Clinical observation on acupoint injection for back pain in patients w ith primary osteoporosis
Hua Ying (华英), Wang Yan (王燕),Wu Shao-chang (吴绍长)
LishuiSecond People'sHospital, Zhejiang 323000,China
Abstract
Keywords:Acupoint Therapy; Hydro-acupuncture;Point, Pishu(BL 20); Point,Shenshu (BL 23);Visual Analog Scale;Osteoporosis;Low Back Pain;Aged
With the aging of the population and people's higher demands for the quality of life (QOL), osteoporosis has become a social problem for m iddle-aged and elderly people,especially for women at this age,whose estrogen level decreases after menopause which leads to the loss of calcium salt in the bone and osteoporosis.A domestic study showed the morbidity of osteoporosis in China was 14.94%before 2008,and increased to 27.96% from 2012 to 2015. Besides, this morbidity in people over 50 years old was twice as high as that in 2006[1].Back pain is a common clinical symptom in primary osteoporosis in elderly people, and is treated mainly by non steroidal analgesics but long-term use may lead to gastrointestinal bleeding and other adverse reactions[2-4]. Therefore, it is of great significance to find a safe and effective treatment. In this study, acupoint injection with salmon calcitonin was adopted to treat back pain in elderly patients with primary osteoporosis.The details are as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
The diagnostic criteria for primary osteoporosis in theGuidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Osteoporosis(2011)[5]were referred.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Those who met the above diagnostic criteria and were aged 65-80 years old; the course of chronic back pain more than 6 months; serum calcium in normal range;acquainted w ith this study and signed the informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those who suffered from secondary osteoporosis caused by endocrine or metabolic diseases, tumors, etc;serious cardio-cerebrovascular diseases;took non- steroidal analgesics a week before enrollment;osteoporotic fracture w ithin 6 months before enrollment; severe liver or kidney dysfunction; allergicto salmon calcitonin.

Table 1.Com parison of the general data between the two groups
1.4 Statistical methods
The SPSS version 22.0 statistical software was used for data analysis.The visual analog scale (VAS)and Chinese Oswestry disability index (CODI) scores were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s). Pairedt-test was used for intra-group comparisons and groupt-test for inter-group comparisons. The counting data were expressed by rate or constituent ratio, and Chi- square test was used for comparisons between groups.Rank-sum test was used for comparison of clinical efficacy. AP-value of less than 0.05 meant a statistically significant difference.
1.5 General data
A total of 76 elderly outpatients with back pain due to primary osteoporosis visiting Lishui Second People's Hospital between July 2016 and January 2018 were selected. According to the method of random number table, they were divided into a treatment group and a control group, w ith 39 cases in the treatment group and 37 cases in the control group respectively. Cases in the treatment group were aged 48-78 years old,with a disease duration between 7 months and 10 years, and the bone-density T-value between-4.94 and-3.23 while cases in the control group were aged 46-78 years old, w ith a disease duration between 6 months and 12 years,and bone-density T-value between-5.01 and-3.29.There were no significant differences in the general data between the two groups (allP>0.05),indicating that the two groups were comparable(Table 1).
2 Therapeutic Methods
Patients in both groups received routine treatment of oral medication:alendronate sodium tablets, 10 mg/time, once a day, taken on an empty stomach w ith warm water each morning; rocaltrol, 0.25 µg/time,once a day; caltrate D3, 600 mg/time, once a day.
2.1 Control group
Patients in the control group received additional gluteus maximus intramuscular injection w ith salmon calcitonin, 50 IU/time, once a day, for 4 weeks.
2.2 Treatment group
Patients in the treatment group received additional acupoint injection w ith salmon calcitonin.
Points: Bilateral Pishu (BL 20) and Shenshu (BL 23).
Methods: Asked the patient to be in a prone position.Diluted the salmon calcitonin injection w ith 4 m L sterile water for injection.The skin around the point was disinfected.Perpendicularly needled bilateral Pishu(BL 20)and Shenshu(BL 23)by 15-20 mm.Liftingthrusting method and twirling or rotating method were adopted for obtaining qi. After the arrival of qi, drew back the syringe if there was no backflow blood and then injected the diluted salmon calcitonin injection 1 m L for each point, once a day, for 4 weeks.
3 Observation of Therapeutic Efficacy
3.1 Observed items
The items were observed before treatment,and 2 weeks and 4 weeks after treatment respectively by clinicians who did not participate in the treatment.
3.1.1 VAS
VAS was used to evaluate pain. Ten pointsmeant intensive pain, 7-9 points for severe pain, 4-6 points for moderate pain,1-3 points for m ild pain and 0 point meant no pain.
3.1.2 CODI
CODI consists of 10 items w ith 6 choices for each question. The highest score is 5 points and the lowest is 0 point for the 6 choices. The higher the final score, the more severe the dysfunction.
3.1.3 Case of taking analgesics
The use of analgesics during the treatment was recorded after the patients began to receive treatment in their groups.
3.2 Therapeutic efficacy criteria
The therapeutic efficacy was evaluated according to the corresponding criteria in theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines[6].
Markedly effective: The pain disappeared completely w ith increase of bone m ineral density.
Effective: The pain was relieved significantly without decrease of bone m ineral density.
Failure: No improvements in each aspect compared w ith before treatment.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Comparison of the clinical efficacy
After 4 weeks of treatment, the clinical efficacy in the treatment group was significantly more significant than that in the control group (P<0.05), (Table 2).
3.3.2 Comparison of the VAS score
Before treatment, there was no significant betweengroup difference in the VAS score (P>0.05). Intra-group comparison: after 2 weeks and 4 weeks of treatment,the VAS scores were significantly decreased in both groups (bothP<0.05). Between-group comparison: after 2 weeks and 4 weeks of treatment, the VAS score in the treatment group was significantly lower than that in the control group (bothP<0.05). Check Table 3 for details.
3.3.3 Comparison of the CODI score
Before treatment, there was no significant betweengroup difference in the CODI score (P>0.05). Intra-group comparison: after 2 and 4 weeks of treatment, the CODI scores were significantly decreased in both groups (bothP<0.05).Between-group comparison:after 2 weeks of treatment, there was no significant between- group difference in the CODI score (P>0.05);after 4 weeks of treatment, the CODI score in the treatment group was significantly lower than that in the control group (P<0.05). Check Table 4 for details.

Table 2.Com parison of the clinical efficacy between the two groups(case)
Table 3.Com parison of the VAS score between the two groupsbefore and after treatment (±s,point)

Table 3.Com parison of the VAS score between the two groupsbefore and after treatment (±s,point)
Group n Before treatment A fter 2 weeks of treatment A fter 4 weeks of treatment Comparison between 2weeks of treatment and before treatment Comparison between 4 weeksof treatment and 2 weeksof treatment t-value P-value t-value P-value Treatment 39 6.52±1.04 4.61±0.98 2.94±1.32 -8.347 0.000-6.343 0.000 Control 37 6.49±1.16 5.16±1.26 3.89±1.27 -4.723 0.000-4.318 0.000 t-value 0.128-2.301-3.458 P-value 0.898 0.023 0.001
Table 4.Com parison of the CODI score between the two groups before and after treatment (±s,point)

Table 4.Com parison of the CODI score between the two groups before and after treatment (±s,point)
Group n Before treatment A fter 2 weeks of treatment A fter 4 weeks of treatment Comparison between 2weeks of treatment and before treatment Comparison between 4 weeksof treatment and 2 weeksof treatment t-value P-value t-value P-value Treatment 39 45.89±8.92 35.08±6.72 29.42±5.82-6.044 0.000 -3.976 0.000 Control 37 45.10±10.34 37.29±7.33 32.79±6.63-3.748 0.001-2.769 0.007 t-value 0.386-5.020-2.549 P-value 0.700 0.616 0.012
3.3.4 Comparison of the case taking analgesics
During the treatment, 2 cases in the treatment group took analgesics versus 8 cases in the control group. The result showed a significant between-group difference(P<0.05), (Table 5).
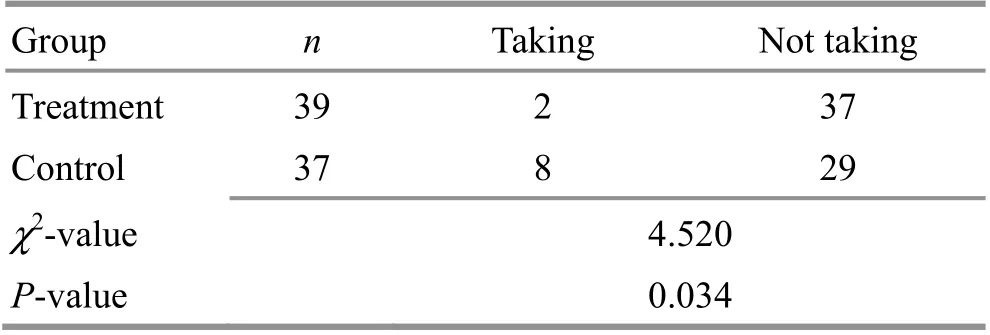
Table 5.Com parison of the cases taking analgesics during treatment between the two groups(case)
4 Discussion
Osteoporosis is a common system ic osteopathy,featured by degeneration of bone m icrostructure and osteopenia, thus resulting in increase of bone fragility and risk of fracture[7-8]. Back pain is a common reason for outpatients w ith osteoporosis to visit hospital. The structure and shape of patients'bone have changed due to osteopenia,and thus the internal bone environment is impaired.The periosteal stress is increased, giving rise to tension pain and involving the surrounding soft tissues, consequently leading to spinal instability.In order to achieve a new mechanical balance, the muscle tension on both sides of the spine increases and leads to spasmodic pain[9-13]. The clinical efficacy of non-steroidal analgesics for back pain in elderly patients w ith osteoporosis is not ideal,but accompanied by many adverse reactions.Salmon calcitonin is a calcium regulating hormone produced by thyroid cells.There are many receptors w ith high affinity for calcitonin in human osteoclasts. Combined w ith calcitonin, these receptors can inhibit osteoclast activity,regulate osteoblast activity,inhibit bone resorption and reduce bone loss. Relevant studies have confirmed that calcitonin can inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandin and increase the level of serum β-endorphin, thus relieving the pain in osteoporosis[14-18].
Although the name of osteoporosis is not recorded in traditional Chinese medicine(TCM),the clinical symptoms of this disease can be seen in ancient TCM books. Osteoporosis falls under the category of ‘bone Bi-impediment'or ‘bone Wei-flaccidity'in TCM.Sufficient kidney essence allows generation and transformation of marrow,and then bones can be nourished and get strong.Insufficient kidney essence w ill lead to flaccidity due to malnourishment of marrow.Clinical symptoms of osteoporosis such as back pain and weakness of legs will present.Spleen is the postnatal root and the source of qi and blood,governing transportation and transformation of the essence from food and drink. It also governs muscles and limbs. Spleen deficiency may cause kidney essence deficiency and weakness bones.Therefore,osteoporosis in elderly people is closely related to the spleen and kidney.In this study,the selected Pishu(BL 20) and Shenshu (BL 23) are points where qi of the spleen and kidney perfuses over the surface of the body,functioning as benefiting the kidney and fortifying the spleen,and benefiting both prenatal and postnatal endowment.Modern studies have found that stimulating Pishu(BL 20)and Shenshu(BL 23)can increase serum estradiol and testosterone levels. Sex hormones are closely related to osteoporosis. Estrogen can stimulate osteoblasts and promote bone grow th,and androgen is of great significance for maintaining normal bone mass[19-22]. In addition, Pishu (BL 20) and Shenshu(BL 23) are located in the back, a common pain-affected area in patients w ith osteoporosis.Acupoint injection at these two points is a selection of local points.
This study showed that for back pain in elderly patients with primary osteoporosis,based on the routine treatment of oral medication,the clinical efficacy of acupoint injection w ith salmon calcitonin at bilateral Pishu (BL 20) and Shenshu (BL 23) was more significant than that of intramuscular injection.Acupoint injection treatment can improve patients'conditions and reduce the use of analgesics.

Conflict of Interest The authors declare that there isno conflict of interest.Statem ent of Informed Consent Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received:24October 2019/Accepted:18December 2019
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年5期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年5期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Clinical observation on electroacupuncture plus Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transform ing Qigong Exercises) for knee osteoarthritis
- Clinical efficacy comparison of moxibustion w ith different doses for knee osteoarthritis
- Clinical observation of acupuncture and traction plus Ba Duan Jin (Eight-brocade Exercise) for improving discogenic low back pain
- Clinical observation on Yi Jin Jing(Sinew-transform ing Qigong Exercises) plus tuina on the neck for stiff neck
- Efficacy evaluation of acupuncture plus rehabilitation training for post-stroke deglutition disorders of qi-deficiency blood stasis pattern
- Clinical observation of acupuncture plus Frenkel exercises for ataxia after cerebral stroke
