Community health nursing courses in baccalaureate nursing programs in China:A descriptive study based on website information
Duanying Cai
School of Nursing,Jiujiang University,Jiujiang,China
Keywords:Baccalaureate nursing education China Curriculum Nursing education
ABSTRACT Objective:To survey current community health nursing (CHN) courses offered in baccalaureate nursing programs in the mainland of China from the perspective on information available on websites of colleges and universities.Methods:A descriptive research design was used.Data were collected from the official websites of colleges and universities providing baccalaureate nursing programs in the mainland of China.A checklist was applied to identify academic year,type of course,credit,and class hours for both theory and practice teaching of CHN courses including Community Nursing,Geriatric Nursing,Rehabilitation Nursing,and Health Education.The prescribed textbooks were consulted for teaching content.Results:Colleges (n=16) and universities (n=26) offering baccalaureate nursing programs with accessible online information for curriculum setting were recruited.The results showed that most of the accessible educational institutions (92.86%) have offered three to four investigated CHN courses.Community Nursing,Geriatric Nursing and Rehabilitation Nursing are generally offered to juniors,while Health Education is offered in half of these institutions in different academic years.Community Nursing is mainly offered as a required course with 2 credits,while Geriatric Nursing,Rehabilitation Nursing and Health Education are provided as elective courses with fewer credits.Around half of the institutions have practice hours for Community Nursing,Geriatric Nursing and Rehabilitation Nursing courses.However,the proportion of practice hours in the courses is generally less than 50%.The teaching content focuses on clinical care competencies instead of complementary competencies.Conclusion:It was revealed that CHN education in China is still in its infancy from website information of colleges and universities.CHN courses should be included in curriculum design,and teaching reforms and innovations should be taken to prepare nursing students to practice in primary health care and community settings.
What is known?
· It is well recognized by Chinese nursing educators that community health nursing (CHN) education is important in preparing community health nurses (CHNs) to promote health for all and to relief workforce intense in community settings.
· CHN education in China has not yet formed a mature professional direction and lacks a scientific and effective teaching system for preparing competent CHNs.
What is new?
· Most of the colleges and universities offer CHN courses as elective in baccalaureate nursing programs,which is employment-oriented to some extent.
· The CHN courses are offered with few practice hours in the curriculum setting,with the ratio of practice to theory in class hours significantly below 1:1.
· The clinical care competences instead of complementary competencies are emphasized in teaching materials.
1.Introduction
World Health Organization (WHO) reported that community health nursing (CHN) plays a key role in health care delivery systems and is crucial for universal health coverage[1].The increasing demand for community health services worldwide calls for more community health nurses (CHNs).It is estimated that nurses account for more than 50%of community health workforce shortage[1].CHN education thus becomes a big challenge for both nurse educators and clinical leaders to prepare students to work in this changing health care context[2].In China,education and training of CHNs to work in primary health care and community settings are in its infancy.This article describes the issues encountered in CHN practice and education,and the current situation of CHN courses in baccalaureate nursing education in China.
1.1.Current CHN practice in China
Nursing services in China have gradually expanded from clinical treatment of diseases to chronic disease management,elderly care,long-term care,rehabilitation care and hospice care,and from medical institutions to communities and families,striving to meet the increasingly diversified and multi-level health care needs of the population [3].According to the report from National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China,the annual number of visits for community health care services with a speed rise trend increased from 610 million in 2017 to 640 million in 2018 [4].Consequently,CHN along with the aging population,burdens of chronic diseases,changes in family structure and an increase in medical expenses in China has become an opportunity and challenge for the development of nursing.
By the end of 2018,the number of community health service institutions had reached at 34,997 in China,including 9,352 community health service centers and 25,645 community health service stations [4].There were 462,000 health care professionals in the community health service centers,with an average of 49 professionals in each center; 120,000 health care professionals in the community health service stations,with an average of 5 professionals in each station [4].Among all the health care professionals in the community,36%of them were CHNs,and a nursedoctor ratio was at 1.07∶1 which was still a gap with the suggestion of the ratio from WHO at 2∶1 to 4∶1 [5].The number of nurses working in the community only occupies approximately 5% of the total number of nurses in China.
In China,to be a community health nurse,a nurse certificate and a community nursing training are required,but a specified nurse certificate in community is not necessary.Most of the nurses engaged in CHN in China are nurses transferred from hospitals.A study conducted in 13 cities in China reported that CHNs included transferred clinical nurses (79%),new graduates from nursing programs (9%) and medical programs (7%),public health workers(1%) and non-degree personals (4%) [6].Compared to hospital nurses,CHNs’education level in China is lower,mainly at secondary school level.The data from four investigations in different areas of China showed 53%-77%,7%-42%,1%-15%,and 3%-16% of community nurses having diploma,associate degree,bachelor degree and no degree respectively [6].Although the regional differences are large,it indicates that education and training of CHNs in China needs to be further improved to ensure the quality and safety of health care services in communities.
For CHN practice,National Basic Public Health Service Standards specified “six in one” services as “prevention,health care,medical treatment,rehabilitation,health education and family planning technical guidance” [7].However,CHNs in China merely duplicate the jobs of hospital nurses [8].It was reported that they took the most of their duty hours for therapeutic work,though the proportion of time spent reduced from 68%in 2004 to 33%in 2010[9].WHO also conducted a survey among 403 participants in 11 countries to explore CHNs’roles and functions.The results showed that 49%of nurses were performing roles in nursing and health care provision and only 6% described their work as health promotion,disease prevention and rehabilitation which are major domains of CHN practice [1].
This reveals that in many countries including China there is a serious misalignment between what community nurses should be trained to do and what they actually do in daily practice.Therefore,a clearer role definition for community nurses is needed to maximize their potentials.In China,a community service team usually includes general practitioners,public health doctors and CHNs,but their work division is unclear.CHNs complained that they had also spent much time and energy doing non-professional trifles(such as charging,data sorting,and data entry) [9].
Overall,the importance of CHN practice in health care delivery system has been widely recognized,but it is not functioning properly in China.
1.2.Current CHN education in China
The first nursing programs at bachelor,master and doctoral level were respectively established in Tianjin Medical University in 1983,in Beijing Medical University in 1992 and in Second Military Medical University in 2003.Up to 2019,there are 209,86 and 21 universities and colleges in China providing nursing programs at bachelor,master and doctoral level respectively[10].However,only few of them offer community nursing programs to cultivate community health nurses.Currently,there are few universities setting up community nursing departments or related teaching and research sections in China.Usually,CHN courses belong to clinical nursing,fundamental nursing or nursing education teaching and research sections.
CHN education in China has experienced a rapid development after the release of Decision of Health Reform and Development from CPC Central Committee and the State Council in 1990s emphasizing the importance of community health care.Many universities henceforth have included a course named Community Nursing into the curriculum.As early as 1995,School of Nursing,Central South University determined Community Nursing as a required course in undergraduate nursing curriculum.Tianjin Medical University has started a program named Geriatric and Community Nursing since 2004 to specifically train students for knowledge and skills to provide health care service to the elderly and community population.Unfortunately,graduates from this program have mainly chosen to be clinical nurses in the tertiary level hospitals [11].
In 2006,Opinions on Strengthening Education of General Medicine and Community Health Nursing in Medical Colleges and Universities issued by Ministry of Education proposed the importance to reform CHN education and suggested the education system should be improved from the aspects of curriculum setting,teaching staff and community practice [12].Since then,many colleges and universities in China have employed experts at home and abroad for curriculum reform.Courses such as Geriatric Nursing,Rehabilitation Nursing,and Health Education have been added into the curriculum.After years of efforts,most educational institutions have set up CHN courses,recruited full-time and part-time teachers,established their community practice bases,and had attempts to reform teaching methods in baccalaureate nursing programs [13].
Generally,CHN education in China has not yet formed a mature professional direction and lacks a scientific and effective teaching system for preparing competent CHNs.This study examined curriculum setting of colleges and universities to disclose the teaching situation of CHN courses offered in baccalaureate nursing programs in China and to identify improvement directions of CHN education.
2.Method
2.1.Research design
A descriptive research design was used.
2.2.Sample
Colleges and universities offering baccalaureate nursing programs in the mainland of China with accessible online information for its curriculum setting were recruited.Both colleges and universities are the educational institutions providing undergraduate and above level education approved by Ministry of Education[14].
2.3.Data collection
The official websites of 209 colleges and universities in the mainland of China providing nursing programs at bachelor level were searched.Data was collected from November to December in 2019.Based on National Basic Public Health Service Standards,curriculum information of CHN courses including Community Nursing,Geriatric Nursing,Rehabilitation Nursing,and Health Education was searched and noted.A checklist was developed to identify curriculum design of CHN courses including the academic year,type of course,credit,and class hours for both theory and practice teaching.In addition,most of the accessible institutions claim that the textbooks from People’s Medical Publishing House which is the national level medical and health press directly under National Health Commission are being used.Therefore,the catalogs of the latest edition of textbooks for CHN courses from People’s Medical Publishing House were consulted to identify the teaching content.
2.4.Ethical considerations
All information analyzed was obtained from the official websites of educational institutions and prescribed textbooks.Ethical approval of the study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of School of Nursing,Jiujiang University (2019-JS-101).
2.5.Data analysis
A descriptive analysis was applied after data collection.
3.Results
Colleges(n=16)and universities(n=26)providing accessible online information for curriculum setting were recruited for data analysis.According to economic development level and geographical location,China is divided into three economic zones:the East,the Middle and the West.The distribution of the accessible educational institutions can be seen in Table 1.
The results showed that all of the accessible baccalaureate nursing programs in this study have offered CHN courses.Community Nursing course is offered in all colleges and universities.Most educational institutions offer Geriatric Nursing(95.2%,40/42)and Rehabilitation Nursing (90.5%,38/42) courses.Twenty one(50.0%,21/42) institutions offer Health Education course.Up to 92.9%of the selected institutions offer more than two related CHN courses in their curriculum (Table 2).
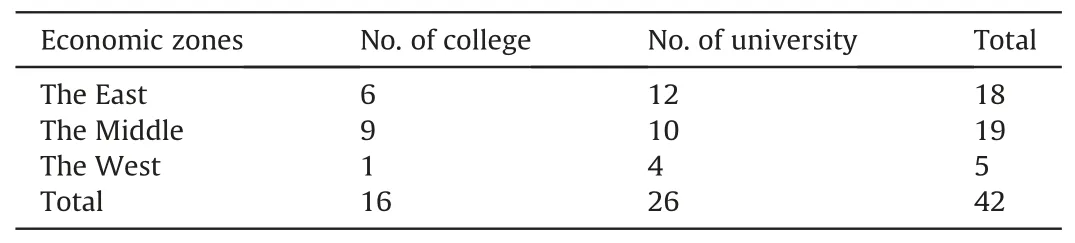
Table 1 The distribution of the accessible educational institutions.
In this study,more than 70% of the included colleges and universities providing baccalaureate nursing programs offer Community Nursing,Geriatric Nursing,and Rehabilitation Nursing courses to juniors.Health Education course is mainly offered to sophomores(38.1%) or juniors (33.3%).Up to 73.8% of institutions set up Community Nursing as a required course.On the other hand,most institutions take Geriatric Nursing (60.0%),Rehabilitation Nursing(81.6%) and Health Education (85.7%) as elective courses.The course hours for each CHN course are from 16 to 40.Among programs surveyed,a large number of institutions set up Community Nursing,Geriatric Nursing,Rehabilitation Nursing,and Health Education courses with 2.0 (42.9%),1.5 (42.5%),1.5 (36.8%) and 1.0(33.3%) credit respectively.For courses of Community Nursing and Geriatric Nursing,above half of institutions have added practice hours within the course teaching.Half of institutions offer Rehabilitation Nursing course with practice.However,Health Education course in most of institutions (71.4%) uses theoretical teaching(Table 3).
The class hours for practice in over half of the institutions who offer practice teaching in Community Nursing,Rehabilitation Nursing and Health Education courses account for 25% and more within the course placement.For Geriatric Nursing course,almost half of the institutions who offer practice hours only provide less than 25% of its class hours for community practice.Moreover,few institutions have more than 50%of class hours for practice in CHN courses in their curriculum.The information can be seen in Table 4.
The teaching content of CHN courses mainly involves basic concepts and theories related to community nursing,geriatric nursing,rehabilitation nursing and health education; community and family health assessment;health care and nursing of children,women and the elderly;management of common chronic diseases in community; community health education and health promotion; and common rehabilitation and nursing techniques in community.
4.Discussion
This study aims to survey current CHN curriculum offered in baccalaureate nursing programs in the mainland of China.Though quite few educational institutions offer a specialty as community nursing to cultivate professionals,it can be seen from the results that most of institutions have integrated CHN courses into their curriculum.Since National Health Commission highlights the increasing demands for community health care should be met with knowledge and ability of health management,rehabilitation and elderly care [3],courses of Community Nursing,Geriatric Nursing,Rehabilitation Nursing and Health Education have been set up in most colleges and universities.It is easy to see that Chineseeducational institutions have realized the importance of introducing the concept of community into nursing courses to adapt to the new roles and responsibilities of nursing professionals.
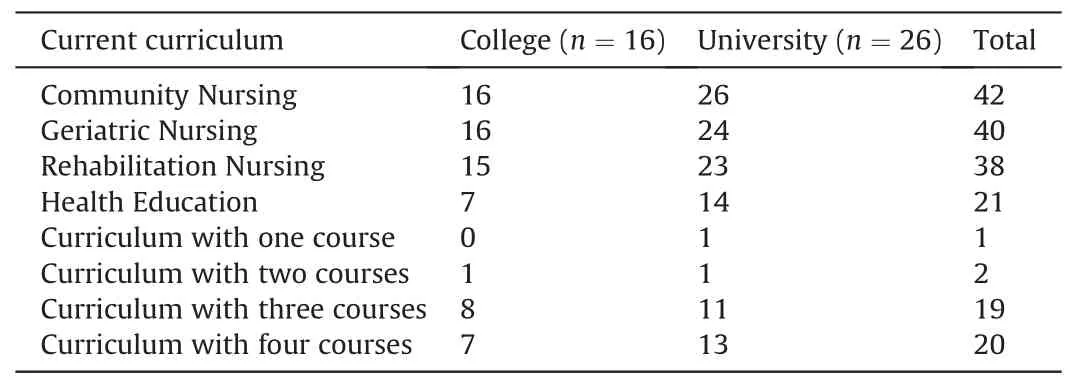
Table 2 Baccalaureate nursing programs offered with curriculum in community health nursing (n=42).
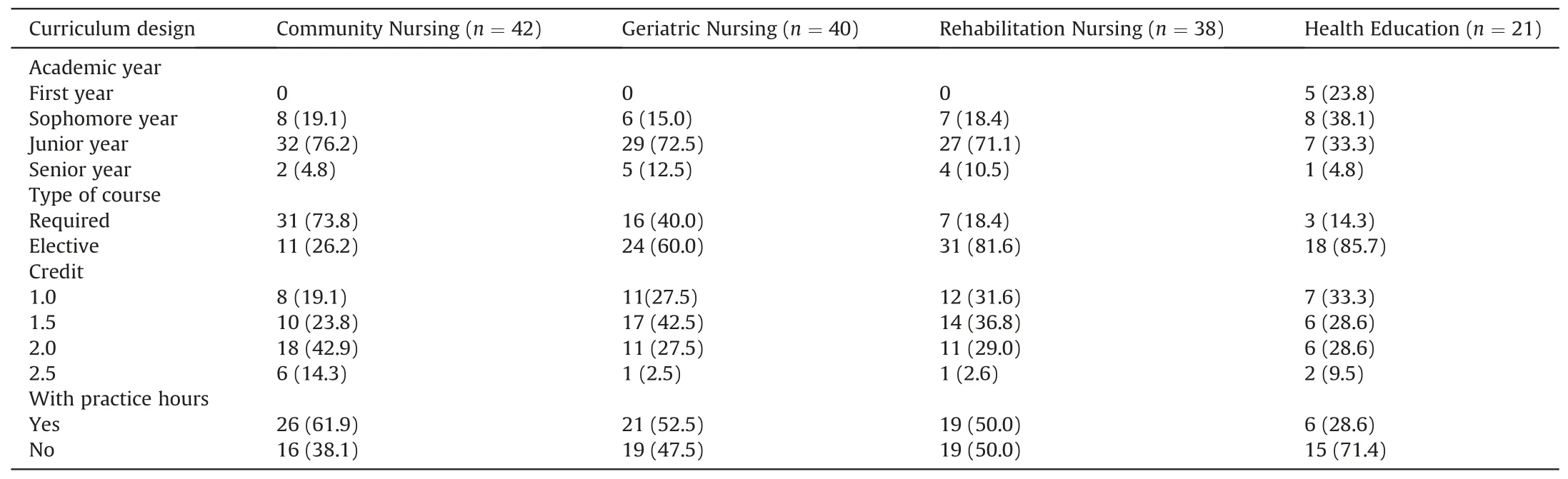
Table 3 Curriculum design of community nursing,geriatric nursing,rehabilitation nursing and health education courses by frequency and percentage (%).

Table 4 Proportion of practice hours in regarding courses in universities and colleges offering practice links.
Based on National Standards for Teaching Quality of Nursing,Community Nursing should be one of the main courses for undergraduate nursing programs [15].It seems that all of the institutions have met this standard.However,although above 90% of the accessible institutions offer three to four CHN courses,yet except Community Nursing,these courses are most elective.In the study,CHN courses are usually offered along with medical nursing and surgical nursing in junior year.The prerequisite courses for CHN include human anatomy,physiology,pathology,fundamental of nursing and health assessment.Follow up courses are usually the specialized nursing courses,such as pediatric nursing,emergency and critical nursing,and psychiatric nursing.However,related courses including family nursing,health promotion,interpersonal communication,social medicine and social research are only offered in few institutions.The credits of CHN courses accounts for a low proportion of total course credits.It is consistent with the comment from more than 10 years ago that the content of CHN courses only accounted for about 5% of nursing curriculum [16].Obviously,CHN still has not achieved enough attention in nursing education in China.
This is probably because that community nurse is still not a popular career option in China,though an appeal is being made by National Health Commission to increase the number of community health care workers.Graduates from baccalaureate nursing programs prefer to work in tertiary level hospitals and are less willing to work in communities than those from diploma programs due to poor working environment,low benefits,low social acceptance and unfamiliarity with community nursing [17].A study conducted in the Netherlands for students’ placement preferences also found that only few students (5.4%) preferred to go to communities and most of students(71.2%)chose to go to general hospitals,since they perceived community nursing as a “low-status-field” with many elderly clients [18].Community nursing is seen with little variety and less challenges in service providing and few opportunities for self enhancement professionally.Though the importance of community nursing in terms of society needs is being accepted,it does not attract students.Therefore,lots of colleges and universities adhere to the employment-oriented curriculum setting,with adding CHN course module as elective courses in professional learning.In this way,students can not only be engaged in clinical nursing in hospitals,but also in community nursing after graduation,which provides more employment opportunities for students.
For teaching content,community health nursing should involve a combination of knowledge and skills derived from nursing,public health and social sciences.Both clinical care competencies and complementary competencies are suggested to be integrated into theoretical and practical teaching of CHN courses [1].Clinical care competencies include health assessment,observation and treatment,disease management and case management.Complementary competencies include cultural sensitivity,leadership,development of tools and guidelines for data collection and analysis,participatory research and experiential learning through action.However,from the suggested teaching materials of CHN courses,CHN education in China focuses on clinical care competencies instead of complementary competencies.In teaching of CHN,the content in community cultures,community health resources evaluation,health program planning,and policy development is lacking,and the abilities in communication,scientific research,economic budgeting,decision-making,and anticipating potential problems are overlooked [13].
For community practice,it increases students’ confidence to assume their role as a community nurse [2].Therefore,practice mentoring in communities is an important way to guarantee the teaching quality.For practice links in China,nursing students travel to hospitals or communities for observation and hands-on learning under nurses’supervision for the first three academic years.In their senior year,there are approximately 40 weeks for internship in hospitals [19].Some of institutions also provide 1-4 weeks for community practice in the last school year in this study.Generally,CHN teaching focuses on theoretical teaching in classroom instead of practice in the field.It can be seen from this study that around half of the institutions do not have practice in the CHN courses and theoretical teaching accounts for a large proportion of class hours.Actually,Ministry of Education suggests the ratio of theory to practice in class hours for CHN courses should be 3∶1 at least and 1∶1 at most[15].It is highly recommended this ratio to be 1∶1 for community health teaching [20]to ensure 50% of learning taking place in practice [2].Unfortunately,most of institutions have not satisfied this proposal.
Based on the current situation of CHN education in China,we must make great efforts in three main aspects.First,reforms and innovations in curriculum design should be initiated and interdisciplinary required stand-alone courses should be included based on a set of defined competencies for students to practice in community nursing.Second,teaching/learning resources including community laboratories and practice bases should be strengthened to support faculty in practice teaching.Besides,policy and funding should be appealed and developed to promote welfare and treatment of CHNs,so that both students and educators would regain their confidence in CHN.
5.Limitations
The limitation of the study was that the information collected and evaluated was only from the institutions whose websites providing curriculum information,so it could not be representative for the whole picture of CHN education in China.Moreover,the teaching content was only assessed based on the textbooks from People’s Medical Publishing House.It may not reflect the actual content being delivered,because the documents for original teaching plans were rarely available outside the institutions.The information of teaching faculty,teaching strategies and community practice bases were not available online.Therefore,it was difficult for the study to reflect the teaching situation as a whole.
6.Conclusion
In conclusion,the importance of CHN education in preparing CHNs to promote health for all and to relief workforce intense in community settings is well recognized by Chinese nursing educators.Most of the colleges and universities in the study offer CHN courses including Community Nursing,Geriatric Nursing,Rehabilitation Nursing and Health Education in baccalaureate nursing program.However,most of CHN courses are offered as elective with few practice hours in the curriculum setting,which is employmentoriented to some extent.Moreover,clinical care competences instead of complementary competencies are emphasized in teaching materials.As the demand for CHN increased,CHNs preparation should not only rely on on-the-job training,but pay attention to reforms and innovations of curricular design to ensure nursing students to acquire abilities to practice in primary health care and community settings through CHN education.
Funding
This work was funded by the Research Project of Teaching Reform in Colleges and Universities from Jiangxi Province [grant numbers JXJG-19-17-5]and by the Cultivation Project for Teaching Achievement from Jiujiang University.
Declaration of competing interest
The author declares that she has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2020.09.001.
 International Journal of Nursing Sciences2020年4期
International Journal of Nursing Sciences2020年4期
- International Journal of Nursing Sciences的其它文章
- An exploration of the breastfeeding behaviors of women after cesarean section:A qualitative study
- The risk factors of postpartum urinary retention after vaginal delivery:A systematic review
- Demands of experiential training for ICU nurses in Hunan of China
- Understanding autism spectrum disorder and coping mechanism by parents:An explorative study
- Association of swallowing problems with frailty in Chinese hospitalized older patients
- Theory-guided interventions for Chinese patients to adapt to heart failure:A quasi-experimental study
