatin,doxorubicin,paclitaxel,and other chemotherapeutic drugs[54].UA was able to up-regulate the expression of PTEN[55]and inhibit PI3K/Akt signal transduction pathway,thereby inhibiting the proliferation and differentiation of human hepatocarcinoma cell HepG2 and reducing drug resistance.
Lei et al.[56]found that UA could significantly inhibit the expression of cyclin D1 protein in liver cancer cells,affecting the ERK signal pathway that directly acts on the G1 phase of the cell cycle,hindering the process from G0/G1 to S phase,and thus inhibiting the proliferation of liver cancer cells.Studies have shown that UA could up-regulate the expression of Bax protein,down-regulate the expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL[57],and regulate the expression of cyclin D1,D2,E,cyclin dependent kinase 2,4 and cyclin 6 through proteina fosforilata 21 wide-type actiated factorlp 1 pathway,to block cell cycle at G1 phase and inhibit cell proliferation.In addition,the antitumor effect of UA was time-and concentration-dependent[58].The apoptosis effect at 60 μg/mL is the best when against human hepatocarcinoma cell HepG2 for 72 hours,reaching to about 79%.
Inducing tumor cell apoptosis
The content of fatty acid synthase[59]in tumor cells is higher than in normal cells,and can promote fatty acid synthesis and meet the needs for tumor cell division and proliferation.Fan et al.[60]found that UA could inhibit the activity of fatty acid synthase,affecting the production of fatty acids and promoting tumor cell apoptosis.
Zong et al.[61]reported that UA was able to down-regulate the expression of p-PI3K and p-Akt and up-regulate the expression of cleaved caspase-3,Bax,phosphorylated N-terminal kinase and C/EBP homologous protein,increasing the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 and significantly increase the inhibition rate and apoptosis rate of human hepatocarcinoma cell HepG2.The regulatory effect of UA is better than that of PI3K specific inhibitors.This exemplifies that UA was able to affect the expression of downstream proteins and induce apoptosis of human hepatocarcinoma cell HepG2 by inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.The experiments of Yu et al.[62]on human hepatocarcinoma cell SMMC-7721 also confirmed that UA down-regulated the expression of anti-apoptosis gene Bcl-2 in a dose-dependent manner,up-regulated the expression of pro-apoptosis gene Bax,and increased the expression of C/EBP homologous protein in liver cancer cells.The high expression of C/EBP homologous protein combined with death receptor 5 gene to induce the expression of death receptor 5[63],activated the caspases pathway and increased the stress level of endoplasmic reticulum,initiating and inducing the apoptotic process.
Reducing tumor angiogenesis
According to Kiran et al.[64],UA could down-regulate the expression of E-selectin,platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1,intercellular cell adhesion molecule,vascular endothelial growth factor,fibroblast growth factor-2 and the receptors,resulting in an increase of PGE2/PGD2,inhibiting neovascularization.UA[65]has also been proved to prevent tumor angiogenesis and inhibit the migration and invasion of vascular endothelial cells,by reducing serum nitric oxide and inflammatory cytokines,and increasing the contents of tissue metalloproteinase-1 and IL-2.
Regulating the body’s immune function
After intraperitoneal injection of a high dose(40 mg/kg)of UA to human hepatocarcinoma cell line H22 tumor-bearing mice for 15 consecutive days,Li et al.[66]found that the abnormally increased spleen index decreased,while the ratio of CD4+/CD8+,the expression of IL-2 and tumor necrosis factor-α increased.Additionally,IL-4 was inhibited,accumulating Th1 cytokines and corrected the imbalance of cytokines in Th1/Th2 subsets.This indicated that UA was able to relieve the immunosuppression of human hepatocarcinoma cell line H22 tumor-bearing mice,improving the immune function and protecting the immune organs of mice.Li et al.[67]analyzed the intestinal bacteria of mice transplanted subcutaneously with human hepatocarcinoma cell line H22 and found that UA regulated the proportion and distribution of microflora in the transplanted tumor mice at a phylum level,reducing the abundance of Muribaculaceae,improving the abundance of beneficial bacteria such asLacetospiraceaeandRumenaceae, positively regulating the structure of intestinal flora,and restoring the disorder of intestinal flora.
Blocking tumor invasion and metastasis
Li et al.[68]designed a control experiment to treat human hepatocarcinoma cell line Bel-7404 with 50 umol/L UA,and concluded that this natural product was able to inhibit the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells by down-regulating the expression of MMP-2 and up-regulating the expression of TIMP-2.Its effects were comparable with 10 mg/L cisplatin.After continuous administration of 300 mg/(kg·d)UA to human hepatocarcinoma cell line H22 transplanted tumor mice for two weeks[69],the tumor inhibition rate reached 55.22%.UA reduced the expression of MMP-2,vascular endothelial growth factor,and Ras-gene in a dose-dependent manner,inhibiting the degradation of extracellular matrix and neovascularization,thereby inhibiting the proliferation,invasion,and metastasis of liver cancer.
Other study found that human hepatocarcinoma cell MHCC-97H could undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhance its capabilities of migration and invasion significantly after being co-cultured with macrophages.The addition of UA[70]can up-regulate the expression of E-cadherin,a marker of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, while down-regulating the expression of N-cadherin and vimentin,meaning UA antagonized the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells induced by macrophages.Its effects may be related to the expression of proteins related to regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition in liver cancer cells.
Summary and prospect
The liver is the largest substantive organ of the human body,occupying an extremely important position in the process of material metabolism.Various factors such as environment,diet,and drug intake can lead to the occurrence and development of liver disease.In recent years,with the development of molecular detection technology,a large number of studies have shown that several genes,proteins,and signal transduction pathways are closely related to the occurrence and development of liver diseases.As a natural hepatoprotective agent,researchers made progress while unveiling UA’s mechanism in treatment of liver diseases.UA is able to protect the liver through multi-targets,multi-pathways,and multi-links in order to repair liver damage,improve liver function,inhibit tumor growth and migration,and others.Nonetheless,more detailed clinical trials using UA are needed,in order to establish the biological importance of this natural product.
Viral hepatitis patients account for a large proportion of the population with liver diseases in China.These infections are of strong infectivity and complex transmission,and these are the main reasons for the occurrence and development of liver cirrhosis and liver cancer[71].However,the role of UA in the treatment of viral hepatitis still lacks sufficient experimental evidence.
UA’s use in clinic is limited due to its hydrophobicity and low.Therefore,scientists prepared nano-preparations of UA which can significantly improve its solubility and bioavailability,enhancing its biological activity[72].For example,UA’s solid dispersion,which is made by mixing UA with PVP-VA64,Soluplus,and other auxiliary materials by using hot melt extrusion technology,can improve its dissolution in vitro[73];the solubility equilibrium of the nano-emulsion in simulated gastric juice,which is uniformly mixed with surfactant,water,and oil,increases UA’s solubility 12.48 times[74],promoting UA to enter small intestinal epithelial cells;UA self-microemulsion freeze-dried preparation presents a slow-release effect and can be used for intravenous injection[75];the water solubility of UA phospholipid complex prepared by solvent-assisted grinding method increase UA’s solubility more than 276 times,enhancing its activity against liver cancer[76].However,most of its research remained at the laboratory stage,as it still needs subsequent optimization and improvement.
In short,with the continuous improvement of preparations containing UA,it has been possible to unveil its pharmacological mechanisms against liver diseases.The hepatoprotective effect of UA has been extensively confirmed,but more high-quality basic and clinical studies are needed to continuously enrich and increase the knowledge toward the development of clinical therapeutic drugs containing UA.
 Traditional Medicine Research2021年4期
Traditional Medicine Research2021年4期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Phytochemical composition,therapeutical and pharmacological potential of Nigella sativa:a review
- Network analysis and molecular docking of the mechanism of Shengmai decoction in treating patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Study on possible synergistic anticancer cachexia effects of the main active compounds of Radix Sophorae flavescentis
- Traditional Chinese medicine of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge:a review of phytochemistry,pharmacology and pharmacokinetics
- Network pharmacology-based approach to investigate the mechanism of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- System pharmacology-based dissection of the potential effective material basis and mechanism of Xiaoxianxiong decoction for type 2 diabetes mellitus
