Status Quo and Future Development of Female Genital Cosmetic Surgery (Intimate Surgery)
Yang LIU,Sunxiang MA,Chen CHENG
Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital,Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine,Shanghai 200011,China
SUMMARY With advances in the standards of living and public perceptions,female genital cosmetic surgery is becoming a new hot topic in the field of plastic surgery,gaining considerable interest recently among beauty seekers and professionals alike.However,the needs of beauty pursuers seem to be exuberant but vague; on the other hand,practitioners who have received strict professional training are still desperately needed.Additionally,interestdriven marketing and promotion render the field prone to chaos,resulting in widespread attention and concerns regarding the scientificity,safety,effectiveness,and necessity of the performance of multiple treatment procedures.Extensive survey of the relevant literature was performed,and several beauty seekers as well as surgeons with working experience of pertinent techniques were consulted,in order to examine the current status and future developments of this field.
KEY WORDS Female genital cosmetic surgery; Labioplasty; Vaginal rejuvenation; Laser therapy
NOMENCLATURE
While its origins remain unclear,the expression“intimate surgery” has been widely accepted by beauty seekers and those served by practitioners.“Intimate surgery”,nevertheless,is not a proprietary term,and its use should be avoided in a formal,academic setting.The academic wording of “female genital cosmetic surgery”calls for a more comprehensive application thanks to its accuracy and standardization.Expressions such as“vaginal rejuvenation”,“cosmetic vaginoplasty”,and “aesthetic genitalia surgery” are also used in the literature,but “female genital cosmetic surgery” is the nomenclature well recognized by the academic community.
CONTENTS AND CATEGORIES
Although there is an increasing trend in the demand for “intimate surgery”,some female patients seeking surgical alteration exhibit a relatively limited and vague perception of the vulvar units and the treatment as well as surgical outcomes of “intimate surgery”.
Anatomically,female genital cosmetic surgery focuses on the perineum,comprising the mons pubis,labia majora,labia minora,clitoris,clitoral prepuce,urethra,urethral orifice,vagina,vaginal orifice,vaginal vestibule,hymen,posterior labial symphysis,perineal body,rectum,and anus.
Female genital cosmetic surgery,when not medically indicated,is offered to beauty pursuers seeking surgical modifications for an aesthetically superior vulva shape or greater sexual satisfaction.
Each structural unit of the perineum can be targeted in surgical intervention because the size,color,texture,and even the relative position between them may alter the shape and aesthetics of the vulva.Other units related to sexual sensitivity and experiences,such as the clitoris,vagina,external vaginal orifice,and perineal body,have become the objects of treatment primarily for enhancing sexual function.
In summary,all parts of the perineum can be involved in the treatment resulting in morphological and functional improvement.
TREATMENT PROCEDURES AND TECHNIQUES
For an emerging field such as female genital cosmetic surgery,multiple treatment procedures,and techniques have been utilized in clinical practice.In addition to traditional surgical plastic surgery,the use of minimally invasive injection,energy-based devices,drug therapy,and physical therapy has also been reported.However,it is important to note that the efficacy of these items varies considerably.Some have a relatively positive efficacy,some present with an efficacy awaiting long-term observation,whereas others have ignited controversy within the academic world.
Surgical Interventions
In response to the plastic needs regarding various structural units of the perineum,multiple surgical options are available,including monsplasty,labiaplasty,clitoroplasty,clitoral preputioplasty,hymenoplasty,vaginal tightening,perineoplasty,and posterior commissuroplasty.
Monsplasty
The mons pubis is a slightly elevated round area covered by pubic hair lying in front of the pubic symphysis; it is rich in fat and elastic tissues and extends inferiorly to connect with the labia majora.For some beauty seekers with a request for a reduction surgery due to the apparent protrusion of the mons pubis,satisfactory results may usually be attained via local liposuction.It should be noted that the fat pad of the mons pubis acts as a buffer for the pelvis,preventing injury from external forces or sexual intercourse.Hence,pubic liposuction should be performed with care.Fat grafting can also be considered for some thin patients with a dry mons pubis to achieve moderate plumpness.
Labiaplasty
Labiaplasty is one of the most commonly sought after vaginal cosmetic procedures.According to the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery statistics,5,000 cases and 10,800 cases of labioplasty of the labia minora were performed in the United States in 2012 and 2017,respectively.This procedure was performed on 95,000 cases in 2015 and 138,000 cases in 2016 worldwide.
The labia majora and labia minora are the major structures greatly affecting the overall appearance of the vulva,and there are wide variations in the size,texture,and shapes of the labia among individuals.To date,no consensus has been successfully established on labial appearance or aesthetics,but women in the east generally prefer a plump,elastic labia majora and a compact,firm labia minora hidden by the former,with both exhibiting a pink tinge.
Regarding the variation in the shape of the labia minora,scholars have reported a broad spectrum of surgical techniques,with each option having its own set of advantages and disadvantages,as shown in Table 1.
Beauty seekers’ preferences and variations in the vulva shape and the clinical competency of the surgeon have been proposed as the factors that influence the surgical choice for the labia minora,which call for thoughtful decision-making following careful consideration and analysis by the surgeon.
A full understanding of the reasons and demands of patients seeking surgical management is necessary during the preoperative period.Their motivations may include discomfort from vulvar friction,inconvenient vulva cleaning due to extra folds of the labia minora,unsatisfactory sexual intercourse triggered by labia minora hypertrophy,and diminished confidence originating from self-perceived unsightly vulvar appearance.Additionally,great emphasis should be placed on the patient’s expectations for the surgical outcome,including their preference for labial shape and color.Preoperative local examination of the patient in a careful and meticulous way is needed for any asymmetry in the labia minora,plumpness of the labia majora,depth of the interlabial sulcus,degree and type of labia minora hypertrophy,combined abnormalities in the clitoris and clitoral prepuce,coloration of the labia minora,and texture as well as elasticity of the labia minora.Moreover,patients are expected to be photographed preoperatively from different views in the upright position and the lithotomy position,and copies of the photos should be retained.
After adequate preoperative preparation,a suitable surgical option can be offered:(1) Generally,the deepest pigment lies in the outer edge of the labia minora.Thus,the edgeresection technique is preferred for women expecting a pinker labia minora after surgery,(2) females with central labia minora hypertrophy are candidates for the wedge resection technique,(3) for those with elastic but sagging labia minora,the inferior wedge resection technique is optimal as it can tighten the labia minora and completely preserve the edge of the labia minora while maintaining the natural vulvar shape,(4) in some cases of labia minora hypertrophy combined with overly long or wide clitoral prepuce,the clitoral prepuce should be adjusted simultaneously with the labia minora plastic surgery.
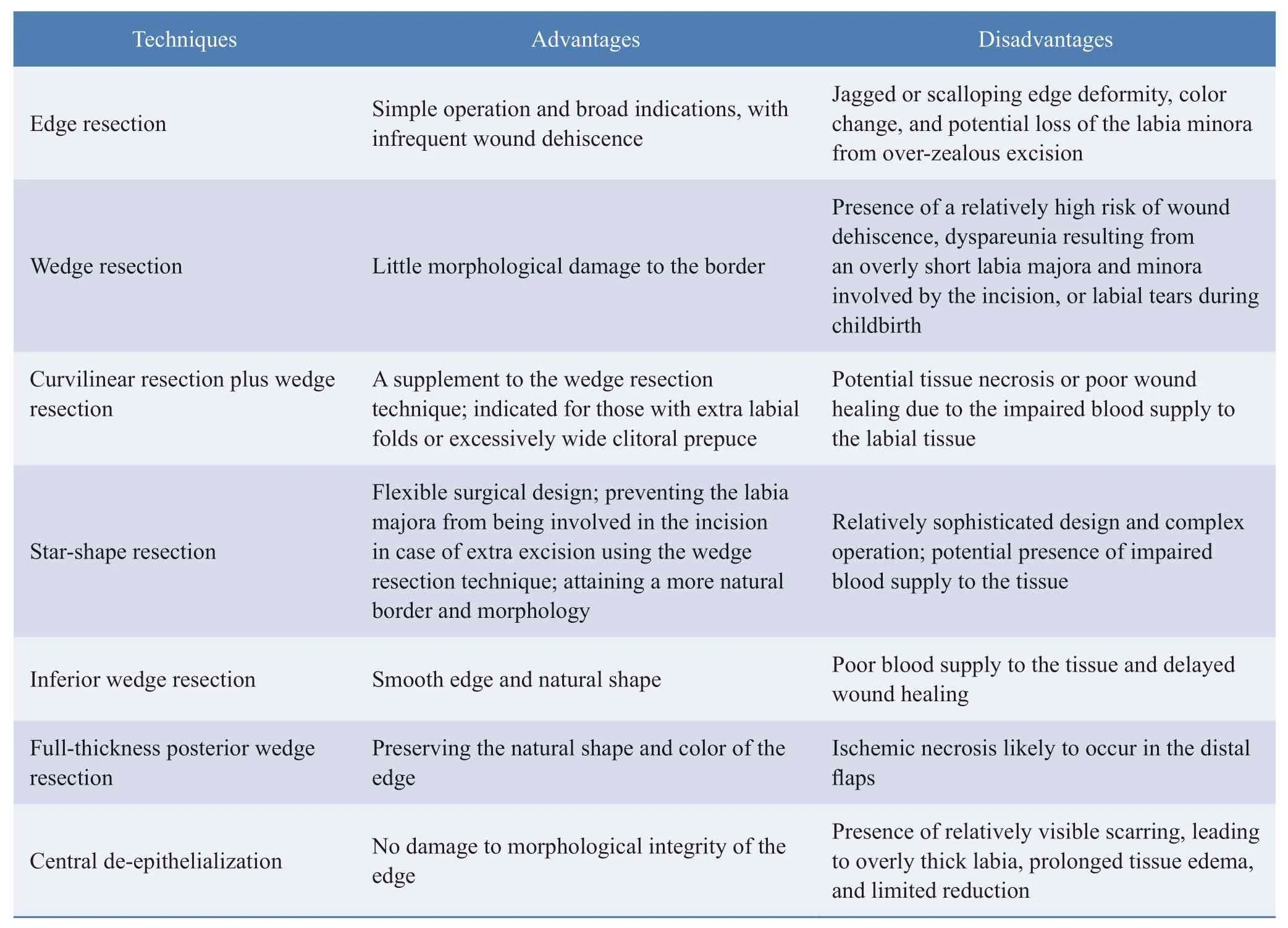
Table 1 Common surgical techniques for labia minora reduction
In summary,a full understanding of the appeal,vulvar characteristics demonstrated in physical examination,and wishes of the patient should be considered when deciding an optimal surgical option for the labia minora.Furthermore,multiple surgical procedures are expected to be utilized flexibly to develop an individualized surgical plan; the basic tenet lies in that no damage shall be done to the normal physiological function of the labia minora while maintaining a natural and appealing appearance.Therefore,leaving tissues is more important than removing part of them during labia minora reduction.It is generally accepted that the vertical distance from the apex of the labia minora margin to the interlabial sulcus should not be less than 1 cm.When the edge resection technique is employed,more skin surface tissues should be preserved relative to those next to the mucosal surface to avoid postoperative eversion of the labia minora.For the labia minora,a unique tissue of the body with no substitutes,the principle of “less outweighs more” is supposed to be observed as reconstruction is hardly done when excess tissue of the labia minora is removed.
Hymenoplasty
A procedure opted by a patient or family member due to conservative ideas or for for seeking psychological reassurance.During the interview,special attention should be paid to the patient’s psychological status and their family members,and appropriate counseling is expected.For example,patients should be informed about the normal variation in hymen and potential rupture during exercise and be aware of the misinterpretation that virginity is manifested by the presence of bleeding.Some patients may be relieved of their burdens and may decide against surgical intervention following the interview.A surgical procedure can be performed for those who insist upon it,provided any genital tract inflammation or disease is excluded.Moreover,caution should be exercised to protect their privacy and a more humanistic care should be provided.
Vaginal tightening and perineoplasty
This is a vaginal cosmetic procedure focusing on functional and aesthetic improvements.A broad spectrum of surgical options has been reported so far.The disparities between them mainly lie in whether the vaginal mucosa is incised or removed and whether the levator ani muscle and fascia are sutured and tightened at the anterior,posterior,or lateral posterior vaginal walls.Anterior vaginal wall tightening is rarely used for fear of possible surgical damage to the anterior vaginal wall as there is a urethra running through it,where females develop sexual sensitivity.The major concern regarding vaginal tightening is the lack of objective and unified endpoints to determine the vaginal laxity as well as surgical indicators and outcomes.Under these circumstances,the authors proposed a scoring method based on the patient’s chief complaints and physical examination findings and classified vaginal relaxation by the scores into three levels:mild,moderate,and severe,to correspond with different procedures,as shown in Table 2.
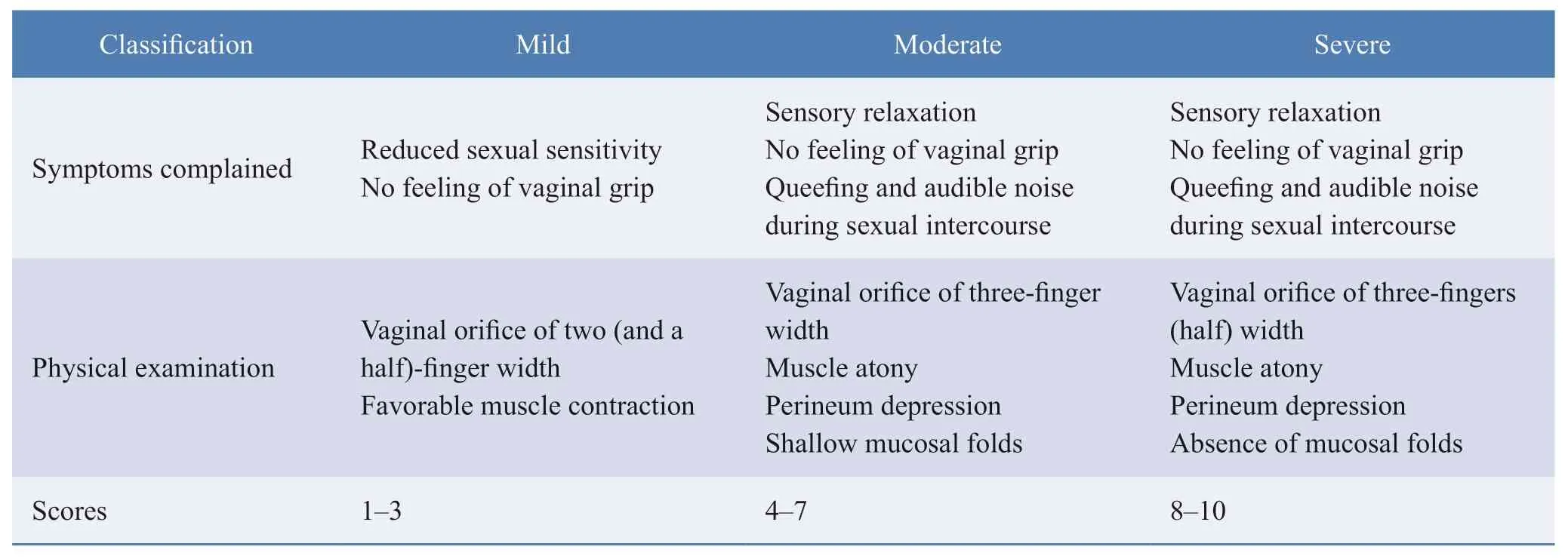
Table 2
For more than moderate vaginal relaxation,vaginal tightening and perineoplasty can be used to suture the levator ani muscle and the perineal central tendon via folding,thereby reducing the vaginal cavity volume,thickening the muscle,and improving the elasticity.However,patients must be informed that many factors may lead to sexual dissatisfaction; surgical intervention can reduce the vaginal volume and enhance muscle thickness and elasticity,which brings about certain benefits to sexual satisfaction and may pose substantial risks such as postoperative pain,bleeding,hematoma,and infection.Hence,patients are expected to weigh whether a surgical procedure is required,and discreetly make autonomous decisions.
Traditional vaginal tightening and perineoplasty are relatively invasive,with a high surgical risk.In recent years,many new treatments have sprung up (though rarely reported),such as thread lift,vaginal submucosal implantation,artificial material injection,or fat grafting.Attempts at new treatment options are justifiable,yet the principles of scientificity and safety must be followed.Taking submucosal fat injection as an example,the vagina is composed of a mucosal layer,a submucosal layer,and a muscle layer.Such a structure suggests that the vagina itself has no fat layer or adipose tissue;second,there is a rectal venous plexus around the vagina,with many thick venous vessels running through it.When operated in blind conditions,patients may have a relatively high potential for fat embolism,which will pose great risks; third,the pelvic cavity where the vagina is located consists of various organs and soft tissues except for the surrounding bones,which enjoy a sizeable elastic space for accommodating the contents.Hence,it is nearly impossible to narrow the vagina even if the fat is smoothly injected below the vaginal mucosa and survives.Therefore,such novel approaches should be attempted with extreme caution.If not theoretically demonstrated,these updated procedures should not be blindly applied in clinical practice.
Energy-Based Interventions
Recently,energy-based devices were made available for female genital cosmetic surgery,mainly including fractional CO2laser,erbium laser,monopolar radiofrequency,and bipolar radiofrequency.The use of these devices reduces vulvar pigmentation,manages vulvar skin folds,improves the vaginal environment,restores vaginal mucosal folds,and vaginal elasticity,and removes excess tissues from the labia minora and vulva.The mechanism of vaginal fractional CO2laser lies in two ways in which this device promotes secretion and remodeling of collagen tissues via energetically stimulating fibroblast proliferation and activation and facilitating vascularization and microcirculation.In addition,the CO2laser employed in the vagina can lead epithelial cells to release glycogen and acidic mucin,which helps restore the pH value of the vaginal mucosa.Increased glycogen enables vaginal lactobacilli to rebalance away from pathogenic bacteria,relieving problems such as dryness,pruritus,and recurrent infections.Therefore,a vaginal fractional CO2laser is used not only for young and middle-aged women with mild vaginal laxity but also for the treatment of atrophic vaginitis and stress urinary incontinence developed following menopause.However,in response to some serious adverse events reported (such as vaginal burns and resultant vaginal scarring,vaginal atresia,and pain during intercourse),the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)issued an announcement on its website on July 30,2018,warning patients and relevant practitioners of the lack of evidence to support the safety and effectiveness of energy-based devices (including laser and radiofrequency)in the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence as well as postmenopausal vaginal symptoms and in the enhancement of sexual function.The manufacturers of these devices have been questioned by the FDA and subjected to sustained monitoring since their involvement in the fields mentioned above is outside the standardized research protocols.Despite the FDA’s warning,the above devices are still active in clinical use.Several reports have been published successively,validating that these devices are safe and effective in treating female stress urinary incontinence,vaginal relaxation,and postmenopausal vaginal symptoms.However,no literature is now available with large sample size and a high level of evidence from long-term follow-ups.
Minimally Invasive Injection
Clinically,materials such as hyaluronic acid and collagen have already been applied to vulvar and vaginal injections,although they have been infrequently reported to date.Additionally,most of the literature concerning G-spot augmentation show negative attitudes.An early attempt to confirm the presence of a G-spot was described by Ostrzenski A.,who successfully dissected it from the anterior vaginal wall and provided a structural description based on the anatomical results of a female cadaver,but the level of evidence reported was merely rated Ⅱ-3.Most of the literature has suggested that G-spots do not exist at all.Jeffrey Spike,a medical ethics expert at Florida State University School of Medicine in the United States,even pointed out that performing G-spot augmentation is a kind of medical fraud to some extent.
EXISTING PROBLEMS
As a nascent therapeutic field,female genital cosmetic surgery is also beset with many problems in the face of opportunities for rapid development.The following aspects call for particular attention.
Psychological Status of Women Seeking Advice
Many patients misinterpret vaginal cosmetic surgery as a remedy to their marriage and relationships and have unrealistic expectations for the surgical outcomes,although most beauty seekers have a positive and healthy mentality.Hence,surgeons should recognize women with psychological concerns and offer appropriate counseling in the clinical setting.If necessary,the patient may be advised to seek treatment and guidance from a specialist psychologist or couple’s counselor.
Deceptive Advertising and Misleading
Deceptive advertisements and promotions are flooding the market,which blindly exaggerate surgical outcomes and intentionally provoke anxiety in females.In response to this issue,the mass media is supposed to empower women to construct correct perceptions,which is,there is a normal variation in female vulva shape,and no uniform standard has been established.Furthermore,practitioners are expected to truthfully inform patients about the lack of a large sample size and long-term follow-up for some surgical options,which allows patients to have a clear sense of the possible risks and outcomes of some treatments.Surgical procedures can only be performed after patients sign the informed consent form.
Qualification of Professionals
Female genital cosmetic surgery should be carried out by specialists who have extensive familiarity with the anatomy and physiology of the female vulva and have received professional training.The non-invasive idea and performance of plastic surgery,tension-releasing suture technique,and flap design and transfer run through the whole treatment process and are also technical guarantees to improve the success rate of treatments and reduce complications.
FUTURE DEVELOPMENT
Many new treatment procedures and techniques have been applied in the emerging field of female genital cosmetic surgery.Nonetheless,there is still a lack of data from high-level clinical studies to support their safety and effectiveness.Therefore,more high-quality clinical studies with a larger sample size are urgently needed.To enhance sexual sensitivity,advances in relevant primary research,such as anatomy,physiology,and mechanism,as well as progress and breakthroughs in stem cell research,are greatly anticipated.
ETHICS DECLARATIONS
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
N/A
Consent for Publication
All the authors have consented for the publication.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.The authors state that the views expressed in the submitted article are their own and not the official position of the institution or funder.
 Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2020年3期
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2020年3期
- Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery的其它文章
- The First Case of Free Radial Forearm Skin Flap:A 40-Year Follow-Up Study
- A Case of Digital Superficial Angiomyxoma
- Meteorological Influence on Tissue Expander-Related Major Infection
- Surgical Management for Diabetic Foot Ulcer:A Bibliometric Study
- Programmed 6-Step Approach of Improved Liposuction-Curettage for Axillary Bromhidrosis
- Foreword from Professor Lee L.Q.Pu
