Inflammatory Mechanism of Total Flavonoids of Chrysanthemum and Medicated Serum on Castrated Dry Eye Animal and Cell Models
SHI Jin,CHEN Li-Ho,LIU Qin-Hong,PENG Jun,TANG Yu,YAO Xio-Lei*,LIU Zu-Guo
a.Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
b.Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory for Prevention and Treatment of Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology Diseases with Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
c.Hunan Provincial Engineering and Technological Research Center for Prevention and Treatment of Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology Diseases with Chinese Medicine and Protecting Visual Function,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
d.Department of Ophthalmology,The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410007,China
e.Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology and Visual Science,Eye Institute of Xiamen University,School of Medicine,Xiamen University,Xiamen,Fujian 361102,China
f.Xiamen Eye Center of Xiamen University,Xiamen,Fujian 361001,China
g.Department of Ophthalmology,The First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China,Hengyang,Hunan 421001,China
ABSTRACT Objective To observe the effects of total flavonoids of chrysanthemum and medicated serum on the expression of related proteins in the lacrimal tissue and dry-eye cell models of male rabbits with dry eye caused by castration.Methods (1) 150 male Japanese rabbits were randomly divided into five groups,with 30 rabbits in each group:normal control group (group A),sham group (group B),model group (group C),androgen control group (group D) and total flavonoids of chrysanthemum treatment group (group E).The androgen deficiency dry-eye model was established by bilateral castration in groups C,D and E.Normal saline was administered to groups A,B and C by gavage;androgen (testosterone propionate) was injected into muscle in group D;and group E was given total flavonoids of chrysanthemum by gavage.All white rabbits were tested the Schirmer I test (SIT) and tear break-up time (BUT).After euthanasia,tear gland tissue was harvested so that we could observe pathological changes in the expression of related inflammatory factors in the lacrimal gland tissue.The expression of interleukin-1β (IL-1β),tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) was detected in the lacrimal gland tissue by immunohistochemistry.Reverse transcription PCR was used to quantit atively detect expression of TGF-β1 mRNA.(2) Male Wistar rat lacrimal epithelial cells were used to establish a model of eye stem cell apoptosis caused by androgen levels.The blank control group was set up without androgen culture,the control group with androgen culture,and the total flavonoids of chrysanthemum group without androgen.The MTT method was used to determine the optimal intervention dosage of drug-containing plasma.Western blot and QPCR were used to detect the expression of AR mRNA,NF-κB phosphorylated protein and TGF-β1 in lacrimal epithelial cells,and the androgen-like effect of total flavonoids of chrysanthemum was observed.Results (1) Immunohistochemistry showed that groups A,B,D and E had significantly lower expression of IL-1β and TNF-α than group C (P <0.05);among these,group E had slightly higher expression than group D (P >0.05).RT-PCR results showed that the relative expression of TGF-β1 mRNA in groups A,B,D and E was significantly higher than in group C (P <0.05),and the relative expression of TGF-β1 mRNA in groups D and E was higher than that in groups A and B (P <0.05).(2) Using the MTT method,the final concentration of interfering cells was calculated to be 13.2%.The expression of AR protein,NF-κB and TGF-β1 in the chrysanthemum flavonoid plasma intervention and testosterone propionate intervention groups was enhanced,and there were significant differences relative to the blank group(P <0.01).The expression level of NF-κB in the total flavonoid containing plasma intervention group was lower than that in the testosterone propionate intervention group (P <0.01).Conclusions The total flavonoids of chrysanthemum can inhibit IL-1β and TNF-α expression in the lacrimal gland tissue of castrated male rabbits with dry eye to increase synthesis of TGFβ1 mRNA and TGF-β1,thereby inhibiting the inflammatory response.The medicated plasma with total flavonoids of chrysanthemum promotes expression of AR mRNA,upregulating expression of NF-κB,further promoting upregulation of TGF-β1 protein expression in lacrimal epithelial cells,inhibiting inflammation by regulating related proteins,and ultimately alleviating the symptoms of dry eye.
Keywords Total flavonoids of chrysanthemum Dry eye disease Interleukin-1β (IL-1β)Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)Androgen receptor (AR)Nuclear factor-к-gene binding (NF-кB)
1 Introduction
Dry eye disease is an ocular surface disease with symptoms that include a sense of dryness,friction,burning,fatigue and visual fluctuation[1].In China,dry eye disease accounts for more than 30% of all ophthalmic outpatients[1],and more than 50% in Japan[2].Due to the high incidence of dry eye,the disease is familiar to many people.Inflammation usually causes dry eye disease[3].While,clinical researches have shown that elderly and perimenopausal women acquire dry eye disease more easily because of their lower sex hormone levels[4-8],and because eye tissue is a target organ for sex hormone action[9].Sex hormones can promote tear secretion and lipid synthesis in the eyes[10,11],thus regulating tear film stability.Therefore,disordered sex hormone levels can disrupt tear film stability.Among these,androgen deficiency can cause apoptosis of the lacrimal gland and affect the normal structure and function of tear film[12],causing dry eye disease[13].Supplementation with androgens can solve this situation,but has major side effects[14-16].Many drugs in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)contain flavonoids,which are similar to androgens in their chemical structure.These have broad application prospects in the field of dry eye treatment,and may replace hormone therapy because of their lower relative side effects.For example,the extract of Buddlejae Flos (Mi Meng Hua,密蒙花) has a strong androgenic effect and can treat dry eye disease[17-20].We are developing new Chinese medicine to expand the selectivity of TCM extracts that can replace hormones.In TCM theory,chrysanthemum can clear the liver and improve vision,and it is frequently used to treat eye diseases.It contains flavonoids[21],and therefore has an androgen-like effect[22].Our team has studied the total flavonoids of chrysanthemum for some time,and designed experiments to verify their function.Our previous experiments have confirmed that total flavonoids of chrysanthemum have an androgen-like effect[23]and can maintain a basic level of tear secretion and tear break-up time (BUT) in castrated male rabbits[24,25].This article will focus on the inflammatory involvement of total flavonoids of chrysanthemum.
2 Materials
2.1 Experimental subjects
(1) 150 healthy 2-month-old male rabbits (species of Japanese white rabbit,SPF grade,outbred line,provided by Shanghai Shrek Experimental Animal Co.,Ltd.,License key:2012-0361) were selected as experimental animals,with weight of 2 - 2.5 kg.The model has a success rate of 97%.(2) One-month-old healthy Wistar male rats,weighing 140 - 200 g [SPF grade,outbred line,provided by Ganzhou Animal Husbandry Research Institute,License key:SCXK(Gan)2013-006] were used to isolate and culture lacrimal gland epithelial cellsin vitro.
2.2 Experimental medicine
Total flavonoids of chrysanthemum (No.JH130804,Suzhou Institute of Industrial Technology,drug purity 97%) were used for experiments.
2.3 Reagents
Rutin reference (rutin >98%;batch number MUST-12040302,Chengdu Must Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,Sichuan,China).IL-1β,TGF-β1,TNF-αmonoclonal antibodies,SABC kit and DAB developer (Wuhan Boster Bioengineering Co.,Ltd.,Hubei,China).Firstchain cDNA synthesis kit,Trizol,prime,2×all-inone TM QPCR mix (Takara,Japan),25 g/L testosterone propionate injection (Jinyao Amino Acid Co.,Ltd.,Tianjin,China).RNase inhibitor (Promega,USA),ethidium bromide (Hangzhou Sijiqing Biological Engineering Materials Co.,Ltd.),IQ5 Real Time PCR Detection System:(Bio-Rad),Oligo (DT) 15(PROMEGA,USA),First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit(Genecopoeia,USA),Reagents and instruments Trizol (Invitrogen,USA).
2.4 Experimental equipment
Thermo Shandon Model 325 paraffin microtome(Shandon Co.,UK),Motic B5 micro camera system(McAudi Industrial Group),and TU-1901 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Beijing General Analysis General Instruments Co.,Ltd.,China),EYELA SB-1100 Rotary Evaporator (Shanghai Ailang Instrument Co.,Ltd.,China),DNP-9162 Electrothermal Constant Temperature Incubator (Shanghai Jinghong Experimental Equipment Co.,Ltd.,China),IQ5 Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad,USA),AL-204 Electronic Balance (Mettler Toledo Company),and MIAS-1000 high-resolution color pathology graphic analysis system.
2.5 Primer sequence
Provided in the public domain by the National Center for Biotechnology Information,Bethesda,MD.
TGF-β1 primers:
upstream chain:5′-ATGGTGGACCGCAACAAC-3′,
downstream chain:5′-ACAGCAATGGGGGTTCTG-3′.
β-actin primers:
upstream chain:5′-TCCTTCCTGGGCATGGAGTC-3′,
downstream chain:5′-GGATGTCCACGTCGCACTT C-3′.
GAPDH primers:
upstream chain:5′-GCCTTCCGTGTTCCTACCCC-3′,
downstream chain:5′-CGCCTGCTTCACCACCTTC T-3′.
AR primers:
upstream chain:5′-CAAAGGGTTGGAAGGTGAGAG T-3′,
downstream chain:5′-AGAGCGAGCGGAAAGTTGT AGTA-3′.
ACTB primers:
upstream chain:5′-CCGTAAAGACCTCTATGCCAAC A-3′,
downstream chain:5′-GAGCCACCAATCCACACAGA GT-3′.
TGF-β1 primers:
upstream chain:5′-ATACGCCTGAGTGGCTGTCT-3′,downstream chain:5′-TGGGACTGATCCCATTGAT T-3′.
3 Methods
3.1 Animal experiments
3.1.1 Animal grouping150 healthy 2-month-old experimental rabbits (SPF grade,outbred line),weighing 2 - 2.5 kg were grouped into 15:A1,A2,A3,B1,B2,B3,C1,C2,C3,D1,D2,D3,E1,E2 and E3.Each group included 10 rabbits.A,B,C,D and E represent the normal,the sham operation,the model,the androgen control treatment and the chrysanthemum total flavonoid treatment groups,respectively.Groups with numbers 1,2 and 3 were fed for one,three and five months,respectively.
3.1.2 Animal modelingCastration was used to create the model in experimental rabbits[26,27].Group A was a blank group without treatment.Group B underwent false castration as a control;only the scrotums were cut,without removal of the testicles.Bilateral orchiectomy (ORX) was administered to groups C,D and E by removing the testes and epididymides of male rabbits.The Schirmer I test(SIT) and tear film BUT were used to determine the success of modeling.Replication in the first,third and fifth months after castration indicates that mild,moderate and severe dry eye models have been established.
3.1.3 Administration methodGroups A,B and C were administered intragastrically 5 mL normal saline once daily;group D was injected intramuscularly (thigh) with androgens (testosterone propionate) once daily;group E was orally administered total flavonoids of chrysanthemum (dissolved in physiological saline at adult equivalent dose) once daily.Groups 1,2 and 3 were administered by gavage for one,three and five months,respectively.During the experiment,the rabbits were fed conventional feed.
3.1.4 Sampling methodAnimals were sacrificed(intravenous air injection),and the lacrimal glands were removed immediately.The lacrimal glands were seperated into two parts:one for 4% paraformaldehyde preservation,conventional paraffin embedding,and continuous sectioning,suitable for immunohistochemical detection;another for cryopreservation,suitable for reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR detection).
3.1.5 Detection methodsIL-1β,TNF-α,TGF-β1 and TGF-β1 mRNA detection was used to investigate the inflammatory mechanism via two methods.
IL-1β,TNF-αand TGF-β1 were detected by immunohistochemistry.Cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and embedded in paraffin for immunohistochemistry.Each group of paraffin blocks was sliced continuously by a paraffin slicer,dewaxed to water,and washed twice with distilled water for 2 min each time.The immunohistochemistry SABC method was used for detection,and the operation was strictly in accordance with instructions.Immunohistochemical staining of lacrimal duct cells and acinar epithelial cells was observed under a microscope.The average optical density of protein staining was measured under a window area of 1.271×106μm2using a Motic B5 micro camera system and an immunohistochemistry measurement system with a pixel length of 2.105 μm2.The total number of inflammatory cells in 5 - 7 high-power fields (400×magnification) was randomly counted,and the average number of cells in these fields was calculated.
The level of TGF-β1 mRNA expression was measured by RT-PCR.The TAQMAN probe method was used to detect TGF-β1 mRNA in rabbit lacrimal gland tissue,and the amount of sampleβ-actin mRNA was detected as an internal reference for relative quantification of target gene detection.Relative expression of TGF-β1 mRNA=TGF-β1 mRNA optical density value/β-actin mRNA optical density value,and the relative expression of TGF-β1 mRNA=TGF-β1 mRNA optical density value/β-actin mRNA optical density value.
3.2 Cell experiments
3.2.1 Extraction of lacrimal gland epithelial cellsMale Wistar rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation and soaked in 75% alcohol for 15 min.Lacrimal glands were removed according to conventional aseptic operation,then washed with phosphate bufler saline (PBS) three times for 3 min each time.Then,ophthalmic scissors were used under a microscope to remove the fibrous connective tissue and adipose tissue next to the gland,as well as the fibrous connective tissue and blood vessels that extend into the tissue;the remainder was the lacrimal tissue.
3.2.2 Culture of lacrimal gland epithelial cellsLacrimal gland tissue was placed in a dish and rinsed with PBS 1 - 2 times for 5 min each.Rinsed tissue was cut into three pieces of 1 - 2 mm each time.Then,2 g/L type II collagenase was added,and the sample was shaken and digested at 37 °C on a thermostatic constant temperature shaker for 25 min.Culture solution was added to terminate digestion,the glandular cell mass was rendered into a single cell suspension.The suspension was filtered through a 200-mesh nylon sieve and centrifuged at 800 r/min for 5 min.The supernatant was removed,a small volume of D-Hank’s solution was added,and the mixture was centrifuged again at 800 r/min.4 - 5 mL of culture solution was added to the precipitate,which was then pipetted into a single-cell suspension,inoculated into a culture bottle,and allowed to stand for 20 min.When observed under an inverted microscope,once the cells were partially adhered and did not float after a little shaking,the culture solution was transferred to another culture bottle together with the unattached cells,and this was repeated three times.Cells were counted,and culture flasks were inoculated in order to observe cell morphology and growth status.
3.2.3 Measuring the amount of medicated serum
The MTT method was used to determine the amount of chrysanthemum total flavonoid medicated serum,measure the absorbance of each concentration of blank serum after treatment of lacrimal gland epithelial cells,and calculate the inhibition rate of the blank serum on the cells:cell inhibition rate=(1 −drug-added group A value/control group A value)×100%.Excluding blank serum concentrations with an inhibition rate of <20%,concentrations for screening the intervention concentration of drug-containing serum were 1%,5% and 10%.The average absorbance and inhibition rate of drug-containing serum at each dose and concentration after intervention in lacrimal epithelial cells were measured.After excluding concentrations with an inhibition rate greater than 20%,the concentrations available for screening were 1%,5% low-dose and 10% medium dose.The concentration at which the inhibition rate is 50%,that is,the concentration at IC50,is the concentration of the drug-containing serum of the interventional cells.The formula is Lg IC50=[Note:Xm=Lg maximum dose;I=Lg (maximum dose/adjacent dose);P=sum of positive response rates;Pm=maximum positive reaction rate;Pn=minimum positive reaction rate].The maximum and minimum positive reaction rates in the formula are the maximum and minimum inhibition rates,respectively.
3.2.4 Establish a cell model and serum interventionFor each group,cultured cells were placed in a DMEM/F12 low-sugar medium containing 15% fetal bovine serum,and cultured at 37 °C and 5% CO2saturation humidity.The cell concentration was adjusted to 1×106/L with culture medium,and cells were seeded in a culture flask when they were in good condition.Cultured cells were randomly divided into an androgen-free flavonoid treatment group (group F),an androgen-containing control group (group G) and an androgen-free blank group(group H).After the cells were fused for 2 d,medicated serum was added to start the intervention.After 48 h of intervention,a final concentration of 100 μmol/L H2O2was added,and the cells were cultured for 60 min to induce apoptosis.
3.2.5 Detection methodTo investigate inflammatory mechanisms,western blot and QPCR detection of AR,NF-κB and TGF-β1 mRNA expression levels were performed.
AR and ACTB mRNA expression levels were detected in lacrimal epithelial cells after medicated serum intervention as follows.PCR reaction were combined and placed in an ice box:10 μL QPCR mix,2 μL primer mixture,6 μL RNase-Free Water,2 μL cDNA.All components except cDNA were combined into a master mix,and 2 μL of each cDNA template was added to 18 μL of this solution.The mixture was centrifuged briefly in a vertical centrifuge to evenly blend the mixture with the template and collect both in the bottom of the centrifuge tube.Pre-denaturation of the template was performed before the QPCR reaction.This was usually set to 95 °C for 2 min;complex or high-GC templates were extended to 5 min.Pre-denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min,denaturation at 95 °C for 15 s,annealing extension at 60 °C for 30 s;denaturation and annealing steps were repeated for a total of 40 cycles.Analysis of melting curve(optional):95 °C for 15 s,60 °C for 15 s,and 95 °C for 15 s.The Ct value and relative expression of genes between different samples was obtained based on instrumental analysis.After drug intervention,QPCR was used to detect the expression of AR mRNA in rat lacrimal epithelial cells,and the amount of ACTB mRNA in the cells was used as an internal reference to perform relative quantitative detection of target genes in the samples.
Detection of AR,NF-κB and TGF-β1 phosphorylated proteins in lacrimal epithelial cells after medicated serum intervention was conducted as follows:culture medium containing serum was aspirated from well-grown lacrimal epithelial cells,serumfree medium was added,and cells were allowed to stand for 12 hours.Expression of AR,NF-κB and TGFβ1 phosphorylated protein was detected by western blot.
Detection of TGF-β1 mRNA expression proceeded as follows.Trizol reagent was used to extract total RNA from cells.The QPCR test was performed with a dye method (SYBRGreenI) to perform a relative quantitative analysis of TGF-β1 mRNA.The experiment was designed according to theΔΔCt analytical method:clear control (reference) samples and processed (unknown) samples were used to obtain the Ct value of the target gene and its housekeeping genes (GAPDH and ACTB) in all samples.The difference between the unknown gene and the housekeeping gene in each sampleΔCt:ΔCt=Ct unknown − Ct housekeeping gene,and the difference between theΔCt of the unknown sample gene and the control sampleΔCt:ΔΔCt=ΔCt unknown −ΔCt control.2−ΔΔCtis the relative content.
3.3 Statistical analysis
Statistical software SPSS 24.0 was used for statistical analysis.The data were expressed as mean ±standard deviation (SD) and a two-sided test was performed.First,the experimental data were tested for normality and homogeneity of variance.If the data were normally distributed and the variances were homogeneous,an analysis of variance was used.Multiple groups were compared after treatment,and the values before treatment were used as covariates for covariance analysis.Comparisons before and after treatment were performed using the pairedttest.If the variance of the data was not uniform,the Satterthwaite method was used to perform a correctedttest.If the data are non-normally distributed,the Wilcoxon rank sum test was used.P<0.05 indicates that the difference between the data is statistically significant,andP<0.01 indicates that there is a significant difference between the data.
4 Results
4.1 Model validation
In our previous study,we measured ocular surface parameters using the SIT and tear film BUT to determine whether the model was established successfully.Results indicated that,in group C,basal tear secretion and tear film rupture time decreased.After the intervention with total flavonoids of chrysanthemum,the amount of tear secretion increased and the time of tear film rupture was prolonged.There was no significant difference between group D and group E (Table1).
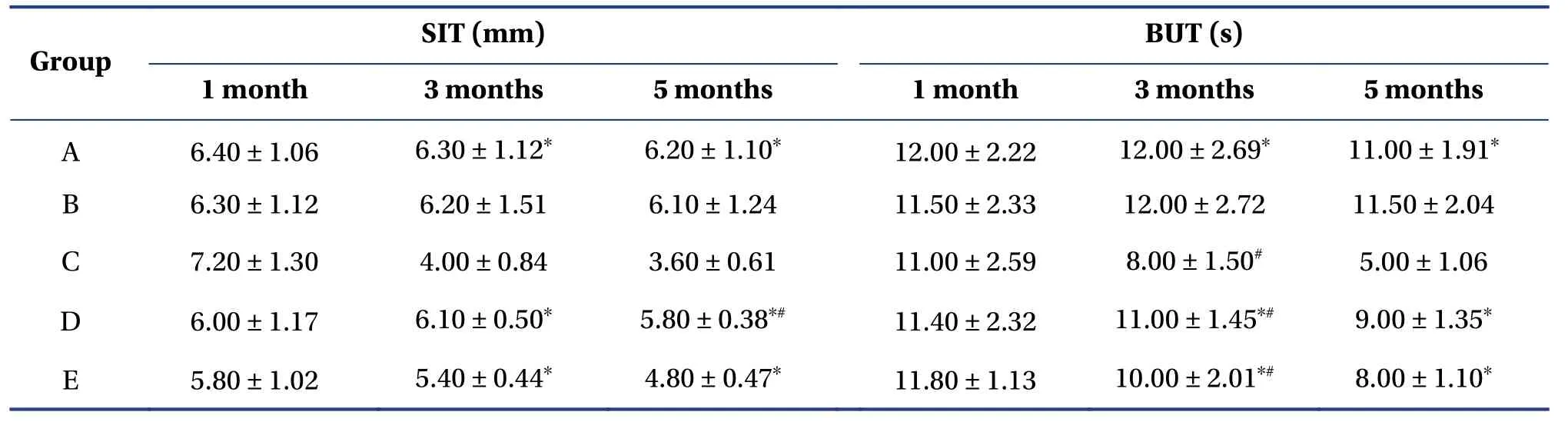
Table1 Comparison of SIT and BUT values in each group (mean ± SD,n=10)
4.2 Animal experiment results
4.2.1 Pathological changesFor IL-1βand TNF-α,normal lacrimal gland epithelial cells have no obvious brown-yellow granules in the cytoplasm.In the experiment,groups A and B showed a few granules after 1,3 and 5 months,indicating that IL-1βand TNF-αare not clearly expressed.However,many particles appeared in Group C after one month,and more tan particles appeared after three and five months,demonstrating that IL-1βand TNF-αexpression was strongly positive.At any given time,only a few brownish-yellow particles appeared in groups D and E,which roughly resembled groups A and B in this respect (Figure1 and 2).
For TGF-β1,normal lacrimal epithelial cells have no obvious brown-yellow granules in the cytoplasm,that is,no positive expression.In the experiment,groups A and B had no obvious brown-yellow particle deposition;that is,there was no positive expression.Group C had a few brown-yellow granules after three months,suggesting that the histopathology had changed.After five months,there was no change in pathology,which showed no positive expression.Groups D and E both had many brown particles after one,three and five months,indicating positive expression of TGF-β1 (Figure3).
4.2.2 Comparison of average optical densityGroups A,B,D and E expressed lower levels of IL-1βand TNF-αthan group C (P<0.05).Group A had significantly lower IL-1βlevels than group E after three and five months,and group B expressed lower levels than group E after one and three months.Group A levels after five months and group B levels after three months were lower than those in group D(P<0.05).However,Group E values were slightly higher than those in group D (P>0.05).After five months,group A expressed lower TNF-αthan groups D and E,group B expressed lower TNF-αthan group E (P<0.05),and group E slightly exceeded group D(P>0.05).For levels of TGF-β1,groups A,B and C were lower than groups D and E at any time point(P<0.05).Group A was lower than gro up C after three months,and group A was lower than group B after five months (P<0.05) (Table2).
4.2.3 RT-PCR detection of TGF-β1 mRNA expressionRT-PCR showed that the relative expression level of TGF-β1 mRNA in the other groups was significantly higher than that of the group C (P<0.05),and groups D and E were significantly higher than groups A and B (P<0.05).After five months,group D was higher than group E (P<0.05)(Table3 and Figure4).
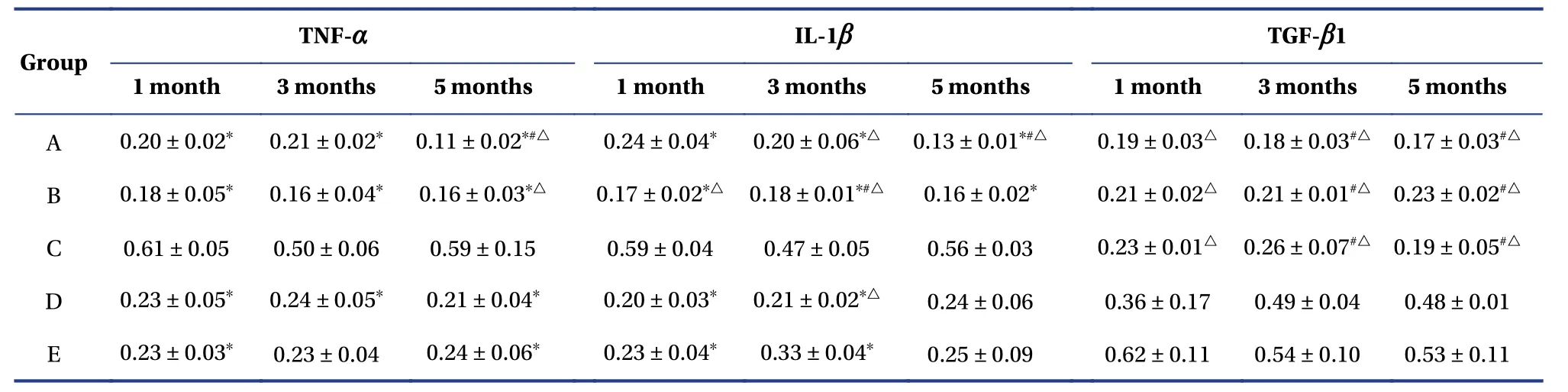
Table2 Average optical density of TNF-α,IL-1β and TGF-β1 positive cells in lacrimal glands in each group(mean ± SD,n=10)
4.3 Cell experiment results
4.3.1 Culture of lacrimal epithelial cellsand identification of rat lacrimal epithelial cellsAfter lacrimal gland cells were cultured for 36 h,it was observed for the first time that most of the cells were adherent,appearing as flat circles or ellipses,with partially protruding pseudopods.After 72 h,most of the cells began to stretch,and the nucleus was visible.It was gradually observed that the cells were round or oval.The cell body was hypertrophic and translucent,the nucleus was located in the center,the cell membrane was clear,and the growth was more active.At day 10,cultured cells were fused,and a small amount of fibroblasts were generated.After the second passage,cells were exchanged for the first time after 48 h.It was found that the cells were basically adherent,all of them were stretched and grown,and the monolayers were fused after 7 d.However,the cells grew slowly and aged after entering the third passage,after which they could not be passaged again.Therefore,all cells used in this experiment were primary cultured cells.The pancytokeratin antibody response of the cultured second-generation lacrimal epithelial cells showed that brown or brown-yellow positive particles were uniformly distributed in the cell cytoplasm,with a positive rate of more than 98% (Figure5).
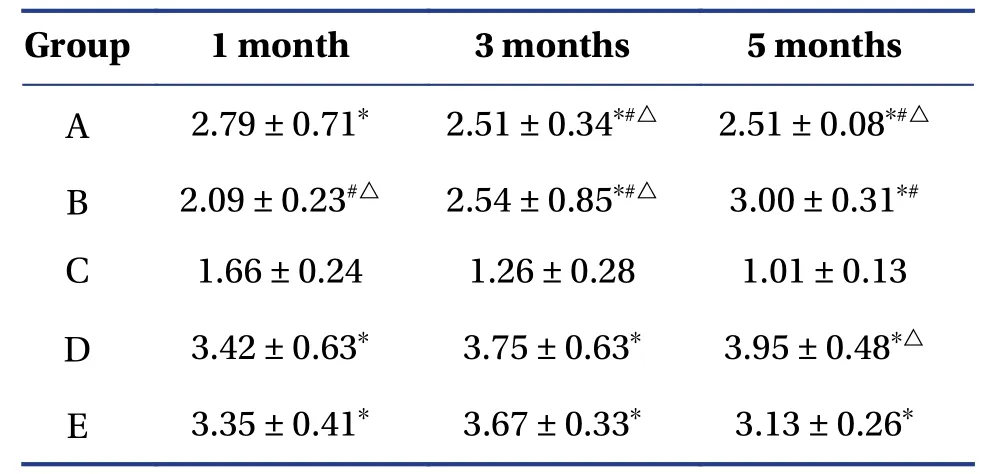
Table3 Relative expression of rabbit lacrimal gland TGF-β1 mRNA (mean ± SD,n=10)
4.3.2 Western blot detection of AR,NF-κB and TGFβ1 expressionFor AR,it can be seen from the electropherogram that each group has a positive band at a relative molecular weight of 117 kD,and a small amount of AR protein is expressed in the blank plasma group.In Table4,Figure6 and 7,it can be seen that the expression of AR protein in the plasma intervention group containing chrysanthemum flavonoids was enhanced,which was significantly different from the blank group (P<0.01).Expression of AR protein was enhanced in the testosterone propionate intervention group,which was significantly different from the blank group(P<0.01),but there was no significant difference compared with the chrysanthemum flavonoidcontaining plasma intervention group (P>0.05).
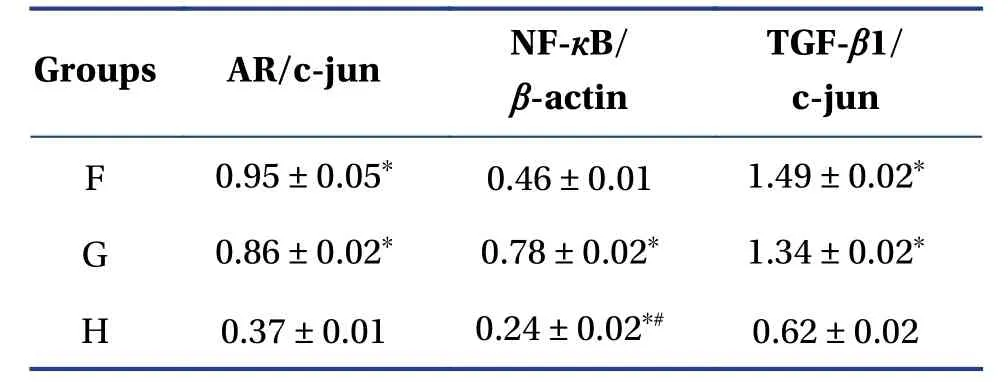
Table4 Relative expression levels of AR,NF-кB and TGF-β1 in different samples (mean ± SD)
For NF-κB,a positive band appeared for each group at a relative molecular weight of 65 kD.There was a small amount of NF-κB expression in the blank plasma intervention group.Expression of NF-κB in the testosterone propionate intervention group increased,which was significantly different from the blank plasma intervention group.The expression level of NF-κB in the chrysanthemum total flavonoidcontaining plasma intervention group was increased,and the difference was significant compared with that in the blank plasma intervention group.The expression level of NF-κB in the total flavonoid-containing plasma intervention group was lower than that in the testosterone propionate intervention group,but there was a significant difference between the two.
For TGF-β1,each group had a positive band at a relative molecular weight of 225 kD and a small amount of TGF-β1 protein was expressed in the blank plasma group.Expression of TGF-β1 protein in the chrysanthemum-containing flavonoid plasma intervention group was enhanced,and there was a significant difference from the blank group (P<0.01).Expression of TGF-β1 protein in the testosterone propionate intervention group was enhanced,which was significantly different from the blank group (P<0.01),but there was no significant difference compared to the chrysanthemum flavonoid-containing plasma intervention group (P>0.05).
4.3.3 QPCR detection of AR mRNA and TGF-β1 mRNA expressionQPCR showed that,after treatment with lacrimal epithelial cells by chrysanthemum-containing serum,AR mRNA expression in cells was increased;AR expression difference was 2.34 ± 0.39,higher than in the blank group.In addition,androgens can also increase the AR mRNA content in cells,and the AR expression difference fold is 4.05 ± 0.63,a stronger effect than produced by the chrysanthemum-containing serum.This may be related to the fact that androgens are naturally AR ligands and can directly contact AR cells.
Regarding TGF-β1,after the chrysanthemum drug-containing serum interfered with lacrimal epithelial cells,it increased the expression of TGF-β1 mRNA in the cells;the fold difference of TGF-β1 expression was 4.56 ± 1.04,higher than that in the blank group.In addition,androgens can also increase the level of TGF-β1 mRNA in cells;the fold difference in TGF-β1 expression is 4.04 ± 0.20,roughly equivalent to that in the chrysanthemum-containing serum.
The ACTB and GAPDH amplification Ct values of different samples are shown in Table5.ACTB and GAPDH have good amplification effects in each sample,indicating that there was no problem with reverse transcription of any sample (Table6 and Figure8).F,androgen-free flavonoid treatment group.G,control group containing androgen.H,control group without androgen culture.
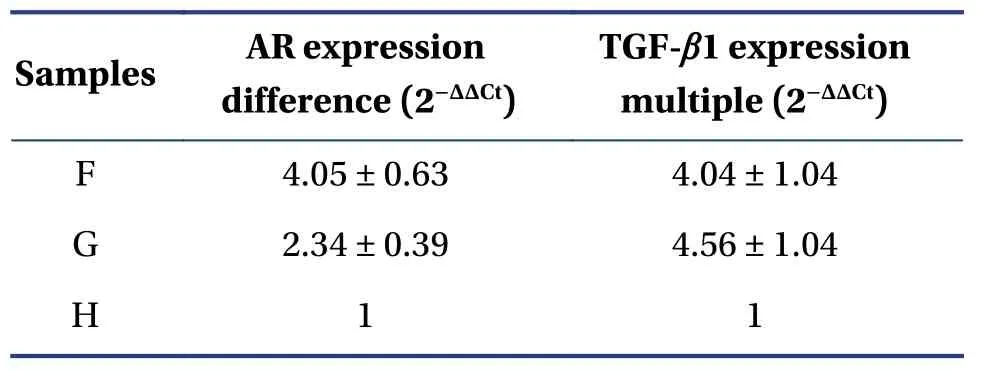
Table5 Differing AR and TGF-β1 mRNA expression in different samples (mean ± SD)

Table6 Ct values of ACTB and GAPDH for each sample (n=4)
5 Discussion
5.1 Therapeutic effects
In a previous study,we measured the ocular surface parameters using the SIT and tear film BUT.From these data,we found that androgen deficiency is a high-risk factor for dry eye.Similar patients need to have interventions in time to prevent the occurrence of dry eye disease.After the disease has lasted for a long time,we found that the role of total flavonoids of chrysanthemum in maintaining tear secretion is reduced;however,tear film stability is not affected.Overall,total flavonoids of chrysanthemum can maintain the basic secretion of tears,prolong the BUT,and maintain the stability of the tear film,making it a good choice for preventing and treating dry eye disease.
5.2 Androgen-like effects and inflammatory mechanism
Sex hormones are closely related to the pathogenesis of dry eye;a decrease in androgen levels can lead to dry eye[28].Some researchers have tested the relationship between serum metabolites and dry eye disease by using the metabonomics method.They found that dry eye disease is highly correlated with decreased serum androgen[29].Our previous research found that the total flavonoids of chrysanthemum can significantly increase the density of androgen receptors in the lacrimal gland[23].
In fact,androgen can cause dry eye disease by affecting the meibomian gland or lacrimal gland.The meibomian gland contains androgen receptor mRNA,androgen receptor protein in the nucleus of the acinar epithelium,and 5α-reductase mRNA of type 1 and type 2.Androgen can regulate meibomian gland function by binding with its receptor,controlling the quality or quantity of lipid produced by the tissue,and promoting formation of the lipid layer of the tear film.With weakening of androgen synthesis,androgen deficiency leads to changes in lipid distribution of meibomian gland secretion,tear film instability,and dry eye evaporation,eventually resulting in meibomian gland dysfunction and related dry eye disease[30].Additionally,the lacrimal gland also contains androgen receptors.Androgen deficiency directly affects the function of the lacrimal gland in secreting tears,which also leads to dry eye disease.
Inflammation is an important pathogenic mechanism of dry eye disease[13].Androgen has an immunosuppressive effect,which can maintain the balance of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors[31].Therefore,we speculate that the mechanism of total flavonoids from chrysanthemum in treating dry eye disease may also be related to inflammatory factors.We took this speculation as a starting point for the design and operation of the experiment.According to previous literature,we selected three indicators closely related to dry eye disease:IL-1β,TNF-αand TGF-β1.IL-1βand TNF-αare the most common inflammatory factors in the body.They are produced by monocytes and macrophages.Their release can destroy the structure and function of the lacrimal gland and ocular surface.TGF-β1 is a growth transforming factor that can modulate lacrimal gland acinar cells to promote their differentiation and repair,thus inhibiting the expression of IL-1β,TNF-αand other inflammatory factors[19].Therefore,we conducted further research on the mechanism at the cellular level.In our study,we found that the total flavonoids of chrysanthemum have a structure and effect similar to that of testosterone propionate.After combining with AR,the total flavonoids of chrysanthemum promotes amplification of AR mRNA in lacrimal epithelial cells and further upregulates AR.NFκB is a downstream effector protein of AR.After total flavonoids of chrysanthemum combines with AR,they enter the nucleus to activate NF-κB.During the continuous activation and inactivation of NF-κB,it stimulates cell differentiation.This facilitates repair and immune regulation,thereby inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors such as IL-1βand TNF-α,and inhibiting the occurrence of inflammation,thus indicating the mechanism of total flavonoids of chrysanthemum in androgen-deficient dry eye.
5.3 Summary and prospect
Chrysanthemum is a Chinese medicine demonstrating excellent safety and usefulness in both medicine and food.Compendium of Materia Medica(Ben Cao Gang Mu,《本草纲目》) records that chrysanthemum is sweet in nature of medicinals,cold in flavor,and has the effect of dispersing wind-heat,pacifying the liver and improving vision.TCM doctors used it to treat eye diseases and have achieved good efficiency.We conducted modern research on chrysanthemum and found that total flavonoids are one of its active compounds[23].In the past,we proved that the total flavonoids of chrysanthemum can prevent and treat dry eye disease by inhibiting the apoptosis of lacrimal gland cells by Bax and Bcl-2[24],as well as Fas and FasL[25]in castrated male rabbits.
This study further verifies the mechanism of action with respect to inflammatory factors.Inflammation is one of the most important mechanisms of dry eye[13].Irrespective of the stage of dry eye,the immune system begins to participate in it and produces inflammation;thus,the ocular surface adapts to stress conditions and returns to a stable state.If dry eye is not treated in a timely way,the inflammation will continue to worsen and circulate,eventually leading to refractory dry eye and irreversible ocular surface damage.Therefore,anti-inflammatory treatment of dry eye is necessary.This study confirmed that the total flavonoids of chrysanthemum can upregulate AR,activate NF-κB,stimulate TGF-β1 differentiation,and inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors such as IL-1βand TNF-α.Our research group will proceed with the following work:conduct relevant research on the total flavonoids of chrysanthemum-containing serum,develop new Chinese medicines such as chrysanthemum granules,and carry out clinical research,eventually realizing chrysanthemum’s further clinical application.
Acknowledgements
We thank for the funding support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81260550),Key Laboratory Construction Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Five Sense Organ Diseases in Hunan Province (No.2017TP1018) and Key Subject Construction Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Ophthalmology of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine(No.ZK1801YK015).
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
——以《本草纲目》日译为中心
 Digital Chinese Medicine2020年4期
Digital Chinese Medicine2020年4期
- Digital Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Acupuncture and Related Therapies for Hyperlipidemia:A Network Meta-Analysis
- Yi Qi Jie Du Formula and Salinomycin Combination Treatment Mediates Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Stem Cell Proliferation,Migration and Apoptosis via CD44/Ras Signaling Pathway
- Silkworm Extract Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Protects Pancreatic β-cell Functions in Rats
- Fabrication of A Folic Acid-Modified Arsenic Trioxide Prodrug Liposome and Assessment of its Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Activity
- Network Biological Modeling:A Novel Approach to Interpret the Traditional Chinese Medicine Theory of Exterior-Interior Correlation Between the Lung and Large Intestine
- Identification of Potential Flavonoid Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease 6YNQ:A Molecular Docking Study
