准噶尔盆地车排子北部地区沙湾组碳酸盐胶结物差异性分布控制因素
赵晓东,杨少春,鞠小玉,陈刚强),许涛)
1)中国石油大学(北京)克拉玛依校区石油学院,新疆克拉玛依,834000;2)中国石油大学(华东)地球科学与技术学院,山东青岛,266580;3)中国石油大学(北京)克拉玛依校区文理学院,新疆克拉玛依,834000
内容提要: 通过铸体薄片、AxioVision图像分析、岩芯常规分析、地层水测试等方法,在明确了碳酸盐胶结物类型的基础上,采用多方法进行了碳酸盐胶结物含量的测定,探讨了准噶尔盆地车排子地区北部沙湾组碳酸盐胶结物差异性分布控制因素,并揭示了其对储层物性、油水分布的影响。研究表明,车北地区沙湾组储层中发育大量的早期碳酸盐胶结物,不均匀充填部分原生粒间孔,具有强烈的非均质性;在岩芯常规测定碳酸盐胶结物含量的基础上,利用多次数、多视域的AxioVision图像分析补充测定了碳酸盐胶结物含量,与岩芯常规测定结果对比相对误差-0.14,弥补了数据点的不足。碳酸盐胶结物含量平面上具有“北高南低”的差异性分布特征,胶结物形成于封闭性好、水体交替停滞的还原环境中,地层水Ca2+含量的差异决定了碳酸盐胶结物分布的差异,而地层水Ca2+含量的差异主要受古地貌控制,古高地水体较浅易富集Ca2+是CaCO3沉淀的良好场所,沉积微相在局部井区起到一定的控制作用。碳酸盐胶结物差异性导致研究区储层物性具有“双峰值”特征,并造成了高黏超稠油油藏复杂的油水分布关系。
碳酸盐胶结物是储层成岩过程中胶结形成的一种自生矿物(Jos et al., 1986; 钟大康等,2007),碳酸盐胶结物的含量、发育的程度对储层的物性、含油性等有着明显的影响(Perri et al., 2008;马永生等,2010;孙海涛等,2010;Li et al., 2014)。有学者在碳酸盐胶结物的形成机理、富集规律、对储层质量的影响等方面开展了较为深入的研究。Jansa等(1990)认为邻近常压系统的超压系统以及泻压带有利于碳酸盐的胶结;王琪等(2010)认为中晚期碳酸盐胶结物形成主要因为长石类颗粒溶解提供了Ca2+;孙思敏和罗家群(2007)认为碳酸盐胶结物的富集与泥岩压实作用、有机质成熟期的酸性孔隙水溶解作用有关;孙致学等(2010)认为碳酸盐胶结物会堵塞孔隙并在局部形成致密钙质层;闫灿灿等(2018)进一步研究了碳酸盐胶结作用对储层孔隙的定量损失;Ren等(2019)在研究柴达木盆地北缘下侏罗统砂岩储层时认为碳酸盐胶结受层序界面控制,层序界面处由于成熟烃源岩酸性流体等流入导致碳酸盐胶结物溶蚀从而改善储层质量;姜平等(2020)认为碳酸盐胶结物受断裂带分布及热流体活动影响,碳酸盐胶结物在断裂带比在凹陷中心更为发育。研究成果丰富,但对于碳酸盐胶结物分布控制的地质因素的相关研究报道较少。
准噶尔盆地车排子地区北部(以下简称车北地区)沙湾组油水分布复杂(赵晓东等,2014;商丰凯等,2020),其控制油水分布的主要原因是碳酸盐胶结物分布的差异性;有学者已经注意到碳酸盐胶结物的含量可能与地层水中的Ca2+含量有关(朱子涵等,2011;刘四兵等,2014;温雅茹等,2015;沈臻欢等,2018),后仅开展了利用地层水中的Ca2+计算碳酸盐胶结物的含量等工作,但对于控制碳酸盐胶结物分布根本的地质因素尚未开展研究。其次,碳酸盐胶结物含量的合理测定也是面临的主要问题之一,碳酸盐胶结物的含量一般是通过岩芯常规分析利用岩石碳酸盐含量测定仪获取,但这种方法受控于岩芯样品有限而获取的数据量不足(Bunch, 2018),在一定程度上影响了碳酸盐胶结物平面分布的研究。将染色的岩石薄片放置于常规电子显微镜和扫描电镜通常也用来测定胶结物含量(王钰婷,2018),该方法虽然可以对碳酸盐胶结物数据点进行补充,但获取的数据受个人经验等影响较大,测定效果较差。因此,本论文在碳酸盐胶结物含量岩芯测定的基础上,通过AxioVision图像分析进行碳酸盐胶结物含量补充测定,弥补了岩芯测定数据点的不足,揭示出研究区碳酸盐胶结物含量与地层水Ca2+的关系,探讨了地层水Ca2+差异分布的控制因素,阐明了控制碳酸盐胶结物分布的地质因素,进一步明确了碳酸盐胶结物对储层物性、油水分布的影响,该认识为该类油藏的勘探开发提供了研究实例和参考依据。
1 地质背景
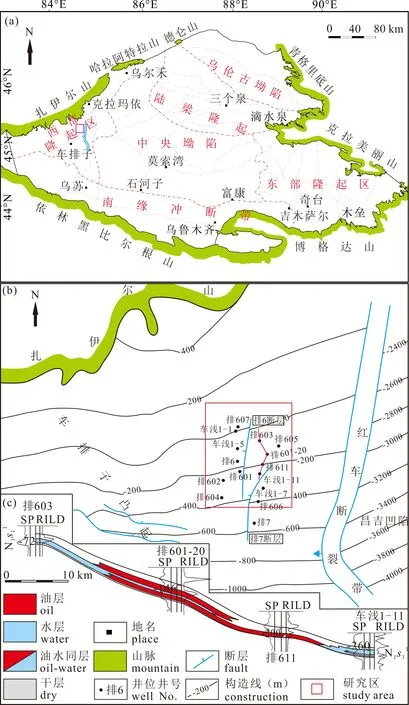
图1 准噶尔盆地车排子北部地区综合地质图Fig. 1 Comprehensive geological map of northern Chepaizi(NCPZ) area, Junggar Basin(a)准噶尔盆地位置图和车北地区位置图,车北地区位于准噶尔盆地西部隆起区;(b)车北地区N1构造图和主要井位分布图,研究区为近东南倾的单斜构造;(c)车北地区近南北向油藏剖面图,油藏位于同一套储层的中部,油水关系复杂。(a) Locations of the Junggar Basin and the NCPZ area. NCPZ area is located at the Western uplift of Junggar basin. (b) Sketch of the NCPZ area and main wells and faults. The structure of study area is a monoclinic with a nearly southeast dip. (c) Reservoirs cross section profile across the research area from North to South. The oil—water relationship is complex, and the same set of connected reservoirs is located in the central part of the structure
2 碳酸盐胶结物类型

图2 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1碳酸盐胶结物镜下特征Fig. 2 Characters of carbonate cements under thin section of N1 in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin(a)排601-21井,490.5 m,碳酸盐胶结强烈,颗粒之间点接触、不接触,单偏光;(b)排601-平192井,602.2 m,碳酸盐胶结强烈,碎屑颗粒“漂浮”在胶结物中,单偏光;(c)排601-4井,510 m,碎屑颗粒未见到明显的压裂纹,正交偏光;(d)排611井,491 m,碎屑颗粒未见到明显的压裂纹,单偏光。(e)排607井,277.4 m,缩颈状喉道和片状、弯片状喉道,连通性好,铸体薄片,单偏光;(f) 排602井,526.1 m,不含碳酸盐胶结物,原生残余粒间孔发育好,铸体薄片,单偏光;(g)排611井,491 m,仅在薄片西南部发育碳酸盐胶结物,原生残余粒间孔发育较好,铸体薄片,单偏光;(h)排607井,277.4 m,原生粒间孔被碳酸盐胶结物充填,原生残余粒间孔发育中等,铸体薄片,单偏光;(i)排602井,526.1 m,碳酸盐胶结强烈,原生粒间孔基本被碳酸盐胶结物充填,原生残余粒间孔发育差,见次生粒内溶蚀孔,铸体薄片,单偏光。PIP—原生孔隙;SIDP—次生孔隙;Cal—碳酸盐胶结物(a) The Well P602-1, 490.5 m, with strong carbonate cementation, point contact and non-contact between particles, single polarized light; (b) the Well P601-p192, 602.2 m, with strong carbonate cementation, particles “float” in the cement, single polarized light; (c) the Well P601-4, 510 m, No obvious crush cracks are seen in the debris particles, cross polarized light; (d) the Well P611, 491 m, No obvious crush cracks are seen in the debris particles, single polarized; (e) the Well P607, 277.4 m, Constricted throat and flaky and curved throat, good connectivity, casting thin section, single polarized; (f) the Well P602, 526.1 m, without carbonate cements, with well-developed primary residual intergranular pores, casting thin sections, single polarized; (g) the Well P611, 491 m, with well-developed primary residual intergranular pores, carbonate cements developed only in the southwest of thin section, casting thin section, single polarized; (h) the Well P607, 277.4 m, with primary intergranular pores filled by carbonate cements, with moderately developed primary residual intergranular pores, casting thin section, single polarized; (i) the Well P602, 526.1 m, with strong carbonate cementation, the primary intergranular pores are basically filled by carbonate cements, the primary residual intergranular pores are poorly developed, only the secondary intergranular dissolution pores are seen, casting thin section, single polarized. PIP—primary pore; SIDP—secondary dissolution pore; Cal—carbonate cements
3 碳酸盐胶结物的测定与平面分布
3.1 碳酸盐胶结物的测定
车北地区沙湾组储层碳酸盐胶结物分布不均,具有较强的非均质性,定量测定碳酸盐胶结物含量对研究区储层物性、含油性研究具有重要的意义。岩芯常规分析方法是一种常规的测定方法,在研究区共选取了10口井的120个岩芯样品通过岩石碳酸盐含量测定仪进行了含量数据测定,检测环境室温20℃、湿度60%,测定工作在中国石化胜利油田地质研究院完成。该方法受控于岩芯样品导致获取的数据量有限,因此,为了增加更多的分析数据点,在有限的10口井岩芯常规分析测定的基础上,利用AxioVision图像分析,对研究区13口取芯井20张染色的岩石薄片进行碳酸盐胶结物含量补充测定。测量原理是利用图像分析软件的增殖法,通过一遍一遍的扫描薄片,标记具有相同性质的像点,直到将全部区域找全为止,由绿色点所圈定的红色区域面积为碳酸盐胶结物所占面积,碳酸盐胶结物所占面积与整个视域的面积比计为碳酸盐胶结物含量。对每张铸体薄片,开展多次数、多视域的碳酸盐胶结物含量测定,然后通过算术平均计算该铸体薄片的碳酸盐胶结物平均含量,该含量为该样品碳酸盐胶结物含量。需要说明的是,同一口井同一套储层若取多个样品,则该储层的碳酸盐胶结物含量为多个样品的平均值;若该储层只有一个样品,则取该样品的碳酸盐胶结物含量近似代表该储层的碳酸盐胶结物含量。图3a—e为排611井487 m碳酸盐胶结物含量的测定过程,分不同视域共测定5次,则该样品碳酸盐胶结物含量为28.89%;图3f—i为排602井526.1 m碳酸盐胶结物含量测定过程,分不同视域共测定4次,则该样品碳酸盐胶结物含量为16.76%。表1为研究区13口井20个样品的AxioVision图像分析测定结果。

图3 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1碳酸盐胶结物的AxioVision图像分析测定Fig. 3 Calculation of carbonate cement by AxioVision image analysis of N1 in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin(a)—(e)为排611井487 m碳酸盐胶结物含量的测定过程,分不同视域共测定5 次,取算术平均值计该样品碳酸盐胶结物含量。(a)—(e)视域碳酸盐胶结物含量分别为27.19%、31.54%、30.75%、28.16%和26.82%,该样品碳酸盐胶结物含量为28.89%。(f)—(i)为排602井526.1m碳酸盐胶结物含量测定过程,分不同视域共测定4次,(f)—(i)视域碳酸盐胶结物含量分别为19.5%、13.68%、23.51%、10.33%,该样品碳酸盐胶结物含量为16.76%(a)—(e) is the determination process of carbonate cements content of sample at 487 m in the Well P611. It was measured 5 times in different visual fields, and the content of carbonate cements in this sample was calculated by the arithmetic mean. The content of carbonate cements in figures (a)—(e) fields are 27.19%, 31.54%, 30.75%, 28.16% and 26.82% respectively, and the average content of carbonate cements in this sample is 28.89%. (f)—(i) is the determination process of carbonate cements of sample at 526.1 m in the Well P602, which was measured 4 times in different fields, the content of carbonate cements in figures (f)—(i) fields are 19.5%, 13.68%, 23.51% and 10.33% respectively, and the average content of carbonate cements in this sample is 16.76%
碳酸盐胶结物含量具有一定的差异性,以排601-平1井和排611井为例,排601-平1井碳酸盐胶结物含量较低,一共分6个视域测定,含量3.4%~10.51%,平均值为6.74%;排611井碳酸盐胶结物含量较高,一共分5个视域测定,含量26.85%~31.54%,平均值28.89%(表1),碳酸盐胶结物含量的差异显示着储层具有强烈的非均质性。为了验证AxioVision图像分析测定结果的准确性,选取了4口井同时开展了碳酸盐胶结物的岩芯常规测定和AxioVision图像分析测定(表2),通过数据对比,碳酸盐胶结物含量低的井误差小,例如排601-4井和排601-平1井,绝对误差分别为-0.99和-0.97,相对误差分别为-0.09和-0.13;碳酸盐胶结物含量高的井误差稍大,例如排607井和排609井,绝对误差分别为-2.88和-5.77,相对误差分别为-0.10和-0.23;总体平均绝对误差为-2.65,相对误差为-0.14,误差较小,表明AxioVision图像分析测定数据具有一定的准确性,可以有效弥补岩芯常规测定数据的不足,为碳酸盐胶结物的平面分布奠定了数据基础。
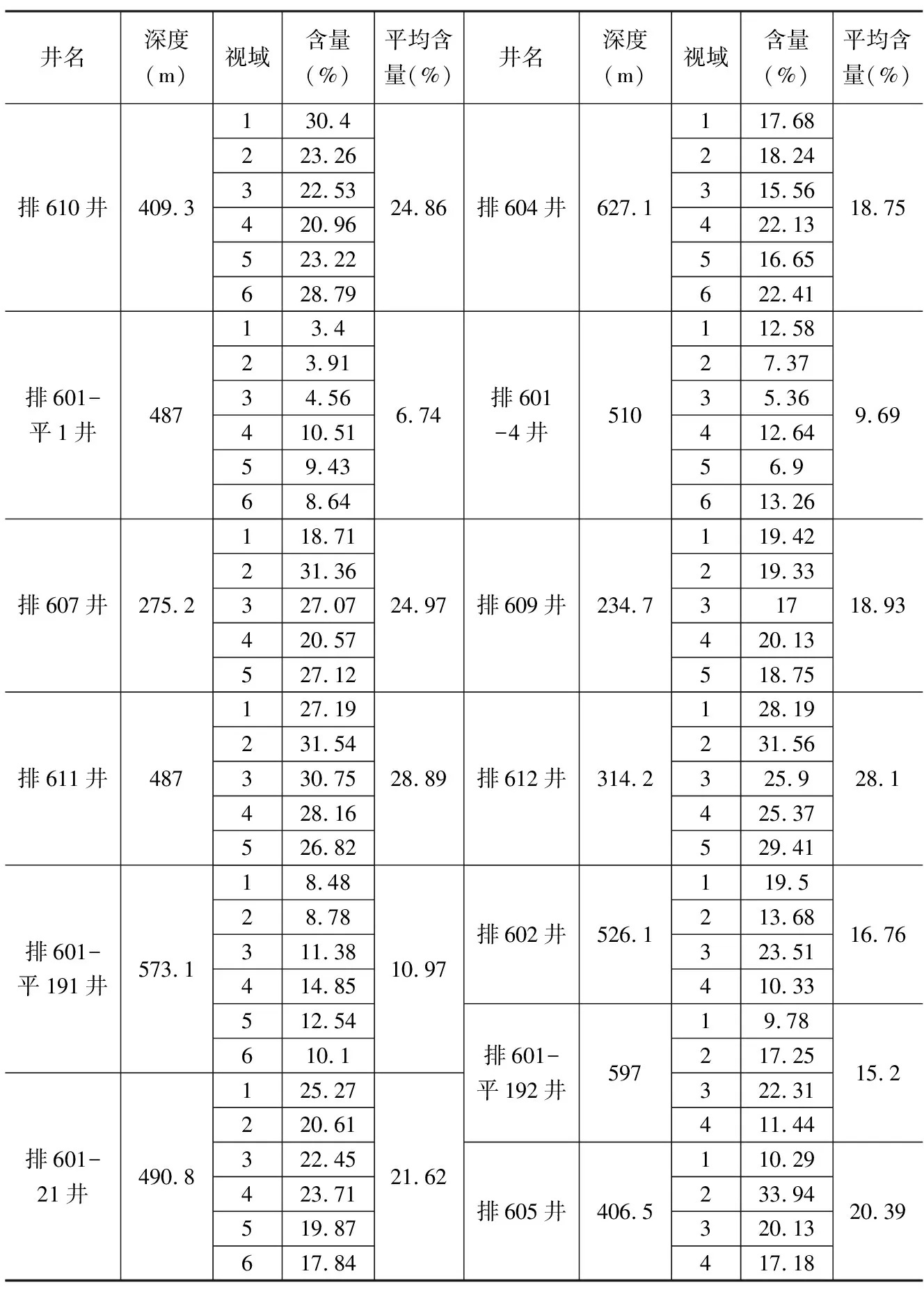
表1 准噶尔盆地车排子地区北部沙湾组碳酸盐胶结物AxioVision图像分析测定结果表(部分样品)
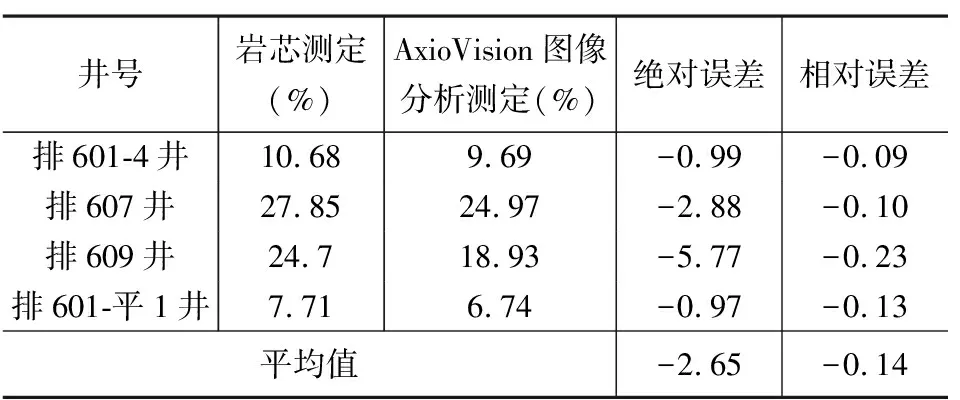
表2 准噶尔盆地车北地区沙湾组碳酸盐胶结物的岩芯常规测定和AxioVision图像分析测定结果对比表
3.2 碳酸盐胶结物平面分布特征
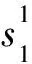
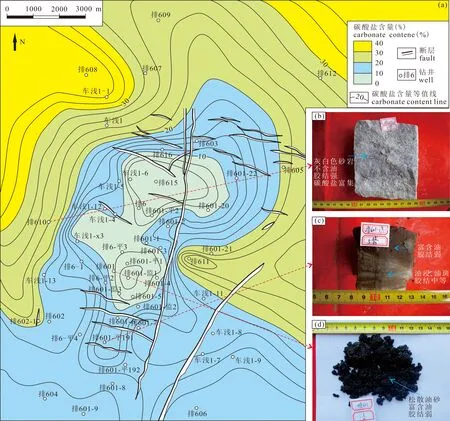
图4 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1碳酸盐胶结物含量平面分布图及部分井岩芯Fig. 4 Distribution of carbonate cement and cores of some wells of N1 in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin(a)碳酸盐胶结物含量平面分布图;(b)排610井,位于绿色区域,412.3 m,碳酸盐胶结物含量24.86%,胶结作用强,不含油;(c)排601-平191井,位于蓝色区域,572.5 m,碳酸盐胶结物含量10.97%,胶结作用弱—中等,含油级别随碳酸盐胶结程度差异而呈非均质性;(d)排601井,490.1 m,碳酸盐胶结物含量3%,胶结作用弱,富含油(a) Distribution of carbonate cements content; (b) the Well P610, located in green area, 412.3 m, carbonate cements content 24.86%, strong cementation, no oil; (c) the Well P601-p191, located in blue area, 572.5 m, carbonate cements content 10.97%, weak to medium cementation, oil-bearing level is heterogeneous with the difference of carbonate cementation; (d) the Well P601, 490.1 m, carbonate cements content 3%, weak cementation, rich in oil
4 碳酸盐胶结物差异性分布控制因素
4.1 碳酸盐胶结物形成环境
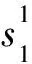

表3 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1地层水性质Table 3 Properties of formation water of N1 in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin
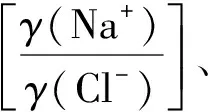
表4 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1地层水主要离子比值表Table 4 Main ion ratio of formation water of N1 in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin
4.2 地层水Ca2+含量差异特征
早期碳酸盐胶结物是由地层水中的Ca2+早期沉淀胶结而形成,此时温度、压力接近常温常压,当地层水中溶解的碳酸盐物质达到过饱和时,就可以直
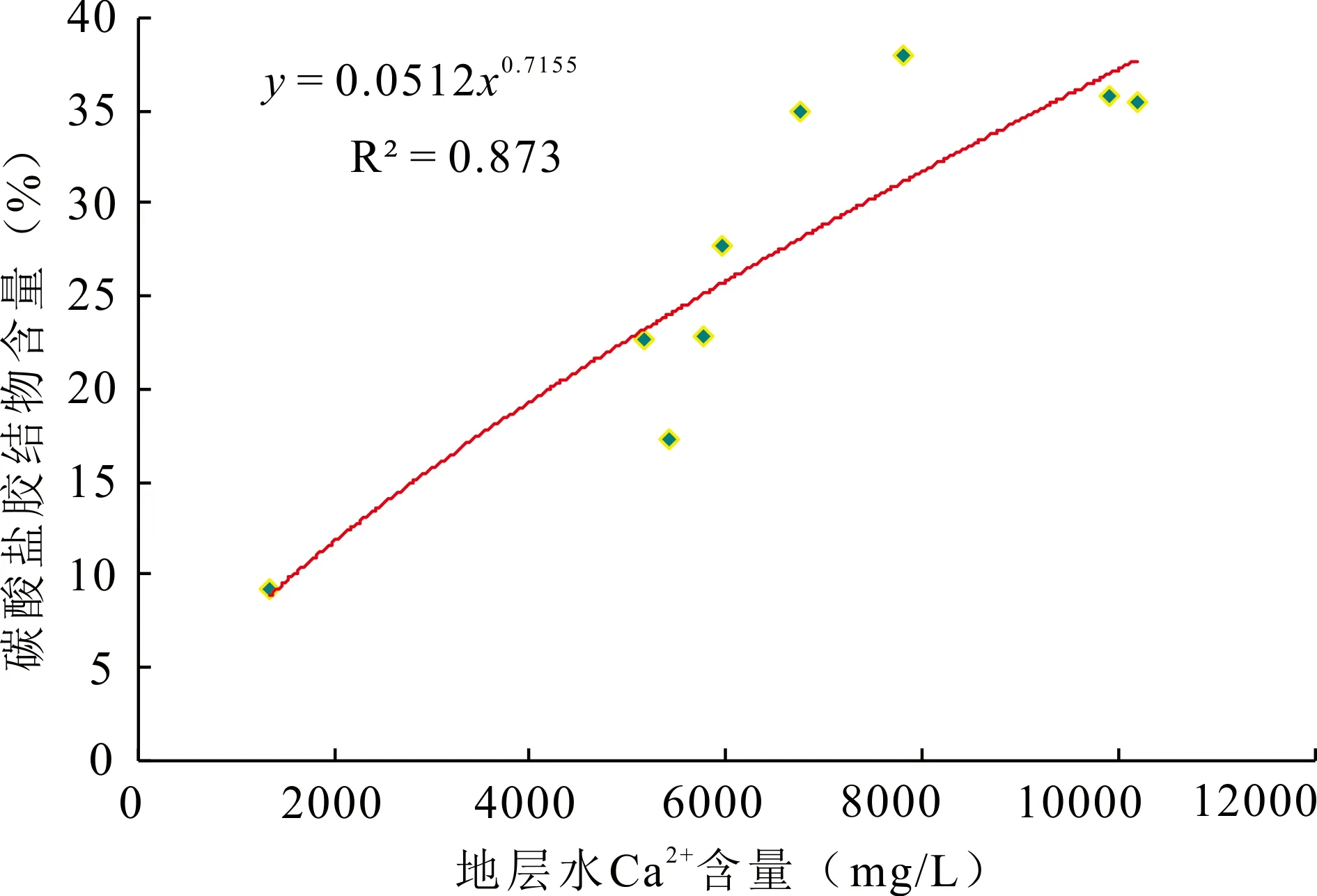
图5 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1碳酸盐胶结物含量与Ca2+含量关系图Fig. 5 Relationship between carbonate cement and Ca2+ of N1 in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin
4.3 地层水Ca2+差异分布的控制作用
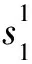
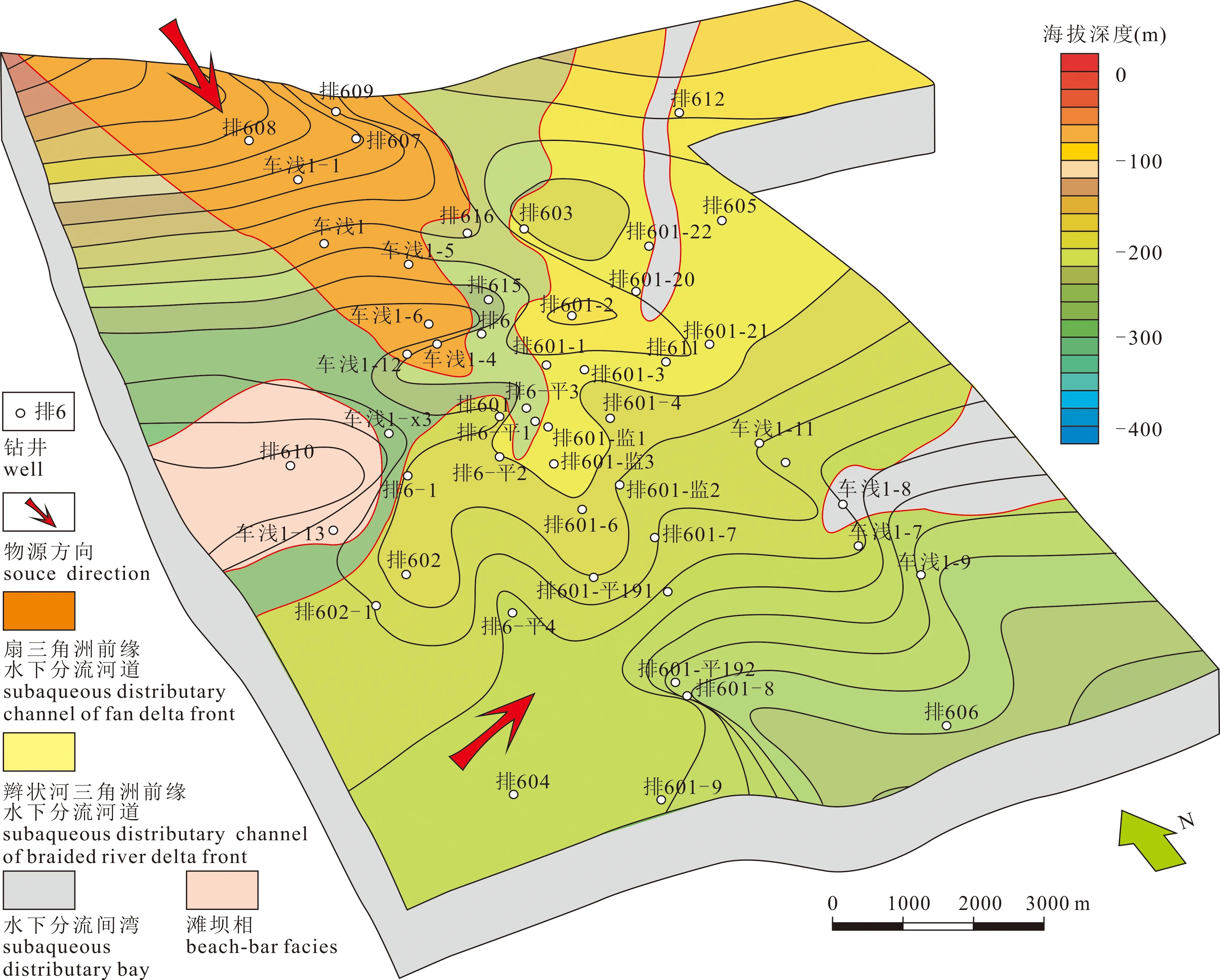
图6 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1沉积前古地貌图Fig. 6 Paleogeomorphology before N1 deposition in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin
5 碳酸盐胶结物的地质影响
5.1 对储层物性的影响
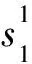
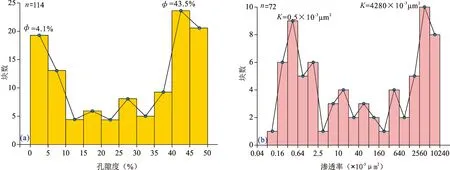
图7 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1储层岩芯孔隙度、渗透率频率分布直方图Fig. 7 Porosity and permeability frequency distribution histograms of N1 reservoir in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin(a)岩芯孔隙度频率分布直方图;(b)岩芯渗透率频率分布直方图(a) Porosity frequency distribution histogram; (b) permeability frequency distribution histogram
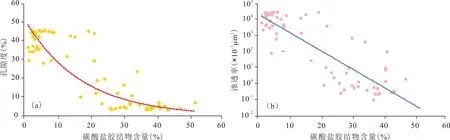
图8 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1碳酸盐胶结物含量与孔隙度、渗透率关系图Fig. 8 Relationship between carbonate cement and porosity and permeability of N1 reservoir in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin

图9 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1储层岩芯特征Fig. 9 Characters of cores of N1 reservoir in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin(a)排601-4井,514.1 m,深黑色粗砂岩,岩芯孔隙度44.8%,渗透率7070×10-3 μm2,碳酸盐胶结物含量10.68%,岩芯松散,含油性好;(b)排601-5井,532.3 m,深褐色含砾砂岩,岩芯孔隙度36%,渗透率4340×10-3 μm2,碳酸盐胶结物含量7.37%,岩芯松散,含油性好;(c)排601-平1井,488.2 m,深黑色粗砂岩,岩芯孔隙度42.4%,渗透率20300×10-3 μm2,碳酸盐胶结物含量7.71%,岩芯松散,含油性好;(d)排609井,231.4 m,灰白色含砾砂岩,岩芯6.8%,岩芯渗透率5.22×10-3 μm2,碳酸盐胶结物含量23.6%,岩芯紧密,含油性差;(e)排605井,407.8 m,灰白色砂砾岩,岩芯孔隙度6.9%,渗透率1.39×10-3 μm2,碳酸盐胶结物含量32.2%,岩芯紧密,含油性差;(f)排607井,276.6 m,灰白色砂砾岩,岩芯孔隙度3.5%,渗透率0.103×10-3 μm2,碳酸盐胶结物含量37%,岩芯紧密,含油性差(a) The Well P601-4, 514.1 m, coarse sandstone, porosity 44.8%, permeability 7070×10-3 μm2, carbonate cements content 10.68%, loose, good oil bearing; (b) the Well P601-5, 532.3 m, brown gravelly sandstone, porosity 36%, permeability 4340×10-3μm2, carbonate cements content 7.37%, loose, good oil content; (c) the Well P601p1, 488.2 m, coarse sandstone, porosity 42.4%, permeability 20300×10-3μm2, carbonate cements content 7.71%, loose, good oil content; (d) the Well P609, 231.4 m, gray gravelly sandstone, porosity 6.8%, permeability 5.22×10-3μm2, carbonate cements content 23.6%, tight, poor oil content; (e) the Well P605, 407.8 m, gray sand conglomerate, porosity 6.9%, permeability 1.39×10-3μm2, carbonate cements content 32.2%, tight, poor oil content; (f) the Well P607, 276.6 m, porosity 3.5%, permeability 0.103×10-3μm2, carbonate cements content 37%, tight, poor oil content
5.2 对油水分布的影响

表5 准噶尔盆地车北地区N1试油数据与碳酸盐胶结物含量统计表Table 5 Table of oil test data and carbonate cement content of N1 in NCPZ area, Junggar Basin
6 结论
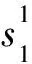
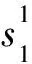
——微网状透光防炫目汽车前挡风玻璃膜的设计研究

