Molecular mechanism of Duhuojisheng Decoction in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on the network pharmacology
Yuan Liu, Bo Xu,3, Jin-Bao Liu,3, Jing-Zhou Zhang, Gang Li,3✉
1. Shandong University of traditional Chinese medicine, Jinan 250014
2. College of traditional Chinese medicine, Shandong University of traditional Chinese medicine, Jinan 250355
3. Department of microsurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of traditional Chinese medicine 250014
Keywords:Duhuoparasitic Decoction Network pharmacology Knee osteoarthritis Signal path
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the molecular mechanism of Duhuojisheng Decoction in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Methods: through tcmsp database and Batman TCM database, the compounds in Duhuo Jisheng decoction, such as Duhuo, sangparasitic, eucommia, Achyranthes bidentata, asarum, Gentiana macrophylla, Poria cocos, cinnamon, Fangfeng, chuanxiong, ginseng, liquorice, angelica, white peony and raw rehmannia, were searched, and their active components and targets were screened The target of KOA was acquired by database; the drug compound target network was constructed by using the software of cycloscape 3.7.2, and PPI network was constructed and analyzed by using string database; go analysis and KEGG enrichment analysis were conducted by using David database (P < 0.05). Results: after screening, 217 components and 155 targets were obtained for the treatment of KOA; 5653 targets were related to koa; 79 proteins were related to PPI core network, including INS, IL6, TNF and VEGFA; 301 go biological processes and 114 related signal pathways were obtained, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoclast differentiation, MAPK signal pathway, HIF-1 signal pathway and PI3K Akt signal pathway , TNF signal pathway, etc. Conclusion: Duhuo parasitic decoction may regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis and inflammatory response to treat koa, which is the result of multi-component, multi-target and multi-channel interaction, providing theoretical support for Duhuo parasitic Decoction to treat KOA.
1. Introduction
Knee osteoarthritis (Knee Osteoarthritis,KOA) is the most common clinical disease based on degenerative pathological changes, which is characterized by cartilage degeneration, narrowing of joint space, osteophyte formation, joint pain and limited movement [1]. Epidemiological surveys show that in China, the risk of knee osteoarthritis in people over the age of 60 is as high as 42.8%, while the risk of KOA is about 40% for men and 47% for women[2]. At present, the western medicine treatment of KOA is mainly conservative treatment and surgical treatment, in which conservative treatment is mainly oral non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs, painkillers, rehabilitation physiotherapy, intraarticular drug injection to alleviate symptoms and improve function [3]. However, long-term use of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs can cause gastrointestinal perforation, ulcer, bleeding and other adverse reactions, with certain limitations [4]. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that KOA belongs to the category of "arthralgia", also known as bone arthralgia and painful arthralgia. The pathogenesis is always due to deficiency and excess, due to deficiency of liver and kidney, poor operation of meridian qi and blood, loss of support of muscles and bones, complex feeling of wind, cold and dampness, and arthralgia; or exogenous wind, cold and dampness, long qi and blood stasis, obstruction of meridians, loss of support of muscles and bones, forming arthralgia syndrome. Compared with the limitations of western medicine in the treatment of KOA, traditional Chinese medicine shows unique advantages in the treatment of KOA.
Duhuojisheng Decoction comes from 《The prescription of preparing urgent Qianjin》, which is composed of Duhuo, Mulberry parasitic, Eucommia, Achyranthes bidentata, Asarum, Gentiana, Poria, Cinnamomum, Fangfeng, Chuanxiong, Ginseng, licorice, Angelica, Radix Paeoniae Alba and Radix Rehmanniae, which has the function of dispelling rheumatism, stopping arthralgia, tonifying liver and kidney, tonifying qi and blood. In the square, he reuses living alone as the king, is good at treating Fu Feng, dispels chronic arthralgia, and dispels the evil of wind, cold and dampness between Xiajiao and muscles and bones. Asarum is good at searching for the evil of wind-cold and dampness in yin meridians, and excluding the dampness of meridians and collaterals; Gentiana macrophylla, fangfeng and rheumatism, relaxing muscles and collaterals, warming the meridians of cinnamon, dispelling cold and promoting blood circulation, strengthening muscles and bones by adding mulberry parasites, Eucommia ulmoides and Achyranthes bidentata to strengthen muscles and bones, and mulberry parasites can also remove rheumatism, and Achyranthes bidentata can activate blood to promote limb muscles and veins. Radix angelicae Sinensis, Ligusticum chuanxiong, Rehmannia glutinosa, Radix Paeoniae Alba nourishing blood and blood, ginseng, Poria cocos, licorice invigorating spleen and tonifying qi. And the combination of Radix Paeoniae Alba and licorice can soften the liver and relax the muscles. Treatment of arthralgia syndrome for a long time, deficiency of both liver and kidney, deficiency of qi and blood, pain in waist and knees, impotence and weakness, unfavorable flexion and extension of limbs. It is recorded in the Lingshu Sutra: "for those with cold arthralgia, Yin evil is real; for those who are powerless, qi and blood deficiency is also." It is Fang Ye, living alone, parasitic, Asarum, Gentiana, Fangfeng, Gui Xin, Xinwen's products. Then the cold arthralgia is gone and powerful. " Duhuojisheng Decoction is a common prescription in clinical treatment of knee osteoarthritis, which has achieved good results in long-term clinical practice[5-7]. In this study, the active compounds and action targets of Duhuojisheng Decoction were screened by the method of network pharmacology, and cluster analysis was carried out to construct a drug-compoundtarget network. The signal pathway analysis was carried out by analysis software to predict the mechanism of its action in the treatment of KOA, so as to provide theoretical reference for the basic experimental research and clinical rational application of Duhuo parasitic decoction in the treatment of KOA.
2. Method
2.1 Collection and screening of compounds in Duhuo parasite decoction
With the help of traditional Chinese medicine system pharmacological analysis platform database (TCMSP, http://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php) and Batman-TCM database (http://bionet.ncpsb.org/batman-tcm/), "Duhuo", "mulberry parasite", "Eucommia", "Achyranthes bidentata", "Asarum", "Gentiana", "Poria", "Cinnamon", "Chuanxiong", "Ginseng", "Glycyrrhiza", "Angelica", "Radix Paeoniae Alba" and "Radix Rehmanniae" were used as key words to search for the chemical constituents of Duhuo parasite. According to the ADME principle, oral bioavailability (Oralbioavailability,OB) indicates the speed and extent at which the active components or active groups of an oral drug are absorbed into the systemic circulation. The higher the OB value, the better the drug-like (DL) of the bioactive molecule of the drug[8-9]. Combined with the literature research, according to the standard of OB ≥ 30% and DL ≥ 0.18, the standard chemical components in the compounds of Duhuo, Mulberry parasitic, Eucommia, Achyranthes bidentata, Asarum, Gentiana, Poria, Cinnamomum, Fangfeng, Chuanxiong, Ginseng, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Angelica sinensis, Radix Paeoniae Alba and Radix Rehmanniae were selected as active components.
2.2 Screening of target proteins and construction of drugcompound-target network
Through the TCMSP platform, the active components selected from Duhuo parasite decoction were searched to find the corresponding target proteins. The corresponding gene names of the target proteins were queried by Uniprot database (https://www.uniprot.org/), the repeated targets were merged, and the proteins without corresponding gene names were deleted. The "drug-compoundtarget" network was constructed by Cytoscape3.7.2 software, and the compounds and targets were analyzed.
2.3 Prediction of potential targets of Duhuo Jisheng decoction in the treatment of KOA
The genes related to KOA were searched with "KneeOsteoarthritis" as the keyword in the disease target screening database[10] (Genecards https://www.genecards.org/) and the toxicity and gene comparison database (CTD http://ctdbase.org/). The screened drug targets were mapped with disease targets to obtain the potential targets of Duhuo Jisheng decoction in the treatment of KOA.
2.4 Construction and Analysis of PPI Network
The potential targets of Duhuo Jisheng decoction in the treatment of KOA were imported into String database[11]. The species was defined as "HomoSapiens" (Homo sapiens), and the protein interaction relationship was obtained. Save the file as TSV format, import the file into Cytoscape3.7.2 software, use the "Networkanalyzer" function of Cytoscape3.7.2 software to analyze the network topology attributes, and filter out the core targets.
2.5 Path analysis of targets
In order to further understand the function of the potential target genes of Duhuojisheng decoction in the treatment of KOA and its role in signal pathway, it was introduced into DAVID database[12] (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp), P < 0.05, the species was defined as "HomoSapiens", and the names of all target genes were corrected to their official name (officialgenesymbol), for GO enrichment analysis and KEGG signal pathway enrichment analysis. GO enrichment analysis selected biological processes (Biologicalprocesses,BP), cell function (Molecularfunction,MF), cell components (Cellcomposition,CC), sorted according to the number of enriched targets, selected the main items, and drew secondary classification bar chart and bubble chart. The KEGG path analysis is visualized by using the drawing tool in the Omicshare Cloud platform (http://omicshare.com/) to draw a bubble chart.
3. Results
3.1 Screening of active compounds in Duhuo parasite decoction
A total of 1587 compounds in Duhuo parasite decoction were obtained by searching TCMSP database and Batman-TCM database. Among them, 99 from Duhuo, 46 from mulberry parasite, 119 from Eucommia ulmoides, 176 from Achyranthes bidentata, 67from Asarum, 27 from Gentiana, 34 from Poria cocos, 100 from cinnamon, 50 from Fangfeng, 189 from Chuanxiong, 190 from ginseng, 280 from licorice, 125 from Radix angelicae Sinensis, 77 from Radix Paeoniae Alba, 8 from Radix Rehmanniae. According to the standard of OB ≥ 30% and DL ≥ 0.18,217 active compounds of Duhuo parasite decoction were selected. Among them, 9 from Duhuo, 2 from mulberry parasite, 25 from Eucommia ulmoides, 20 from Achyranthes bidentata, 8 from Asarum, 2 from Gentiana, 15 from Poria cocos, 10 from cinnamon, 11 from Fangfeng, 7 from Chuanxiong, 22 from ginseng, 92 from licorice, 2 from Angelica sinensis, 13 from Radix Paeoniae Alba, 3 from Radix Rehmanniae. Table 1 is the basic information of some active compounds in Duhuo parasite decoction.
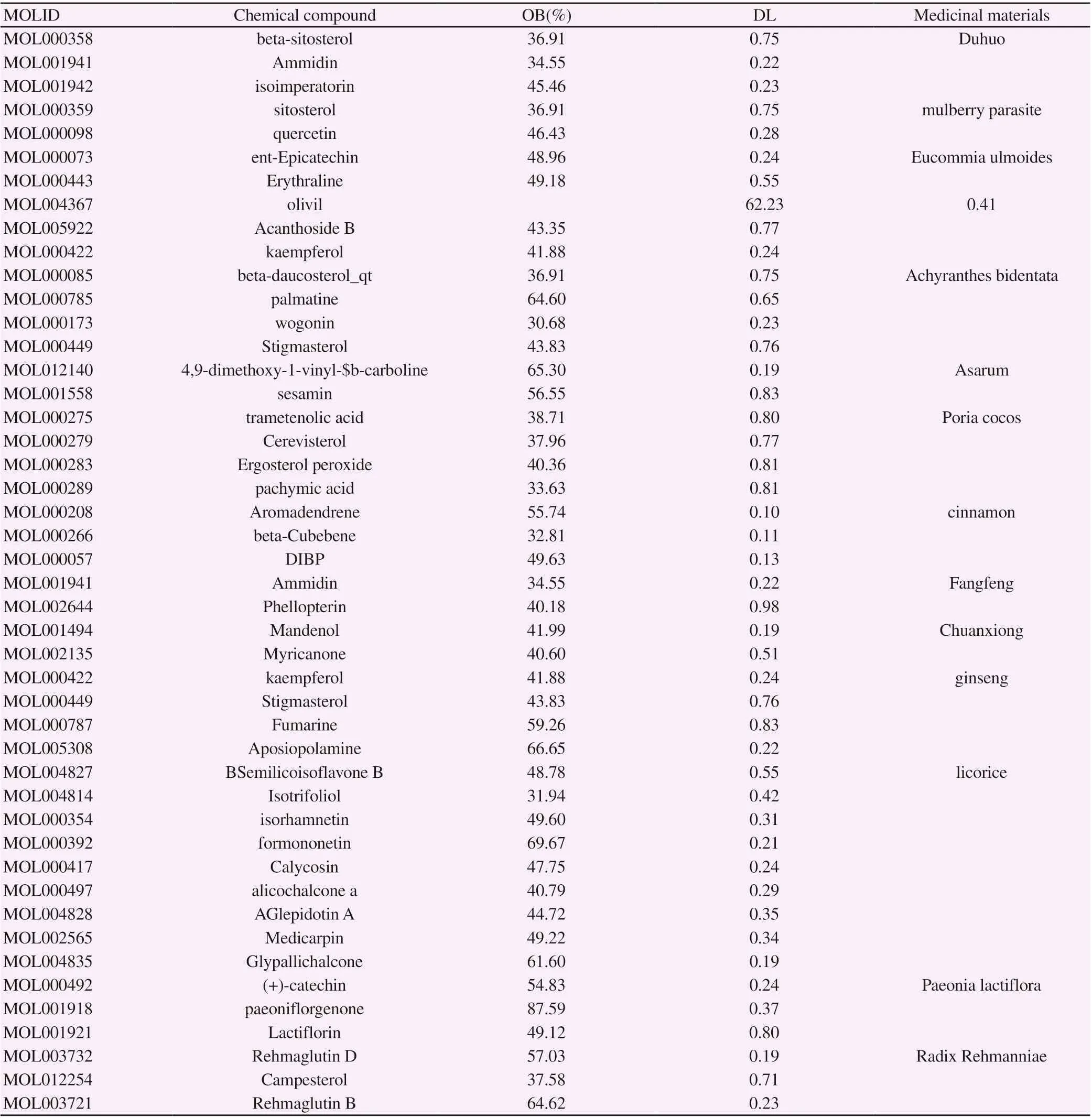
Table 1 Basic information of some active compounds in Duhuojisheng Decoction
3.2 Construction and analysis of drug-compound-target network
The drug-active compound-target network in Duhuo parasite decoction shown in figure 1 was constructed by Cytoscape3.7.2 software. The network has a total of 387 nodes, including 15 drug nodes, 217 active compound nodes and 155 target nodes, with a total of 3507 edges. In the network, the blue hexagon represents the drugs in Duhuo parasite soup, the red diamond represents the active compound, and the green inverted triangle represents the target gene. Each edge in the network represents the active compounds contained in the drug and the interaction between the active compounds and the target genes. The value of a node represents the number of connections between the network node and other nodes, and the topological attributes of the network are analyzed with the help of the "Networkanalyze" function in the Cytoscape3.7.2 software. Among them, the grade value (Degree) and center value (BetweennessCentrality,BC) are two important parameters to measure the key of a node in the network. The nodes with larger grade value (Degree) and center value (BetweennessCentrality,BC) are selected. These nodes play a pivotal role in the network and may be key compounds or targets. In this network, each active compound interacts with 18 targets on average, and each target interacts with 21.05 active compounds on an average, so there is an active compound interacting with multiple targets in Duhuo parasite decoction. At the same time, there are multiple active compounds acting on the same target, which reflects the characteristics of multi-components combined with multi-targets in traditional Chinese medicine compound prescription to play an overall regulatory role[13]. In terms of compounds, there were more than 20 targets in 101 compounds. By analyzing the center value and grade value of compound-target, it was found that the top five active compounds were MOL000098- quercetin, MOL000422- kaempferol, MOL000358- β-sitosterol, MOL000449- stigmasterol and MOL000173- baicalein, which could interact with 91, 61, 58, 47 and 37 target proteins, respectively. In terms of targets, a total of 35 can interact with 21 or more compounds, and the top 6 are ESR1, AR, PTGS2, NOS2 and DPP4, which can interact with 166,163,146,131,127 active compounds, respectively.
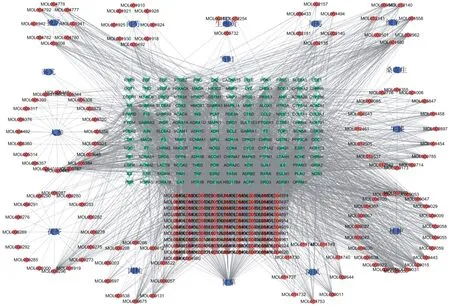
Fig.1“Drug -Component-Target”Network
3.3 Predict the potential targets of Duhuojisheng decoction in the treatment of KOA.
A total of 5653 potential KOA targets were obtained by searching GeneCards database and CTD database. The Venny diagram was drawn by using Venny online platform (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/), and the targets regulated by the active components of Duhuo parasitic decoction were mapped and intersected with the potential targets of KOA, and a total of 114 cross targets were obtained, which are the potential targets of Duhuo parasitic decoction in the treatment of KOA, as shown in figure 2.
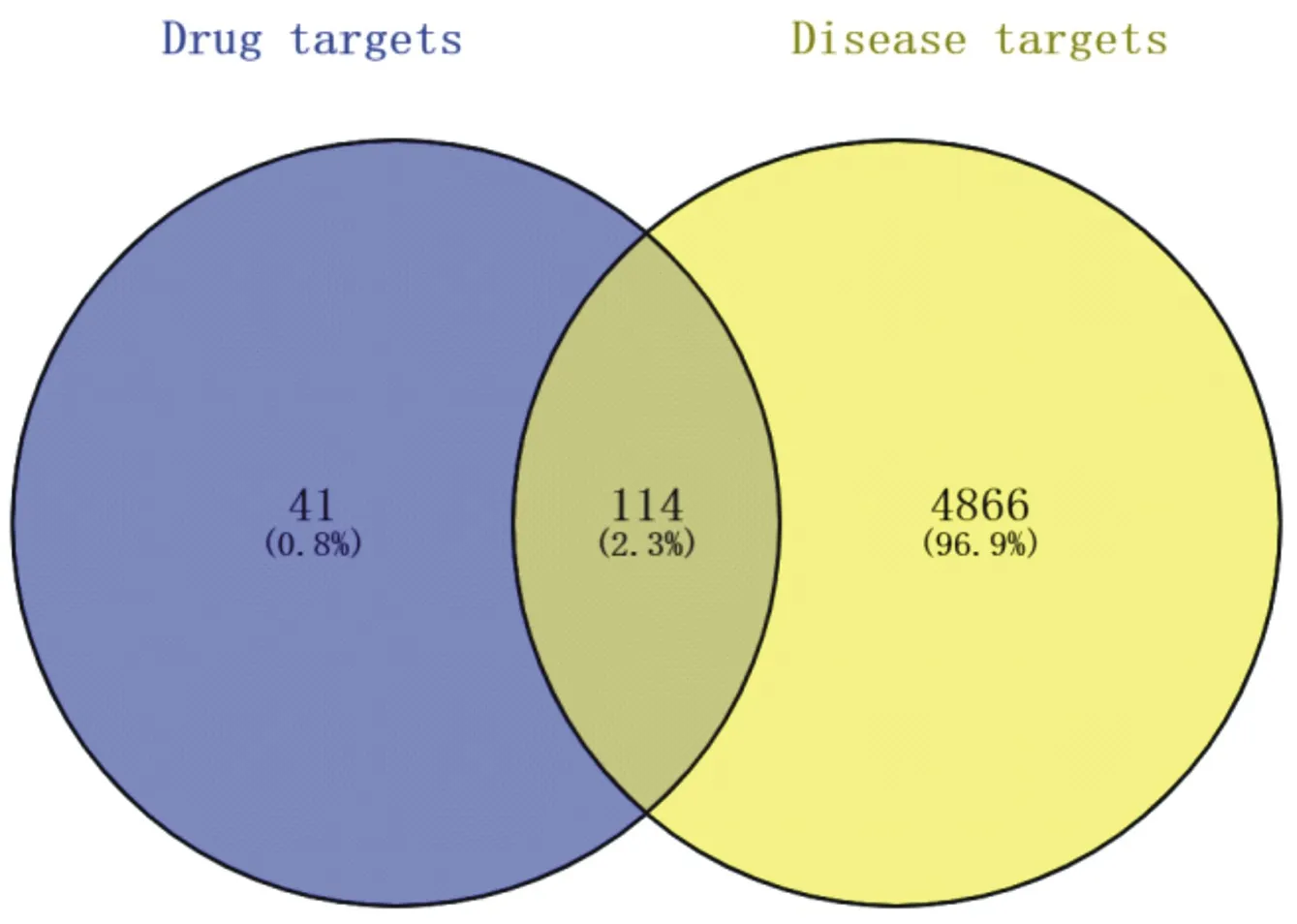
Fig.2 venn map of potential target of KOA treated with Duhuojisheng Decoction
3.4 Construction and Analysis of PPI Network
The PPI network of Duhuo parasite decoction is shown in figure 3 (the dot represents the target, the darker the color represents the more connections between the node and other nodes, the closer the relationship, and the lighter the color represents the less connection between the node and other nodes, the more distant the relationship). 114potential target genes of KOA treated by Duhuo parasitic decoction were inputted into STRING, and the protein interaction network was obtained. The network consists of 79 nodes (of which 35 proteins are not involved in the construction of the network) and 956 edges. The average node value of target protein is 24.20, of which 36 target proteins are ≥ 24, indicating that these 36 target proteins are likely to be the key targets for Duhuo parasitic decoction to exert pharmacological action. 10 key nodes (Hub nodes) in the network were selected with the help of "cytoHubba" plug-in in Cytoscape3.7.2, as shown in Table 2.
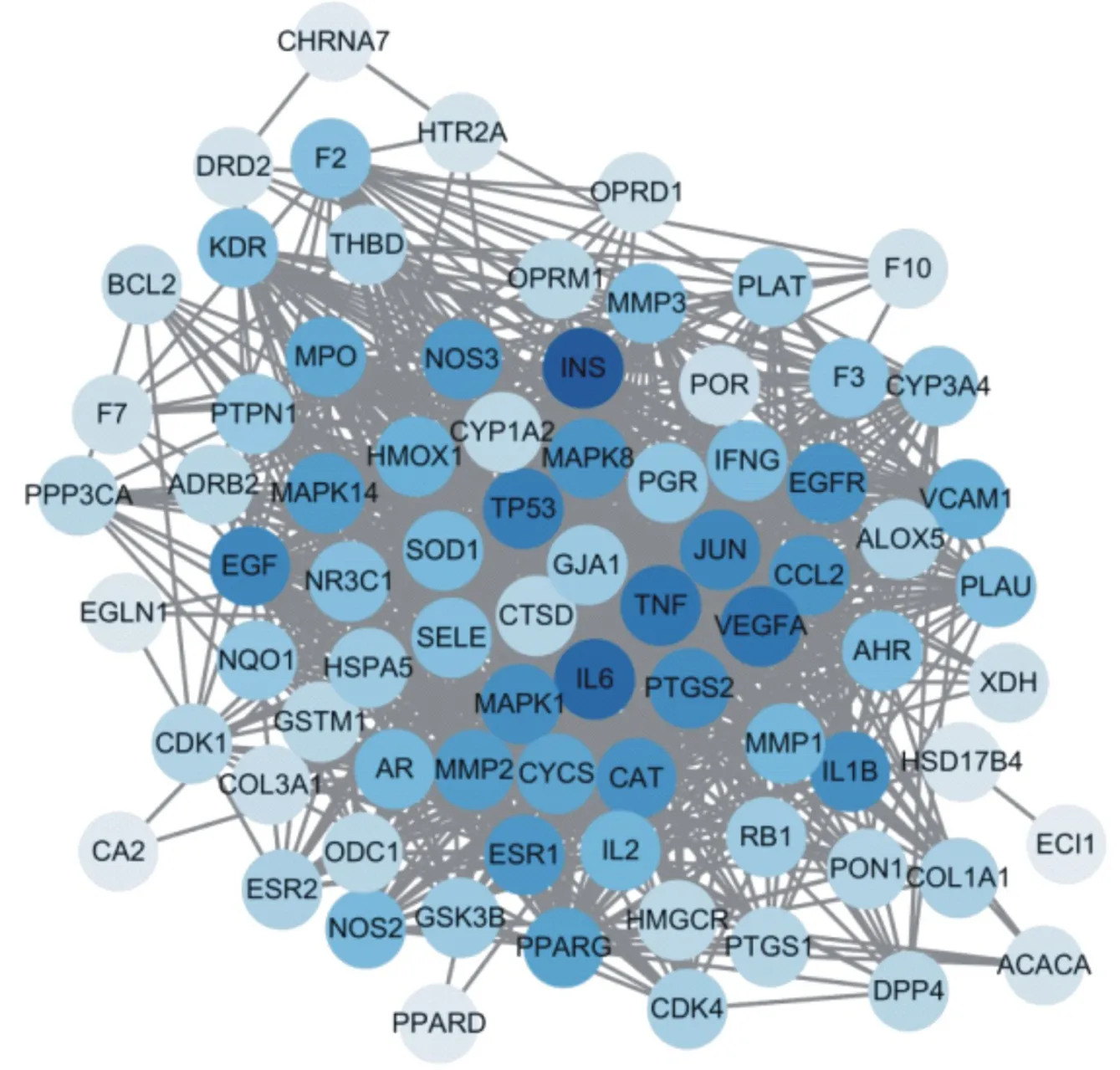
Fig.3 "protein protein interaction" (PPI) network of Duhuojisheng Decoction
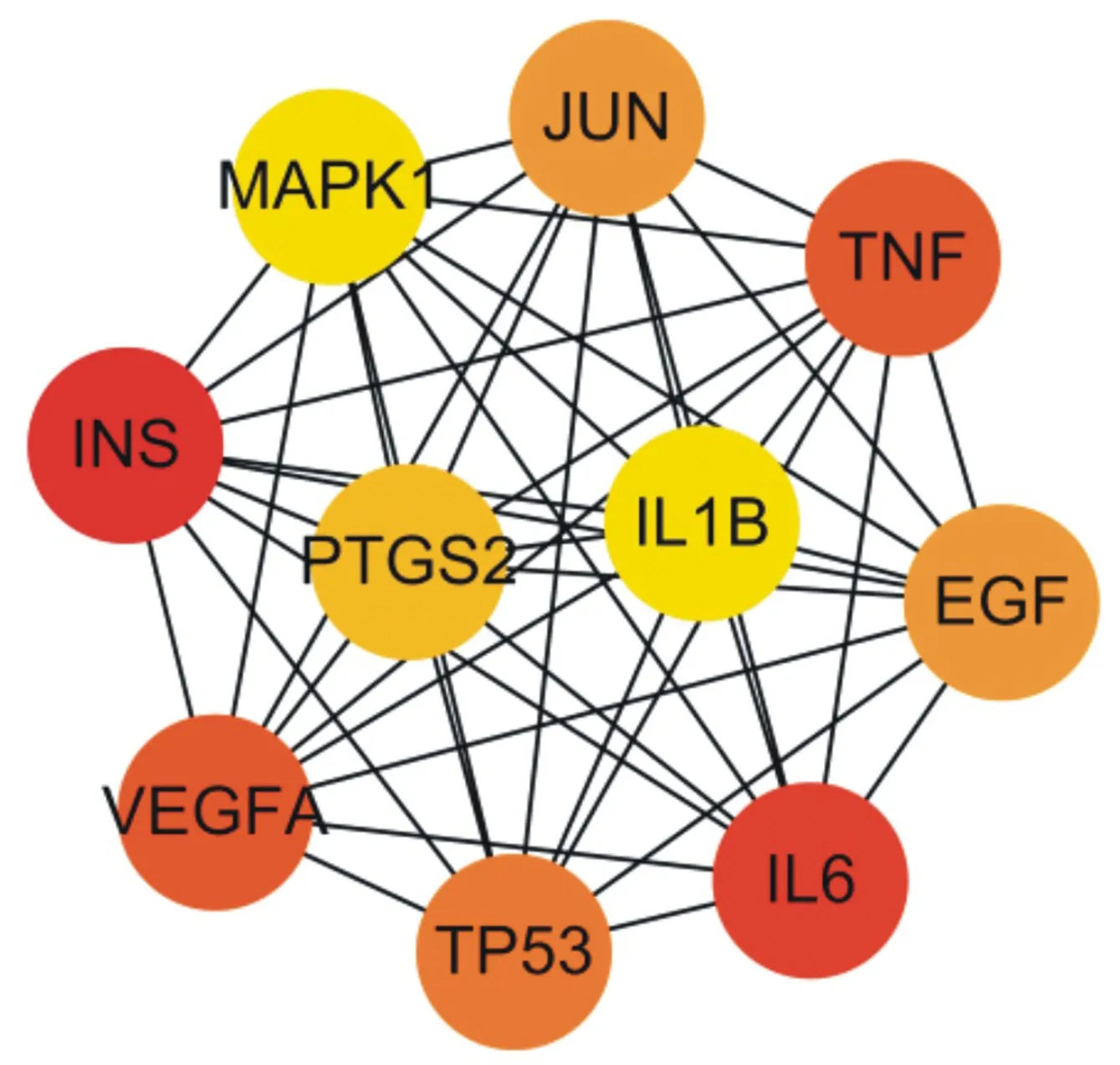
Fig. 4 Key nodes of PPI network
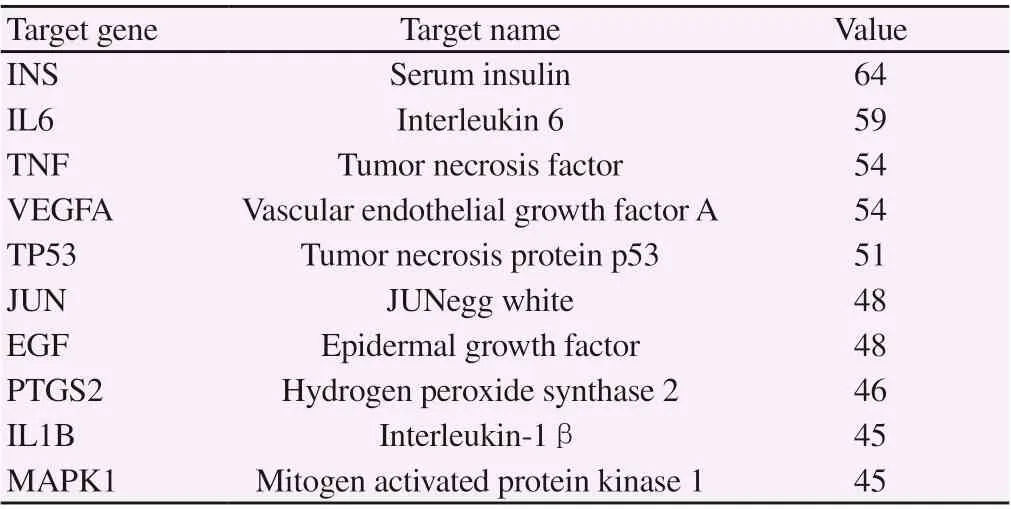
Table 2 key target information of Duhuojisheng Decoction in the treatment of KOA
3.5.Target GO enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis.
114potential targets of Duhuojisheng decoction in treating KOA were inputted into DAVID database, and a total of 421 GO enrichment items were obtained, including 301 biological processes (Biologicalprocesses,BP), 73 cellular functions (Molecularfunction,MF) and 47 cellular components (Cellcomposition,CC). Select the top 20 GO entries for enrichment genes and visualize them with a bubble chart, as shown in figure 5. BP is mainly enriched in cell proliferation, cell metabolism, signal transduction, inflammatory reaction, apoptosis process, etc.; MF is mainly enriched in oxidoreductase activity, cyclin binding, peroxidase activity, acetylcholine binding; CC, in plasma membrane, nucleus, cytoplasmic sol, extracellular space, exocrine gene enrichment accounts for a large proportion.
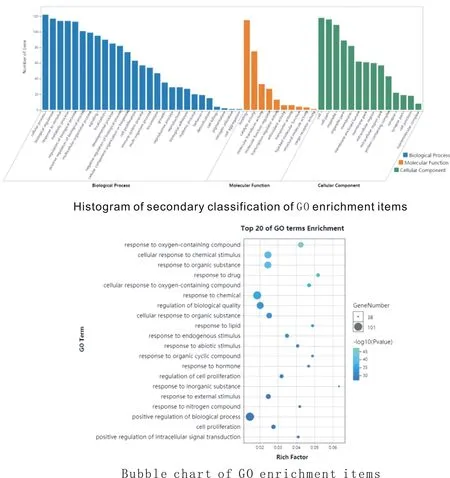
Fig.5 enrichment analysis of target GO
99 signal pathways were screened by KEGG pathway enrichment analysis, which were mainly related to rheumatoid arthritis (Rheumatoidarthritis), osteoclast differentiation (Osteoclastdifferentiation), MAPK signal pathway (MAPKsignalingpathway), HIF-1 signal pathway (HIF-1signalingpathway), PI3K-Akt signal pathway (PI3KAktsignalingpathway), TNF signal pathway (TNFsignalingpathway) and so on. The first 20 pathways of enriched genes were selected to draw the corresponding bubble diagram, as shown in figure 6 (Y axis represents the name of the pathway, X axis represents the percentage, and bubble area represents the number of enriched genes in the pathway). According to the relationship between the protein target and the signal pathway, the key pathway is selected, and the "target-pathway" network diagram is established (figure 7), in which the diamond represents the path and the circle represents the target.
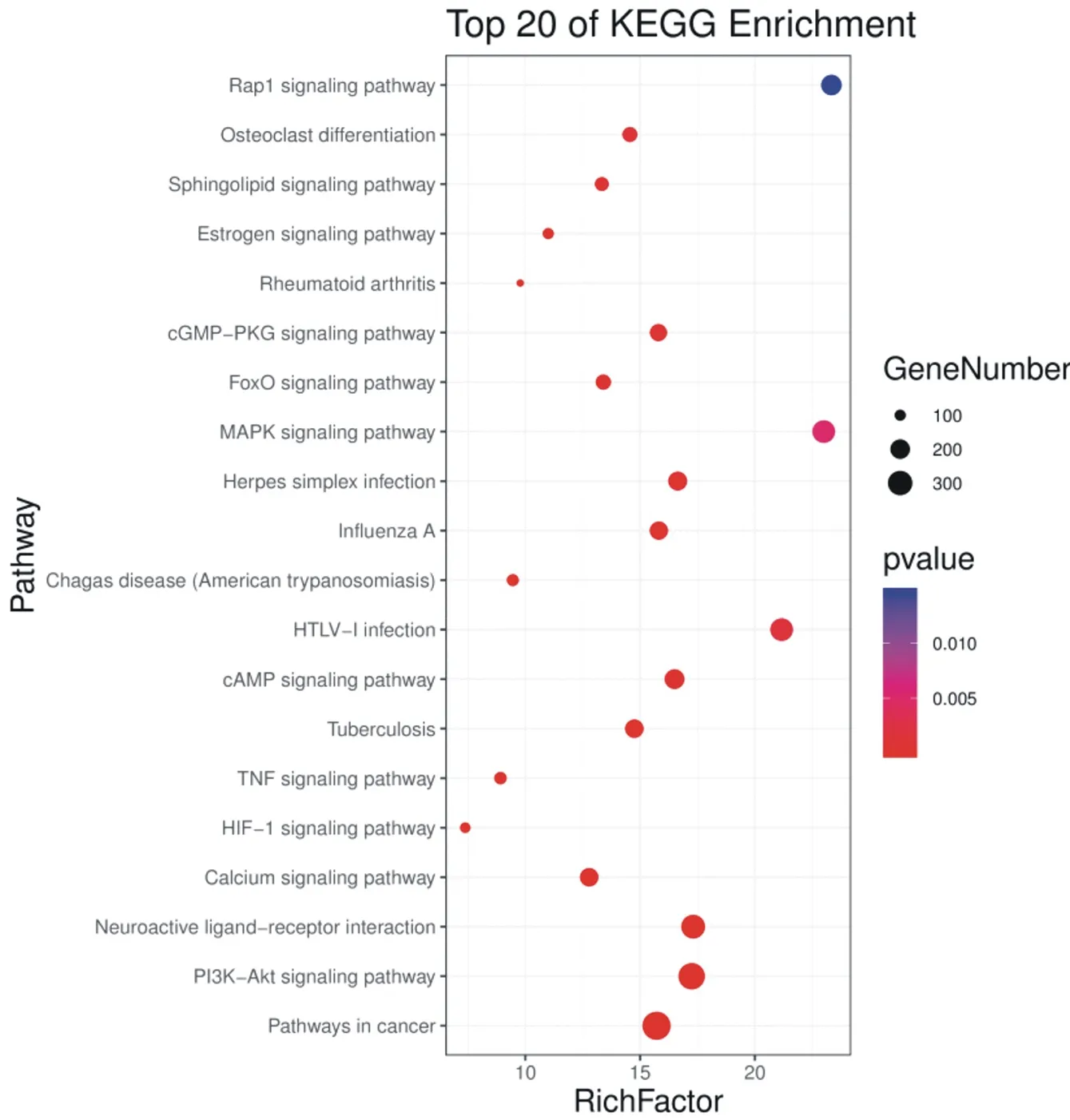
Fig.6 Bubble chart of enrichment of KOA KEGG pathway treated with Duhuojisheng Decoction
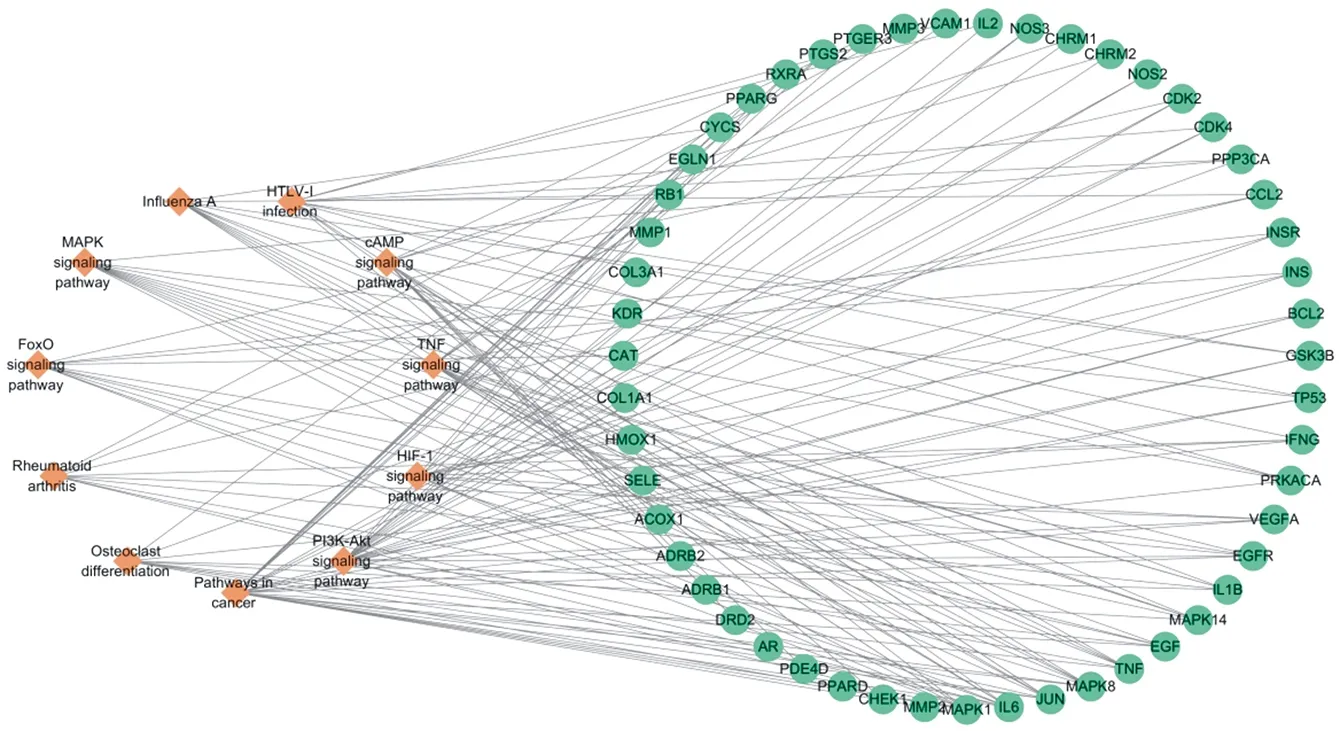
Fig.7 Target-pathway network
4. Discussion
KOA is a common chronic degenerative bone and joint disease in clinic, which is more common in the middle-aged and elderly. Its etiology and pathogenesis have not been fully elucidated. It is
mainly caused by the wear and destruction of articular cartilage, hyperplasia, joint space stenosis, and then cause synovitis, meniscus injury, osteophyte formation and articular cavity effusion and so on. At present, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers are mainly used as the first choice. Although some clinical effects have been achieved, long-term use will lead to adverse reactions and dependence, and symptoms are easy to relapse after drug withdrawal[5]. KOA belongs to the category of arthralgia syndrome in traditional Chinese medicine, also known as bone arthralgia and knee arthralgia. In the Theory of Plain Bi, it is recorded: "Wind, cold and dampness are mixed together as arthralgia". "arthralgia lies in that the bone is heavy, that the pulse coagulates but does not flow, that the tendon does not stretch, and that the flesh is not benevolent." The pathogenesis of KOA is mostly caused by deficiency of liver and kidney, strain or invasion of wind, cold and dampness, and local qi and blood stasis. Duhuo parasitic decoction has the function of dispelling rheumatism, stopping arthralgia, benefiting liver and kidney, tonifying qi and blood. Meta analysis, clinical observation and animal experiments show that Duhuo parasitic decoction can significantly improve the clinical symptoms of patients with KOA[14-17]. It shows the unique advantages of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of KOA.
In this study, 1587 compounds, 217 active components, 155action targets and 114potential targets of Duhuo parasitic decoction in the treatment of KOA were screened by the method of network pharmacology, indicating that Duhuo parasitic decoction has the characteristics of multi-components and multi-targets in the treatment of KOA. According to the "drug-active compound-target" network, 101 key active compounds were screened. According to the center value and grade value, the top 5 were quercetin, kaempferol, β-sitosterol, stigmasterol and wogonin. Among them, the number of targets interacting with quercetin was the most, up to 91, indicating that quercetin may play the most significant role. Quercetin has pharmacological effects such as antioxidation, antiinflammation, bone and joint protection, anti-apoptosis, inhibition of osteoclast absorption and immune regulation[18]. Jia Qingyun et al.[19]found that quercetin can significantly improve the joint swelling symptoms of CIA mice, and can effectively reduce joint damage and reduce joint inflammation index, and there is no liver damage. In addition, quercetin can also protect articular cartilage by reducing the expression of inflammatory factors and inflammatory complex mRNA, inhibiting leukocyte aggregation and the production of inflammatory factors[20]. Kaempferol has a significant inhibitory effect on the activities of TRAP and cathepsinK, and promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts[21]. β-sitosterol and stigmasterol are common phytosterols, both of which have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Among them, CHEN et al.[22] evaluated the knee joint of KOA rabbits by gross morphology and histology, and found that stigmasterol could significantly inhibit the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) and cartilage degradation, indicating that stigmasterol has the potential to treat osteoarthritis; wogonin belongs to flavonoids, which plays an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the expression of inflammation-related factors.
There were 79 target proteins in the PPI network analysis of Duhuojisheng decoction in the treatment of KOA. Through the network topology analysis, it was found that IL6, TNF, VEGFA, IL1B, MAPK1 and other targets were the main targets of Duhuojiesheng decoction in the treatment of KOA. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1 β (IL1B) are important inflammatory cytokines. Pathology shows that TNF and IL-6 are the main mediators in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and participate in the regulation of inflammatory response[23]. The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) is closely related to synovitis, chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degeneration. Some studies have shown that VEGFA can promote the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-3 in the development of osteoarthritis and accelerate the process of arthritis. At the same time, it also promotes the destruction of articular cartilage tissue[24]. MAPK1 belongs to the family of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MitogenactivatedProteinKinase,MAPK). The MAPK subfamily includes extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (erk1/2), c-jun N-terminal kinases (jnk1/2) and p38, which are involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and inflammation[25]. Among them, p38MAPK signal pathway is not only involved in regulating the growth and development of chondrocytes, but also involved in the degradation of collagen and proteoglycan, so in the study of KOA, the role of p38MAPK pathway and its mechanism are worthy of attention.
GO enrichment analysis of the target of Duhuojisheng decoction in the treatment of KOA shows that its biological processes are mainly related to cell proliferation, apoptosis, inflammation and so on, which play a key role in the treatment of KOA with Duhuo parasitic decoction. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis showed that the potential targets of Duhuojiesheng decoction in the treatment of KOA were mainly related to rheumatoid arthritis, osteoclast differentiation, MAPK signal pathway, HIF-1 signal pathway, PI3K-Akt signal pathway, TNF and other signal pathways. Further analysis shows that MAPK1 and TNF, are involved in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoclast differentiation, MAPK signal pathway, HIF-1 signal pathway, PI3K-Akt signal pathway and TNF signal pathway related to arthritis. Whether the active components of Duhuo parasite decoction regulate rheumatoid arthritis, osteoclast differentiation, MAPK signal pathway, HIF-1 signal pathway, PI3K-Akt signal pathway and TNF signal pathway by acting on MAPK1 and TNF targets, thus play a role in the treatment of KOA need to be further studied. Both MAPK signal pathway and P13K-Akt signal pathway belong to osteoclast differentiation signal pathway, and this signal pathway is the most important signal transduction pathway to induce osteoclast differentiation, which affects the development of the disease by regulating the balance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts[26]. Among them, MAPK signal pathway can regulate the expression of osteoblast-specific genes by phosphorylating osteoblast-related transcription factor antibodies, and affect osteoblast differentiation and apoptosis[24]. Up-regulation of P13K/Akt/mTOR signal pathway can promote the proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes, reduce the loss of chondrocytes and the exfoliation of cartilage layer, thus improve the symptoms of KOA[27].
To sum up, this study uses the method of network pharmacology to explore the mechanism of Duhuojisheng decoction in the treatment of KOA, and expounds the overall regulation of multi-components, multi-targets and multi-pathways of the compound on the body from the molecular level, which may play a therapeutic role by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation, which provides theoretical support for the treatment of KOA with Duhuo parasitic decoction. However, this study has some limitations, the use of traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions need to be combined with the clinical symptoms of patients based on syndrome differentiation, can not be taken privately. In addition, due to the incomplete database data, ignoring the content of traditional Chinese medicine components, drugs and their interactions and other pharmacokinetic effects in vivo, so its specific mechanism needs in-depth research and experimental verification.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年16期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年16期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Meta-analysis on clinical efficacy of Simiao Yong'an decoction in treatment of peripheral arterial occlusive diseases
- Network pharmacology-based elucidation of molecular biological mechanisms of Kanglaite injection for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- Effect of Qishen decoction on dedifferentiation of sinusoidal endothelial cells by autophagy
- Research on the rules of Professor Dai Xiaohua's medication for coronary heart disease and chronic heart failure based on data mining
- Clinical study on the treatment of bronchiectasis in remission period by embedding thread combined with Jianpi Qushi Huayu plaster
- Comparative study of 99Tc-MDP and zoledronic acid in the treatment of osteoporosis
