Cu Sn Cu互连微凸点电迁移仿真研究
张潇睿

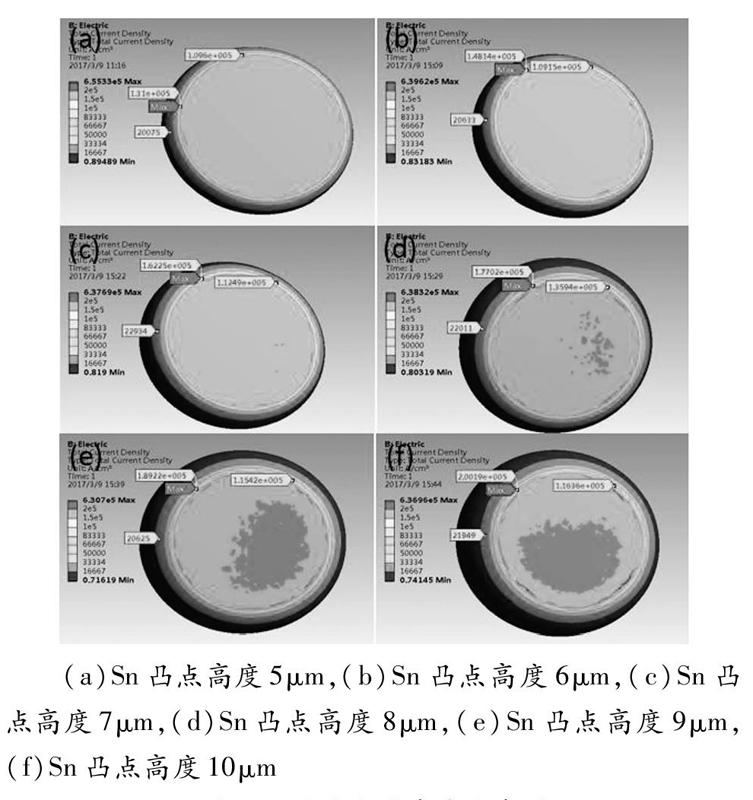

摘要:随着微电子领域朝着微型化的不断前进,产品封装密度越来越高,微焊点的尺寸和间距也日益减小,电迁移现象更加频繁的出现。本文针对一种CuSnCu结构互连微凸点,基于ANSYS软件,研究了不同Sn层高度以及结构对称性变化对凸点内部电流密度分布的影响,得到了电流密度在不同结构下的分布规律,为实际电迁移实验研究提供了理论参考。
关键词:微凸点;电迁移;电流密度;仿真
中图分类号:TN403
Simulation of micro bump electromigration in CuSnCu interconnects
Zhang Xiaorui
Aviation Engineering College,Civil Aviation Flight University of ChinaSichuanGuanghan618307
Abstract:With the miniaturization of the microelectronic products,packaging density is getting higher and higher,and the size and spacing of micro solder joints are also decreasing,electromigration occurs more frequently.This paper focuses on a CuSnCu micro solder joints,the effects of different Sn layer thickness and structural symmetry on the current density distribution inside the bump are studied by using ANSYS.The distribution of current density in different structures was obtained,and it provides a theoretical reference for the experimental study of electromigration.
Key words:Micro solder joints;Electromigration;Current density;Simulation
微电子产品的微型化发展带来了更高的封装密度,微凸点尺寸和间距的减小造成高电流密度的产生,从而导致微凸点中出现电迁移现象。电迁移发生后,微凸点内部会出现相应的组织、结构演变,给相关产品带来了严重的可靠性问题[13]。
电迁移的主要影响因素包括:电流密度、温度、凸点下金属层以及凸点材料等[4]。电迁移会造成在凸点或互连线内部阴极附近产生空洞、裂缝,在阳极附近由于金属粒子堆积而形成晶须。同时,阴极和阳极的金属间化合物会随着时间逐渐粗化生长,且阳极的金属间化合物更厚。郝虎[5]等人对结构为Cu/Sn58Bi/Cu的焊点进行了电迁移实验,实验结果显示出来了一种异常极化效应。HAO HSU[6]等人对无铅凸点的研究就发现凸点高度越低,凸点中背应力梯度越大,对电迁移的抑制作用越明显。黄明亮[7]等人对Ni/Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Cu結构的焊点进行了研究,发现电流方向对Cu基板的消耗起着决定性的作用。本文利用ANSYS软件,研究了不同凸点结构对电流密度分布的影响。

