Comparison of Spring Radish Varieties with Entire Leaves
Xiaomin YU Chenchen XIAO Weizhen LI Yijia GAO Shisheng LI




Abstract [Objectives] This study was conducted to select spring radish varieties with better growth, higher yield and better nutrition.
[Methods]A new spring radish combination (2019MUA×Lixiang) was obtained through traditional hybridization methods, and various characters of this line were compared with its parents and commercial spring radish. The radish varieties such as Lixiang radish, 2019MUA×Lixiang, 2019MUA, commercial variety Zhongluo No.1 and Huangzhou radish were respectively compared and studied in detail in terms of botanical characters, entire leaf bolting ratios, nutritional physiological indexes and so on.
[Results] The new radish combination 2019MUA×Lixiang has better indexes, and is more suitable for spring planting.
[Conclusions]The study provides a reference basis for the selection on radish planted in Spring.
Key words Spring radish; Botanical characters; Rate of bolting; Physiological index
Received: August 18, 2021 Accepted: October 20, 2021
Supported by Special Fund for the Central Government to Guide Parochial Science and Technology Development(2018ZYYD019).
Xiaomin YU (1984), female, P. R. China, master, devoted to research about plant biotechnology and academic publishing.
*Corresponding author. E-mail: 21581872@qq.com.
Spring radish refers to radish that is sown in spring and is one of the main vegetables in China. It has strong adaptability, good tolerance to storage and transportation and good commodity. It is also the main direction for the majority of farmers to choose[1]. For spring radish, we must choose varieties with strong winterness, fast growth at low temperatures, good quality, and strong disease resistance to minimize the risk of early bolting. The comparison experiment of radish varieties can provide a basis for the selection of radish varieties[2]. In order to select spring radish varieties with better growth, higher yield and better nutrition, we carried out a comparative experiment of multiple spring radish varieties, hoping to provide reference for the majority of farmers.
Materials and Methods
Experimental materials
The tested radish varieties were female parent radish material 2019MUA, male parent radish materials Lixiang radish, Lixiang×2019MUA, Zhongluo No.1 and Huangzhou radish. Zhongluo No.1 was provided by Southern Economic Crop Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and the rest were provided by Huangzhou Radish Research Center, Dabie Mountain Germplasm Resource Bank of Huanggang Normal University.
Experimental methods
From March to June in 2020, the experiment was set up in the germplasm nursery of Huanggang Normal University. The soil of the plots was sandy loam, and the previous crop was radish. Each plot was 21.6 m2, which was built with deep furrows and high rides, and hole sowing was adopted. Each radish variety was set with one treatment, in three replicates, arranged in randomized blocks. Sowing was carried out on March 21, 2020, with a plant spacing of 20 cm and a row spacing of 30 cm, and radishes were harvested on June 5, 2020, with a growth period of 70 d. Imge-JI.4 was used to determine botanical characters, and SPSS15 was adopted for variance analysis of related characters. The bolting situation was observed with naked eyes, and the bolting rate of radish plants was calculated for all tested plots (the percentage of bolted plants with flower buds in the total number of investigated plants). The fleshy roots of various varieties were collected in June and stored in a low-temperature refrigerator for the determination of nutritional physiological indexes such as vitamins, protein and dry matter, which were determined based on national food safety standards GB5009.86-2016 Determination of ascorbic acid in food , GB5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food and GB5009.3-2016 Determination of moisture in food .
Results and Analysis
Botanical characters of tested spring radish varieties
The root part of traditional radish is the main edible part, so its commerciality is mainly reflected in roots. In order to ensure the full growth and development of radish roots, early vegetative growth is very important. In the process of vegetative growth, the above-ground leaves obtain nutrients and energy through photosynthesis, and the underground roots absorb various nutrients from the soil through the root system. The growth and development processes of the tested spring radish varieties were observed (Fig. 1), and the roots, leaves and other important botanical characters of the spring radish varieties were also compared (Table 1).
From the perspective of root shape, all the tested spring radishes were long and cylindrical (Fig. 2). Table 1 shows that the fleshy roots of the new combination 2019MUA×Lixiang had the largest root length of 30.00 cm, the largest root width of 7.25 cm, and the largest root weight of 0.88 kg. In terms of yield, the new combination 2019MUA×Lixiang had the largest and most ideal yield. In addition, the leaves of 2019MUA×Lixiang were the most, and the height of the fleshy roots of 2019MUA×Lixiang exposed from the ground was the largest. On the whole, when choosing radish varieties, the weight of radish fleshy roots, the number of leaves, and the spread degree of leaves were all important reference indexes. The data also showed that planting 2019MUA×Lixiang could obtain largest fleshy root yield and good commodity benefit. In addition, 2019MUA×Lixiang was of the semi-upright type, which is more suitable for dense planting than radish of the horizontal leaf type.
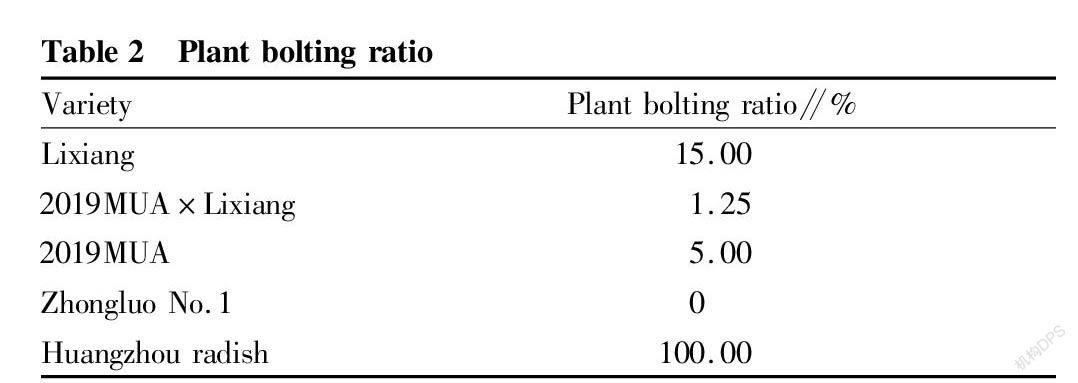
Plant bolting ratio
Plant bolting ratios were compared in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that among all tested radish types, all Huangzhou radish plants bolting ratio was the highest at 100%, and Lixiang radish was the second with a bolting ratio of 15%. The bolting ratios of 2019MUA×Lixiang and 2019MUA were moderate. Zhongluo No.1 had the lowest bolting ratio of 0%.
Radish bolting means that it is converted from vegetative growth to reproductive growth, and plant nutrition will be transferred from the vegetative organs to the reproductive organs. Fleshy roots are an important nutrient organ that affects the commercialization of radish. The growth and development of fleshy roots directly affects the economic value of radish. Therefore, once bolting, the nutrition of radish fleshy roots and other vegetative organs will be transferred to the reproductive organs, which will ultimately greatly affect the yield and nutrition of radish fleshy roots and limit the economic value of radish. A high bolting ratio will seriously affect the production and edible effect of radish. Combined with the bolting ratios of the tested varieties, Zhongluo No.1 and the new combination2019MUA×Lixiang were more suitable for spring planting.
Nutritional physiological indexes
Statistical comparison of nutritional physiological indexes of spring radish in Table 3 shows that the Vc content of Zhongluo No.1 was the highest, the protein content of 2019MUA was the highest, and the dry matter content of Huangzhou radish was the highest. Taken together, the nutritional and physiological indexes of 2019MUA×Lixiang and Zhongluo No.1 were good.
Vc can effectively enhance the human body’s antioxidant capacity and ultimately delay aging[3]. Therefore, the emergence of high-content Vc in radishes can better improve the existing medicinal effects of radishes, and make the use of radishes as a kind of medicine and food dual-purpose vegetable more obvious. The protein content index of radishes is a direct reflection of the content of flavor substances in radishes[4]. So the protein content of radishes is an index of the edible effect of radishes, and a high protein content of radishes can greatly promote the edible value of radishes. Dry matter content is one of the indexes for evaluating whether radishes are suitable for pickling[4], and a high content of dry matter indicates that radishes are more suitable for pickling.
Conclusions
By comparing the botanical characters, bolting ratios and nutritional physiological indexes of various tested spring radish varieties, the results showed that the spring radish combination 2019MUA×Lixiang had a strong growth trend, and its fleshy roots with a high yield and a long root type also had content advantages in nutritional physiological indexes such as vitamin C and dry matter. After bolting and flowering of plants, it has a significant impact on the growth and development of plant vegetative organs, and it is necessary to avoid bolting and flowering in advance for root and leaf vegetables[5-6]. The new radish combination 2019MUA×Lixiang in this study is better than its parental materials in flowering and bolting performance, and is very suitable for low temperature cultivation in spring. Huangzhou radish is a local characteristic vegetable of Huanggang. Because of its higher dry matter content, it is more suitable for pickling. The new combination has a dry matter content close to local Huangzhou radish which is very suitable for pickling, indicating that it is also suitable for pickling[7]. In addition, the combination 2019MUA×Lixiang is a plate-leaf radish line with a semi-upright growth type, and is thus more convenient for actual planting and harvesting. Therefore, the combination 2019MUA×Lixiang is a new combination with relatively good commodity. This study analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of each tested spring radish from the aspects of botanical characters, nutritional and physiological indexes and yield, which can provide reference basis for the majority of farmers to choose spring radish varieties.
References
[1] CHEN WS, ZHENG M. Comparison test of spring radish varieties[J]. Shanghai Vegetables,2005(2): 15-16. (in Chinese)
[2] XU JB, ZHANG XK, LI DC, et al. Comparison test of summer radish varieties[J]. Shanghai Vegetables, 2015(3): 19-20. (in Chinese)
[3] ZHUANG J, CHEN HJ, WU X.Research progress of vitamin and its derivatives in anti photoaging of skin[J]. China Cleaning Industry, (4): 7. (in Chinese)
[4] LI S, ZHANG N, LI J, et al. A new male sterile line of "Duanye-13" radish ( Raphanus sativus L.) produced by ethyl methanesulfonate mutagenesis[J]. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 2019(66): 981-987.
[5] FU J, PENG YB, WANG LL, et al. Investigation on characteristics of early flowering of Huangzhou radish and its countermeasures[J]. Journal of Huanggang Normal University, 40(6): 6. (in Chinese)
[6] REN ZW. Study on the bolting mechanism of welsh onion and regulation technology[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese)
[7] GE CJ, YAN L, LI SS, et al. National geographical indication protected product: Huangzhou radish[J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2021(2): 38-39. (in Chinese)
- 农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Rice Blast Resistance-associated Genes Based on Different RNA-seq Resources
- Research Progresses on QTLs for Main Grain Shape Genes in Rice
- Effects of Raising Chickens Under Moringa oleifera
- Preliminary Research on Radiation Breeding of Pteroceltis tatarinowii Maxim
- Occurrence and Chemical Control Techniques of Rice Black-streaked Dwarf Disease in Rongshui County
- Overview of Research on Tissue Culture and Rapid Propagation Technology of Pholidota

