Protective effects of modified Wendan decoction on hippocampal neurons in a rat model of depression
Li-Ping Zhang,Yun-Sha Zhang,Ting Xue,Shan-Yan Yin,Ying Chen,Lei Xu,Rui-Wen Song*
1Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 301617,China.
Abstract:
Objective:To study the effects of modified Wendan decoction on hippocampal neuron plasticity in a rat model of depression.Methods:Thirty-two rats were randomly divided into a blank control group,model group,traditional Chinese medicine(modified Wendan decoction)group,and Western medicine(fluoxetine)group.Isolation in conjunction with the chronic unpredictable mild stress(CUMS)method was used to replicate depression in rats from the experimental groups.The rats were treated for 28d following successful modeling.After treatment,transmission electron microscopy(TEM)was used to observe the ultrastructure of hippocampal dentate gyrus(DG)region in the rats.Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA)was performed to measure the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor(BDNF)and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor(GDNF)in hippocampal tissue.Additionally,RT-PCR was used to measure hippocampal BDNF and GDNF mRNA expression levels.Results:Compared to the control group,there was significant swelling,disordered cell arrangement,pyknosis,deepening of cytoplasmic staining in the hippocampal neurons,and severe hippocampal injury in the model group.Following treatment with the traditional Chinese medicine intervention,hippocampal neuronal injury was significantly alleviated,hippocampus structure was normal,and brain injury was significantly reduced in the depression rat model.Compared to the control group,hippocampal BDNF and GDNF mRNA levels in the model group were reduced(P<0.05).Compared to the model group,hippocampal BDNF and GDNF mRNA levels in the traditional Chinese medicine group increased(P<0.05).Conclusion:Modified Wendan decoction can increase hippocampal neurotrophic function and repair hippocampal neuronal injury,thereby preventing depression.
Keywords:depression;modified Wendan decoction;neuron plasticity;neurotrophy
Introduction
Depression is a common psychiatric disorder that negatively affects patients’lives;importantly,its pathogenesis and etiology have not been fully elucidated[1].The hypothesis of neuroplasticity states that neuronal damage is the main cause of depression,and the promotion of neuron regeneration is the mechanism by which antidepressants treat depression[2-3].Brain-derived neurotrophic factor(BDNF)and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor(GDNF)have important regulatory functionsin maintaining neuronalactivity,synaptic transmission,and synaptic plasticity[4].Animal studies have found that there is a downregulation of BDNF and GDNF expression in the hippocampus of depression modelanimals[5-7].Ourgroup previously used double immunofluorescence labeling and discovered that modified Wendan decoction could reverse the progression of the regeneration defect of decreased hippocampal neuron proliferation and differentiation in a rat model[8]as well as alleviate neuronal atrophy caused by neuronal ultrastructure damage of the hippocampal cornu ammonis 3(CA3)region[9].The current study examined the neurotrophy angle and further investigated whether a modified Wendan decoction could regulate the expression of neurotrophic factors BDNF and GDNF and affect hippocampal neuron plasticity,thus producing antidepressant effects.
Materials and methods
Materials
Experimental animals.A total of 48 clean-grade male and female SD rats weighing 200±20 g were provided by the laboratory animals center of the Health Environmental Science Research Center,Academy of Military Medical Sciences of the PLA.The approval certificate of the animals was SCXK-(Beijing)2016-0008.The animals were housed in the Institute of Radiation Medicine,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences at a room temperature of 25℃ for1 week during acclimatization.During the acclimatization period,animals were given free access to food and water.The housing and use of animals met the international animal ethics.
Drug preparation.Drug materials of modified Wendan decoction[10]were provided by Beijing Tong Ren Tang Co.,Ltd.The drug was decocted to the concentration of 1.5 g/mL and was stored at 4℃.The specification of fluoxetine hydrochloride was 20 mg/pill(batch number:H20170003),which was purchased from Patheam France(packaged by Lilly Suzhou Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.).A mortar and pestle were used to homogenize the fluoxetine,and saline was used to prepare a 0.6 mg/mL solution.The solution was stored at 4℃.
Main equipment.H-7500 transmission electron microscope(Hitachi,Japan),UC-7 ultramicrotome(Leica),1/15M phosphate buffer,1% osmium tetroxide,acetone,embedding solution,uranyl acetate,and lead citrate were provided by the Electron Microscopy Center of Hebei Medical University.
Study methods
Grouping and preparation of the depression rat model.An open-field experiment was performed to screen for 32 rats with the same behavioral score.These rats were randomized into 4 groups using a number table with 8 rats in each group and 4 rats of each gender.These 4 groups were the blank control group,model group,fluoxetine control group(referred to as the Western medicine group),and modified Wendan decoction group(referred to as the traditional Chinese medicine group).No stimulation was given to the blank control group.Isolation in conjunction with chronic unpredictable mild stress(CUMS)was used to construct the depression rat model in the 3 experimental groups as done in previous investigations.Rats were given 9 types of stimulation(water fasted for 24 hours,food fasted for 24 hours,subjected to overnight illumination,heated in a 45℃oven for 5 minutes,swam in 4℃cold water for 5 minutes,subjected to high-speed horizontal vibration for 3 minutes,subjected to 1 minute of tail pinching,1 minute of tail suspension,and 100V electric shock to the soles for 1 minute)in a random order for 21 days,with 1 stimulation each day.Each stimulation occurred 2-3 times and non-consecutively so that animals could not predict the upcoming stimulation[10].
Dose and drug administration method.The blank control group was given free access to food and water.After the successful modeling of the other drugs,drug was being administered(equivalent to 70 kg of adult human weight).The model group was given 2 mL/(kg·d)of saline by oral gavage.The Western medicine group was given 1.8 mg/(kg·d)of fluoxetine by oral gavage.Finally,the traditional Chinese medicine group was given 12 g/(kg·d)of modified Wendan decoction by oral gavage.Oral gavage was carried out for 4 continuous weeks.
Testing markers and methods.Transmission electron microscopy(TEM)was used to observe changes in the neuronal ultrastructure of the hippocampal dentate gyrus(DG)region,including the nucleus,mitochondria,rough endoplasmic reticulum,and Golgi bodies.An ELISA was performed to measure hippocampal BDNF and GDNF levels.RT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression of hippocampal BDNF and GDNF.
Statistical analysis
SPSS statistics 24.0 was used.Quantitative data was denoted as χ ± s using a one-way ANOVA.A LSD-t-test was used for multiple-group comparison.A difference with a P-value<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
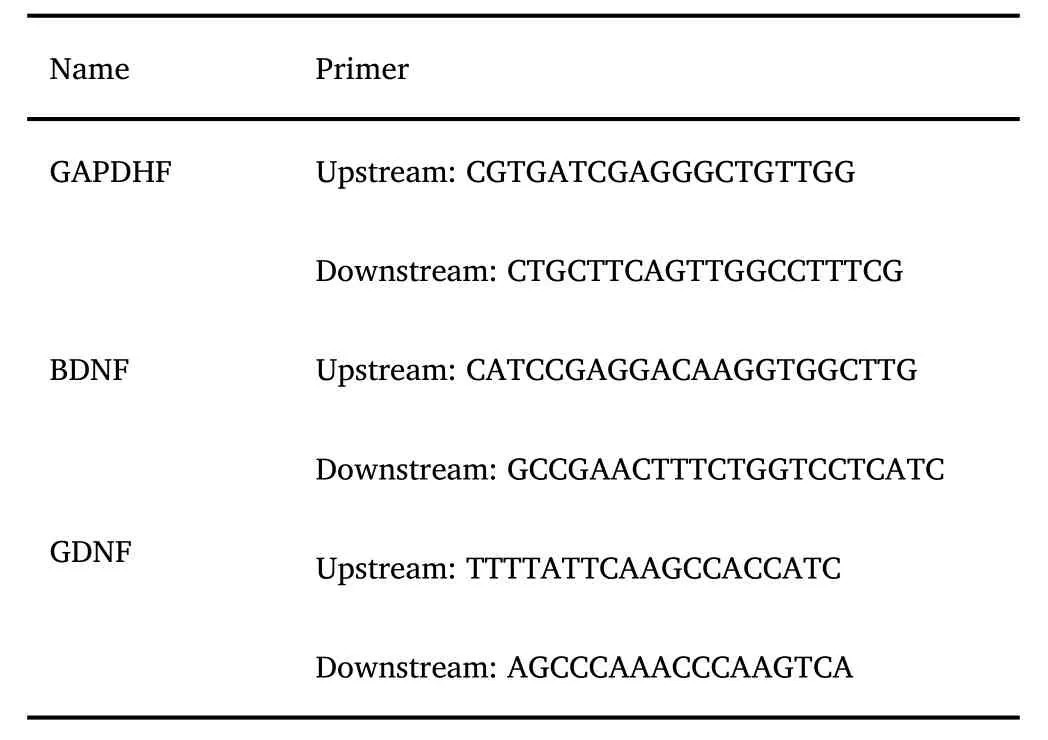
The design of BDNF and GDNF primers is as follows
Results
Neuronal ultrastructure of hippocampal DG region
In the normal group,the neuronal mitochondria were intact,cristae were arranged in a regular manner,and matrix density was normal.The rough endoplasmic reticulum was neatly arranged,and many ribosomes were distributed on the membrane surface.In the model group,the neurons shrank in size;nuclear heterochromatin was increased,appeared in blocks,and clustered toward the edges;perinuclear space was increased and nuclear edges were not smooth;cytoplasmic mitochondria were swollen,with some appearing like vacuoles;cristae of some mitochondria were blurry,with increased electron density,and vacuolization was seen in a few mitochondria;and the rough endoplasmic reticulum was slightly expanded.In the traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine groups,neurons were generally normal,perinuclear space was generally normal,and nuclear edges were smooth;mild swelling was seen in some mitochondria,with blurry mitochondrial cristae,and electron density was increased;and the Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum were normal.Results are shown in Figure 1.
Changes in neurotrophic factors(GDNF and BDNF)in the hippocampal DG region
Compared to the blank control group,hippocampal GDNF and BDNF levels were significantly decreased in the model group.Compared to the model group, hippocampal GDNF and BDNF levels were significantly increased in the modified Wendan decoction group.See Table 1 for results.
Changes in mRNA expression of neurotrophic factors(GDNF and BDNF)in hippocampal DG region
Compared to the blank control group,hippocampal GDNF and BDNF mRNA expression levels were significantly decreased in the model group.Compared to the model group,hippocampal GDNF and BDNF mRNA expression levels were significantly increased in the modified Wendan decoction group.See Table 2 for results.
Discussion
Depression is a common psychiatric disorder,and its pathogenesis has not been fully elucidated.However,studies have shown that stress plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of depression [11].Furthermore,long-term chronic stress not only causes neuronal atrophy,degeneration,and death in the hippocampus but also causes defective neuronal regeneration in the hippocampus and other brain regions[12].On the other hand,,long-term antidepressant treatment can increase the number of hippocampal neurons,enhance their functions,and increase neuronal plasticity.
Neurotrophic factors are endogenous proteins that regulate neuronal metabolism and function and guide neuronal repairs that promote neuronal survival,growth,and differentiation during neuronal injury.Therefore,neurotrophic factors play an important role in regulating neuronal plasticity[13].Two neurotrophic factors that have been identified as contributors of neuronal plasticity regulation are BDNF and GDNF.CUMS can decrease both hippocampal GFAP and BDNF levels in rats [14],while antidepressants have been shown to regulate the expression level of the astrocyte marker,GFAP[15-16],and promote BDNF and GDNF release through astrocytes[17].Therefore,changes in the level of neurotrophic factors are considered to be an important mechanism of the pharmacological effect of antidepressants[18].
In the current study,TEM was used to observe changes in hippocampal ultrastructure in the depression rat model.The study found that the neuronal ultrastructure of the hippocampus was significantly damaged in the model group,and apoptotic changes occurred in some cells.ELISA and RT-PCR results found that the protein levels of neurotropic factors BDNF and GDNF,along with their mRNA expression,were decreased.After modified Wendan decoction Intervention,the severity of hippocampal neuron injury was reduced and the protein levels of BDNF and GDNF,along with their mRNA expression,were significantly increased.Taken together with the results of a previous study by our group during the same period[19],it is speculated that modified Wendan decoction can enhance neuroprotection in the TRP-KYN pathway and activate astrocyte expression in the hippocampus of rats,which repairs astrocyte injury to some extent,thereby carrying out antidepressant effects by promoting the release of BDNF and GDNF and reversing neuronal injury.
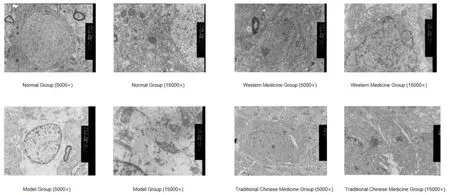
Figure 1 Hippocampal ultrastructure of rats in different groups
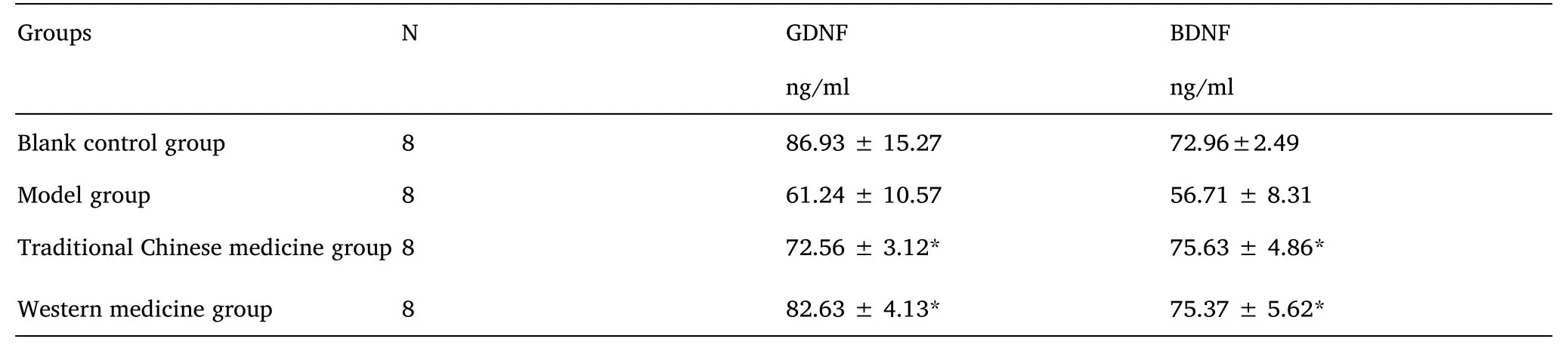
Table 1 GDNF and BDNF levels in different groups(x±s)
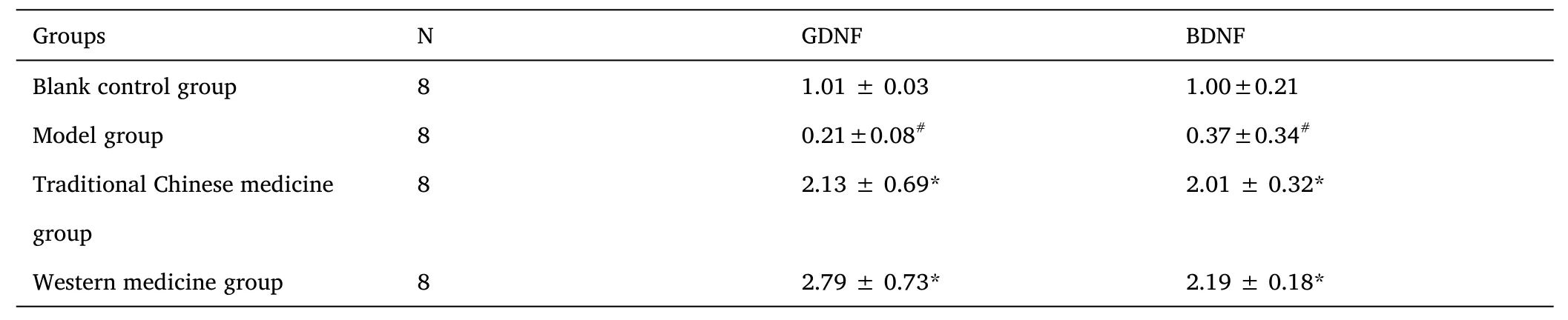
Table 2 GDNF and BDNF mRNA expression levels in different groups(x±s)
 Precision Medicine Research2021年4期
Precision Medicine Research2021年4期
- Precision Medicine Research的其它文章
- Mini-review on personalized medicine:a revolution in health care
- Preparation and evaluation of mucoadhesive bioflexy films from Cocos nucifera biopolymer using Tiagabine moiety
- 18F-Deoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Multiple Myeloma
- Targeting SARS-CoV-2 with therapeutic monoclonal antibodies
