Effects of Electroacupuncture on Pain Threshold and Prostaglandin E2 in Spinal Cord in Postoperative Pain Rat
WANG Jin-kun (王瑾琨), YU Xue (于 雪), CAO Kang-di (曹康迪), YE Chen (叶 晨), CHEN Yu-qi (陈宇琦),LIU Huai-wei (刘怀伟), XUE Na-ying (薛娜英), XI Meng-qi (係梦琪), REN Xiu-jun (任秀君)
1. School of Acupunture-Moxibusion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2. School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
#: is co-first author
Correspondence to: Prof. Ren Xiu-jun, Tel: 010-53912199, E- mail: rxiujun@163.com
ABSTRACT Objective:Electroacupuncture (EA) is good at post-surgical pain. But point selection method in treating incision-induced pain remains a major clinical challenge. We reasoned that different acupoints may work though adjusting prostaglandin E2 in spinal cord. We wish to explore the analgesic mechanism of electroacupuncture on plantar incision pain rats and provide more therapeutic ideas for acupuncture analgesia.Methods: A total of 50 male rats were randomly divided into a sham operation group, a model group, an EA 1, EA 2 and a drug group (n=10, each). A rat model of left plantar incision pain was established. The rats in EA1 group was needled at ipsilateral Yanglingquan (GB34) and Taixi (KI3). The rats in EA2 group was needled at ipsilateral Quchi (LI11) and Hegu (LI4). EA stimulation (2/100Hz, 1-2-3 mA)was administered 30 minutes immediately after operation. The rats in drug group were fed with Fenbid by gavage 20 minutes before incision (30 mg/kg, p.o.). The hot plate pain detector was used to measure the thermal pain threshold (TPT) before and 24 hours after operation Prostaglandin E2 content of spinal cord was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) at 1 and 24 hours after operation.Results:Compared with sham operation group, the TPT in model group decreased 41%. Compared with the model group, the TPT increased 56% in EA1, 29% in EA2, 190% in drug group (P>0.05 ). At 1 h after operation,compared with the sham operation group, PGE2in model group increased 15%. Compared with the model group, PGE2in drug group decreased 5%. At 24 hours after operation, compared with sham operation group, PGE2in model group increased 9%. Compared with model group, it decreased 4% in EA 1 group, 8%in drug group and increased 3% in EA2 group.Conclusion: Both the drug and the electroacupuncture can adjust the 24-hour pain threshold and PGE2in spinal cord. The curative effects of the drug are better than that of electroacupuncture. The proximal point is better than that of the distal point. Electroacupuncture can treat postoperative pain by regulating PGE2in spinal cord.
KEYWORDS Electroacupuncture; Postoperative pain; Pain threshold; Spinal cord; Prostaglandin
INTRODUTION
Postoperative pain is the most common type of acute pain, and it is a strong acute pain. Although the duration is short, it disturbs patient lives clinically and affects the quality of life seriously[1]. The rat plantar incision pain model was established by Brennan Research Group in the mid-1990s[2]. In this study, after 1-cm longitudinal incision of the skin and muscle of the hind paw, the rats experienced several days of hyperalgesia to mechanical stimulation,and then gradually recovered. It is similar to clinical postoperative pain. It is currently widely used to study the mechanism of postoperative pain.
Prostaglandin (PG) is one of the main metabolites of arachidonic acid, which is related to many pathophysiological processes such as inflammation,tumor, microcirculation of blood flow, pain and reproduction, and also has important significance in maintaining cell stability and proliferation[3].
Acupuncture analgesia is a characteristic treatment method in traditional Chinese medicine,and has been widely used in various surgical operations such as craniocerebral surgery,thyroidectomy, pneumonectomy, gastrectomy and cholecystectomy. Acupuncture can not only relieve the pain of patients, but also regulate the body's immune function and accelerate the repair of wounds. The acupoint combination, the selection method of acupoint, affects the clinical effect of acupuncture treatment. However, it is rare to compare the analgesic effect and PG content through acupuncture treatment of plantar incision pain in different acupoint groups.
In order to study the effect and mechanism of acupuncture analgesia, SD adult rats were used and postoperative pain was induced by 1-cm incision in left hind paw. In this study, we want to investigate whether EA at different acupoints improve heat threshold through adjusting the expression of PGE2level in the spinal cord.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals
Male SPF adult Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat,180±20 g, provided by SPF (Beijing) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Animal License Number is SCXK (Beijing)2016-0002. The room temperature is 24±1℃ and in 12-h light/dark cycle. The rats were freely fed water and food. 5 rats were in one cage and adapt to the environment for 2 days before experiment.This experiment strictly follows the guidance on treating experimental animals issued by the Ministry of science and technology in 2006 and procedures were approved by an institutional animal care and use committee of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine.(BUCM-4-2018120201-4003)
A total of 50 rats were randomly divided into a sham-operation, a model, an EA 1 and EA 2 group with 5 rats in each.
(1) Sham-operation group: Touching the hind paw with a brush; (2) Model group: a 1 cm longitudinal incision was made at the hind paw;(3) EA1 group: Needling at left Yanglingquan(GB34) and Taixi (KI3) for 30 minutes immediately after plantar incision; (4) EA2 group: Needling at left Quchi (LI11) and Hegu (LI4) for 30 minutes immediately after plantar incision; (5) Drug group:Rats were treated with Fenbid by gavage feeding 20 minutes before incision (30mg/kg, p.o.). In the EA group, rats were fixed with soft cloth bags with EA for 30 minutes. Rats in other groups were fixed with soft cloth bags for 30 min at the same time. There were 2 time points in each group, 1 h and 24 h after operation. There were 5 rats in each time point.
Establishment of Pain Model
Surgery was performed as previously described[2]. Briefly, rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate(350 mg/kg, i.p.). After the left plantar surface was disinfected, a 1 cm longitudinal incision was made with a number 10 scalpel, through skin and fascia of the plantar aspect of the paw, starting 0.5 cm from the proximal edge of the heel and extending toward the toes. Then the skin was closed with 4-0 nylon suture and cleaned by 0.9% saline solution.
Electroacupuncture Stimulation
GB34, KI3, LI11 and LI4 on the left side were used according to Experimental Acupuncture[4].GB34 is located 2 mm anterior inferior of the fibula head. KI3 is located in the middle between the medial malleolus and Achilles tendon of the hind leg. LI11 is located in the depression in front of the elbow joint outside the proximal radius. LI4 is located between the first and second metacarpal bones of the forelimb. After disinfection with 75%alcohol, acupuncture needles (0.25×25mm, Suzhou Acupuncture and Moxibustion Products Co., Ltd.Suzhou, China) were inserted 5mm vertically into acupoints. Rats were needled left GB34, KI3 in EA1 group and left LI11 and LI4 in EA2 group. The needles were connected with electroacupuncture instrument (LH202, Beijing Huawei co., Ltd.)respectively. The EA frequency was adjusted to 2/100Hz, while the intensity was 1-2-3mA.The EA session was 30 minutes.
Thermal Pain Threshold (TPT)
The rat plantar thermal pain threshold was measured before and 24 hours after operation by a thermal pain threshold analyzer (PL-200, Chengdu Taimeng Science and Technology, Co., Ltd.). The surface temperature of the hot plate is maintained at 53±2℃. The rats were placed on the surface of the hot plate surrounded by a clear Perspex cylinder(20 cm diameter, 27 cm height). When the rat licked the hind paw, the timer was stopped immediately.The time displayed on screen is the TPT. In order to avoid tissue damage, the hot plate test time of rats should not exceed 60 s[2]. Three times of continuous measurement were performed at intervals of 5 minutes, and the average of the three incubation periods was determined as the TPT.
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Tissue processing
Rats were placed in prone position after anesthesia. Along the midline of the back, the skin was cut from the sacrum. The T8-L6 vertebral bodies were quickly cut with scissors. 10 ml of ice saline was quickly ejected from the vertebral column with a syringe. The entire spinal cord was flushed out and the L1-L6 portion (100-120 mg) was cut off with scissors. Samples were then placed in liquid nitrogen and then placed in a freezer at –80℃.
Quantitive determination of spinal PGE2
According to the reference[5], after the spinal cord samples were taken out, the same size of samples was cut out and placed into EP tubes. Each sample was added with an equal volume precooled RIPA protein lysate (Applygen Technologies Inc., Beijing, China), ground by an ultrasonic crusher (VCX-130 PB, Sonics & Materials,Inc., Danbury, CT,USA), and centrifuged at 4℃,15000 rpm for 15 minutes (ST16R, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The concentration of proteins was tested by BCA protein quantitative kit (Applygen Technologies Inc., Beijing, China).The concentration of prostaglandin E2 in rat spinal cord was determined by ELISA (Abcam company,Cambridge, UK, ab 133021), and the concentration was determined by multi-wavelength microplate reader (Infinity M1000, Tecan Trading AG,Männedorf, Switzerland, wavelength=570 nm).
Statistics
SPSS 20.0 statistical software (IBM Corporation, Armonk, New York, USA) was used to analyze the experiment data. All data were expressed as mean± standard deviation (SD). Oneway analysis of variance was used between different groups. If there was a homogeneity of variance, it was followed by the Least Significance Difference(LSD). If the variance was not uniform, nonparametric test was used.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Behavioral Observation
Rats in each group weren't irritable after operation. They didn't show pain related behaviors,such as biting the limbs, shaking tails, raising hind legs, licking their hind paws, reducing appetite, and so on.
TPT
There was no significant difference in TPT between groups before and 24 hours after operation(P>0.05). Compared with the sham-operation group, the TPT in the model group decreased 41%(P>0.05). Compared with the model group, the TPT increased 56% in EA1 group, 29% in EA2 group and 190% in drug group (P>0.05). Compared with EA1 group, the TPT decreased 17% in EA2 group(P>0.05). (Table 1, Figure 1)
Table 1. Thermal Pain Threshold (±s; n=5)
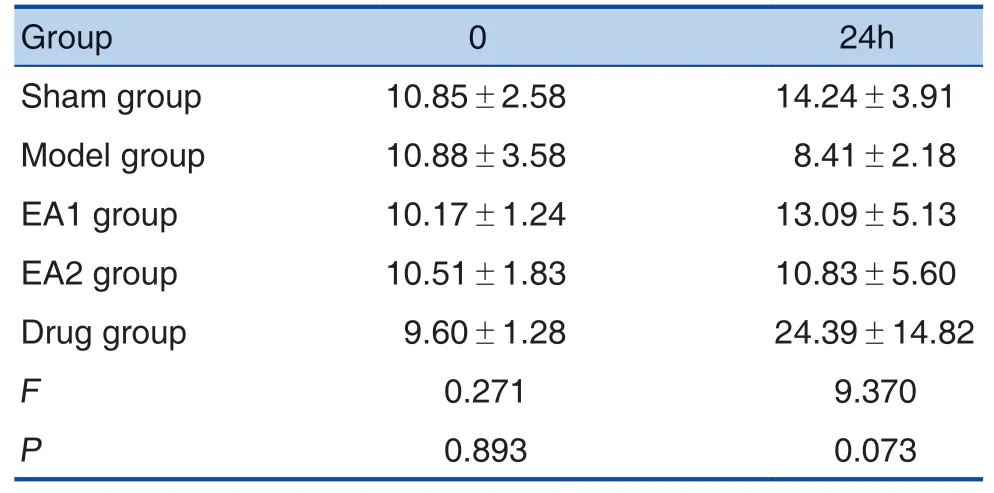
Table 1. Thermal Pain Threshold (±s; n=5)
Note: Sham-operation group: Touching the hind paw with a brush; Model group: a 1 cm longitudinal incision was made at the hind paw; EA1 group: Needling at left GB34 and KI3 for 30 min immediately after plantar incision; EA2 group: Needling at left LI11 and LI4 for 30 immediately after plantar incision; Drug group: Rats were treated with Fenbid by gavage feeding 20 minutes before incision (30 mg/kg, p.o.). The pain threshold was measured before and 24 hours after operation.
?
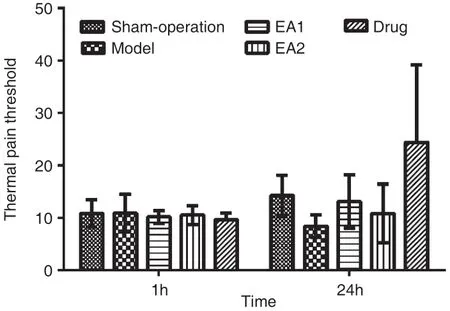
Figure 1. Thermal Pain Threshold
Prostag landin E2
The content of PGE2in spinal cord of rats in each group was detected. ELISA standard curve was made by plotting the absorbance and concentration log of the standard. Regression equation y = –1.758 x+5.1476;R2=0.9645. (Figure 2)
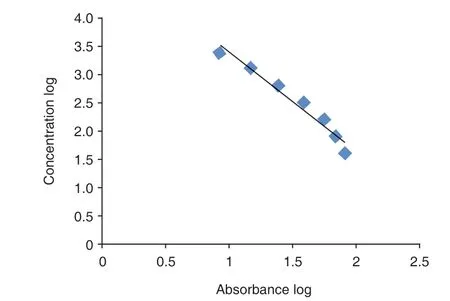
Figu re 2. Standard Cu rve o f Quan tity o f PGE2 in Sp inal Co rd by ELISA
There was no significant difference in PGE2between groups before and 24 hours after operation(P>0.05). At 1h after operation, compared w ith sham operation group (337.07±40.75), PGE2in the model group (387.54±46.08) increased 15%. Com pared w ith model group, PGE2in the drug group (366.85±140.13)decreased 5%. 24 hours after operation, com pared w ith sham operation group (330.00±48.76), PGE2in the m ode l group (360.53±148.58) increased 9%. Com pared w ith model group, PGE2decreased 4% in EA1 g r oup (345.93±96.66), 8% in d rug group (331.78±57.61), increased 3% in EA2 group(369.83±100.19). (Table 2, Figure 3)

Table2.PGE2 Content oftheSpinal Cord After the Operation (pg/100 ug;±s; n=5)
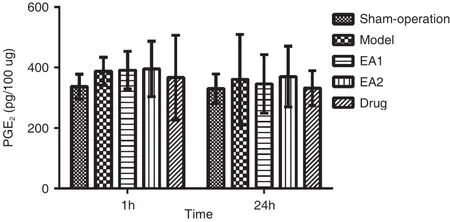
Figu re 3. PGE2 Con tent in Sp inal Co rd
DISCUSSION
Acupunc t u r e is a m a jo r inv en t ion o f t he Chinese nation, and also an im portant contribution to m ankind[6]and it rem ains w ide ly used in Asian m ed ica l sys t em s[7]. I t ha s b een s how n t ha t acupuncture is safe and m inimally invasive, w ith very few adverse effects[8]. Acupuncture is arguably the most researched and widely accepted comp lementary m edicine m odality[9]. Postoperative incisional pain is a unique acute pain. It can induce the exaggerated pain states, which disturbs and impact on patients' lives[10].Superfi cia l, l oca l and sharp pain, w hich com es from incision on skin and deep tissue, can lead to postoperative pain[11]. Electroacupuncture is one therapy of traditional Chinese medicine. It combines traditional acupuncture w ith electric machine. A small electric current pass between pairs of acupuncture need les[12]. It is good for p reventing and treating different types of pain, such as postoperative pain[13].Acupuncture has been w idely practiced; however,its m echanism s o f ac tion rem ain unanswe red[14].Most pain specia lists be lieve acupuncture shou ld be considered for managing pain[15]. Not only pain cond iti ons bu t a lso m uscu la r dys f unc ti on and tension and psychosom atic disorders, as well as dysregulation of the lym phatic and immune system s,respond w e l l to acupunc tu re trea tm en t, as has been con f i rm ed by num erous scienti f i c studies[16].After acupuncture treatm ent, back and neck pain,osteoarthritis, headache and shoulder pain were signi f i cantly improved[17]. The acupuncture stimulation of m yofascial trigger points m ight be most effective on chronic neck pain in elderly patients. Acupuncture could then be used as an adjunct to relieve pain,enabling patients to partake in a more rigorous treatment program for their lower back.[18]In addition,acupuncture appeared to be more effective than analgesic injection (at intragluteal site with analgesic or local infiltration with anesthetic) in reducing pain[19].
Acupuncture activates the pain control system in vivo through the peripheral and central nerves system, inhibits the transmission of nociceptive signals at different levels in central nervous system.It is a complex physiological adjustment process.At the same time, many neurotransmitters and neuromodulators participate in the acupuncture analgesia process, such as endogenous opioid peptides, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), norepinephrine(NE), dopamine (DA) and acetylcholine (Ach) and PGE2. Recent studies have investigated that acupoint electrical stimulation reduces acute postoperative pain and impact on daily lives in lumbar spinal surgery patients. Degree and frequency and of pain reduced in patients with EA[20]. EA attenuated post incision pain through opioid receptor activations and daily EA treatments result in analgesic accumulation[21].EA can inhibit the high expression of PGE2in the spinal cord and raised thermal withdrawal latencies on neuropathic pain rat model. Proximal acupoints is better than distal acupoints[5].
The prescription of acupuncture and moxibustion refers to the realization of points according to the decide principle under the guidance of traditional Chinese medicine theories especially meridian theories. Point is the first indispensable condition in acupuncture and moxibustion prescription.According the meridian theory, disease can be treated by stimulating the acupoints where the meridians pass through. There is a famous saying that "Where the meridian passes through, disorders happened at that area can be treated by puncturing the corresponding meridian." Thus, stimulating acupoints has analgesic effect though dredging meridians and harmonizing qi and blood. The timing,duration, and retention of the acupuncture treatment might impact analgesia efficacy.
In this study, we compared the effect of EA on different acupoints with Fenbid in plantar incision pain rat model. The acupoints are GB34, KI3, LI11,LI4. GB34 is acupoint in gallbladder meridian of foot shaoyang. It is located on the leg. One branch of gallbladder meridian connects with liver meridian of foot jueyin, which goes to the plartar. KI3 is acupoint in kidney meridian of foot shaoyin. The kidney meridian travels to the sole of the foot. LI11 and LI4 is acupoints in large intestine meridian of the hand yangming.The large intestine meridian connects with stomach meridian of the foot yangming, which goes to the foot. In conclusion, all acupoints can be used to treat plantar pain, because the meridians of four acupoints go to foot. But the distance of acupoints is different.GB34, KI3 is close to the foot. They can be name as proximal acupoints. LI11, LI4 are far from the foot and can be name as distal acupoints. We want to test the clinical efficacy of different acupoints combination and explore their mechanism of relieving pain.
Prostaglandins are derived from arachidonic acid and a key regulator of nociceptive processing during inflammation[22]. The substance widely exists in the brain and spinal cord of the human body. When the cell is stimulated by some mechanical stimulation or chemical substances, phosthantidase A2 in the cell membrane is activated, phospholipids is hydrolysed and arachidonic acid is released, then productions such as PGE2are generate throughseries of enzymes'function[23]. It can directly activate nociceptors to cause pain. PGE2is a key proinflammatory mediator and plays an important role in inflammatory hyperalgesia.It is synthesized by constitutive cyclooxygenase-1(COX-1) and COX-2 and important in nociceptive processing and sensitization in the spinal cord[24].PGE2works through increasing intracellular CAMP levels, activating PKA pathway and cation channels.In addition, prostaglandins can cause hyperalgesia by increasing the sensitivity of sensory nerve endings to release other inflammatory mediators (Histamine,5-HT, Bradykinin, etc.). It is called pain amplifier and has important clinical significance. At the site of needle insertion acupuncture can also bring upon the release of neuropeptides involved in pain modulation and local vasodilatation, such as calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) and substance P. It has been suggested that manual acupuncture at the site of needling can produce anti-inflammatory effects via adenosine release[25].
In this study, we compared the effects of acupuncture at GB34+KI3 with LI11+LI4 on the pain threshold in the plantar incision pain rat model.The result showed that the thermal pain threshold reduced 24 hours after plantar incision. After needling GB34+KI3, LI11+LI4, pain threshold raised.GB34+KI3 was better than LI11+LI4. The drug had better therapeutic effect than EA. At the same time,PGE2content in spinal cord showed similar tendency.The level of PGE2increased after operation and continued to 24 hours after operation. The level of PGE2at 1h was higher than that at 24h. After needling GB34+KI3, LI11+LI4, the level of PGE2reduced,especially at 24h. GB34+KI3 showed good curative effect in adjusting the spinal level of PGE224h after operative. The drug had better therapeutic effect than GB34+KI3. EA stimulation can reverse hyperalgesia central sensitization by adjusting PGE2in spinal cord.
In modern clinical practice, acupuncture analgesia treatment is generally taken adjacent acupoints. In traditional Chinese medicine, there is a treatment method of "treat the lower to cure the upper diseases and treat the upper to cure the lower diseases". According to this theory, this study innovatively proposes to compare the analgesic effect of GB34 + KI3 and LI11 + LI4. From the conclusion,the author found that at one hour after the operation,the analgesic effect of the two methods is similar,and at 24 hours after operation, the analgesic effect of proximal acupoint selection was better. This also provides a way for clinical practice. When shortterm analgesia is needed, both proximal and distal acupoints can be selected. When long-term analgesia is needed, proximal acupoints should be selected first.
In conclusion, PGE2was involved in the treatment process of electroacupuncture stimulation in plantar incision pain rat model. EA stimulation can reverse hyperalgesia central sensitization by adjusting PGE2in spinal cord.
EA stimulation has a therapeutic effect on postoperative pain. Both GB34+KI3, LI11+LI4 are effective. GB34+KI3 is proximal acupoints.LI11+LI4is distal acupoints. The effect of proximal acupints is better than that of distal acpoints. It suggests that doctors prefer proximal acupoints to distal acupoints in postoperation pain.
However, because the sample number was small and the observation time was limit, the experimental results need to be further confirmed. We wish we can have chance to explore the mechanism of EA in postoperation pain treatment deeply in the future.
CONLUSION
Overall, the results in the current study show that both the drug and the electroacupuncture can adjust the 24-hour heat pain threshold and prostaglandin E2 in spinal cord in rats. The effects of proximal points is better than that of the distal point.Electroacupuncture can treat postoperative pain by regulating prostaglandin E2 in spinal cord.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from National University Students' Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training project (No.201810026036) and a grant from the National Key Basic Research and Development Program "973" Project (No.2007CB512503).
Authors Contributions
JW got student found. JW designed this study under the guide of Dr. XR. XY and JW wrote this study. XY was responsible for elisa experiment. JW,KC, CY, YC, HL did experiment together. NX, MQ helped get samples.
Conflicts of Interests
The authors declare no financial interest or scientific conflicts with regard to the research described in this manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine for funding this study. We would like to thank REN Xiao-xuan, GUO Meng-wei, ZHAO Ya-fang, School of Acupunture-Moxibusion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, for kindly providing research support.
 World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2020年4期
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2020年4期
- World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- A Brief History of the Development of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine
- INSTRUCTION FOR AUTHORS
- A Study to View International Standard Terminology from the English Translation of Terms Related to Tongue Proper in an Original Foreign Work
- Intradermal Acupuncture on the Prevention and Adjuvant Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Systematic Evaluation of Maren Runchang Pill (麻仁润肠丸) in the Treatment of Patients with Senile Constipation
