Comparative analysis of physical performance and fishing efficiency between biodegradable PLA gill net and conventional PA gill net
SHU Aiyan,ZHANG Min,YU Wenwen,WANG Yue,SHI Jiangao,WANG Lei,MIN Minghua
(1.College of Marine Sciences,Shanghai Ocean University,Shanghai 201306,China;
2.East China Sea Fisheries Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences,Shanghai 200090,China)
Abstract:With the development of fishery economy,fishing gear materials,such as cotton,which are generally biodegradable,have been replaced by synthetic materials,such as polyethylene(PE),polypropylene and polyamide(PA),which are difficult to decompose.Synthetic fiber materials exhibit the advantages of high strength,wear resistance and corrosion resistance.Currently used fishing netmaterials can be classified into PA,PE and polyester,among which PA is themost commonly used and has been used for the longest time.However,fishing netsmade from synthetic fibers,such as PA,are not able to degrade in marine environment for decades.When they are lost or abandoned at sea,they will continue to trap fish and other animals,becoming“ghost fishing”gears.Fish and other marine organisms trapped in the abandoned fishing netswill eventually die and become baits to lure other creatures,forming a vicious circle.To conserve the marine environment and mitigate the threats of“white pollution”and“ghost fishing”,the use of environment-friendly degradable materials instead of conventional materials has become one of the major innovations in the sustainable development of modern fisheries.In this study,we assessed the physical performance ofmonofilamentsmade from a biodegradable resin,polylactic acid(PLA),in the laboratory,and compared and analyzed the fishing efficiency of gill netsmade of PLAmonofilaments and conventional PA monofilaments in sea trials conducted on Langya Island from September to October 2019.Results showed that the biodegradable PLA gill net captured 75.0% less Portunus trituberculatus but 90.0% more Pneumatophorus japonicus than PA gill net.The total catch number by PLA gill net was slightly lower than that by PA gill net,and the fishing efficiency of PA gill netwas approximately 60.0% higher than thatof PLA gill net.Moreover,mechanical tensile tests showed that themesh breaking strength of the two gill nets was both significantly reduced after the fishing operation.In addition,PLA meshes were more vulnerable to damage than conventional PA gill net due to the poor toughness and lack of elasticity and flexibility of PLA monofilaments.At the same time,themicroscope picture showed that the damage of PA gill net appeared in the middle of the mesh,while PLA gill net in the knot.Furthermore,the breaking strength of PLA monofilamentswas significantly lower than that of PA,so PLA gill netmeshesweremore easily to be broken.Although PLA gill net is not as efficient as PA gill net in terms of fishing performance,it exhibits a potential advantage in reducing“ghost fishing”and plastic pollution in the ocean,so the usage of PLA gill net can be extended with improvement on strength performance.
Keywords:degradation;gill net;polylactic acid(PLA);polyamide(PA);monofilament;physical performance;fishing efficiency;fishing gearmaterials
High-quality,light-weight,low-cost and highperformance polymer materials have been widely used in all industries and many aspects of our lives because of their powerful functions and practicability.However,“white pollution”caused by the non-degradable conventional polymer materials has seriously threatened the marine ecological environment and has elicited widespread attention[1-3].Fishing nets made from synthetic fibers,such as polyethylene(PE)and polyamide(PA),are not able to degrade even after decades of exposure to seawater environment[4-7].When these nets are lost or abandoned at sea,they will continue to trap fish and other animals,becoming“ghost fishing”gears.PA exhibits excellent strength,wear resistance and corrosion resistance;it is also easy to process[8].Thus,PA is widely used in the field of fishery.Nylon fishing nets,also called PA fishing nets,are frequently used in drift nets,purse seine,offshore cages and other fishing gears.Fishing gears made of nylon nets exhibit good economic benefits,fishing performance and operating efficiency[9-10].In drift nets manufacturing,PA monofilaments are the most commonly used materials[11].PA fishing nets abandoned at sea will decompose into tiny microplastic particles due to photodegradation and other weather phenomena.Microplastic pollution in oceans has become a global environmental problem[12-15].Given that marine fishery ecoenvironmental protection has been gradually becoming worldwidely concerned,the development and application of degradable materials to fishing gears have elicited increasing attention among researchers[16-18].
Biodegradable polymer materials can be decomposed by microbial enzymes or light under certain conditions[19-20].Polylactic acid(PLA)is a new type of biodegradablematerial.It ismade from raw starch materials that can be extracted from renewable plant resources(e.g.,corn).PLA will eventually decompose into carbon dioxide and water in nature and organisms,and thus,it exerts the minimal negative effect on the ecological environment[21-23].PLA fiber is considered one of the most promising green fibers[24-25].It has continuously received attention from various fields of study in recent years[26-27].Fishing gears made from biodegradable plastic materials,such as PLA,are considered a potential solution for mitigating“ghost fishing” and plastic pollution[28-29].GRIMALDOet al.studied the fishing efficiency of gill nets made from a new biodegradable resin,polybutylene succinate co-adipate-co-terephthalate,relative to that of conventional(nylon)nets;their results generally showed better catch rates for nylon gill nets[30].
In the current study,the physical performance ofmonofilaments made of PLA were studied in the laboratory and the fishing efficiency of gill netsmade of PLA and PA monofilaments was compared on Langya Island from September to October 2019.This study aims to evaluate the physical performance and fishing efficiency of biodegradable PLA monofilament gill nets and provide a reference for the application of new degradable fishingmaterials.
1 M aterials and methods
1.1 Biodegradable PLA
PLA,also known as polylactide,is a highmolecular-weight polymer obtained from polymerization with starch as the primary raw material.PLA was purchased from Total Investment Co.,Ltd.,and PLA monofilaments were prepared through melt spinning. Then 0.2 mm PLA monofilaments were woven into a PLA gill net through double-knotting.A PA gill netwith 0.2 mm PA monofilaments was also produced through the samemethod.
1.2 Experimental gear design
To assess the fishing performance of biodegradable gill nets,experimental gill nets were manufactured with the same design and dimension requirements as commercial gill nets that targetPortunus trituberculatusin the coastal areas of Langya Island,Qingdao.Gill netting was selected for the experiments because it is a common fishing method in China,and nets are frequently lost when using this method.Each gill net was made of double-knotted 0.2 mm monofilaments,with 140 mm nominalmesh opening size.Each net includes8×946 meshes,and was approximately 50 m in width and 1 m in height.The schematic of the biological PLA gill net was shown in Fig.1.Six biodegradable nets and six conventional nylon nets were used in the fishing trials.One biodegradable net and one conventional nylon net were engaged in operations in the fishing ground every day.The nets were renewed after 24 h,and the catch was counted.
1.3 Sea trials for evaluating fishing efficiency
From September to October 2019,gill netting trials were conducted on Langya Island’s fishing grounds using one to two commercial fishing vessels.The fishing ground is located near Langya Island,Huangdao District,Qingdao City.It is a common fishing area for ships based on Langya Island.Fishing depth varied from 12 to 18 m.Fishing duration was 24 h.
In September2019,the fishing performances of six biodegradable PLA gill nets and six conventional PA gill nets,were compared during fishing trials conducted under commercial fishing conditions.The density of gill netmaterials was similar.Thus,we provided similar buoyancy to both types of gill nets.In particular,to evaluate the fishing efficiency of PA and PLA gill nets,we used themethod of YANGet al.to compare the collected data of two gill nets[31]. The calculation method for fishing efficiency is as follows:

WhereEiis the fishing efficiency of thei-th netting,wiis the fishing yield of thei-th netting(kg),andhiis the duration of thei-th netting operation(h).

Fig.1 Schematic diagram of biodegradable PLA gill net
1.4 Tensile strength tests
To determine and compare the physical properties of biodegradable PLA and conventional PA monofilaments and their gill nets,their breaking strength(tensile strength at break)and elongation at break were measured.The measurements were conducted in compliance with GB/T 21292-2007 using the universal testing machine Instron 4466(USA)in tensilemode(i.e.,clamping distance is 100 mm and tensile speed is 100 mm·min-1).Tensile strength tests were performed on the biodegradable and nylon gill nets before and after the fishing operation.
1.5 Gill net damage assessment
We evaluated the degree of damage by calculating the number of brokenmeshes of each gill net and using amicroscope to examine each gill net sample.The degree of damage of each gill net was analyzed.The resultswere presented as percentages of the total quantity of knots from the sample.
1.6 Wear test
The wear test used the TABER®Model 5750 reciprocating linear abrader(USA). The test machine stroke was 75 mm,the wear test speed was 60 times perminute,and the sandstonemodel used for the wear test was H-18[32].The wear test was conducted under two conditions:dry friction and water lubrication(tap water was used as the lubricating medium).Before the wear test,the abrasive body of the H-18 sandstone should be polished using a metallographic sandpaper of the samemodel.Then,the H-18 sandstone waswashed with tap water and dried for later use.During the wear test,certain pressure loads(2.5 N and 5.0 N)must be added to ensure that the abrasive body was pressed tightly to the compound fishing PLA and PA monofilament test samples.
2 Results
2.1 Physical performance ofmonofilaments
The mechanical properties of PLA and PA monofilaments were studied. PLA and PA monofilaments are mostly used as knots and woven into gill nets in fisheries.Thus,we tested the knotting strength of the monofilaments(Fig.2).The linear density of PLA and PA monofilaments was 44 tex and 57 tex,respectively.Under dry condition,the corresponding knotting strength of PLA and PA monofilaments was 2.5 cN·dtex-1and 3.0 cN· dtex-1respectively.Under wet condition,the knotting strength of PLA and PA monofilaments was 2.3 cN·dtex-1and 2.9 cN·dtex-1respectively.Compared with the knotting strength of PLA and PA monofilaments under dry condition,the knotting strength under wet condition decreased by 8.0% and 3.3%,respectively,and the decrease in the mechanical strength of PLA monofilaments was greater than that of PA monofilaments.
2.2 Wear resistance of PLA and PA monofilaments
Under the same friction conditions,a sample was rubbed sufficiently until it broke.The wear resistances of PLA and PA monofilaments were studied.

Fig.2 M echanical properties of PA and PLA monofilaments under dry and wet conditions
Tab.1 presented the test results of wear times of PLA and PA monofilaments.As shown in the table,wear resistance underwater-lubricated friction was better than that under dry friction condition under the same pressure load.As pressure load increased,the wear times of the monofilament test sample decreased.Friction condition exerted a significant impact on wear times.Simultaneously,the wear resistance of PLA monofilamentswas better under dry friction condition.By contrast,the wear resistance of PA monofilaments was better under water lubrication.

Tab.1 Comparison of wear times for PLA and PA m onofilaments
2.3 Catch statistics
Two types of experimental gill nets were engaged in operations for six times in the fishing ground.The weight and length of all species caught by the two types of gill nets were measured.The catch wasmostly composed ofP.trituberculatusandPneumatophorus japonicus,with very fewParthenope validus.However,the number ofParthenope validuswas too small(i.e.,less than five),and thus it was not included in the study.A total of 44 were caught using 12 gill nets.Among which,21 were caught by PLA gill nets and 23 by PA gill nets(Tab.2).

Tab.2 Catch statistics of PLA and PA gill nets
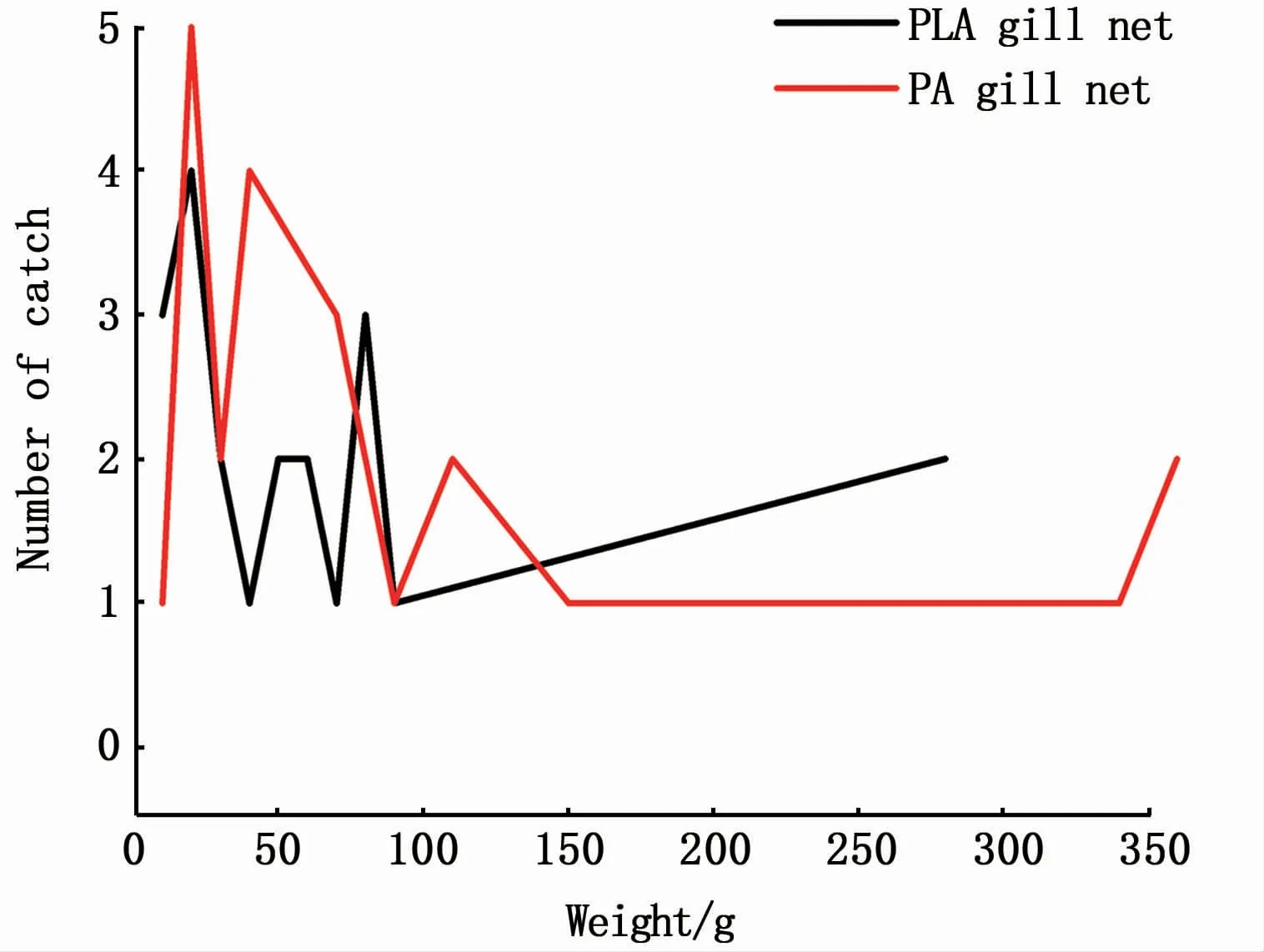
Fig.3 Statistics of different weight intervals by PLA and PA gill nets
As indicated in Fig.3,PLA gill net catch ranged from 10 g to 280 g,and PA gill net catch ranged from 10 g to 360 g.Theminimum weight of fish caught by PA gill nets was 18 g and the maximum was 367 g;the minimum weight of fish caught by PLA gill nets was 12 g,and the quantity wasmore than that by PA gill nets,the maximum was 284 g.The number ofP.trituberculatuscaught by conventional PA gill netswas slightly higher than that by biodegradable PLA gill nets(16 versus 4).The case with the most important bycatch species was the opposite(1 versus 10P.japonicus).A slight difference was observed in the overall number of total catch between the PLA and PA nets(21 versus 23).

Fig.4 Fishing efficiency of PLA and PA gill nets
Then,fishing efficiency was calculated(Fig.4).The results showed that the average fishing efficiency of PLA gill nets was 0.20 kg·h-1,and that of PA gill netswas 0.32 kg·h-1.The fishing efficiency of PA gill nets was 60% higher than that of PLA gill nets.The number of gill nets used in this experiment was limited,and the catch was relatively few. We will continue the fishing experimentwith the same experimentalmaterials in 2021 and combine the subsequent catch data for statistical significance analysis,and summarize it in a follow-up research paper.
2.4 Gill net damage
Tensile strengthmeasurements performed before and after the fishing experiment showed that the breaking strength of PLA gill nets decreased by 8.7% (from 12.7 N to 11.6 N)and that of PA gill nets decreased by 4.0% (from 18.5 N to 17.7 N).

Tab.3 Tensile strength and broken percentage of PLA and PA gill nets
PLA gill nets had more severely damaged or broken knots(26%),and PA gill nets were damaged by 12%. PLA gill nets were more damaged than PA gill nets(Tab.3).At the same time,the microscope picture showed that the damage of PA gill net in the middle of the mesh,and for PLA gill net in the knot.The damage in the knotswas apparently caused by normal use and wear throughout the fishing season(i.e.,abrasion in the haulingmachine,friction due to contact with hard surfaces when gill nets were operated on deck),which turned the smooth surface of the materials(when new) into rough after fishing trials.Microscopic pictures showed that damage to PLA gill nets was due to the breakage of an entire monofilament at the knot.Meanwhile,damage to PA gill nets mostly manifested as damage to the monofilaments(Fig.5).
3 Discussions
The physical performance results of PLA and PA monofilaments showed that compared with the knotting strength of PLA and PA monofilaments under dry condition,knotting strength under wet condition decreased by 8.0% and 3.3%,respectively.The samples exhibited lower knotting strength under wet condition than under dry condition[33].This result was as expected because water acted as a plasticizer that reduced entanglement and bonding between molecular chains, increasing their volume and mobility.Consequently,the absorbed water decreased tensile modulus,but increased elongation at break.The knotting strength of PLA monofilaments decreased more than that of PA monofilaments,indicating that PLA monofilaments absorbed watermore easily.

Fig.5 Dam age degree of PLA and PA gill nets before and after the experiment
The wear resistance results of PLA and PA monofilaments showed that the wear resistance of PLA monofilaments was greater under dry friction conditions, while the wear resistance of PA monofilaments was better under water lubrication.This finding may be attributed to the absorption of more water on PLA surface[34].Water diffused into the amorphous regions of PLA, leading to plasticization, swelling and softening, and consequently a reduction in hardness and poor wear resistance.
The biodegradable PLA gill nets caught75.0%lessP.trituberculatusthan PA gill nets,PLA gill nets caught 90.0% moreP.japonicusthan PA gill nets,and the total catch of PLA gill nets was slightly lower than that of PA gill nets.The fishing efficiency of PA gill nets was 60.0% higher than that of PLA gill nets.This finding was consistent with the results of the physical performance and wear resistance tests of the monofilaments. PLA monofilaments exhibited a greater decrease in knotting strength under wet condition.Thus,PLA monofilaments were more likely to absorb water,resulting in reduced hardness and poor wear resistance.Therefore,the fishing efficiency of PLA gill netwas evidently inferior to that of PA gill net.The results of sea trials indicated that further study of biodegradable materials should focus on the improvement of fishing efficiency. The results generally showed better catch rates by PA gill nets than by PLA gill nets,particularly for largeP.trituberculatus,despite of having similarmesh sizes.The physical properties of gill netmaterial variated with time and might have affected its fishing efficiency.Tensile strength measurements before and after the fishing experiments showed that the fracture strength of both gill nets was significantly reduced.Compared with PA gill nets,PLA gill nets were damaged more,indicating that the mechanical properties of PLA material still require considerable improvement.When new,the strength of both types of nets was remarkably similar.By the end of the fishing season,the reduction in tensile strength and the loss of elasticity can explain themajor difference in catch efficiency between PA and PLA gill nets,particularly for largeP.trituberculatus.CHENet al.studied the degradability of polylactic acid/starch composite materials in seawater environment and suggested that biological degradation was probably a cause of tensile strength and elasticity reduction of biodegradable gill nets[35].On the basis of our experience,we can not distinguish the degree of strength reduction caused by biodegradation from the degree of strength and elasticity reduction caused by use and wear.Although PLA gill nets are not as efficient as PA gill nets,they are effective in reducing marine “ghost fishing” and plastic pollution,providing a reference for alleviating these major fishery environmental problems.
Notably,if biodegradation is combined with daily use and wear of the material,then the degradation process may be somehow accelerated[30].Nylon gill nets are well-documented to be highly resistant to degradation,but they do eventually lose their capability for“ghost fishing”depending on the seafloor conditions(e.g.,substrate type, sea temperature, and light condition)[36-38].Furthermore,nylon gill nets do not disappear entirely.They just break into smaller plastic particles, commonly known as“microplastics”,which may continue to disturb important processes in marine ecosystems[39-40].In contrast to conventional nylon gill nets, if biodegradable gill nets get lost at sea,bacteria,algae and fungi will more rapidly degrade the material into carbon dioxide,methane and water,and therefore,they will have no negative impact on marine ecosystems. KIMet al. reported that biodegradable gill nets started to degrade after two years of being immersed in seawater[41].However,this conclusion was based on a degradation experiment with monofilament samples immersed in seawater,and thus,the samples were not affected by physical damage from daily use and wear.Determining how fast a biodegradable gill net can lose its “ghost fishing” capability depends considerably on the age of the netwhen it is lostand how much it has been used.In fishery,degradation materials and antifouling materials are collectively referred to as functional materials[42-43]. The research and development of new functional materials for fishing can gradually solve the"ghost fishing"problem of fishing gears and the antifouling problem of aquaculture netting(such as the netting of deep-sea cages,deep-sea enclosures,etc.),so as to promote the sustainable development and modern construction of modern fishery[44-45].China’s modern fishery has a bright future,but there is still a long way to go for the work of functional novelmaterials for fishery.

