Instant Monitoring of Metabolomic Profile for Trace of Whole Blood Using Conductive Polymer Spray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
LI Chao,SONG Xiao-wei
(1.Department of Pharmaceutical Science,Beijing Hospital;National Center of Gerontology;Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Science;Beijing Key Laboratory of Assessment of Clinical Drugs Risk and Individual Application(Beijing Hospital),Beijing 100730,China;2.Department of Chemistry,Fudan University,Shanghai 200438,China)
Abstract:The blood's metabolism could be used to provide a precise evaluation on the post-surgery physiological status,which poses an urgent technical demand for a point-of-care test for global metabolomic profiling.Therefore,the practical value of conductive polymer spray ionization mass spectrometry(CPSI-MS) in the multiplex monitoring of endogenous metabolites in a trace volume of whole blood was presented in this paper.The fabricated conductive polymer was composed of carbon nanotube(CNT) and polymethyl methacrylate(PMMA).After applying a high voltage of 4.5 kV for generating charged droplet spray,trace volume of extraction solvent(methanol-H2O,1∶1,5 μL) was enough to extract,desorb and ionize over 600 endogenous metabolites and lipids in the only 1 μL of diluted dried blood spot deposited on the tip,covering more than 20 fundamental metabolism pathways including the energy metabolism,amino acids metabolism,nucleotides metabolism,and lipids metabolism,etc.To give a proof-of-concept illustration,the C57BL/6 mice experiencing the hepatectomy were selected as the model objects.The individual differences in physiological recovery were precisely characterized by capturing hundreds of metabolites changes with a period of 48 h.Finally,a panel of metabolites mainly in the Krebs cycle,arginine metabolism,glycerolipids metabolism,and glycerophosphorylcholine metabolism could give a prognostic reference for the functional recovery of the mice from the hepatectomy.
Key words:conductive polymer spray ionization(CPSI);point-of-care test;metabolomic profile;prognostic marker;hepatectomy
Ambient ionization mass spectrometry(AIMS) is referred to the MS technique that directly collects data of the analytes in native sample matrices under the atmospheric condition[1-3].Because of the advantage in free of laborious sample pretreatment,AIMS had shown its great potential in these practical scenarios which need on-site sample collection or a quick readout-feedback about the test results,such as clinical screening and diagnosis[4],therapeutic drug monitoring[5],intraoperative biopsy[6],public security[7],etc.A wide range of chemical species has been successfully covered including synthetic drugs[8],natural products[9],antibiotics[10],metabolites[11],lipids[6],and proteins[12],etc.
Paper spray ionization(PSI)[13],as one of the earliest AIMS methods,has gained great interest,especially in the dried blood spot analysis because of its “all-in-one” strategy that integrates the sample loading,long-term storage,matrix filtering,as well as the on-tip trigger of the nano-electrospray ionization process[14-15].However,during the long-term practice of PSI in our daily analytical works,we find that PSI still exists space for further technical improvement especially in the metabolomic profiling of biological samples.For instance,its native impurities tend to generate strong peaks in the mass spectrum that can suppress the endogenous components' ionization.Although the paper fibers' hydroxyl group and porous nature help to hinder those macromolecules in the biological matrix,it also poses strong retention to the hydrophilic metabolites and causes the dilution of the analytes due to the extraction solvent's disorientated diffusion[16-17].
To increase the sensitivity of certain species,alternative materials and functional modification were introduced on the paper surface such as hydrogel[18],carbon nanotubes(CNT)[19],and silica[20],etc.Alternatively,a thorough replacement of porous medium with polymer materials also become an important branch of AIMS substrate such as organosiloxane[21],Teflon[22],polystyrene[23],molecularly imprinted polymers[24],etc.No matter for the PSI or polymer-based spray ionization,the solvent system serves as both extraction agent and the conductive medium for triggering the ionization by high voltage[25].To reduce the use of the solvent system,we introduced the conductive polymer that was composed of CNT and polymethyl methacrylate(PMMA)[16].Our previous work had already proved that this conductive polymer performed ideally in yielding strong ion signals in the mass spectrum for these polar metabolites than those in the PSI-MS analysis.A conductive polymer spray ionization mass spectrometry method(CPSI-MS) was developed for salivary metabolic profiling and oral cancer screening[26].
In this article,it was our first time to systematically investigate what types of endogenous metabolite species could be detected by the CPSI-MS.It helped us to clarify to what extent this AIMS method could gain in-depth coverage for the untargeted metabolomics study.To illustrate the values of CPSI-MS in preclinical and clinical translation,we selected C57BL/6 mice that have gone through hepatectomy to mimic the real surgery in clinical practice as the proof-of-concept study cases.Hundreds of fundamental metabolites from each individual trace blood were monitored within successive 48 h after surgery by CPSI-MS,giving a precise and panoramic characterization of the global physiological recovery only under the cost of whole blood less than 10 μL.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and specimens collection
Methanol and distilled water were purchased from the Fisher chemical.Polymethyl methacrylate(PMMA) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes(MWCNT,ID 2-5 nm,OD<8 nm,length 10-30 μm) were purchased from Adamas and J&K Scientific,respectively.The conductive polymer composite was fabricated according to the previous report[16].C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co.,Ltd.An LTQ orbitrap mass spectrometer(Thermo Fisher,CA,USA) was employed for data acquisition.There were 10 C57BL/6 mice(5 female,and 5 male) aged from 6 to 8 weeks included in the experiment.The hepatectomy was carried out after the model mouse was fixed and anesthetized.The resection proportion was 60% including the median lobe(ML) and right liver lobe(RLL)[27].After the hepatectomy,the incision was sutured and all mice were supplied with water and food again.The whole process was in strict obedience to the animal ethics.The whole blood was collected from the mouse tail by being poked with a sterilized needle and quickly aspirated by a borosilicate glass capillary(ID 1.0 mm,length 10 cm).The collection time points were set at 0,3,6,12,24,48 h after the surgery.
1.2 CPSI-MS data acquisition
The collected whole blood was firstly transferred and diluted with an equal volume of pure water.Then the 1 μL diluted whole blood was loaded onto the tip of the conductive polymer to form a dried blood spot(DBS).A droplet of methanol-water(1∶1,by volume,5 μL) was used as the extraction solvent system and spiked onto the DBS for 30 seconds to fully dissolve endogenous metabolites.Then,a high voltage(4.5 kV) was applied on the polymer tip positioned at 8.0 mm away from the MS inlet and trigger the strong electric field-induced droplet spray ionization.This process carried the metabolite ions into MS for recording untargeted metabolic profiles within the range ofm/z50-1 000 under both polarities.The MS capillary temperature was set at 275 ℃.The S-lens voltage was set at 55 V.The micro-scan number was set at 1 scan which lasted for 400 microseconds as maximum injection time.
1.3 Data analysis
The Xcalibur software(Thermo Fisher Scientific,CA,USA) was employed for data conversion from raw to cdf format.The in-built functions and self-programmed scripts under the MATLAB 2020a(Mathworks,MA,USA) platform were used for further data preprocessing such as importing cdf files,creating average mass spectra,total ion current normalization.SIMCA-P(Umetrics,Umea,Sweden) was used for principal component analysis(PCA) of metabolic profiles.
1.4 Searching metabolites and metabolism pathways
The unknown ions were searched through HMDB(http://hmdb.ca/) with the mass tolerance set at 5.0 ppm.The MS/MS experiment was also implemented to match the CID fragmentation pattern either with given standards or recorded MS/MS spectra in the database.After tentative metabolite annotation,the metabolites of interest were put into the open-source platform,MetaboAnalyst(https://www.metaboanalyst.ca) to search for these altered metabolic pathways.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Method validation
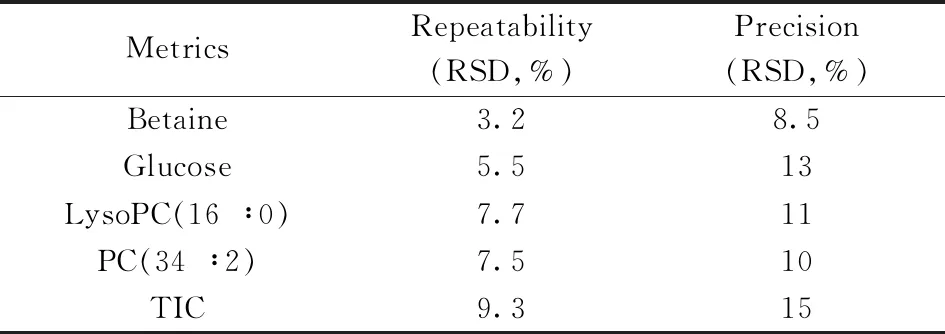
Table 1 Summary of the method validation for CPSI-MS analysis
In the beginning,we assessed the performance of the CPSI-MS method to guarantee a stable and feasible test result in untargeted metabolomics.Some basic metrics for the method validation were investigated including repeatability,precision,and sensitivity.First,six diluted blood samples(1 μL) from one same C57BL/6 mouse harvested at a certain time were loaded onto different pieces of conductive polymer tips for separate data acquisition of metabolic profiles.The total ion current(TIC) and the metabolites(betaine,carnitine,glucose,LysoPC(16∶0),PC(34∶2)) ranked in the top 5 from the mass spectrum were selected to evaluate the ion signal variation.Then,six replicates of blood samples were tested for three consecutive days to evaluate the inter-day precision with the same targets of interest as above.As shown in Table 1,the RSD values for each metabolite ions and the TIC from the six repeated blood samples all fall within 15% that set as the upper limit for RSD value in the biological analysis using LC-MS,demonstrating that the fabricated conductive polymers could promise to achieve repeatable results.The inter-day precision of TIC and metabolite ions also indicated the inter-day variation was in an acceptable range of less than 15%.
Furtherly,the sensitivity(characterized by 3S/Nratio) was evaluated using the exogenous drugs,streptomycin,and berberine hydrochloride.Under the consistent sample loading volume(1 μL),the minimum absolute detection amount of berberine and streptomycin were as low as 3.0 pmol and 2.0 pmolinvitro(referred to its content in solution),and 30 pmol and 86 pmolinvitro(referred to its contents in DBS).It has to be admitted that the sensitivity is directly related to the ionization efficiency which is dependent on various external factors like biological matrix,analytical conditions(such as solvent,voltage,MS acquisition mode),and the internal factors about compound's physicochemical properties.We chose these two model compounds for their totally different in chemical species.One is a highly water-soluble polysaccharide derivative that keeps strong retention in conventional PSI tests,the other one is an alkaloid that is hard to be solved in water.Therefore,we posted these results just for a relatively fair reference that to which extent the CPSI-MS can at least achieve.But it does not represent the maximum limit in sensitivity that it can reach.
In terms of whole blood metabolomic profiling,the blood cells severely suppress the components' desorption and ionization due to their high viscosity and abundance in phospholipids.Therefore,it was necessary to dilute the collected whole blood with an equal volume of pure water to alleviate this strong ion suppression.We investigated the mass spectral profile of the plasma and the equal amount of the diluted whole blood.The total ion current(TIC),total number of detectable ions,as well as five representative hydrophilic metabolites(glucose,choline,carnitine,betaine,acetyl carnitine) were used to evaluate the relative matrix effect of diluted whole-blood compared to the plasma.As a result,it was found that the TIC of whole blood dropped from 5.4×106to 4.6×106.The number of detectable ions reduced from 6 254 to 5 754 whereas 424 out of these lost 500 ions were mainly distributed among these low abundance ions with intensity less than 1.0×103which was the exclusion threshold we set in this program.As for the five representing polar metabolites,although their intensities performed the 14%- 55% decrease compared to that of the plasma,they were still rank in the top metabolite within the lower mass range ofm/z50-300.Given the fact that a single mouse has very limited blood volume,whole blood instead of plasma or serum was still a more practical choice under a certain extent of sacrifice in species coverage to avoid excessive blood collection.
2.2 Coverage of metabolites and metabolism pathways
After investigating the basic performance of CPSI-MS,we systematically reviewed how many metabolites that CPSI-MS can detect under positive and negative modes.After the sample's mass spectrum was subtracted by that from the blank solvent,these peaks with the absolute ion intensity higher than 1×103were preserved for further database searching.As a result,it was estimated that around 650 metabolites can be either tentatively annotated or structurally identified.Categorized from the point of functional groups and chemical structures,they included carbohydrates,amino acids,carboxylic or dicarboxylic acids,alcohols and phenols,polyamines,purines,pyrimidines,fatty acids,acyl carnitines,glycerolipids,glycerophosphorylipids,sphingomyelins,and cholesterol esters,etc.The range of each species in the mass spectrum was presented in Fig.1.The representing identified metabolites were listed in Table 2.
The percentage of each type of metabolite was displayed in Fig.2A.The glycerophospholipids ranked in the first place(23%) largely because it was the main component of all cells' bilayer membrane.The rest of the species with considerable ratio were mainly those nutrients such as amino acids(15%),purines and pyrimidines(9.9%),fatty acids(9.6%) and carbohydrates(4.9%).They can be generally considered as the nutrient,energy fuels and building blocks for proteins,nucleotides,glycolipids and glycans which maintain the basic biological functions such as transportation,catalysis,signaling,and immune recognition,etc.As for the amines(3.9%),vitamins(2.5%),peptides(2.5%),sulfur-contained metabolites(2.5%),and sphingomyelins(2.3%),although they were relatively low in numbers,many important biological roles were undertaken by these species such as methyl group donor and carrier(e.g.methionine,S-adenosylmethionine),signaling regulators(e.g.ceramides,spermidines,histamines),anti-oxidant(e.g.glutathione).In summary,the metabolism pathways that the discovered metabolites involved were displayed in Fig.2B and 2C.These results demonstrate that CPSI-MS can capture key metabolites in the whole metabolism network.This in-depth coverage guaranteed the possibility of CPSI-MS not only to provide a pool of characteristic markers for clinical diagnosis but also to gain insight into further molecular mechanism research.

Fig.1 Representative CPSI mass spectra acquired from the dried blood spot under positive(……) and negative(-) modes

Table 2 Putative annotation of the representing metabolite ions
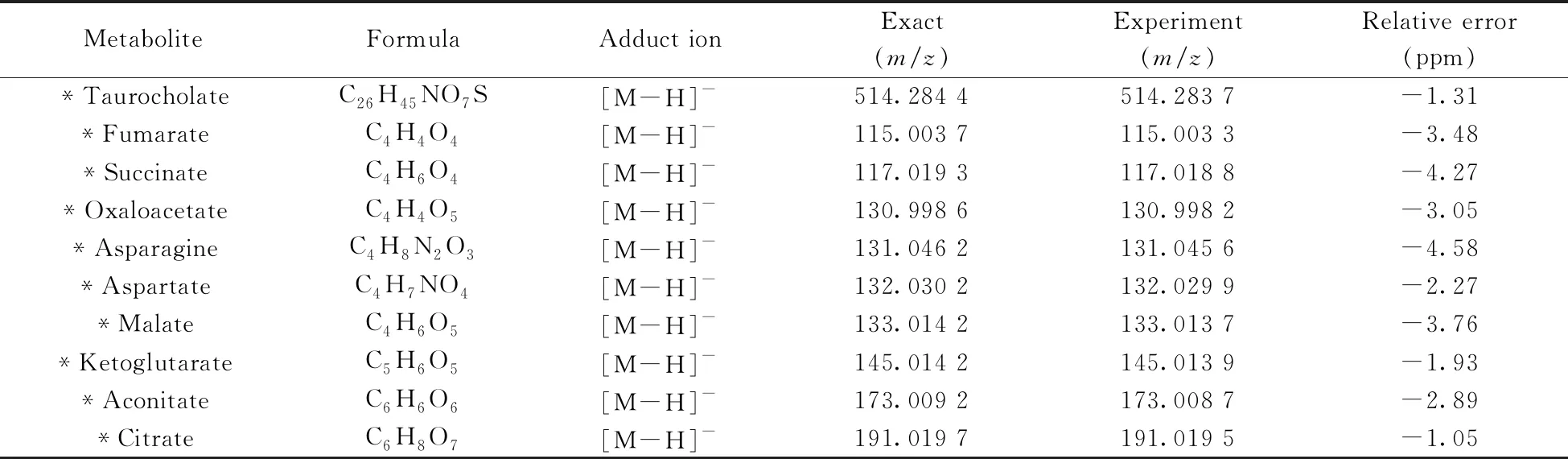
(Continued Table 2)
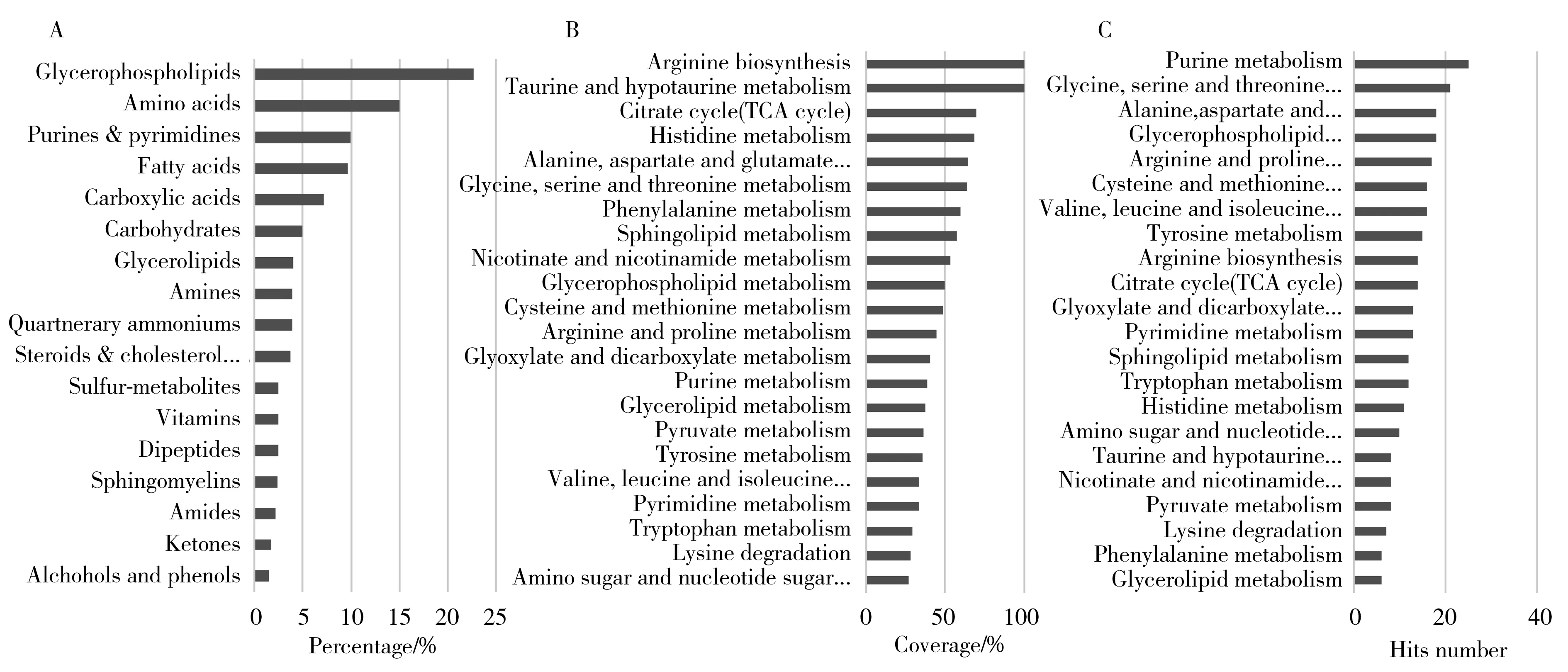
Fig.2 Coverage of the metabolite species and metabolism pathwaysA:each chemical species’ percentage among all detected metabolites;B:the coverage percentage of detected metabolites in each metabolism pathway;C:the number of detected metabolites in each metabolism pathway
2.3 Pattern recognition by multivariate analysis
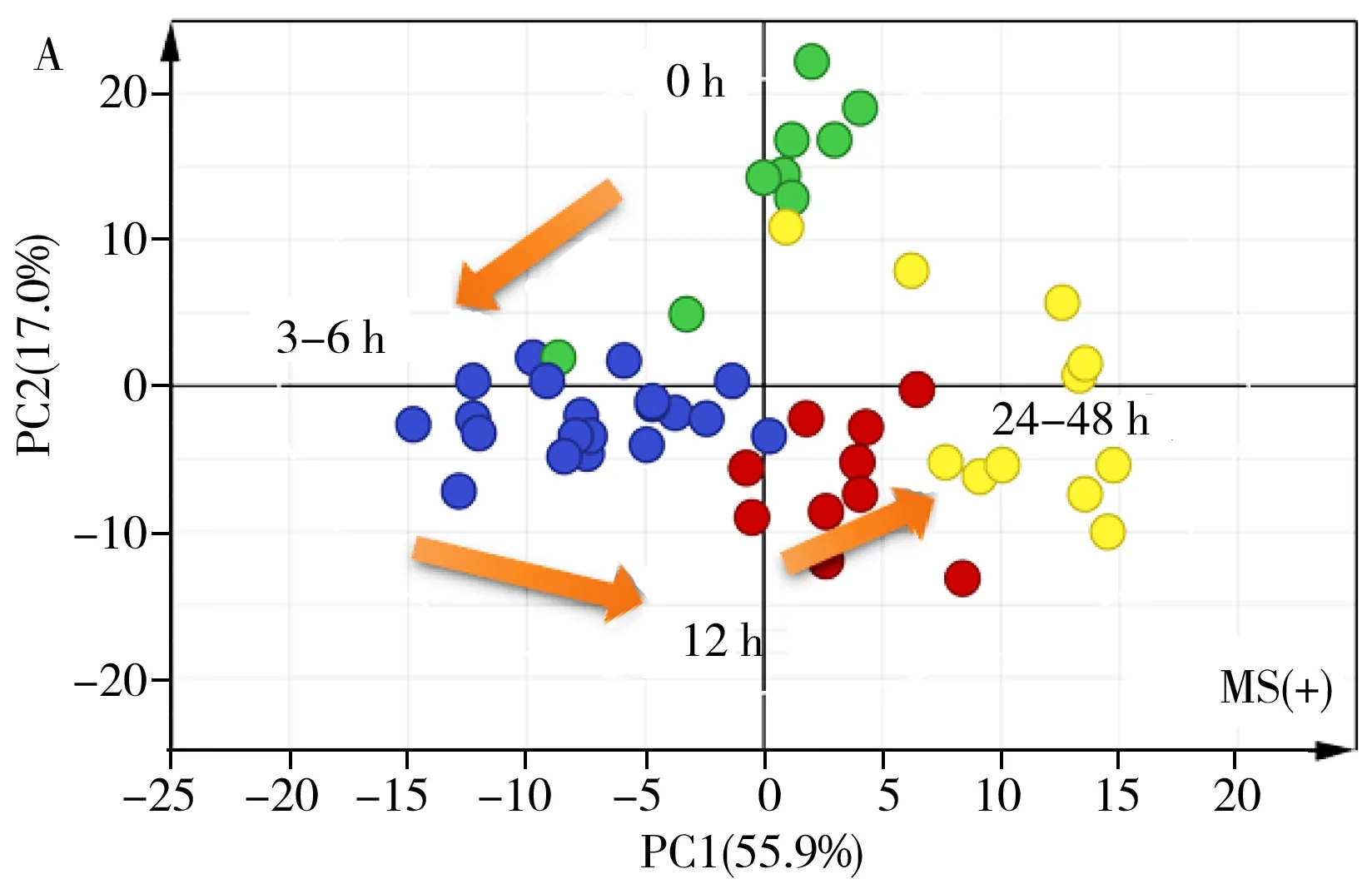
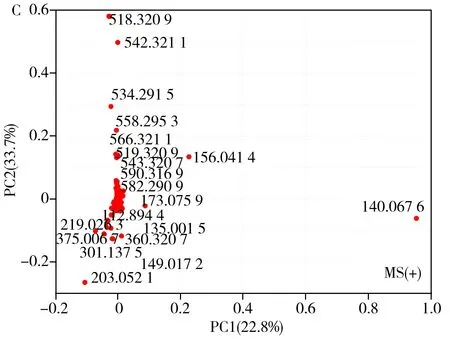
After CPSI-MS data acquisition,all the mass spectra from the 10 mice at 6 time points were constructed into a matrix with 930 peaks(positive) and 1 033 peaks(negative) as input variables for pattern recognition.The score plots by the principal component analysis(PCA) was used to give a clustering result shown in Fig.3A and 3B.The metabolic profile from these 6 time points can be roughly divided into four clusters interpreted as follows:the normal stage before surgery at 0 h,and the metabolic perturbation stage I(3-6 h),stage Ⅱ(around 12 h) and stage Ⅲ(24-48 h).This result gave an intuitive understanding that the acquired metabolic profiles can generally characterize the global changes in metabolism status that happened after the surgery.
Thereafter,the loading plots were drawn to clarify which metabolites made major contributions to the discrimination of the metabolic profiles at different stages.As shown in Fig.3 C and 3D,several ions were found to be assigned with high weight coefficients in the first and second principal components.Through identification,they were lactate(m/z89.024 4[M-H]-,135.001 5[M+2Na-H]+),glucose(m/z203.052 1[M+Na]+,219.026 3[M+K]+,215.031 5[M+Cl]-),betaine(m/z140.067 6[M+Na]+,156.041 4[M+K]+),dodecanoic acid(m/z199.169 5[M-H]-),palmitoleic acid(m/z253.216 4[M-H]-),palmitic acid(m/z255.232 1[M-H]-),taurocholate(m/z514.283 7[M-H]-),LysoPC(16∶0)(m/z518.320 9[M+Na]+),LysoPC(18∶2)(m/z542.321 1[M+Na]+,558.295 3[M+K]+) and LysoPC(20∶4)(m/z566.321 1[M+Na]+) .Based on these facts,we supposed there was at least a substantial change in energy metabolism such as the Krebs cycle,anaerobic glycolysis,and lipid mobilization.
2.4 The perturbation and recovery of energy metabolism
Based on the multivariate analysis results,we paid a special focus on these detected metabolites that were mainly involved in the energy metabolism.The mean curve of the relative abundance of each metabolite(characterized by the intensity with TIC normalization) versus time was plotted in Fig.4.As the source and key hub of energy metabolism,the level of glucose increased whereas the pyruvate decreased with the time.In contrast,the lactate,as the end product of the anaerobic glycolysis,continued increasing after surgery.This may indicate that a shortage in energy supply due to the loss in normal liver function because of the hepatectomy.
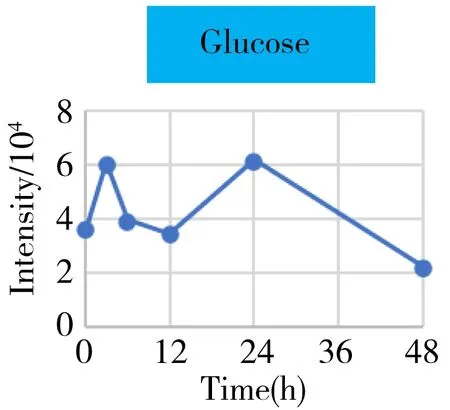

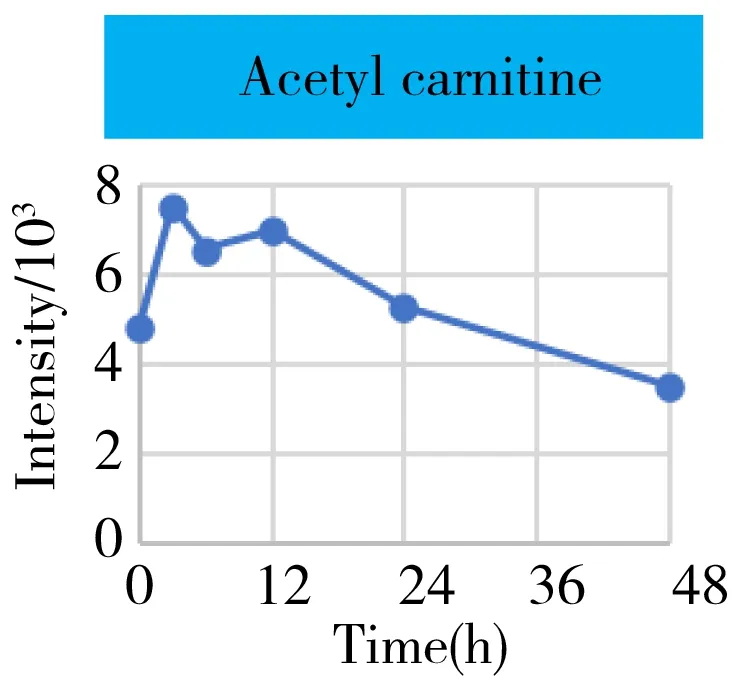
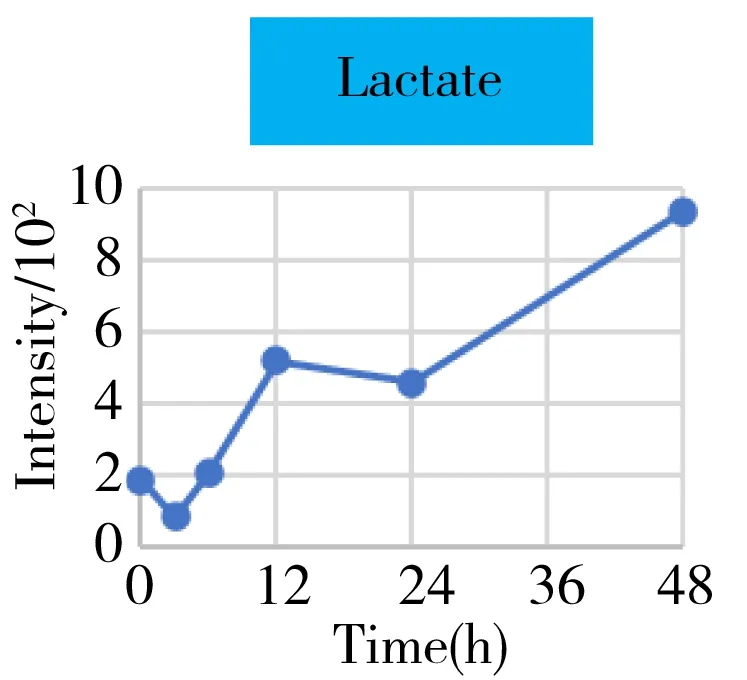
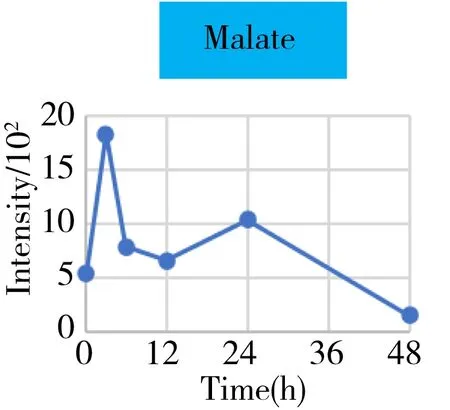
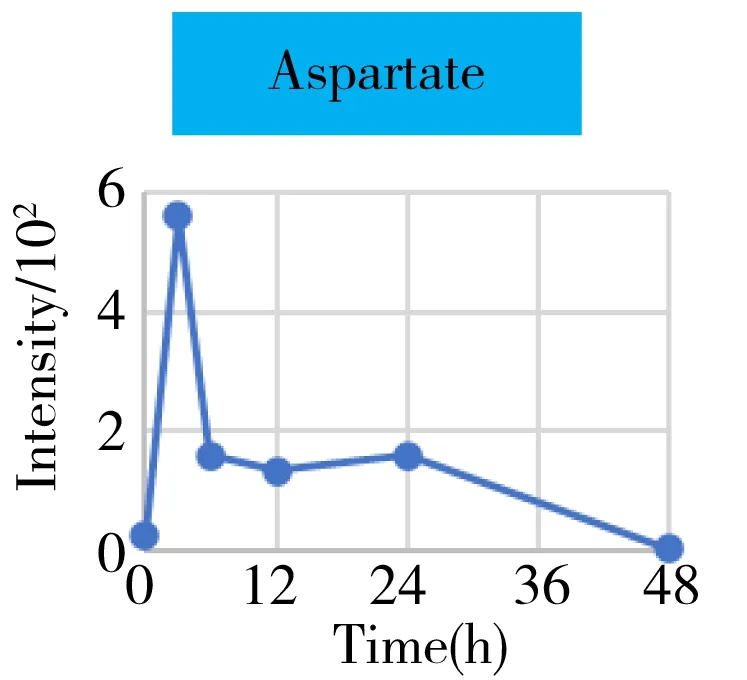
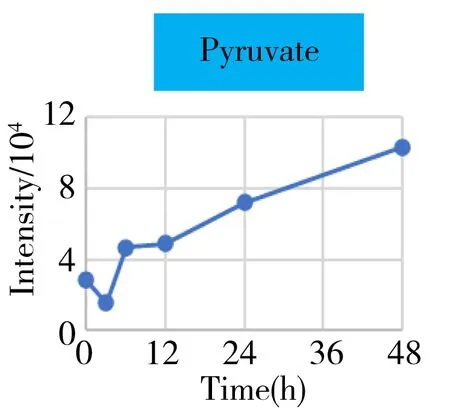
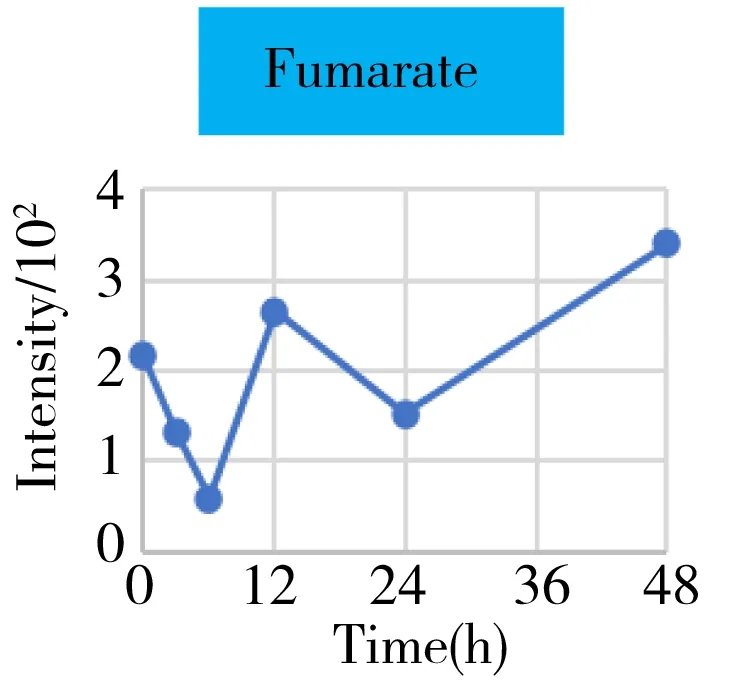
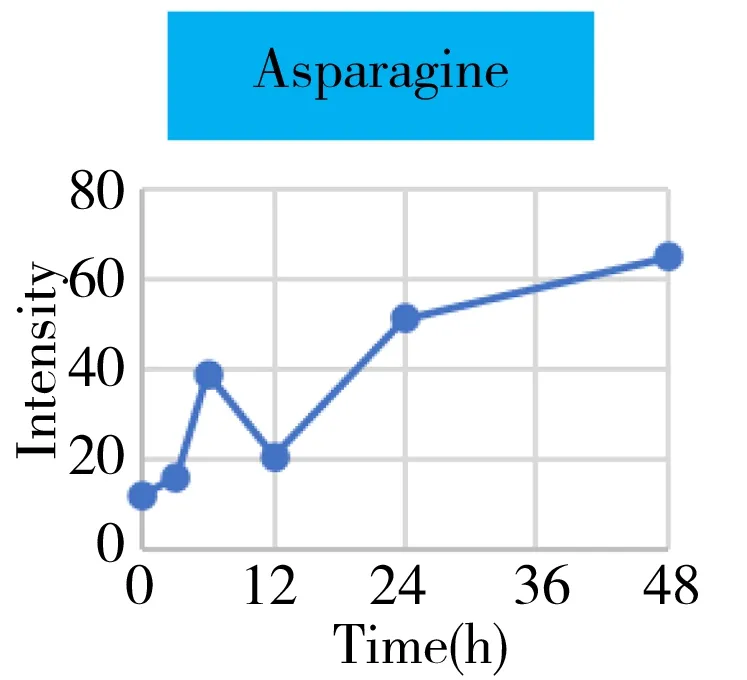
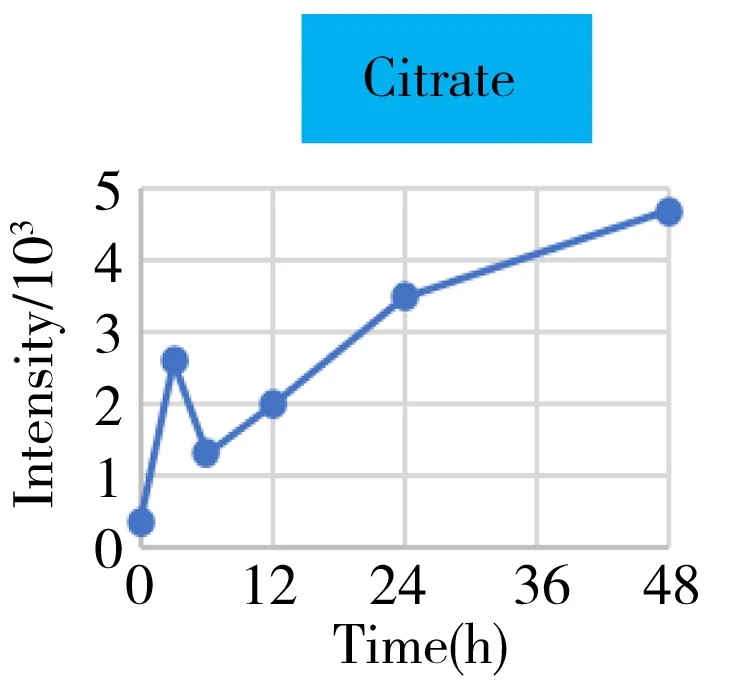
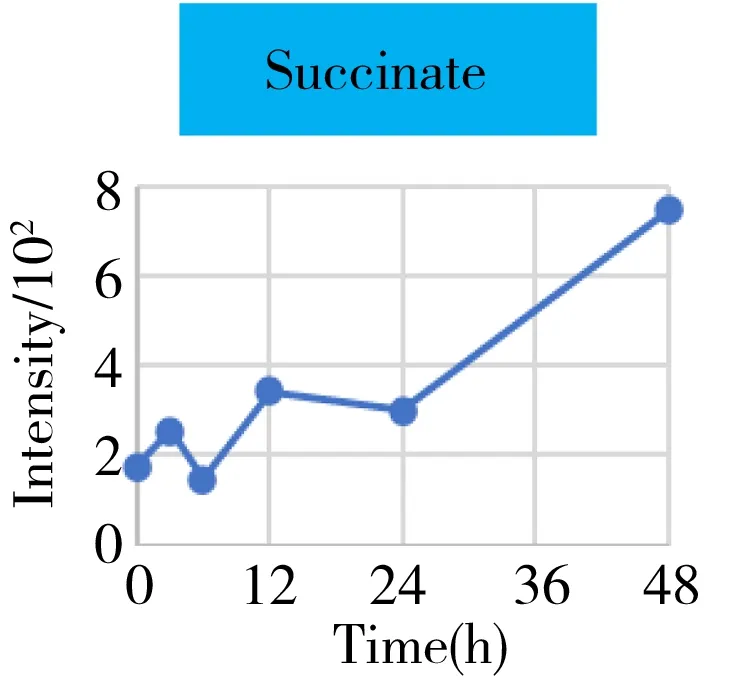
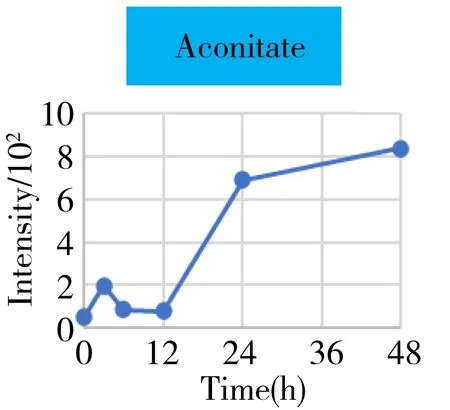
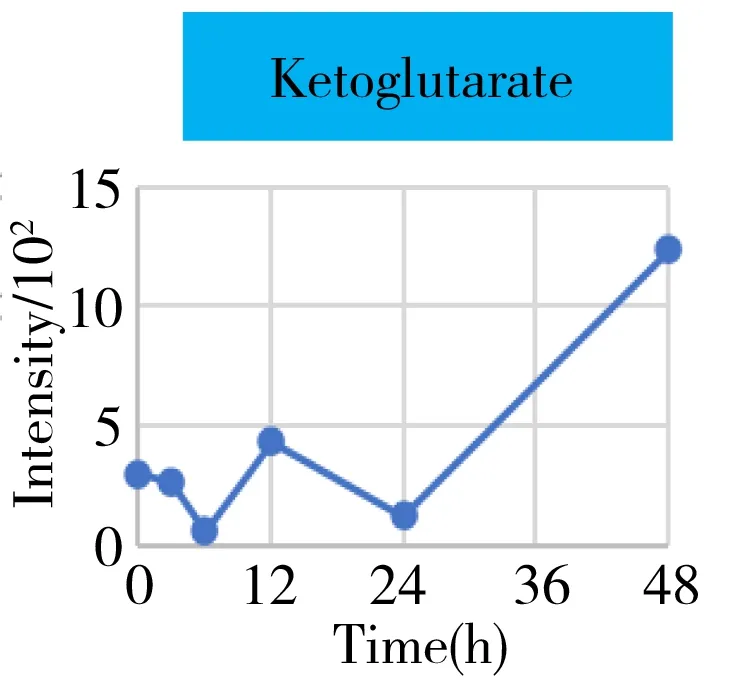
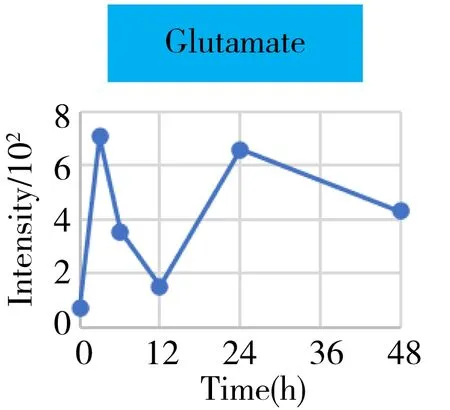
Fig.4 The intensity-time change curves of these metabolites related to the energy metabolism
It was well known that the Krebs cycle played a central role in energy supply.We focused on the key points of this route and found that they behaved the diverse change tendencies.Generally speaking,most points like citrate,aconitate,α-ketoglutarate,succinate,fumarate fluctuated from 3 h to 24 h(perturbation stage Ⅰ and Ⅱ in PCA),and they were finally up-regulated when the time reached to 48 h.But the malate and oxaloacetate performed in a different trend from the other metabolites.They went through a consistent increase during the 24 h after surgery,but finally returned back approximately to the original level or even lower.Given the fact that the metabolites in the Krebs cycle also bridged the connection with other metabolism pathways like amino acids,nucleotides,and lipids.The underlying mechanism to explain these change tendencies need a wider vision shifted to their branched routes as well as the upstream functional enzymes' expression.In this article,we only gave a check about the most important three branches auxiliary with the Krebs cycle,including glutamine/glutamate,aspartate/asparagine,and acylcarnitines metabolism.It was assumed that the transitions of glutamine/glutamate and aspartate/asparagine probably supported the Krebs cycle from the sites ofα-ketoglutarate and oxaloacetate,respectively.As the representative of acylcarnitine,the acetyl carnitine's decrease implied that it supplemented the Krebs cycle through acetyl CoA(not detected).
2.5 Potential prognostic metabolites markers
Hepatectomy is a clinical surgery to remove a proportion of the liver for the organ transplant or resection of the carcinoma region.We have generally characterized the physiological recovery status from the aspect of global metabolic profiling.The specific attention on energy metabolism also helped us to understand what was exactly happening to the individual metabolism after the hepatectomy,and gaining more detailed insight into the underlying mechanism.However,from the point of clinical practice,it was also urgent to know what types of metabolites can be used as the prognostic markers for evaluating the post-surgery recovery condition on a personal basis.Therefore,we systematically go through each mean content-time curve of the metabolite within the metabolic profile matrix.At least 30 metabolites' mean can recover back to the previous normal level after going through a gradual increase or decrease such as histamine,arginine,carnitine,ornithine,creatinine,etc.(Fig.5).They belonged to the basic amino acid metabolism,especially involved in the arginine metabolism and urea cycle.
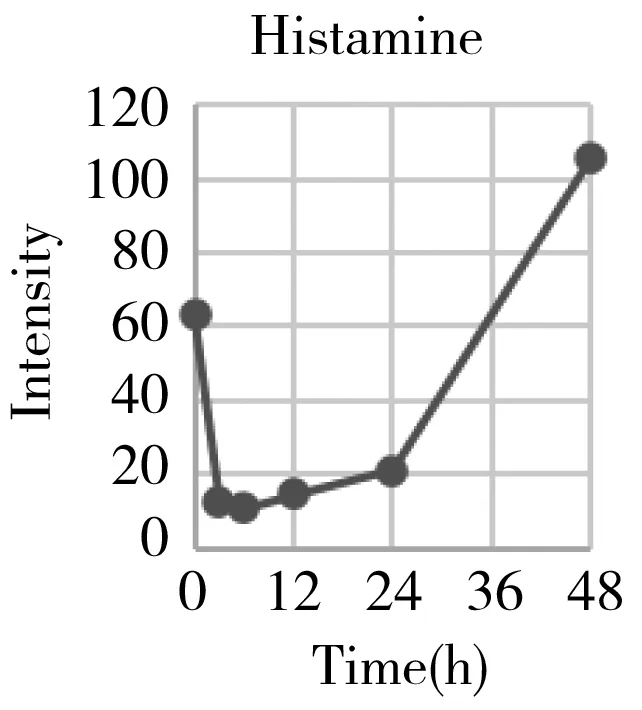
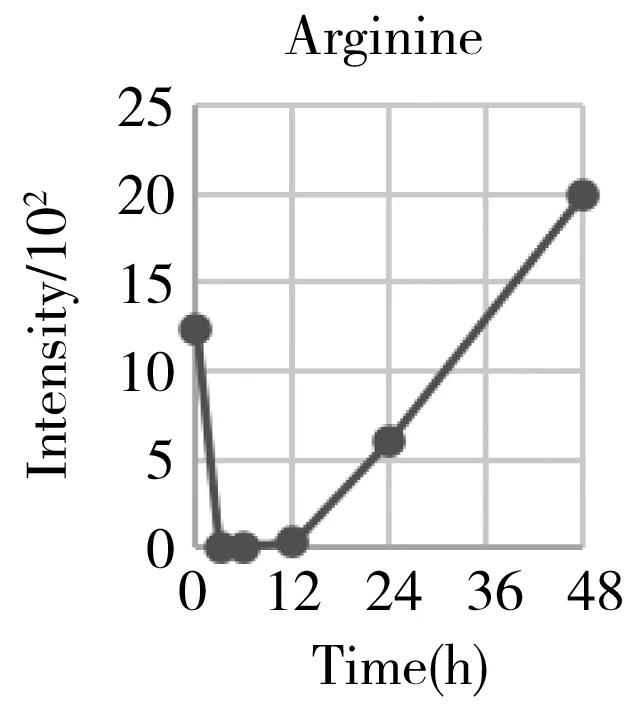
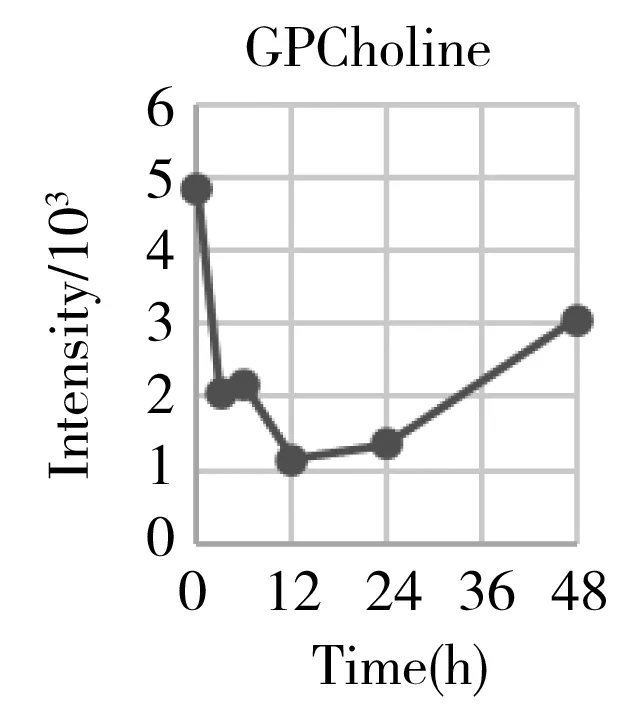

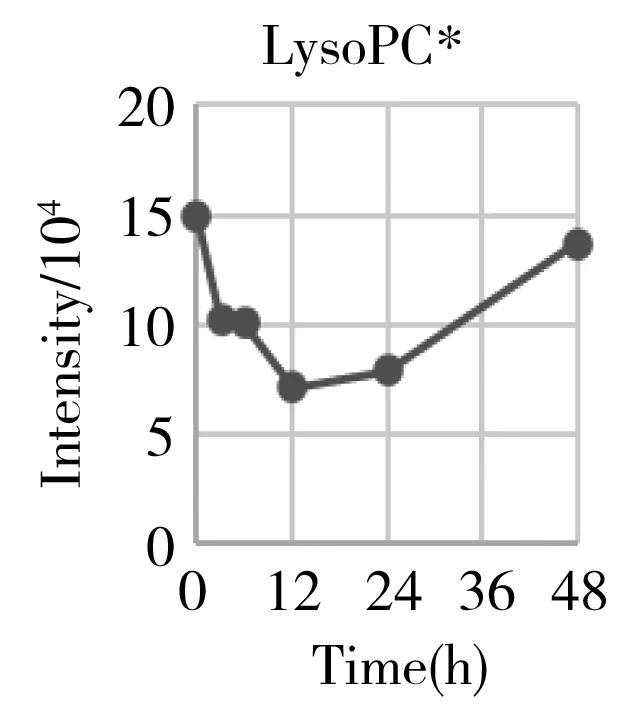
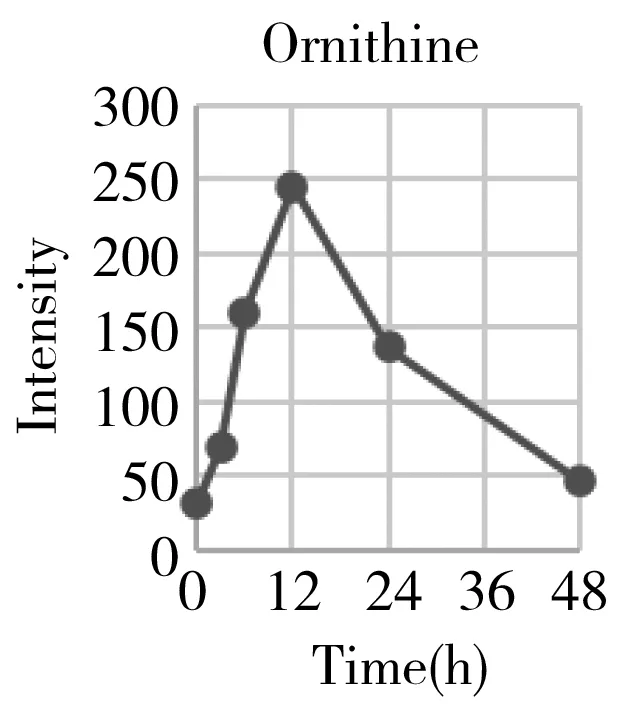
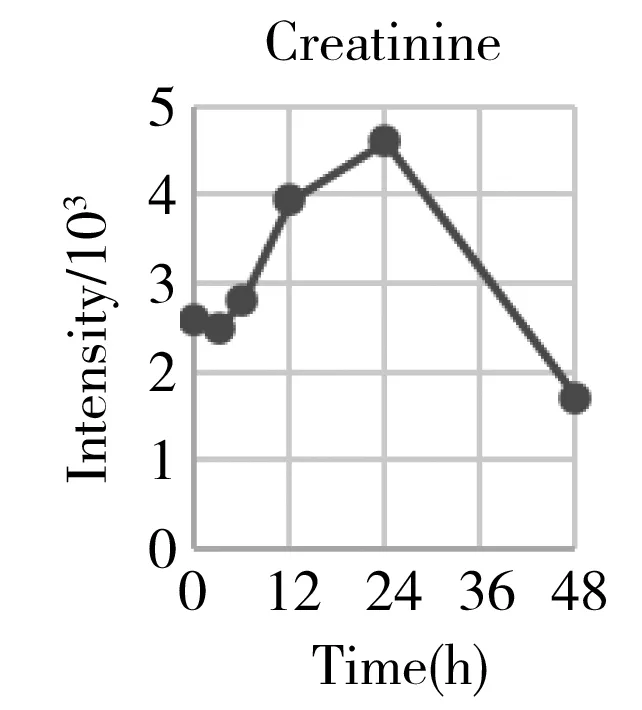
Considering that many of them were the series derivatives that share the same parent structure and biological function,we also provide some total components' intensities changes to get a combined index such as acylcarnitines,total lyso-phosphorylcholines(LPC),total polyamines,and total diacyl glycerolipids(DAG).They belonged to the lipids metabolism especially the glycerolipids(GL) and glycerophosphocholine(GPL) metabolism.From Fig.5,we can initially conclude that the GPL,GL,and arginine metabolism can provide important references for evaluating the functional recovery from the hepatectomy.
3 Conclusion
A systematic investigation was carried out to find that CPSI-MS can successfully detect various endogenous species in the whole-blood sample,including carbohydrates,amino acids,fatty acids,vitamins,polyamines,nucleotides,glycerolipids,and glycerophospholipids,etc.Thus,a series of metabolism pathways and even network can be largely covered,providing not only the source of the possible characteristic markers but also further insight into the underlying pathophysiological mechanism.Compared to the traditional LC-MS platform,CPSI-MS avoids the laborious sample pretreatment and brings many conveniences to the clinical practitioner for multiplex monitoring of blood metabolites,giving quick feedback on personal physiological status.In the aspect of preclinical biological analysis,those test animals with a very limited volume of blood can survive from the long-term,successive sampling at multiple time points because it only consumes as low as 1 μL native biological fluid.Therefore,it also shows great potential in preclinical pharmacokinetics study and therapeutic drug monitoring.

