金属磁性对超高频RFID标签增益的影响
李柏杨 韩冬桂 刘芳 李达 燕怒
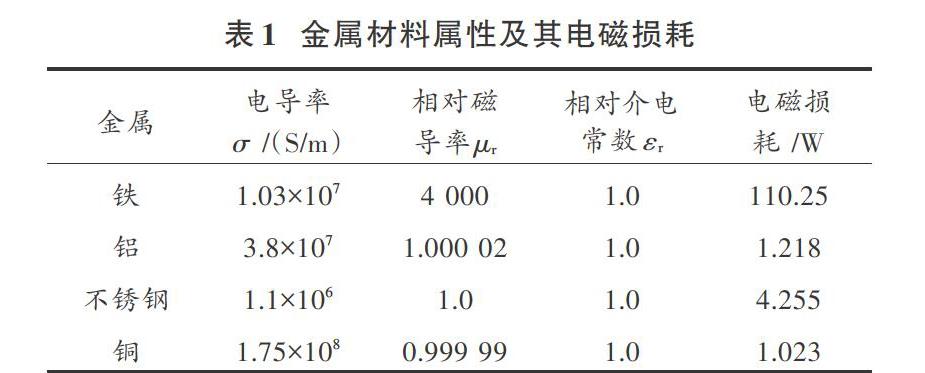

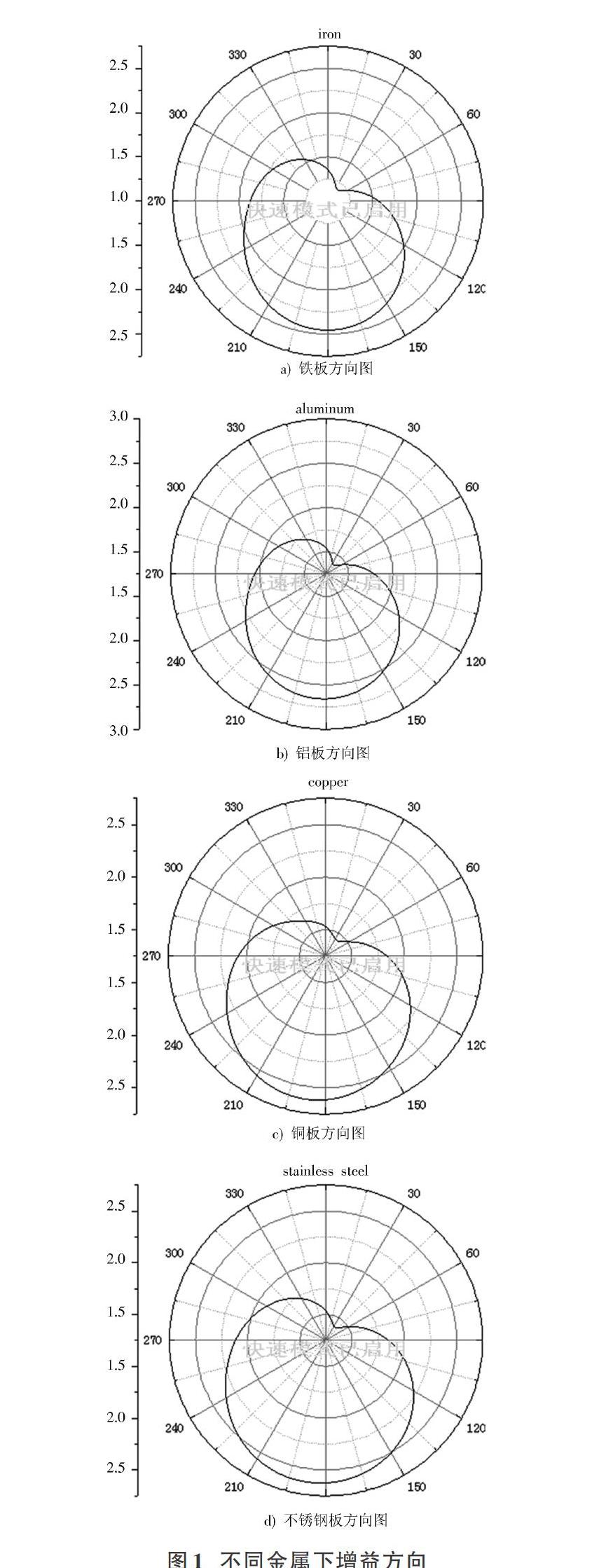
摘 要: 金属介质尤其是磁性金属对UHF射频信号存在干扰,严重影响了超高频射频识别(UHF RFID)技术的有效应用。该文采用电磁仿真软件Ansoft Maxwell分析不同金属内电磁损耗的差异,并运用Ansoft HFSS软件研究了超高频RFID标签天线在磁性金属与非磁性金属表面工作的特性。结果显示磁性材料金属内电磁损耗远大于非磁性金属,表现为对电磁波的吸收作用。金属磁性对标签天线辐射方向性影响不明显,但对天线增益抑制作用较为严重,并随着磁导率损耗正切tan μ从0增大到0.5,磁性金属表面天线的增益从2.41 dB衰减到1.72 dB。基于理论分析及仿真分析结果,该文提出一种将陶瓷基板与添加环形微带线相结合的天线结构设计方法增大辐射阻抗,提高天线增益,从而减小金属磁性对天线工作性能的影响。
关键词: 金属磁性; 超高射频识别; 天线增益; 电磁损耗分析; 天线设计; 辐射阻抗匹配
中图分类号: TN123.34?34; TP391.4 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1004?373X(2020)22?0023?04
Abstract: The metal media, especially magnetic metals, interferes with UHF RF signals, which seriously affects the effective application of ultra high frequency radio frequency identification (UHF RFID) technology. In this paper, the electromagnetic simulation software Ansoft Maxwell is used to analyze the difference of electromagnetic loss in different metals, and the Ansoft HFSS software is used to research the performance of UHF RFID tag antenna working on magnetic metal and non?magnetic metal surfaces. The results show that the electromagnetic loss in the metal of the magnetic material is much larger than that of the non?magnetic metal, which is manifested as the absorption of electromagnetic waves. The metal magnetism has no obvious effect on radiation directivity of tag antenna, but it has a serious effect on antenna gain suppression. As the increase of magnetic permeability loss tangent tan μ from 0 to 0.5, the gain of magnetic metal surface antenna decreases from 2.41 dB to 1.72 dB. Based on the theoretical analysis and simulation analysis results, an antenna structure design method combing the ceramic substrate with the added circular microstrip line is proposed to increase the radiation impedance and improve the antenna gain, so as to reduce the influence of metal magnetism on the working performance of the antenna.
Keywords: metal magnetism; UHF RFID; antenna gain; electromagnetic loss analysis; antenna design; radiation impedance matching
0 引 言
超高頻射频识别(Ultra High Frequency Radio Ident?
ification,UHF RFID)的电子标签具有数据传输快、读取距离远、成本低等优点,被广泛应用于物流、工业自动化、医疗、交通运输、控制管理等多个领域及行业。RFID标签的工作环境中会不可避免地接触到金属物体,例如汽车与集装箱之类等,这些金属材料具有的磁性会严重影响UHF标签的读写性能[1]。因此,为了改善金属介质对RFID标签性能的影响,国内外学者和工程师开展了众多研究。Allison J Mercer等学者发现金属环境会降低RFID系统整体工作性能[2];Leena Ukkonen等人通过软件仿真和实际测量,指出金属板的尺寸会对标签性能产生影响[3];N Ghannay等人通过仿真实验得出金属表面天线的输入阻抗,回波损耗、辐射方向图均会发生严重变化[4]。目前,学者们研究的内容主要集中在金属对RFID系统本身的影响和具有抗金属性能的标签结构设计两个方面。然而,金属介质自身电磁参数等因素的不同对标签工作性能的影响也存在差异[5]。UHF无源标签的工作性能主要取决于两个方面:标签天线的增益大小和天线与芯片之间的阻抗匹配[6]。在假设天线与芯片之间阻抗共轭匹配的情况下,标签天线增益的大小成为判断标签工作性能优劣的重要依据。因此,研究金属的磁性对标签增益的影响具有重要的意义。由于电磁波会被金属反射与吸收,金属板内产生的电磁损耗会吸收提供给标签工作的射频场总能量,导致普通标签在金属表面无法正常工作,严重影响了其应用范围。本文在分析金属对标签影响机理的基础上,着重从金属自身特性的不同,即材料、电磁参数对天线的增益影响程度,研究了金属介质对UHF标签天线工作性能的影响,并提出一种采用高介电常数的陶瓷基板及将环形微带与偶极子结构结合的方式,实现了在金属环境下高增益的优化。

