Research on teaching reform of rehabilitation nursing major based on modern apprenticeship system†
Yue Liu
Rainbowfish Rehabilitation and Nursing School, Hangzhou Vocational and Technical College, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310018, China
Abstract: Objective: To determine the specific indicators of nursing students’ competency in rehabilitation nursing posts; to form a training mode of competency of nursing students in rehabilitation nursing posts based on a modern apprenticeship system; and to preliminarily explore the effect of this training mode.
Keywords: competence • nursing • rehabilitation
1. Introduction
Nursing competence is the integration of nurses’ knowledge, ability, and attitude, which are embodied in nursing ethics, clinical nursing, nursing education, and scientific research.1“On the implementation of the hospital nurse position management guidelines,” the policy points out2that it is an important method to carry out post-management to study the post competency model of clinical nurses. With the aging of the population and the increasing number of people with chronic diseases and disabilities, the social demand for rehabilitation care is increasing. According to the study,3–5the competency of rehabilitation nursing posts should involve the ability to improve the quality of life of disabled people by using assistive technologies, implement nursing and multidisciplinary health interventions based on evidence-based management and promote self-management. The students of rehabilitation nursing major will serve as the reserve army of future frontline rehabilitation nurses. If we can pay attention to the training of the post competence of rehabilitation nursing in the teaching stage at school, it will be of positive significance to integrate into the work environment and improve the quality of nursing service as soon as possible in the future.
The education mode of modern apprenticeship is to integrate enterprise-oriented training with schooloriented education, build a deep mentoring relationship, and complete the inheritance and accumulation of technical skills through “teacher leading students.”6,7The development of modern apprenticeship is a strategy to serve the needs of current economic and social development and expand the growth channel of technical and skilled personnel.8Based on the modern apprenticeship system, the research on the training mode of nursing students’ competence for the rehabilitation nursing posts is to adopt the modern apprenticeship training mode for nursing students in the rehabilitation nursing profession based on constructing the competency index for the rehabilitation nursing posts, which is in line with the development of the industry today. It aims to explore the role and effect of the modern apprenticeship system in improving the nursing students’ competence in the post of rehabilitation nursing and provide a reference for improving the training of rehabilitation nursing talents.
2. The establishment of specific indicators of the post competence of nursing students
2.1. Set up a research group
The research team consisted of six members, including one dean of the school of nursing, who was responsible for the overall guidance of the research; one director of the nursing department, one teaching officer of the nursing department, and one head nurse, who were all responsible for data collection; and two teachers from nursing school, who were responsible for data analysis.
2.2. Literature review
Relevant literatures were searched respectively by“nursing student competence,” “nursing specialist competence,” and “rehabilitation nurse competence” in the past 20 years in databases such as the Wanfang database, Weipu database, Chinese biomedical literature database, Embase, CNKI, PubMed, and so on. Meanwhile, referring to the relevant contents of the professional post competency of rehabilitation nursing at home and abroad, the common indicators of the professional post competency of nursing students were extracted from the relevant data.
2.3. The Delphi method
2.3.1. Form a correspondence questionnaire
The questionnaire included a research note letter;main content “evaluation table of the post competency of nursing students in rehabilitation nursing”;expert general situation questionnaire, expert familiarity questionnaire, and expert judgment according to the questionnaire. The main content was developed according to professional knowledge, professional technology, and professional ability. The importance of the indicators was developed according to Likert grade 5 score, which ranges from very important, important,general, unimportant, and very unimportant, respectively corresponding to the score of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1,and a remark column was left for experts to write opinions. After the preliminary experiment of 5 experts,the first round of correspondence questionnaire was formed. According to the results of the first round of consultation, the second round of consultation questionnaire was formed.
2.3.2. Choose experts to attend the letter consultation
Objective sampling was used to select 15 experts from nursing colleges, 12 experts from tertiary hospitals, and 3 experts from secondary hospitals. The basic information of experts is shown in Table 1.
2.3.3. Conduct expert consultation by letter
Two rounds of questionnaires were distributed and collected by the researcher.
2.3.4. Statistical analysis
The data were recorded into SPSS 21.0 program for statistical analysis. The indexes were selected basedon the mean value of importance assignment ≥3.5 and coefficient of variation <0.3. And the indexes were also modified by expert opinions.
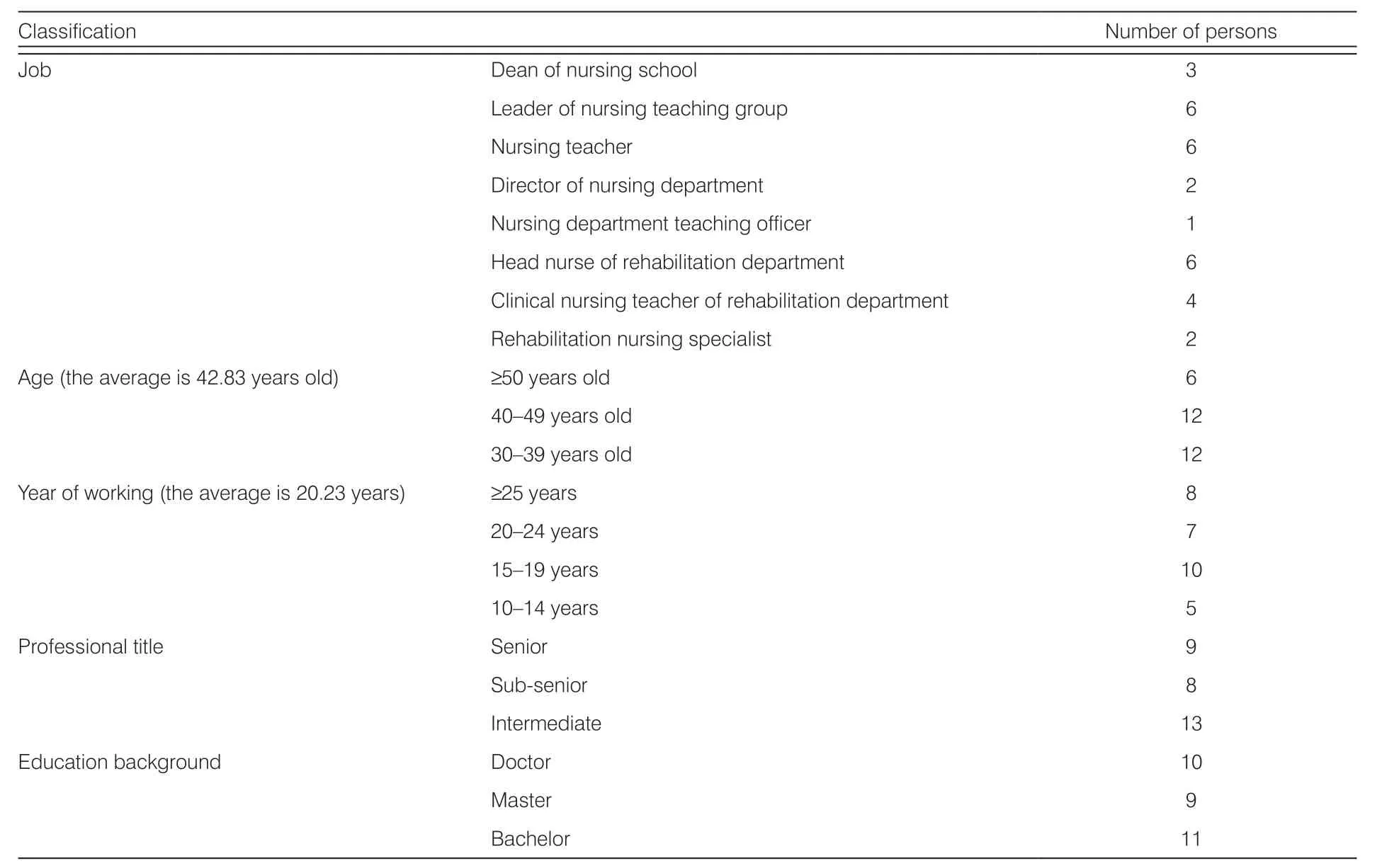
Table 1. The Delphi method expert basic information.
3. Form a training model of nursing students’ competence in rehabilitation nursing posts based on the modern apprenticeship system
The main body of this talent training mode was nursing college, which was responsible to train students.The leading party was a rehabilitation nursing institution, which was not only in charge of training students but was also responsible for the internship guidance of relevant rehabilitation departments in the in-post internship. And this institution absorbed the graduates who were jointly trained to work in the rehabilitation nursing institution. The auxiliary party was a general hospital, whose main responsibility was to jointly train students and undertake the internship guidance of the non-rehabilitation department in the internship link.
3.1. Set up a working group on modern apprenticeships in the nursing profession
Based on the school nursing professional construction steering committee, medical institutions were amalgamated. The apprenticeship working group was composed of higher education experts, medical personnel,and nursing teachers. The duties of the working group included formulating professional personnel training programs, constructing the nursing professional curriculum system featured by rehabilitation, improving the teaching guarantee mechanism and quality control mechanism, establishing of personnel training evaluation system, and selecting outstanding staff of medical institutions as the students’ mentors.
3.2. Develop training programs jointly by schools and medical institutions
From the point of view of improving the students’ competence in rehabilitation nursing, the corresponding teaching content and form of cooperation are determined.Based on learning from the experience of developed countries,9–11the teaching quality evaluation standards and evaluation methods were reformed, and students’ work performance and teacher evaluation were included in the students’ academic evaluation standards. Under the guidance of the talent training goal, the curriculum system was rebuilt according to the competency index of rehabilitation nursing posts. A curriculum system characterized by “professional basic courses + professional core courses + professional development courses” would be formed to improve comprehensive quality as the core and be task-oriented. According to the needs of medical institutions, with the joint efforts of curriculum experts, the backbone of medical institutions and school teachers, project-based suitable courses would be developed for the front-line of the industry. Besides,medical institution experts and professional teachers jointly undertook the teaching tasks, especially the professional training.
4. Implement the training model of nursing students’ competence in rehabilitation nursing posts based on the modern apprenticeship system
4.1. Select outstanding employees of medical institutions as external mentors
The application was made by the individual employee of the medical institution, and the professional title of intermediate or above was usually required. The leader of the nursing department assessed the employees who applied. The apprenticeship working group members discussed the final list based on the assessment result.External mentors got offers, and a resource bank for mentors was set up.
4.2. Optimize the construction of teachers
External mentors paired up with school teachers to grow together and promote teamwork, such as group lesson preparation between school teachers and external ones.Educational ability training was be carried out for external campus mentors and clinical skills training for school teachers. Strengthened communication with medical institutions helped them to understand the industry standards quickly. Symposiums were held by external mentors and school teachers every 2–3 months to discuss students’ performance, teaching methods, and so on.
4.3. Organize and carry out teaching
The quality platform course and professional basic course of the school were mainly taught by the school teachers. The professional core curriculum was taught by external mentors and school teachers. The internship was undertaken by medical institutions with the participation of teachers in the school, and it was implemented by the mode of different nursing grades and diseases.The hierarchical mentoring model was listed in Table 2.
4.4. Carry out teaching evaluation and assessment
The quality platform course and the professional basic course theory teaching were examined by the school.Medical institutions and schools were jointly responsible for the assessment of professional core courses, practical teaching, and graduation assessment.
Take the practice teaching as an example, its examination step included: (1) To formulate training contents and internship plans for in-post internships, and to establish qualified projects for junior college; (2) To determine the department and mentor for the internship, and to carry out one-to-one teaching mode; (3) To complete the department internship objectives, including knowledge objectives, ability objectives and quality objectives. (4)To establish the examination mechanism of the internship, including theoretical knowledge test and practical training operation test. (5) To set up a two-way evaluation mechanism between teachers and students.
4.5. Realize resource sharing between medical institutions and schools
The shared content included training sites and equipment as well as technical forces. Medical institutions provided external mentors, training equipment, and positions to guide students. The school offered training to medical institutions in the technical strength and teaching ability of staff.
5. Evaluate the effect
44 nursing students who participated in the modern apprenticeship training were selected as the experimental group and 44 nursing students who received the traditional model were selected as the control group.Traditional training mode referred to nursing students according to the previous arrangement of class; in addition to general nursing courses, these students took courses related to rehabilitation nursing. When the students were enrolled, the school teachers and external mentors jointly evaluated the competency indexes of the rehabilitation nursing posts of the experimental group and the control group and took the average score.Before graduation, nursing students in the experimental group were evaluated again, while those in the control group were evaluated randomly by teachers. Theindex score is expanded according to the Likert grade 5 score, which is very consistent, consistent, general, not consistent, and very inconsistent, respectively, corresponding to the score of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1. The mean and standard deviation were used to describe the total competency score. The difference of competence between the experimental group and the control group was tested by χ2test.
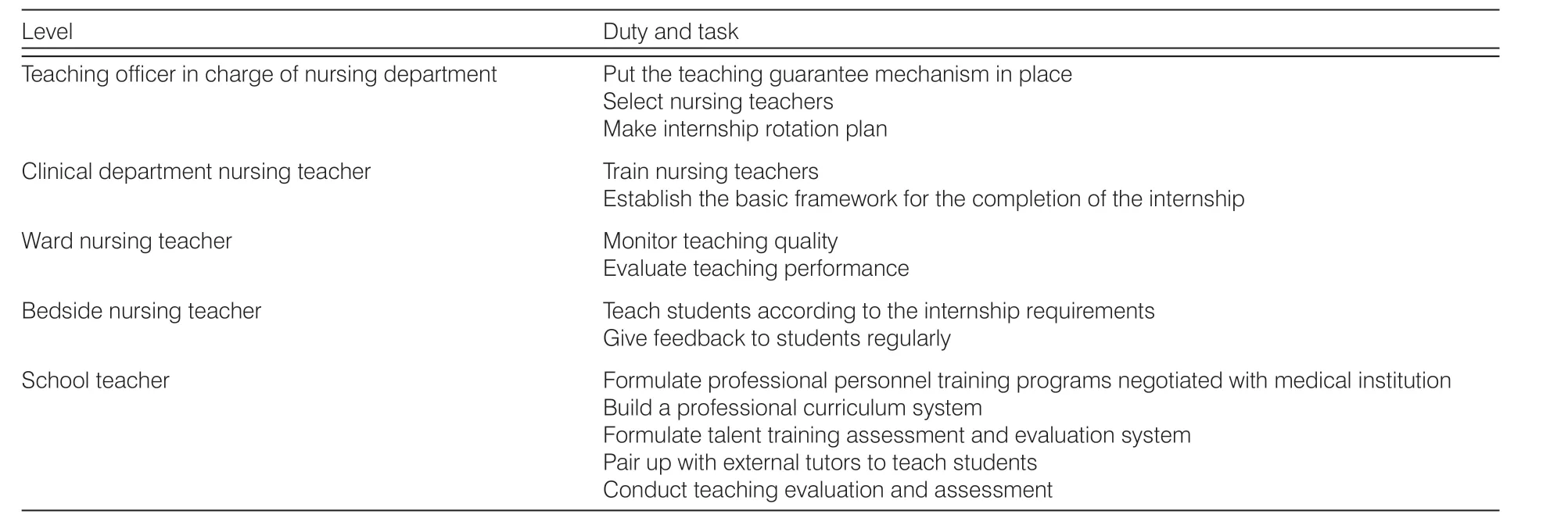
Table 2. Hierarchical mentoring model.
6. Results
6.1. Competency index of nursing students in rehabilitation nursing posts
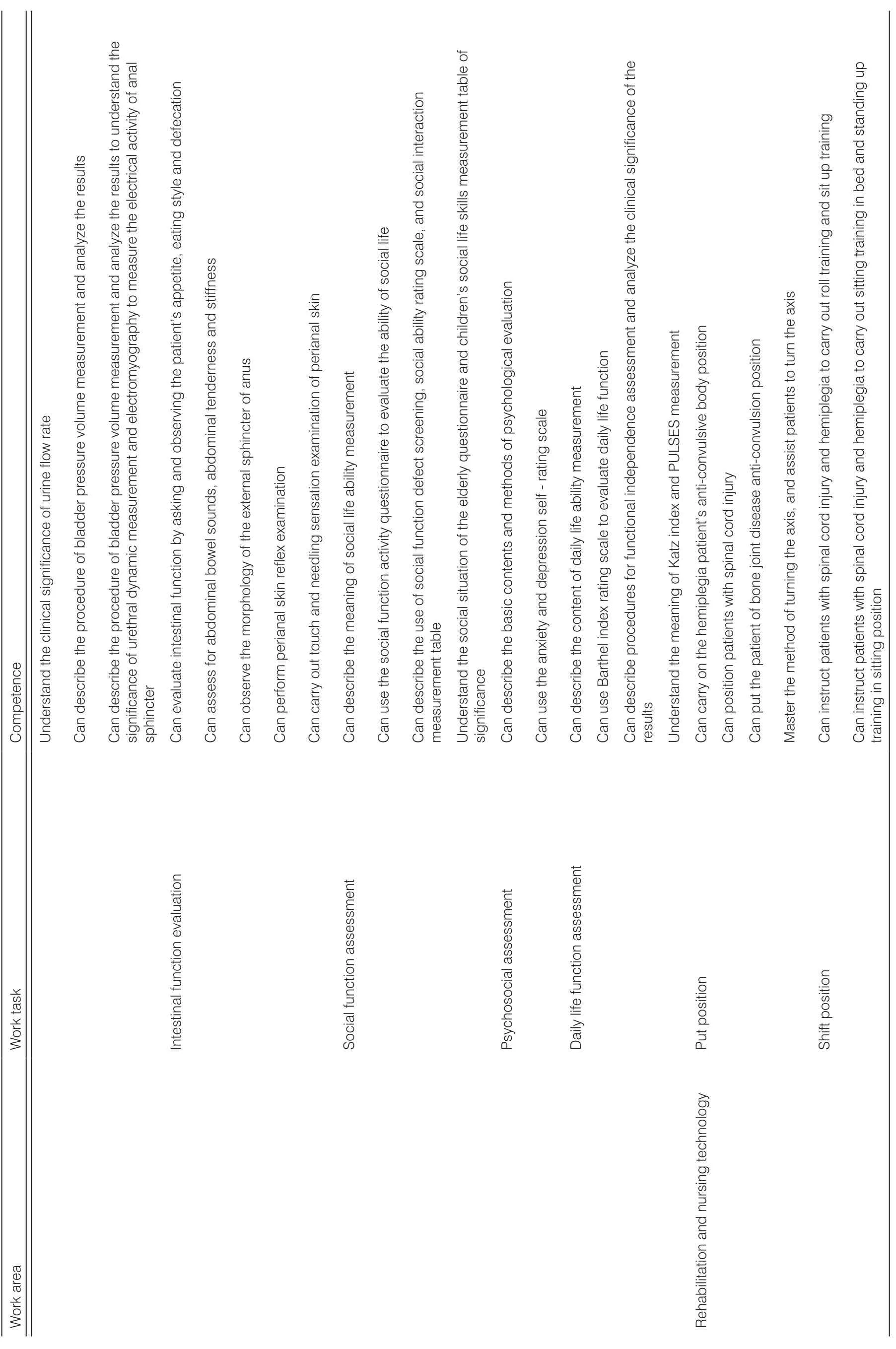
The Delphi method expert authority was 0.75–0.90 and the mean was 0.82. Thirty copies of questionnaires were distributed to both the rounds of mail inquiries and the effective recovery rate was 100%. In the first round,the total number of indicators was 217, among which 26 indicators were deleted with an average value of <3.5.In the second round of letter inquiries, the total number of indicators was 191, and the mean value of the importance of all indicators was ≥3.5. The formed indicators of nursing students’ competence in rehabilitation nursing posts were shown in Table 3.
6.2. Operation effect of training mode of nursing students’ competence in rehabilitation nursing posts based on the modern apprenticeship system
When the students were enrolled, there was no significant difference in the score of competence between the experimental group and the control group (P> 0.05).Before graduation, the competency scores of the two groups were shown in Table 4. Due to the varying numbers of competency indicators in each task, the final score of the competency of each task was also different.
7. Discussion
7.1. The training mode of rehabilitation nursing post competency based on modern apprenticeship system can improve the competency of nursing students
According to this study, among the 30 tasks involved in rehabilitation assessment, rehabilitation nursing technology, rehabilitation nursing of common diseases, and rehabilitation nursing management, the score of competency required for 24 tasks of nursing students in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P< 0.05). It has some similarities with the research results of Jacinta,12Smith13and Carr.14The reasons are as follows: (1) The Delphi method expert of this study was engaged in nursing education or clinical nursing or nursing scientific research for many years, familiar with the research content. The results of the letter consultation showed that the degree of expert authority, the degree of positive, the degree of expert opinion concentration,and the degree of expert opinion coordination were all good, indicating that the indicators of nursing students’ competence in rehabilitation nursing posts obtained in this study were scientific and representative to a certain extent, which could provide a basis for the construction of the subsequent talent training model. (2) The talent training model of this study reconstructed the curriculum system from the perspective of competency so that the competency training of rehabilitation nursing posts ran through the theoretical and practical links of nursing students, and was fully targeted. (3) Apprenticeships led to faster adjustment and integration into rehabilitation and nursing positions. When students encountered problems related to professional learning, the instructor could help them to improve their ability promptly. (4)The optimization of the examination program made the nursing students no longer immerse themselves in the mechanical theoretical knowledge memory, but focus on the technical skills evaluation of the front-line nursing posts to improve the matching degree of the nursing students.

(Continued)
(Continued)

(Continued)

(Continued)

(Continued)

(Continued)

(Continued)

Table 3. Indicators of nursing students’ competence in rehabilitation nursing posts.
7.2. Discussion on the reasons for insignificant differences in scores of a few tasks
According to this study, among the 30 tasks involved in rehabilitation assessment, rehabilitation nursing technology, rehabilitation nursing of common diseases, and rehabilitation nursing management, there was no significant difference between the scores of 6 tasks required by the nursing students in the experimental group and those in the control group (P> 0.05). The reasons are as follows: (1) It is related to the development of clinical rehabilitation nursing. The development of rehabilitation nursing in mainland China mainly stemmed from chronic diseases, such as stroke and diabetes, etc. In recent years, the rehabilitation nursing of acute and severe diseases has gradually begun to receive attention.15–18The emergency departments and intensive care units in general hospitals mostly focus on the clinical treatment of the disease itself, but there is a lack of understanding of the importance of rehabilitation nursing. This may be the reason why nursing students score low in the task competence of critical care nursing in the field of “common disease rehabilitation and nursing.” (2) It is related to the work content of nursing students’ contact in the practice stage. For example, in the field of “rehabilitation assessment,” the tasks of “cognitive function assessment” and “social function assessment” involve the use of scales and questionnaires to assess patients’ cognitive and social functions. Nursing students expressed that the departments in which they practice are mostly evaluated by specialized doctors. Another example is the “traditional Chinese medicine fumigation and washing” task in the field of “rehabilitation and nursing technology,” which is the nursing operation performed by nurses according to the doctor’s advice, and it has a certain relationship with whether the department is good at using traditional Chinese medicine to treat diseases. In non-TCM hospitals or departments with less TCM treatment, nursing students cannot have sufficient opportunities to practice this technique,resulting in lower scores of competency.
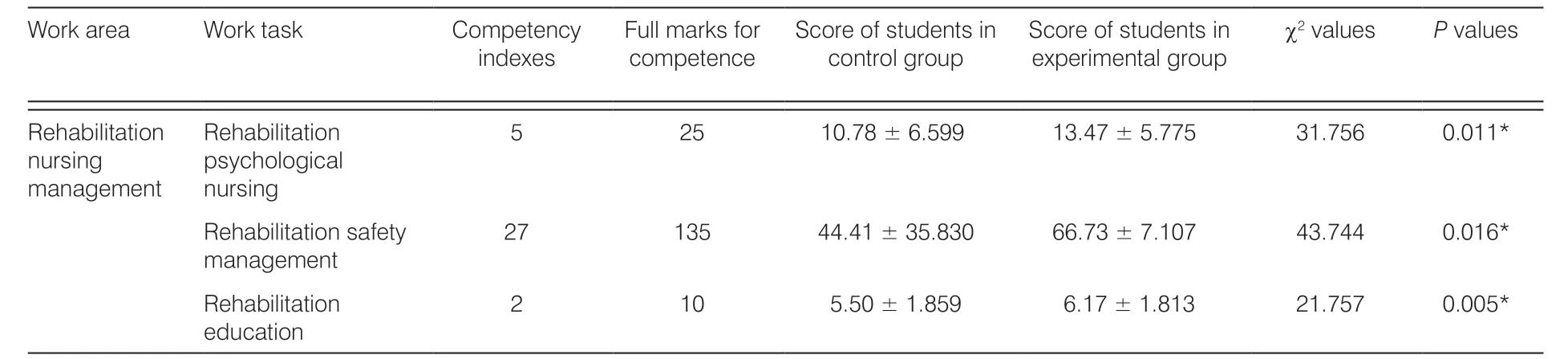
Table 4. The score of the post competence of the nursing students in the experimental group and the control group before graduation (N = 88).
8. Conclusions
Opinions on carrying out the pilot work of modern apprenticeship” by the Ministry of Education showed that all educational institutions were required to enrich the forms of professional personnel training and to increase the scope and scale of modern apprenticeship pilot programs.19“National plan for the development of nursing” by the National Health and Family Planning Commission indicated that it was necessary to strengthen the contact and cooperation between nursing education institutions and medical and health institutions, and adhere to the post demand as the guidance.20In combination with the industry development trend, based on the latest policy guidelines, aiming at improving the competence of nursing students and promoting the matching degree of nursing students, this study constructed a teaching reform model based on modern apprenticeship, and achieved certain effect and innovation in the trial operation stage. The follow-up study suggests expanding the scope of operation and carrying out the research among nursing students in different regions and at different levels, to provide a reference for the training of nursing personnel in rehabilitation specialty.
Ethical approval
Ethical issues are not involved in this paper.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
- Frontiers of Nursing的其它文章
- Evaluation of the intervention of home-based pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Relationship between decreased visual acuity and physical activity time in school age children
- Study on the quality of life and its related factors for older adults in communities in Beijing, China†
- Study and promotion of safety culture using mixed methods research
- Development of a questionnaire assessing nursing staff’s knowledge, attitude, and practice on the prevention of the nosocomial infection in elderly patients:testing reliability and validity†
- The effectiveness of dalethyne dressings for reducing bacteria in diabetic foot ulcers

