基于GNS3的IPv6园区网络仿真与实现



摘 要:互联网协议第六版(IPv6)是互联网升级演进的必然趋势、网络技术创新的重要方向、网络强国建设的基础支撑。近年来,我国政府加速推进IPv6发展。电子信息类等高校的园区网络,应率先尝试IPv6全链条、全业务、全场景部署,边试点、边总结、边推广,以点促面,整体提升IPv6规模部署和应用水平。实验模拟典型的园区网络,在网络环境下仿真实现IPv6的各种通信方式,为未来的IPv6全网通信提供技术支撑。
关键词:IPv6;规模部署;园区网络
中图分类号:TP393 文献标识码:A 文章编号:2096-4706(2021)12-0090-04
Abstract: Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the inevitable trend of internet upgrading and evolution, an important direction of network technology innovation, and the basic support for the construction of a network powerful nation. In recent years, our government has accelerated the development of IPv6. The campus network of colleges such as electronic information colleges should take the lead in trying the full chain, full service and full scenario deployment of IPv6, pilot, summarize and promote at the same time, promoting the area with points, and improve the scale deployment and application level of IPv6 as a whole. The experiment simulates the typical campus networks, simulates and realizes various communication modes of IPv6 in the network environment, and provides technical support for the future IPv6 whole network communication.
Keywords: IPv6; scale deployment; campus network
0 引 言
2021年,我國加快推进互联网协议第六版(IPv6)规模部署和应用工作,IPv6规模部署势在必行。文中实验旨在模拟在规模部署实施IPv6后,四川信息职业技术学院等园区网络中存在的多种选择通信办法:
(1)使用全IPv6。
(2)使用IPv6、IPv4双栈网络。
(3)使用传统IPv4网络。
而在具有相当规模的IPv6网络环境中,园区网络使用双栈协议是较好的过渡方式,最终与大环境一起推行全网IPv6,但不能忽略有些网络节点存在IPv4网络。以四川信息职业技术学院为例,有大部分业务无法切换到IPv6网络,还需探索这类网络如何在全IPv6网络中实现通信。此实验旨在为处境相同的园区网络提供一种解决思路。
1 实验简介
在此次仿真实验中,校区本部A使用纯IPv6网络,分校区B使用IPv6、IPv4双栈网络,云计算中心为满足各类用户需求使用IPv6、IPv4双栈网络,校区本部访问云计算中心即为全IPv6访问,分校区访问云计算中心为双栈协议访问或者通过隧道访问。拓扑图如图1所示。
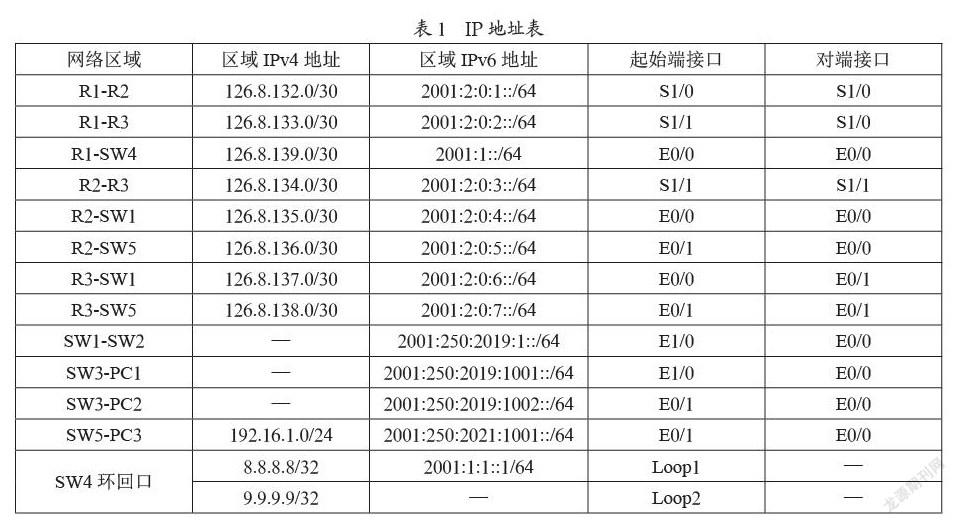
本部校区使用2001:250:2019::/48 IPv6地址,云计算中心使用2001:1::/32 IPv6地址,分校区使用2001:250:2021::/48 地址,分校区同时使用公网IP地址192.16.1.0/24。在SW3接入交换机下PC1、PC2模拟本部校区用户区域,在SW6接入交换机下PC3模拟分校区用户。各个区域IP地址表如表1所示。
实验最终实现效果为,PC1通过IPv6访问SW4上的IPv6网络,PC3通过IPv6网络、IPv4网络、IPv4隧道访问SW4上的对应网络。
2 配置实施
按照难易程度与通信需求,仿真实验配置分为以下几个步骤。
2.1 基础配置
基础信息配置属于网络基础配置,包含接口IP、端口描述、接口开启关闭等,篇幅所限,这里仅以R1、PC3为例写出配置:
(1)R1基础信息配置:
inter e0/0
des Con_To_SW4
ip add 126.8.139.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 add 2001:1::1/64
no shut
exit
inter s1/0
des Con_To_R2
ip add 126.8.132.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 add 2001:2:0:1::1/64
no shut
exit
inter s1/1
des Con_To_R3
ip add 126.8.133.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 add 2001:2:0:2::1/64
no shut
exit
inter loop0
ip add 101.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
no shut
Exit
(2)PC3基礎信息配置:
hostname PC3
no ip routing
ip default-gateway 192.16.1.1
int e0/0
no shut
ip add 192.16.1.2 255.255.255.0
ipv6 add 2001:250:2021:1001::2/64
2.2 本部校区OSPFv3配置
SW1配置OSPFv3:
ipv6 uni
router ospfv3 10
router-id 104.4.4.4
address-fa ipv6 unicast
redis bgp 104
exit
exit
int e1/0
ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
SW2配置OSPFv3:
ipv6 uni
router ospfv3 10
router-id 104.5.5.5
int e0/0
ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
exit
int vlan 10
ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
exit
int vlan 20
ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
2.3 BGP配置
R1 BGP配置:
router bgp 101
no bgp default ipv4
neighbor 2001:2:0:1::2 remote-as 102
neighbor 2001:2:0:2::2 remote-as 103
neighbor 126.8.132.2 remote-as 102
neighbor 126.8.133.2 remote-as 103
address-family ipv6
neighbor 2001:2:0:1::2 acti
neighbor 2001:2:0:2::2 acti
redistribute static(此处由于SW4与R1之间未运行路由协议,使用静态路由,需要把静态路由重分布到BGP中)
address-family ipv4
neighbor 126.8.132.2 acti
neighbor 126.8.133.2 acti
redistribute static
R2 BGP配置:
router bgp 102
no bgp default ipv4
neighbor 2001:2:0:1::1 remote-as 101
neighbor 2001:2:0:3::2 remote-as 103
neighbor 2001:2:0:4::2 remote-as 104
neighbor 2001:2:0:5::2 remote-as 105
neighbor 126.8.132.1 remote-as 101
neighbor 126.8.134.2 remote-as 103
neighbor 126.8.135.2 remote-as 104
neighbor 126.8.136.2 remote-as 105
address-family ipv6
neighbor 2001:2:0:1::1 activate
neighbor 2001:2:0:3::2 activate
neighbor 2001:2:0:4::2 activate
neighbor 2001:2:0:5::2 activate
address-family ipv4
neighbor 126.8.132.1 activate
neighbor 126.8.134.2 activate
neighbor 126.8.135.2 activate
neighbor 126.8.136.2 activate
R3 BGP配置:
router bgp 103
no bgp default ipv4-uni
neighbor 2001:2:0:2::1 remote-as 101
neighbor 2001:2:0:3::1 remote-as 102
neighbor 2001:2:0:6::2 remote-as 104
neighbor 2001:2:0:7::2 remote-as 105
neighbor 126.8.133.1 remote-as 101
neighbor 126.8.134.1 remote-as 102
neighbor 126.8.137.2 remote-as 104
neighbor 126.8.138.2 remote-as 105
address-family ipv6
neighbor 2001:2:0:2::1 activate
neighbor 2001:2:0:3::1 activate
neighbor 2001:2:0:6::2 activate
neighbor 2001:2:0:7::2 activate
address-family ipv4
neighbor 126.8.133.1 activate
neighbor 126.8.134.1 activate
neighbor 126.8.137.2 activate
neighbor 126.8.138.2 activate
SW1配置BGP:
router bgp 104
no bgp default ipv4
neighbor 2001:2:0:4::1 remote-as 102
neighbor 2001:2:0:6::1 remote-as 103
neighbor 126.8.135.1 remote-as 102
neighbor 126.8.137.1 remote-as 103
address-family ipv4
neighbor 126.8.135.1 acti
neighbor 126.8.137.1 acti
address-family ipv6
neighbor 2001:2:0:4::1 activate
neighbor 2001:2:0:6::1 activate
redistribute ospf 10 match internal external 1 external 2 include-connected
aggregate-address 2001:250:2019::/48 summary-only
SW5配置BGP:
router bgp 105
no bgp default ipv4
neighbor 2001:2:0:5::1 remote-as 102
neighbor 2001:2:0:7::1 remote-as 103
neighbor 126.8.136.1 remote-as 102
neighbor 126.8.138.1 remote-as 103
address-family ipv4
neighbor 126.8.136.1 acti
neighbor 126.8.138.1 acti
network 192.16.1.0
address-family ipv6
neighbor 2001:2:0:5::1 activate
neighbor 2001:2:0:7::1 activate
network 2001:250:2021:1001::/64
2.4 隧道、路由配置
SW4隧道、路由配置:
interface Tunnel5
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
tunnel source 2001:1::2
tunnel mode gre ipv6
tunnel destination 2001:2:0:7::2
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 126.8.139.1
ip route 192.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel5
ipv6 route ::/0 2001:1::1
SW5隧道、路由配置:
interface Tunnel5
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252
tunnel destination 2001:1::2
tunnel mode gre ipv6
tunnel source 2001:2:0:7::2
ip route 9.9.9.9 255.255.255.255 Tunnel5
R1路由配置:
ip route 8.8.8.8 255.255.255.255 126.8.139.2
ipv6 route 2001:1:1::/64 2001:1::2
3 現象测试
按照仿真实验搭建之初拟定的几个测试要求进行测试:
(1)PC1使用IPv6访问SW4模拟的IPv6网络资源,源地址为2001:250:2019:1001::2,经过设备SW2-SW1-R2-R1后到达SW4上目的地址2001:1:1::1,结果如图2所示。
(2)PC3使用IPv6访问SW4模拟的IPv6网络资源,源地址为2001:250:2021:1001::2,经过设备SW5-R2-R1后到达SW4上目的地址2001:1:1::1,结果如图3所示。
(3)PC3使用IPv4访问SW4模拟的IPv4网络资源,源地址为192.16.1.2,经过设备SW5-R3-R1后到达SW4上目的地址8.8.8.8,结果如图4所示。
(4)PC3使用IPv4地址经过IPv6隧道访问SW4 模拟的IPv4网络资源,源地址为192.16.1.2,经过设备SW5直接到达SW4上目的地址9.9.9.9,结果如图5所示。
结果显示:使用纯IPv6网络访问IPv6網络资源一切正常,在有双栈协议的网络上,IPv6与IPv4也可正常访问,即使是全面部署IPv6后,也可通过隧道访问IPv4网络。按照仿真实验结果在真实设备中写入上面相关配置后,可实现对应结果,证明仿真实验部署IPv6园区网络具有可行性。
4 结 论
从上述园区网络模拟实验中可以发现:根据互联网IPv6部署规模,园区网络访问互联网资源有多种方式可供选择。现阶段,较多的园区网络可使用现有设备选择双栈协议过渡,在当前互联网IPv6规模不足的情况下不影响网络业务正常使用,在IPv6网络规模不断增加的情形下,园区网络可由双栈网络逐渐转变为全IPv6网络,实现全IPv6网络访问。
参考文献:
[1] 曹利,陈亮,王军.基于GNS3仿真的QoS部署与性能测试 [J].计算机时代,2019(3):5-8.
[2] 孙光懿.基于GNS3的EIGRP路由设计与实现 [J].首都师范大学学报(自然科学版),2019,40(2):16-23.
[3] 吴志森.基于GNS3的IPSec-VPN仿真设计与实现 [J].九江职业技术学院学报,2019(1):21-23+17.
[4] 何淑玲,陈世清.IPv6规模部署下网络安全风险防范 [J].金融科技时代,2021,29(4):64-67.
[5] 高秋燕.基于高校的IPv6网络安全研究与实现 [J].信息系统工程,2021(2):55-56.
作者简介:向阳(1991—),男,汉族,四川简阳人,信息中心干事,助理工程师,理学学士,研究方向:网络安全、网络优化。

