Prospects of Yacon (Polymnia Sohchifolia Poepp. & Endl) Using for Astronauts Life Support
Lidiya Mishchenko,Olga Molodchenkova,Alina Dunich,Ivan Mishchenko,Anna Dashchenko
(1. Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv,Kyiv 01601,Ukraine;2. Plant Breeding&Genetics Institute-National Center of Seed and Cultivar Investigations,Odessa 650036,Ukraine;3. National University of Life and Environmental Sciences of Ukraine,Kyiv 03041,Ukraine)
Abstract:During long-term manned space flights, biological life support systems are required, so food becomes an instrument of paramount importance. Plants are an accessible source of biologically active compounds. Antioxidant deficiency decreases the body's functional activity. Vegetable foods, including non-traditional and medicinal crops, are the main and most affordable source of antioxidants for humans. Yacon (Polymnia sonchifolia Poepp. & Endl.) is one of the most promising introductory species for Ukraine, and has recently started growing as a vegetable crop in our country. The leaves of this plant contain high concentrations of flavonoids, chlorogenic, coffee acids, selenium, vitamins, minerals in, which gives it strong antioxidant properties. It is shown that Yacon root tubers have a high content of sugars, most of which are fructosans (over 60%). Most of the fructosans and sugars are in root tubers grown in the Kyiv region. The amount of HCA based on chlorogenic acid is up to 4.5% DW in the tops of Yacon leaves in the Poltava region. Its content is the largest in root tubers (2.3%) of plants grown in Kyiv region (stem reproduction).The biochemical composition of different parts of Yacon has proved that it is promising for the diverse and healthy nutrition of astronauts for their life support in long-term space missions.
Keywords:Yacon (Polymnia sohchifolia);sugar;total phenolic content;total flavonoid content;antioxidant activity;healthy nutrition
Introduction
In space programs around the world, plant biology studies are a top priority. Ukraine is rightly considered a space country. There are four stages in the development of life support systems for astronauts. The first group includes the systems that do not use the processes of substances cycle. First of all, it is a food support system[1].During long-term manned space flights, specific biological life support systems are required, as the cosmonaut is subjected to tremendous physiological and psychological stress, which can adversely affect his health. In this regard,such means are needed to protect crew members, so food becomes an instrument of paramount importance. Plants are an accessible source of biologically active compounds for human. Thousands of species of wild and cultivated plants give antioxidants and trace elements extremely important for the functioning of our body. Deficiency of antioxidants reduces the functional activity of the body,which increases the risk of various diseases and leads to a sharp decrease in resistance to adverse environmental factors, including microgravity, increased levels of radiation etc. Since the end of the last century, scientists have been tasked with antioxidant protection of humans[2].Vegetable foods, including non-traditional and medicinal crops, are the main and most affordable source of antioxidants for humans. Yacon is one of the most promising introductory species for Ukraine, and has recently started growing as a vegetable crop in our country. Yacon (Polymnia sonchifoliaPoepp. & Endl.) is a perennial herb of theAsteraceaefamily. The main habitat for Yacon is the middle latitudes of South America, and we were introduced to Ukraine in 2011—2012[3-4]. The leaves of this plant contain high concentrations of chlorogenic, caffeic acid, and selenium in high concentrations, which gives it strong antioxidant properties. Previously, the focus was on the properties of only the underground part of the plant, later it was shown that the leaves have antioxidant properties too. Yacon also contains vitamins, fiber, fats, protein, free amino acids,macro and microelements[5]. Previously, we have shown that tuberous roots contain from 36 to 45% of fructosans depending on the growing region and weather conditions[6].Yacon has the ability to accumulate selenium, which is characterized by antioxidant properties, increases immunity and prevents the aging of the body. Its content was the highest in the Yacon leaves grown by us in Poltava region (5.62 mg/kg)[7]. The use of Yacon leaves in teas with antioxidant properties is already important today,since studies of the content of microelements and low molecular weight antioxidants in popular varieties and brands of 14 tea samples did not revealed selenium[8].Analysis of alcoholic extracts from the leaves and root tubers of the Yacon of Ukrainian introduction showed the presence of phenolic compounds, fructosans, inulin, the content of which exceeded 2 times that in Jerusalem artichoke. We have developed a vitamin and antioxidant tea based on medicinal plants and leaves ofPolymnia sohchifolia, which is relevant and promising for use in the diet of astronauts[9]. The importance of Yacon for nutrition is described in many papers[10-11].
Therefore, the aim of our work was to investigate the biochemical composition of Yacon plants (Polymnia sohchifoliaPoepp. & Endl) under conditions of different growing regions of Ukraine and climate change; and the possibility of its use in the diet of astronauts.
1 Materials and methods
Introductory Yacon studies were conducted under various agro-environmental conditions of Ukraine in accordance with conventional methods[3,6-7].
Root tubers, rhizomes, peel of root tubers and leaves of all storeys (Polymnia sohchifoliaPoepp. & Endl) grown in three experimental variants were analyzed: variant 1-gray forest loamy soil (Kyiv region) under drip irrigation conditions; variant 2-gray forest soil (Kyiv) under periodic surface irrigation; variant 3-on the black soil typical,medium-loamy (Poltava region) under conditions of periodic surface irrigation. Protein content was determined by Kjeldahl method, ash content was determined by classical gravimetric technique.
The amount of fructosans based on dry matter and 5'-hydroxy me-thylfurfural were determined spectrophotometrically by standard methods at X=285 nm using a UV 1 700 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan). To quantify fructosan fractions, the Selivanov color reaction was used(heating fructose with hydrochloric acid to produce hydroxy methylfurfural that gives a cherry-red color with resorcinol, the intensity of which is determined by spectrophotometry)[12].
The total amount of Hydroxy-Hinnamic Aacids(HCA) in the leaves of the 2nd tier and the leaves of the 1st to 4th tiers (an average sample) were estimated by direct spectrophotometry of ethanol extracts (X = 325 nm;UV 1 700, Shimadzu, Japan) and expressed based on chlorogenic acid and dry matter[13].
The total flavonoid content of individual extracts was measured as per the Dowd method. An aliquot of 1 mL of extract solution (25-200 μg/mL) or quercetin (25-200 μg/mL)were mixed with 0.2 mL of 10% (w/v) AlCl3 solution in methanol, 0.2 mL (1 M) potassium acetate and 5.6 mL distilled water. The mixture was incubated for 30 min at room temperature followed with the measurement of absorbance at 415 nm against the blank. The outcome data were expressed as mg/g of quercetin equivalents in milligrams (micrograms) per gram (mg QE/g) of dry weight[14].
β-Carotene was extracted from Yacon plants for“Reversed phased HPLC system”. 10 g of sample was homogenized in 30 mL of acetone and then 0.1% (BHT)solution in acetone was added as an antioxidant. The resulting extract was filtered through Buchnar’s funnel.The residue was washed twice with acetone till it become colorless. The residue was discarded and the filtrate was combined with 20 gm of anhydrous sodium sulphate. The anhydrous sodium suphate was removed through filtration and the volume of extract was reduced by rotatory evaporator. The extract was transferred quantitatively to 100 mL volumetric flask and the volume was made up to the mark with acetone and water, so that the final extract contains 80% of acetone.
Standard Preparation of Beta Carotene Standard of beta carotene (1g enclosed in vial) was obtained from Merck. Stock solution of bets carotene was prepared by taking 10 mg in 100 mL n-hexane. The concentration of stock solution was equal to 100 ppm. The stock solution was diluted to different known concentration e.g. 20, 40 and 60 ppm, dilutions were obtained in 5 ml of each nhexane solutions. Each working standard solution was injected into HPLC system “Gilson” (France) using column Thermo Hypersil-Keystone: ODS, Particle Size 5 мкм, Pore Size (A): 120, psi:1 300, speed of 0.5 ml/ min,as eluent used acetone / H2O (60/40). Detection of βcarotene was carried out at 450 nm. β-carotene content was determined in two analytical replicates and was given in μg per 1 g of dry weight. The concentrations of the beta carotene standards were plotted against the peak area to obtain a straight line/Each sample of beta carotene extract in 80% acetone was used for HPLC assay like standard;each sample (20 μL) was taken by micro liter syringe. The peak was automatically identified and quantified by comparing its retention time of the sample with the standard retention time[15].
The content of the reduced form of ascorbic acid was determined by an iodometric method based on titration of ascorbic acid in colored extracts of potassium iodate in acidic medium, in the presence of potassium iodide and starch[16].
The sugar content was determined by the anthron method[17].
The content of vitamins B1t and B2 was determined by the fluorimetric method according to State standard 29 138-91 and 29 139-91, respectively.
Cellulose was determined on an automatic Fibertec 1 023 Tecator Foss analyzer according to the methodological principles[17].
The data were processed by the normal variant distribution parametric criteria, and standard deviation was calculated by the standard method using the Microsoft Excel 2010 package and programme. The results obtained were calculated using the arithmetic mean (M) and the standard error from the mean (SEM), taking into account the significance atp< 0.05.
2 Results and discussion
Experiments on the introduction of Yacon were conducted in Kyiv and Poltava regions in 2016 — 2018.The results of cultivation of Yacon plants under different agro-ecological conditions of Ukraine are given in previous publications[3,6-7].
The most suitable for the growth and development of the Yacon were the gray forest soils of the Kyiv region that is clearly visible in Fig. 1.

Fig. 1 Yacon reached a height of more than 160 cm,Kyiv region, September 23, 2016
Such wonderful plants are usually gave a good yield every year. True, this was facilitated by drip irrigation. In Fig. 2 and 3 a general view of root tubers is shown. They are very juicy and brittle (fragile), so they dig carefully.

Fig. 2 The Yacon plant has just been dug, October,7, 2018, Kyiv region

Fig. 3 Root tubers of different shapes, 2018, Kyiv region
In recent years, root tubers have not always been formed due to excessive droughts in summer. For example, in the Poltava region (a zone of arid climate) in 2019 they were not formed at all.It is known that the conditions of cultivation of Yacon plants can significantly affect not only the yield of raw materials, but also on the change of its chemical composition[5].
The conducted studies have established the influence of growing conditions on the biochemical composition of the underground and aboveground parts of Yacon and Jerusalem artichoke plants (for comparison). For example,the quantity of fructosans in the root tubers of the Yacon in 2017 was 54.7% (in variant 1) and 52.1% (variant 3).The content of carotenoids in the leaves of Yacon was 28.6 mg / 100 g of dry matter (variant 1) and 63.73 mg /100 g (variant 3). Content of HCA was highest in root tubers and leaves of Yacon in variant 3 (1.15 and 4.80,respectively)[18]. Carotenoids and phenolic compounds,including HCA, are known to have antioxidant properties.This determines their radioprotective, immunomodulatory and anticancer activities. The results of studies of Yacon plants grown in 2018 showed that different agroecological conditions of cultivation have an ambiguous effect on the biochemical composition of the aboveground and underground organs of plants (Table 1).
Studies have shown that Yacon root tubers have a high content of sugars, most of which are fructosans (over 60%), sugars content - over 80%. Rhizomes and peel of root tubers have a high content of sugars too. Different content of fructosans and sugars in other organs of the plant and at different development stages Yacon is also found. It is worth noting that such high sugar content is also observed in wheat at the tillering sites.
The amount of HCA in terms of chlorogenic acid was up to 4.5% in the tops of Yacon leaves in Poltava region on the eve of frost (September 30, 2018). Its content was the largest in root tubers (2.3%) of plants grown in Kyiv region (stem reproduction). It is noteworthy that the peels of root tubers also have a considerable HCA content (more than 2% in plants from Poltava region). The rhizome,which serves as the main reserve organ for plant reproduction, contains 3.6% of HCA (NULESU). By the way, with excess rhizomes, they can also be used for the preparation of teas, candied fruits etc. Because they contain up to 51% fructose, 79% sucrose and the highest amount of flavonoids, 198 mcg / g (grown in Poltava region). German scientists[19]investigated the content of fructosans, glucose, sucrose, flavonoids and antioxidant activity in the root tubers of seven cultivars of Yacon and also proved that they are most contained in the flesh and whole tubers compared to their peels. Our results are consistent with them. The high antioxidant activity of Yacon is also mentioned in[20].
The high levels of fructooligosaccharides and chlorogenic acid, some mineral elements, such as K, Ca and P,and essential amino acids, were determined in Yacon syrup[21]. Our studies also revealed high levels of vitamins C (20 to 90%), B1 (up to 0.358 mg / 100 g) and B2 (up to 1.695 mg / 100 g) and protein (over 7%) depending on the organ of the Yacon plant. Particularly, rich in vitamin C are leaves and stems of Yacon. Twenty three chemical elements have previously been identified in leaves,rhizomes, root tubers and peels[7]. Our results and literature provide conclusive evidence that they can really be used for the healthy and multiform nutrition of astronauts for their sustenance in long-term space missions.
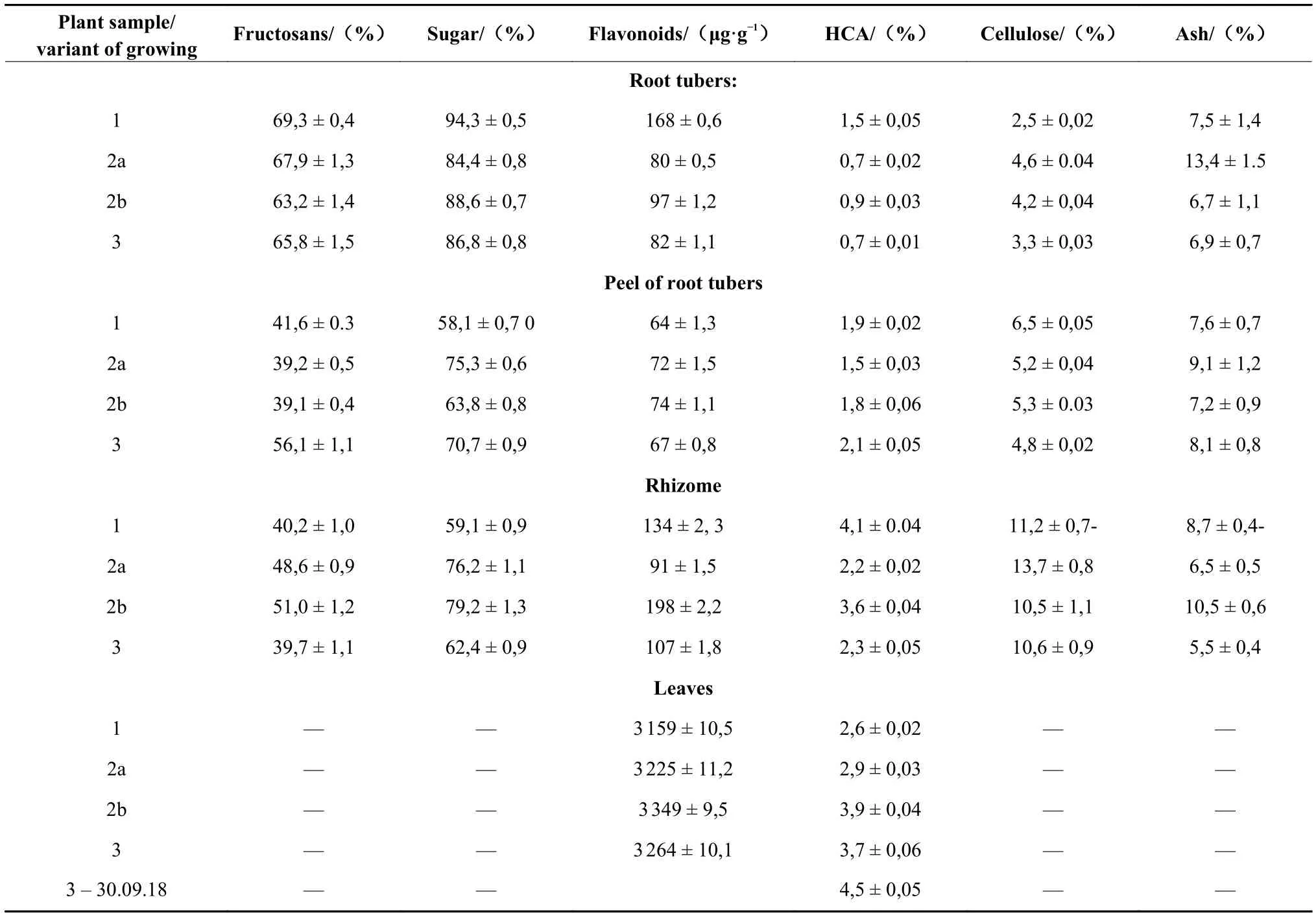
Table 1 Total content of biologically active substances in Yacon plants cultivated in different agro-ecological conditions, 2018
Despite the fact that the Yacon grown in Poltava region often contains much higher biochemical parameters,we recommend to grow Yacon in the Kiev region on gray forest soil, which is much lighter in mechanical composition than Poltava chernozem. They are less suitable for growing root crops, which include the culture of Yacon. It is possible to get from 2.0 to 4.2 kg of root tubers of Yacon from one plant in Vasylkiv district of the Kyiv region. In terms of sugar, it will be at least 2.5 t / ha,which is not inferior to other European researchers which yielded 1.9-2.2 t / ha[22]. We emphasize that cultivation of Yacon is not easy to some extent. But it is possible to work out the technology. We noted that the yield and biochemical composition of Yacon is slightly higher in plants that were "older", namely, their reproduction began immediately after harvesting - the stems, compared with the cuttings from the grown rhizomes and their separation.Our investigations are similar to[23]which outline the main aspects of Yacon breeding.
Thus, despite some difficulties (problems) in Yacon growing, it should be grown in many countries, including Ukraine and China, with the purpose of its use for a healthy, delicious and variety nutrition not only ordinary citizens, but also astronauts in their long space missions.

