Deformation early-warning index for heightened gravity dam during impoundment period
Bo Chen ,Zi-shen Huang Teng-fei Bao Zheng Zhu
a State Key Laboratory of Hydrology-Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering,Hohai University,Nanjing 210098,China
b College of Water Conservancy and Hydropower Engineering,Hohai University,Nanjing 210098,China
Received 3 September 2020;accepted 12 December 2020 Available online 17 March 2021
Abstract The mechanical parameters of materials in a dam body and dam foundation tend to change when dams are reinforced in aging processes.It is important to use an early-warning index to reflect the safety status of dams,particularly of heightened projects in the impoundment period.Herein,a new method for monitoring the safety status of heightened dams is proposed based on the deformation monitoring data of a dam structure,a statistical model,and finite-element numerical simulation.First,a fast optimization inversion method for estimation of dam mechanical parameters was developed,which used the water pressure component extracted from a statistical model,an improved inversion objective function,and a genetic optimization iterative algorithm.Then,a finite element model of a heightened concrete gravity dam was established,and the deformation behavior of the dam with rising water levels in the impoundment period was simulated.Subsequently,mechanical parameters of aged dam parts were calculated using the fast optimization inversion method with simulated deformation and the water pressure deformation component obtained by the statistical model under the same conditions of water pressure change.Finally,a new earlywarning index of dam deformation was constructed by means of the forward-simulated deformation and other components of the statistical model.The early-warning index is useful for forecasting dam deformation under different water levels,especially high water levels.© 2021 Hohai University.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Keywords:Concrete gravity dam;Parameter inverse analysis;Structural health monitoring;Early-warning index;Finite element simulation
1.Introduction
With continuous economic development,existing water conservancy projects are unable to satisfy the increasing demands for water and hydropower resources.Instead of building new water conservancy projects,heightening and strengthening existing hydraulic structures has advantages such as reducing economic costs,shortening construction periods,and fully exploiting the existing structures.To maximize the synthetic benefits of existing projects,hundreds of dams around the world have been heightened and strengthened,including the Er Roseires Dam in Sudan(Alrajoula et al.,2016),the Fariman Dam in Iran(Omran and Abbas,1999),and the Songyue Dam in China(Lu et al.,2018).The advantages of dam-heightening construction have been demonstrated and verified through these engineering projects.
When a dam is heightened or strengthened,the dam behavior changes(Su et al.,2015).In addition,the external loads,such as the reservoir water level,increase to unprecedented levels.To ensure the safety and durability of heightened projects,it is important to identify the dam behavior accurately and assess the structural state reasonably(Zhu et al.,2007;Wang et al.,2016;Kang et al.,2017).Monitoring models based on deformation data have been extensively used for intuitive and reliable measurements(Dai et al.,2018).In general,these models can be divided into three main categories:data-driven statistical models(Fanelli,1975),deterministic simulation models(Bonaldi et al.,1977),and hybrid models(Chen et al.,2002;De Sortis and Paoliani,2007;Niu,2020).These models have played important roles in dam structural health monitoring.However,statistical models have poor extension ability and are deficient in reflecting conceptions of structural mechanics.Deterministic models require complex and heavy computation work when the finite element model(FEM)is used to calculate the distribution of effect quantities under various loads.By contrast,hybrid models,combining the advantages of statistical theory with FEM-based simulation analysis,can effectively overcome the defects of the statistical and deterministic models in practical applications.
The accuracy of hybrid models depends on mechanical parameters of materials.However,if these parameters are obtained solely from material tests or other engineering techniques,they cannot characterize the evolution of dam material properties under the synergistic effects of water level,temperature,structural damage,fluid-solid coupling,joint cracks,and material aging(Gu et al.,2020;Wu et al.,2019;Topçu and U˘gurlu,2007).Therefore,an inverse analysis of mechanical parameters based on prototypical monitoring is required to estimate the constitutive parameters of the dam body and dam foundation(Wang et al.,2012;Zhou et al.,2016;Dou et al.,2019).The significant feature of this method is that it associates the actual dam structure with the virtual simulation model(Sevim et al.,2012).To solve the problems of local optimal solutions and slow convergence of inverse analysis,artificial intelligence algorithms,such as the support vector machine,the clustering algorithm,neural networks,particle swarm optimization,and fuzzy mathematics,have recently been used in these parameter inverse analysis methods(Ma et al.,2020;Su et al.,2019;Bui et al.,2018;Y.C.Gu et al.,2020).
Through the hybrid models of dam deformation and parameter inverse analysis,mined information and summarized rules of dam behavior are extracted.Afterward,they can be fed back into the subsequent engineering operation for further engineering evaluation,such as control of the critical load during dam operation,determination of the actual dam safety degree,and early-warning index formulation.Previous studies have focused on early-warning indexes of dam safety,real-time dam behavior identification,and prediction of the dam"s ability to withstand possible loads,which are crucial for effective dam health evaluation(Lei et al.,2011;Su et al.,2017).Common methods of early-warning index calculation include the typical low probability method,confidence interval method,and structural analysis method(Li et al.,2019;Gu et al.,2017;Huang et al.,2013).These methods usually require historical monitoring data.They can reveal numerical change ranges of effect quantities under different load combinations and be used to determine the warning and extreme values of dam deformation under extreme load conditions.Overall,early-warning indexes can be used to quickly evaluate the safety level and accurately identify hazardous situations,providing a theoretical basis and decision support for longterm service and operation management of water projects(Gu et al.,2016).
In this study,a hybrid model for monitoring the horizontal displacement of typical dam sections was constructed.This model used deformation monitoring data of a heightened gravity dam in the impoundment period,a finite-element numerical simulation scheme,and statistical regression analysis.Combined with the traditional genetic algorithm of stochastic optimization,a fast optimization inverse analysis method was proposed to determine the mechanical parameters of dam materials,which can improve the efficiency and reliability of dam structural behavior analysis.After the mechanical parameters of the dam body and foundation were obtained from the inverse analysis,the change of deformation in a heightened concrete dam under different working conditions was simulated for comprehensive evaluation of the dam safety status.Finally,a new early-warning index was developed to monitor the deformation safety of a heightened gravity dam during the impoundment period.This index has the potential to efficiently evaluate the working state of a dam with the reservoir water level exceeding the maximum historical level.
2.Methodology
2.1.Hybrid model of dam displacement
Considering the structural behavior of a dam under different load conditions,dam displacement can be divided into several parts,accounting for the effects of hydrostatic pressure,ambient temperature,and time.The displacement model of a heightened gravity dam can be expressed as follows:

whereδis the horizontal displacement,δH0is the water pressure component at the initial water level,ΔδHis the difference between the water pressure components at the initial level and measured water level,δTis the temperature component,δais the aging component,andα0is a constant.The temperature and aging components of dam horizontal displacement can be described by a statistical expression(Wu,2003):
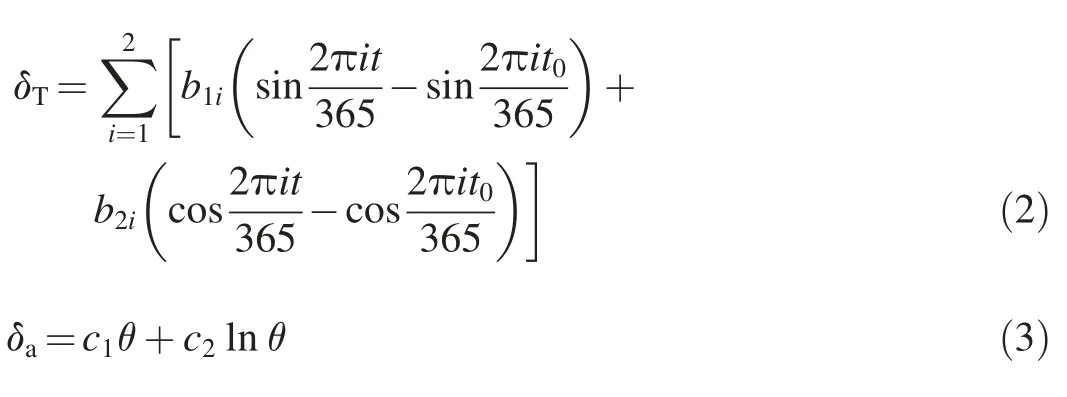
whereb1iandb2i(i=1,2)are the regression coefficients of the temperature component,t0is the starting time of modeling relative to the initial monitoring(in days),tis the time of monitoring relative to the initial monitoring(in days),θ=t/100,andc1andc2are the regression coefficients of the aging component.
The water pressure component of the hybrid model is calculated with FEM.Given that the dam material is homogeneous concrete,a linear-elastic constitutive model is used as the equilibrium equation of the entire structure,which is expressed as

where K,δH,and RHare the global stiffness matrix,node displacement array,and node load array of FEM within the global computational domainΩ,respectively.The global stiffness matrix is expressed as follows:

where keand ceare the stiffness matrix and the transformation matrix of elemente,respectively.keis as follows:
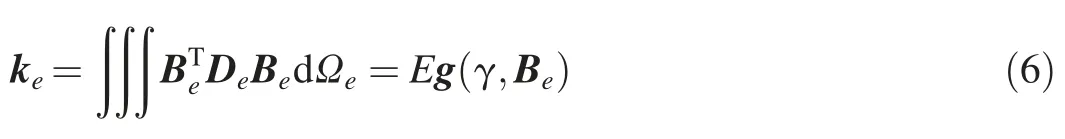
whereEandγare the elastic modulus and Poisson"s ratio,respectively;Deis the element elastic matrix,with De=Eh(γ),where h(γ)is a constant matrix;Beis the element geometry characteristic matrix;and g(γ,Be)=∫∫∫BTeh(γ)BedΩe,whereΩeis the computational domain of elemente.For the generated FEM mesh,both Beand g(γ,Be)are the constant matrices.Therefore,the displacement induced by the water pressure load is derived as follows:

where G-1(γ)is the inverse matrix of G(γ),and G(γ)=
2.2.Finite element method
2.2.1.Simulation of joints and cracks
In a heightened gravity dam,joints and cracks are often the most vulnerable areas of a structure because they contain many microdefects.They are important factors influencing the dam safety(Luo et al.,2016).Therefore,the threedimensional(3D)contact surface element(Lee and Fenves,1998),a spatial eight-node non-thickness contact element,was used to simulate joints and cracks in this study.
When joints in the concrete body are well-cemented during the grouting process,they resist tension,compression,and shear forces.Once the tensile or shear strength of a bonding surface exceeds its limit,the bonding surface immediately changes to cracking surfaces.There are three states of cracking surfaces:the disengaged state,static friction state,and sliding friction state.A shear transfer model of the cracking surface was constructed as follows:

whereσnis the normal contact force of the contact surfaces;τsandτtare the tangential stresses of the two contact surfaces in thex-andy-directions,respectively;Δϖnis the normal displacement difference of the contact surfaces;dis the initial opening degree of the contact surfaces;ΔuandΔvare the tangential displacement differences of the two contact surfaces in thex-andy-directions,respectively;Knis the normal stiffness of the contact surfaces;andKsandKtare the tangential stiffness of the two contact surfaces in thex-andy-directions,respectively.KandK′are estimated as follows:
(1)For a closed contact state,withΔϖn+d≤0,K=Kn.

(4)For open contact surfaces,withΔϖn+d>0,K=K′=0.In this case,the contact remains in a free sliding state with zero contact force.
2.2.2.Principle of parameter inversion
The elastic modulus of dam materials changes during the engineering operation process.According to Eq.(7),the displacement caused by water pressure is inversely proportional to the elastic modulus of dam materials.This feature can be used to estimate the elastic modulus of the dam body and dam foundation.Based on forward analysis,the displacement δcalculated with the simulation model can be expressed as the function of material parameters,boundary conditions,and computational load:

wherePis the total load applied to the model,Γrepresents the constraint conditions of the model,andΔis the sum of other factors.Typically,in the inverse analysis,the square sum of residuals between the observed displacementδmiand calculated displacementδciat the pointiis used as the objective function:

whereNis the number of observation points,andQis the square sum of residuals between the calculated and measured displacements.When the objective functionQis minimized,the inversed result of the elastic modulus can be obtained.
2.3.Fast optimization inversion method
2.3.1.Improvement of traditional objective function
The traditional parameter inversion method based on a gradient search has certain disadvantages in practical engineering.If results depend on initial values,it is difficult to perform multi-parameter optimization,and the optimized results tend to fall into local extreme values.In this study,to increase the efficiency of the traditional inverse analysis method,an optimization iteration method was adopted to optimize the traditional objective function.For constantsP,Γ,Δ,γ,andδmiin Eqs.(9)and(10),the original equation for the model materialEcan be rewritten as a continuous functionF,and ann-level Taylor expansion of the functionF,with its initial valueE0,is expressed as follows:whereF(E0)represents the square sum of residuals between the assumed and initial parameter values.
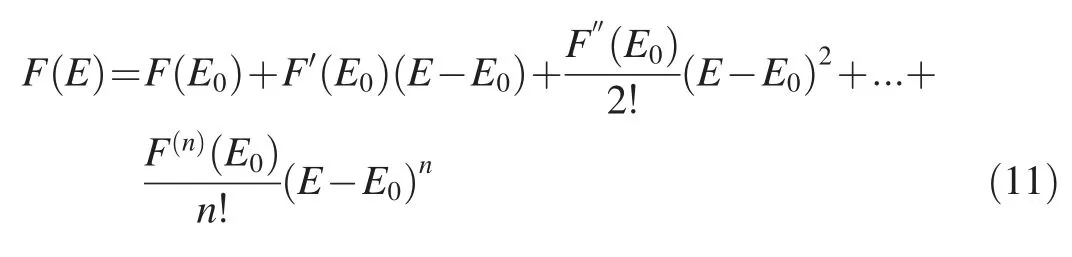
By settingQ0=F(E0),Q1=F′(E0)(E-E0),…,andEq.(10)can be rewritten as follows:

The first derivative of the functionFatE0is given as
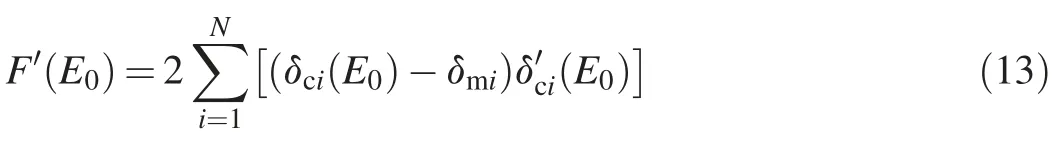
Thenth derivative of the functionFatE0is expressed as follows:

wherenis determined according to the calculation accuracy and the actual engineering situation,the multinomial coefficientaiis estimated with the Taylor expansion formula,and the derivatives of the structural displacementδcatE0are calculated with the structural equilibrium equation of FEM.
By substituting Eqs.(13)and(14)into Eq.(11),an improved objective function can be obtained.This improved objective functionF(E0)is only related to the initial elastic modulusE0,and it can reduce the frequency of the forward calculation in subsequent operation,improving the computational efficiency.
2.3.2.Genetic optimization algorithm
The genetic algorithm is a random search algorithm based on genetics and natural selection.Its global convergence properties and robustness can ensure the reliability and credibility of inverse analysis results.Additionally,this algorithm is often adopted to develop an efficient optimized inversion program(Yao et al.,2019).
In the genetic algorithm,the initial valueE0is set as the average of the individuals in the random initial population.To approach the optimal parameter combination,the calculation process should effectively guide the search leading to parameter optimization.Therefore,with the aforementioned optimization inversion objective function,the fitness function(S)of the genetic optimization algorithm is formulated as follows:
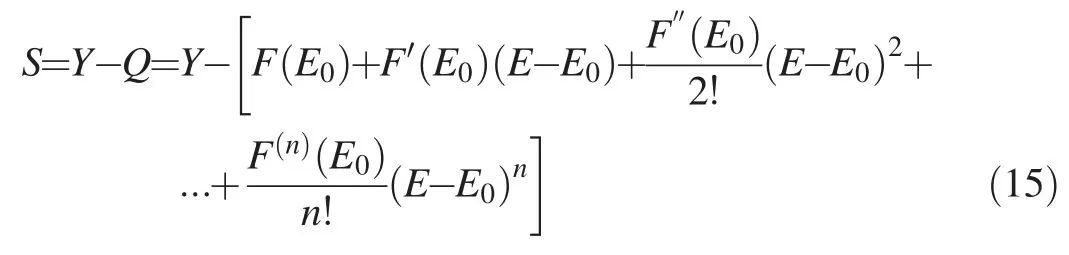
whereYis an arbitrary positive value,with a value sufficiently larger thanQ.It can be determined for a specific situation.The new individualEis produced by a genetic operation,and the corresponding fitness function is determined by(E-E0)n.Throughout the calculation process,the objective function is independent of parameter gradients,and a simple algebraic operation is used to directly search for the optimal parameter set in the parameter space,significantly reducing the number of iterations.Consequently,the search speed and accuracy of the algorithm are significantly improved.
2.4.Deformation early-warning index
The structural analysis method was used to calculate the early-warning index.The method mainly adopts the strength and stability as the constraint conditions.Given that the dam displacement is an implicit function,the explicit relationship between the displacement and load combination is used to deduce the corresponding dam deformation early-warning index:
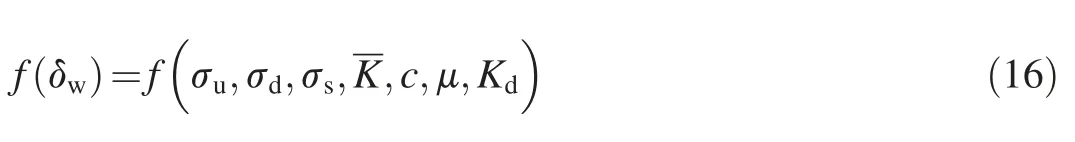
whereσu,σd,andσsare the dam heel stress,dam toe stress,and allowable concrete compressive stress under different load combinations,respectively;KdandKare the safety coefficient and the allowable safety coefficient against sliding stability under different load combinations,respectively;candμare the design values of the cohesion force and friction coefficient,respectively;andδwis the dam deformation early-warning index,representing the monitoring reference value of the downstream horizontal displacement.
With consideration of the most unfavorable water level and temperature conditions for the project safety and the aging influence,the calculation formula for the dam deformation early-warning index is as follows:
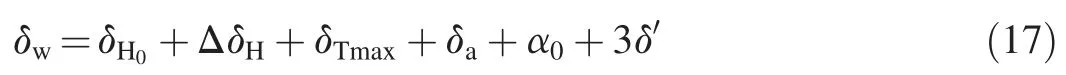
whereδTmaxis the component corresponding to the difference between the highest temperature and initial temperature,andδ′is the residual standard deviation of the hybrid model.
As shown in Fig.1,the deformation early-warning index of a heightened gravity dam in the impoundment period was constructed via three procedures as follows:
(1)Forward analysis:A 3D FEM for the dam was established,with consideration of the effects of fault fracture zones and special joint surfaces.This model was validated with the calculated distributions of deformation and stress.Afterward,a statistical model of the horizontal displacement along the river was developed to extract the water pressure component.
(2)Inverse analysis:With the developed statistical model,representative monitoring points in typical dam sections were selected for inverse analysisof the mechanical parametersof dam materials.Based onthe change inwater pressure components,the deformation modulus of the dam foundation was optimized.Subsequently,the elastic modulus of the dam body was calculated via inverse analysis.
(3)Forward analysis:According to the parameters from inverse analysis,the deformation caused by water pressure under different water levels was simulated during the impoundment period.An early-warning index system under the most unfavorable load conditions was established with the structural analysis method.The system was used to evaluate the structural safety of heightened projects.
3.Results and discussion
3.1.Data preparation for inverse analysis
A water conservancy project,including earth and rockfill dams on both river sides,a main concrete dam,power stations,and ship lifts,was selected as the research object to verify the rationality and feasibility of the proposed earlywarning index(Fig.2).The earth and rockfill dams on the river sides are connected to the concrete dam built on the riverbed,and a concrete overflow dam and a dam-rear power station were also built on the riverbed.Owing to the lack of construction preparation and experience,this concrete gravity dam was constructed in two stages.In the first stage,the elevation of the dam crest was set as 162 m,with a normal storage level of 157 m.To satisfy the increasing regional water resources demand,this dam has been heightened recently,and it was strengthened to be a level-I water conservancy project according to Chinese standards.Compared with the initial project,the dam was heightened by 14.60 m.Its normal storage level was increased from 157 m to 170 m,and the storage capacity was augmented to 33.91 billion m3.
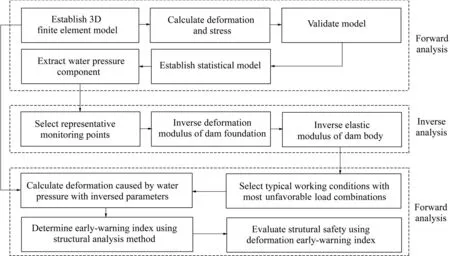
Fig.1.Flow chart for establishing deformation early-warning index for heightened gravity dam during impoundment period.

Fig.2.Heightened gravity dam for case study.
Given that the concrete pouring of the dam body was conducted many years ago,the dam materials have endured a long-term aging process,and several irregular reinforcements have been conducted over the main structure.Owing to uneven construction quality,it is difficult to determine the mechanical parameters of dam materials accurately according to the design and initial measurements.The elastic modulus of the aged typical concrete section should be determined through inverse analysis of observations at some representative monitoring points.
To comprehensively reflect the working state of the dam,the #13 dam section(retaining dam section)and #18 dam section(spillway dam section)were selected as typical sections.The major cracks on the upstream surface were severe,and should be considered,particularly in the#18 dam section.
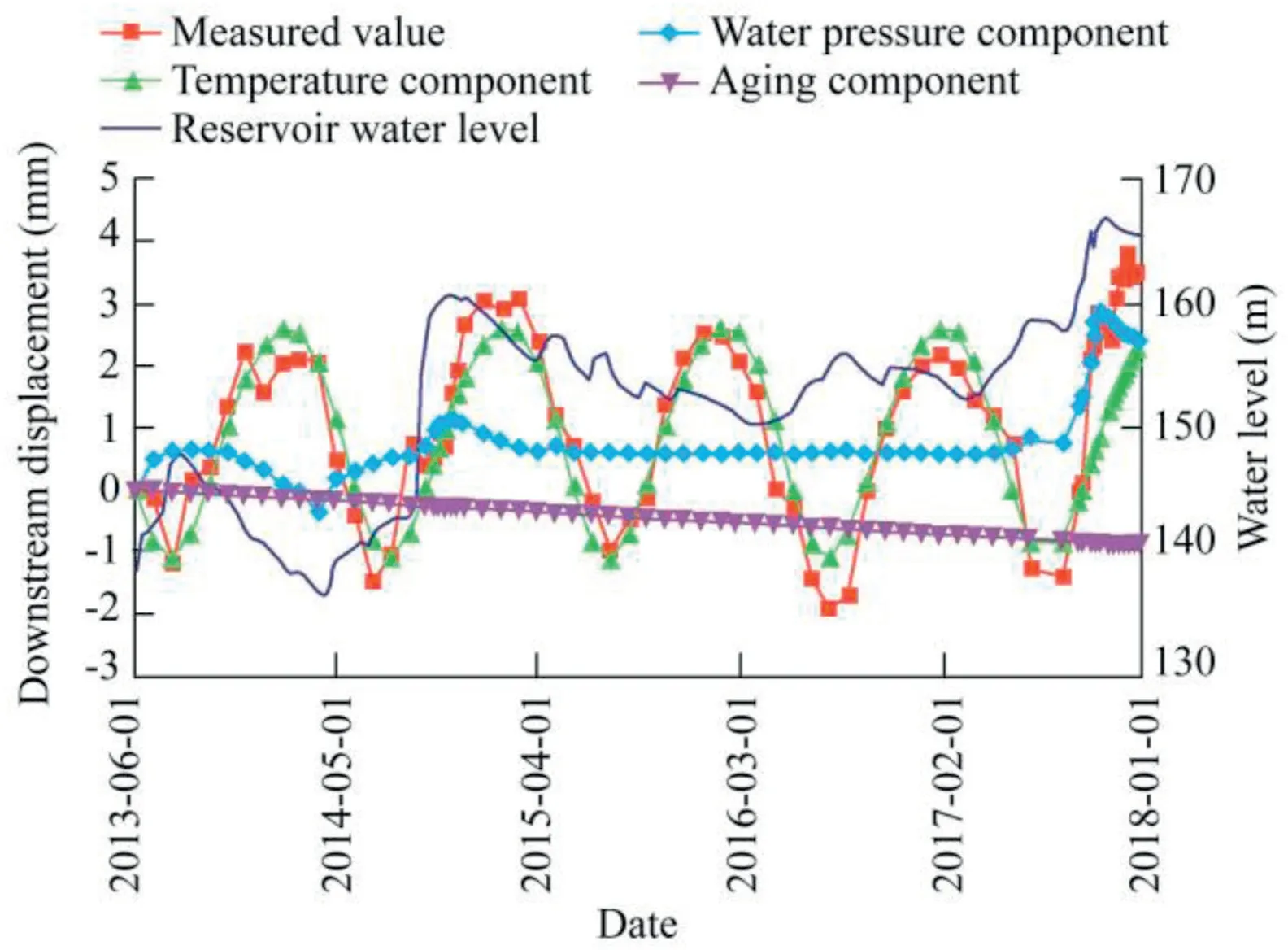
Fig.3.Simulated displacement and its components from statistical model at monitoring point PL02HC183 in #18 dam section.
According to the monitoring data of the horizontal displacement of typical dam sections along the river from June 1,2013 to December 31,2017,the displacement statistical model for each monitoring point was established,including the water pressure,temperature,and aging components.Fig.3 shows displacement variations at the monitoring point PL02HC183 in the #18 dam section obtained from the statistical model.As shown in this figure,the displacement induced by water pressure gradually increased as the reservoir water level rose,indicating that the displacement along the river was significantly affected by the water pressure.Therefore,it is necessary to introduce the water pressure component in parameter inverse analysis.
To obtain a high accuracy in inverse calculation of the displacement at representative monitoring points in a typical dam section,many factors should be considered,including the reliability of monitoring data,the multiple correlation coefficient and standard deviation of the statistical model,the proportion of water pressure component,and the elevation layout of monitoring points.After comprehensive consideration,the monitoring point IP01HC24 was selected for calculation of the elastic modulus of the dam foundation,and the monitoring points PL02HC133 and PL02HC183 were selected for calculation of the elastic modulus of the dam body.The water-level rising period from August 24,2017 to October 19,2017 was selected as the calculation period.For the calculated displacement of point PL02HC133 in the #13 typical dam section,a correlation coefficient of 0.958 and a standard deviation of 0.463 mm were obtained,and those for the calculated displacement of point PL02HC183 in the #18 typical dam section were 0.957 and 0.673 mm,respectively.This indicates that the statistical model was accurate.In addition,the water pressure components accounted for 38.67% and 29.52% of the displacement along the river at points PL02HC133 and PL02HC183,respectively.Hence,the two monitoring points were suitable for inverse analysis.
3.2.Development of FEM
Based on recorded documents on dam structure design,geological surveys,and project reinforcement and heightening,an integrated 3D comprehensive FEM was constructed for typical dam sections.Simulation of the interface between the new and aged dam parts is currently a research hotspot(Liu,2016).The deformation of major cracks that were treated after the rise of water level affected dam operation.Additionally,fissured fault structures in the dam foundation area were confirmed via engineering geological surveys.Therefore,in the modeling process,the fault fracture zones and special dam joints were fully considered,along with the difference of concrete materials between the aged and new concrete parts.In the FEM,eight-node hexahedron isoparametric elements were used.The six-node pentahedral and five-node pentahedral isoparametric elements were adopted in regional simulation to assess the influence of topography and geology.To conveniently compare the observations with the simulation results,the model nodes were arranged at the dam deformation monitoring points.In addition,contact surface elements were introduced to simulate contact surfaces and cracks.The constitutive model of adhesive surfaces was used to simulate treated cracks and interfaces between the new and aged concrete parts that had a certain tensile strength and shear strength.By contrast,the constitutive model of crack surfaces was used to simulate existing cracks and newly cracked adhesive surfaces with low shear strength and without tensile strength.Finally,FEMs of typical dam sections were developed,as shown in Fig.4.
3.3.Inversion process of material parameters
The fast optimization inversion method was used to calculate the mechanical parameters of the dam foundation(Fig.5).The monitoring point IP01HC24 in the #24 dam section was used as an example.According to previous test results of drilling samples of the aged concrete during the dam heightening period,the initial deformation modulus of the dam foundation was assumed to be 20 GPa.Through iterative calculations,the average ratiokof the increment of the measured displacement to that of the calculated value was found to be 0.832 3,and the calculated result of the deformation modulus was 24 GPa.Subsequently,the initial deformation modulus of the dam foundation was adjusted to 24 GPa.After further iterative calculations,the average ratiokwas found to be 0.998 0,which was close to 1.Therefore,the inversion process was terminated,and the calculated deformation modulus of the dam foundation in the#24 dam section was 24 GPa.
According to the statistical model,the water pressure components obtained at other inverted vertical line monitoring points of the dam foundation were close to zero,and the multiple correlation coefficients were relatively low.Therefore,only the water pressure component at IP01HC24 was selected in the inverse analysis of the deformation modulus of the dam foundation.Given that the geological conditions of typical dam sections were relatively similar,the deformation modulus of the dam foundation in other dam sections was determined to be 24 GPa.
After the deformation modulus of the dam foundation was calculated,the elastic modulus of the dam body was inversed.With the initial elastic modulus of the dam body of 25 GPa,the elastic moduli of the dam body in the #1,#13,#18,#21,and #31 typical dam sections,were calculated with the fast optimization inversion method.The results were 25.40,30.50,26.80,25.00,and 25.20 GPa,respectively.Fig.6 demonstrates the inversion process of mechanical parameters at monitoring point PL02HC133 in the #13 dam section.
Table 1 shows that the estimated mechanical parameters for typical dam sections of the dam foundation and dam body from inversion analysis had changed compared to the initial parameter values.The initial mechanical parameter values were selected based on historical material tests,and would gradually increase with time according to engineering experience.Therefore,the material mechanical parameters determined by the fast optimization inversion method are consistent with current professional knowledge.
3.4.Determination of deformation early-warning index
With the mechanical parameters of aged dam parts obtained from the inverse analysis and the designed elastic modulus of the new dam parts(36.5 GPa),3D FEMs were established for the #13,#18,#21,and #31 dam sections.Afterward,with the strength and stability as constraint conditions,the deformation early-warning index of the heightened gravity dam was estimated with the structural analysis method.
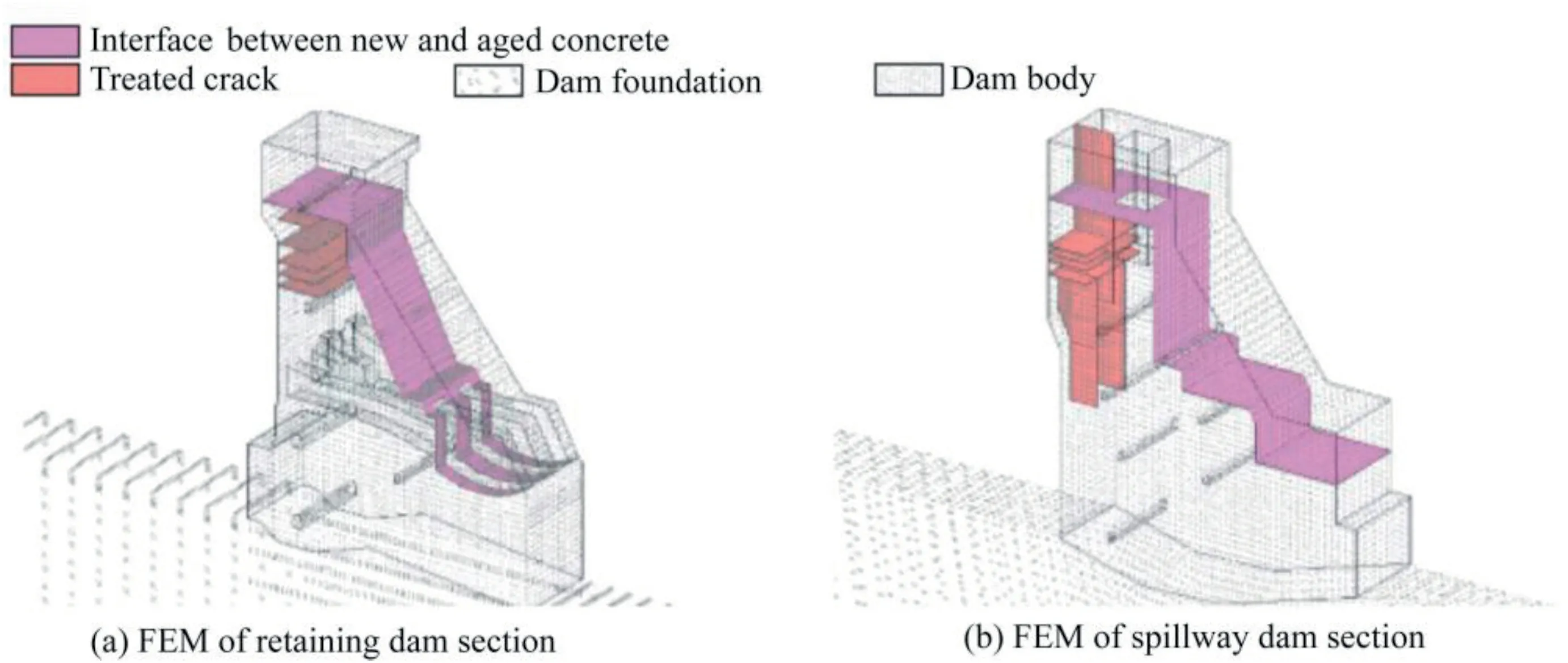
Fig.4.FEMs of typical dam sections in heightened gravity dam considering joints and cracks.
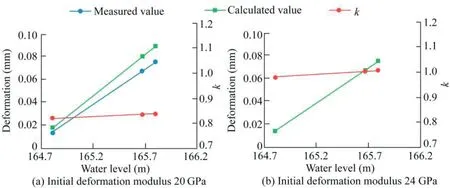
Fig.5.Iterative process of mechanical parameter inversion at monitoring point IP01HC24 in #24 dam section.
According to the analysis of deformation monitoring data,the maximum downstream displacement of the dam body occurred at low temperature and a high water level.Therefore,the maximum reservoir water level and extreme temperature drop were selected as the ultimate load cases to evaluate the downstream displacement.It should be noted that the considered temperature component was obtained from the most unfavorable perspective.If the specific period of reservoir storage is determined,accurate results of temperature component can be obtained according to Eq.(2)or through temperature field analysis.
To provide references for dam safety evaluation during the impoundment period,different operation conditions should be considered.Three typical working conditions were selected:the normal water level of 170.00 m,design flood level of 172.20 m,and check flood level of 174.35 m.The earlywarning index of the heightened gravity dam was calculated with the structural analysis method under different conditions.Using monitoring point PL02HC133 in the#13 dam section as an example,the calculated deformation early-warning index for point PL02HC133 was 7.13 mm under the normal water level,7.73 mm under the design flood level,and 8.35 mm under the check flood level.
As shown in Fig.7,the deformation early-warning index of the heightened gravity dam was composed of the water pressure component derived from the 3D FEM,constant term,temperature component,aging component,and residual standard deviation based on the statistical model.When the reservoir water level was increased from the normal water level to the design flood level and further raised to the check flood level,the water pressure component derived from the 3D FEM gradually increased with the rise of the corresponding safety early-warning index.
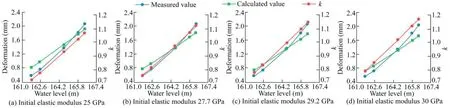
Fig.6.Iterative process of mechanical parameter inversion at monitoring point PL02HC133 in #13 dam section.
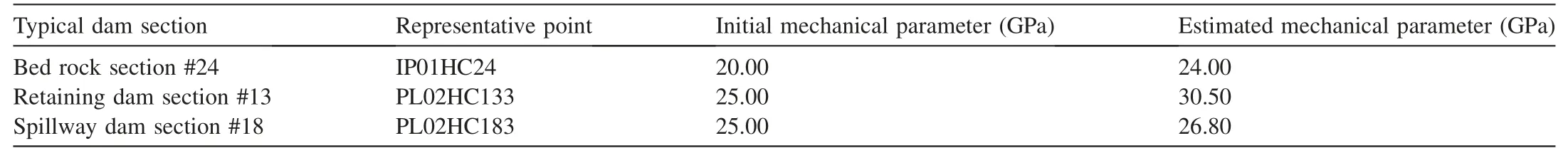
Table 1Mechanical parameters in heightened gravity dam estimated from inversion process.
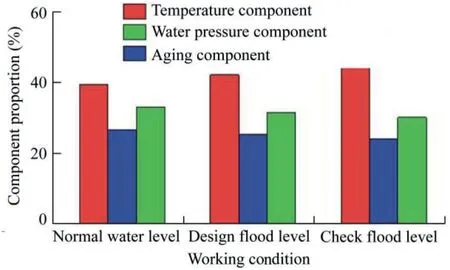
Fig.7.Composition of deformation warning index under different water levels.
Compared with the upper limit of the deformation earlywarning index obtained with the confidence interval method,the deformation early-warning index obtained with the structural analysis method was significantly higher,as shown in Fig.8.The deformation early-warning index obtained with the confidence interval method has been used worldwide because of its simplicity and seamless operation.However,when the dam lacks the experience of an unfavorable load combination or has a short-time series of monitoring data,the earlywarning index based on the confidence interval method is prone to misreporting and underestimation.Currently,the mathematical model based on the monitoring data can only be used to predict the effect quantities in the range of encountered dam loads and does not always include the warning value under the most unfavorable load.From June 1,2013 to November 11,2017,the upstream water level for the studied dam has changed from 136.51 to 167.00 m,and the project has not experienced extreme conditions,including the new normal water level,design flood level,and check flood level.Thus,the confidence interval method is not suitable for safety monitoring during the impoundment period.By contrast,the earlywarning index based on the structural analysis method has distinct physical meanings and clear mechanical definitions.Therefore,this method is feasible for solving the problems of short monitoring data series and incomplete monitoring data through simulation of load conditions that have never occurred.
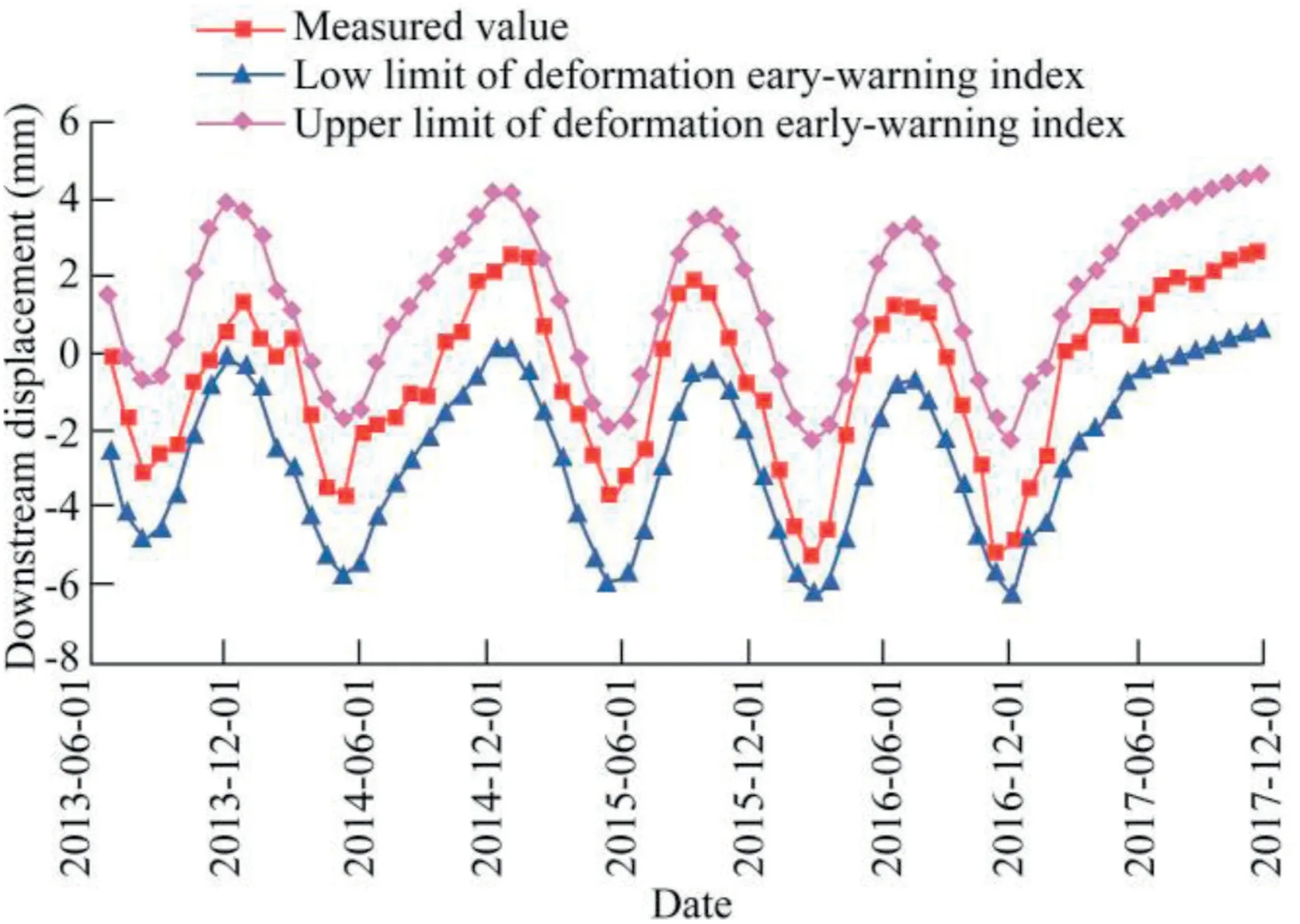
Fig.8.Process lines of measured deformation and deformation earlywarning indexes obtained with confidence interval method at point PL02HC133 in #13 dam section.
3.5.Verification of early-warning index
To investigate the reliability and rationality of the earlywarning index of dam deformation,the estimated earlywarning index was verified against the monitoring data and calculated structural behavior.Fig.9 demonstrates the calculated early-warning index and monitored deformation under different water levels.This figure shows that the monitored deformation value was slightly lower than the warning index when the reservoir water level changed from 138 m to 168 m.It should be noted that a gravity dam is essentially a type of cantilever beam structure.Thermal expansion and contraction caused by temperature change are the main causes of deformation but not the main causes of overload failure.In the case study,the water pressure change was considered the major factor,and the influence of temperature change was considered at its maximum value.However,the rationality of the early-warning index can still be evaluated with the data at deformation monitoring points near the line of the earlywarning index.With the closest point to the line as an example,at the water level of 138.91 m,the monitored deformation was 1.40 mm,and the calculated early-warning index was 1.96 mm.In general,although the estimated early-warning index slightly exceeded the maximum monitored deformation at the same water level,it was numerically reasonable.
Fig.10 displays the calculated results of stress distribution and the crack status of the #13 dam section under the check flood level(174.35 m).When the reservoir water level reached the maximum flood level,the vertical stress of the dam would be in a compression state with a maximum value of-0.687 MPa,which meets the requirement that the maximum vertical stress of a gravity dam should not be in the tension state.As to the stress state of the crack surface at the joints of the aged concrete and new heightened concrete sections,the tension areas(in blue color in Fig.10(b))mainly appeared at the slope position near the downstream surface.Considering that the connected reinforcements,including rebars and keyways,were not simulated in FEM,these tension areas would run safely in the actual heightened dam under the highest reservoir water level.
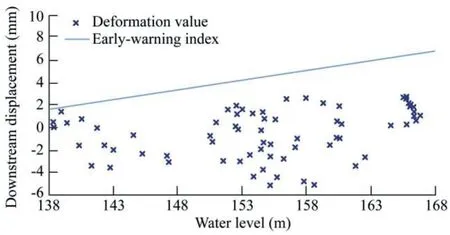
Fig.9.Comparison of deformation monitoring value and earlywarning index at different water levels.
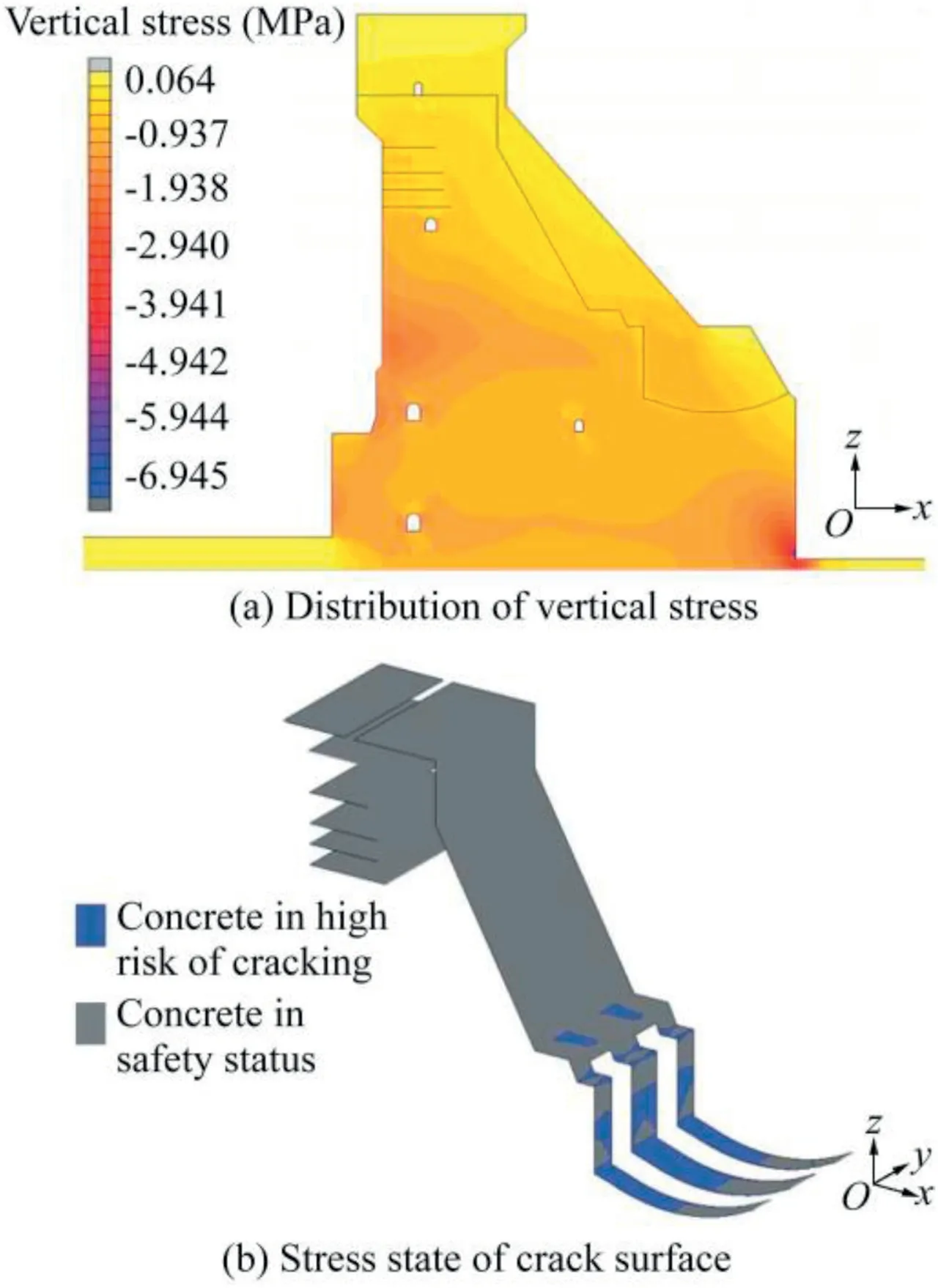
Fig.10.Calculated structural behavior of#13 dam section with joints and cracks under check flood level of 174.35 m.
In conclusion,the proposed early-warning index slightly overestimated deformation values at corresponding water levels.Meanwhile,the structure was in a relatively normal state under the check flood level according to calculated results of the inverse and forward analysis methods.Therefore,the proposed early-warning index can be used as a reference for safety forecasting of the heightened concrete gravity dam.
4.Conclusions
In this study,a new early-warning index of dam deformation was constructed using historical structural health monitoring data and finite element simulation.The proposed index has the potential to evaluate the safety status of a dam under different water levels,especially under an extremely high water level.The main conclusions of this study are summarized as follows:
(1)Three-dimensional FEMs using contact surface elements were established for typical dam sections,with consideration of the effects of joints and cracks.Subsequently,the elastic modulus of the dam body and the deformation modulus of the dam foundation in typical dam sections were obtained according to the separated water pressure component in the statistical model of monitored horizontal displacement.The material parameter was estimated with a rapid optimization inversion method,which significantly improved the search accuracy and calculation efficiency of parameter inverse analysis.
(2)The structural analysis method was used to develop a deformation early-warning index for a heightened gravity dam in the impoundment period.The method effectively solves the problems of short-time monitoring and incomplete monitoring data,and the index provides a theoretical basis and decision support for real-time assessment of the safety status of heightened gravity dams from the viewpoint of structural evolution mechanisms.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
 Water Science and Engineering2021年1期
Water Science and Engineering2021年1期
- Water Science and Engineering的其它文章
- Drought variability and its connection with large-scale atmospheric circulations in Haihe River Basin
- Impacts of climate change on water quantity,water salinity,food security,and socioeconomy in Egypt
- Simulation of maize drought degree in Xi"an City based on cusp catastrophe model
- Diffusion analysis and modeling of kinetic behavior for treatment of brine water using electrodialysis process
- Ultrafiltration for environmental safety in shellfish production:A case of bloom emergence
- Ported wall extension hydraulics
