Macrophage regulation of graft-vs-host disease
Ya-Qun Hong,Bo Wan,Xiao-Fan Li
Ya-Qun Hong,Xiao-Fan Li,Fujian Institute of Hematology,Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory on Hematology,Department of Hematology,Fujian Medical University Union Hospital,Fuzhou 350000,Fujian Province,China
Bo Wan, Faculty of Life Sciences and Medicine,King's College London,London WC1N 3BG,United Kingdom
Xiao-Fan Li, INSERM U1160,Hospital Saint Louis,Université Paris Diderot,Paris 94430,France
Abstract
Key words:Macrophage;Graft-vs-host disease;Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation;Polarization;Cytokine;Regulation
INTRODUCTION
As a therapy to cure hematopoietic malignancy,allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has greatly improved the survival rate of many malignant hematologic diseases.However,graft-vs-host disease(GVHD)can occur after transplantation as a major complication and cause non-relapse mortality principally[1].GVHD is classified into acute GVHD and chronic GVHD.It is not the temporal relationship to transplantation,but clinical features that should be considered to identify acute or chronic GVHD syndromes[2].Three classic target organs of acute GVHD,including skin,gastrointestinal(GI)tract and liver,and eight essential organs of chronic GVHD,including skin,mouth,eyes,GI tract,liver,lung,joint and fascia,and genital tract,are recommended to calculate the score of chronic GVHD based on the global scoring system evaluating targeted organs and general status.GVHD severity is described as mild,moderate,and severe[3,4].
The mechanism of GVHD is not clearly understood.Tissue damage caused by conditioning regimens,chemotherapy,and total body irradiation is essential in GVHD biology[5].Recipient human leukocyte antigen mismatching is a great risk of GVHD[6-8]because it can prime the alloreactive T cell reaction with the help of antigen presenting cells.Alloreactive T cells recognize the recipient as non-self,attack the target organs of recipients,and initiate GVHD[9].Antigen presentation,naive T cell differentiation,evoked cytolytic machinery,and cytokine regulation network establish the process of acute GVHD[10-13].The final effect of these mechanisms in acute GVHD is apoptosis caused by cytolytic effector and cytokine storms from adaptive and innate immune cells,whereas end-organ fibrosis is a prominent feature of chronic GVHD[12].Characteristic chronic GVHD is caused by impaired thymic damage,reaction of pathogenic germinal center(GC)B cells and macrophages,unbalanced T cells differentiation with accumulation of Th17/Tc17 and T follicular helper(Tfh)cells and suppression of T regulatory(Treg)cells,antibody disposition and concomitant cytokine production(e.g.,increased transforming growth factor(TGF)-β,interleukin(IL)-17 from Th17,IL-21 produced by Tfh driving GC B cell formation and antibody secretion)[14,15].Therapies have workedviatargeting T cells or B cells,infusing immune regulatory cells,and using cytokine antagonists[11,16-18].The process of GVHD manifests an aberrant homeostasis of immune response.
Studies have reviewed the mission of many adaptive and innate immune cells,such as B cells,Treg cells,natural killer T cells,dendritic cells,and innate lymphoid cells in GVHD,but the role of macrophages in GVHD has not been reported before[19-23].In this review,we outlined the role of macrophages in GVHD,focusing on the macrophage infiltration,cytokine production,and their interaction with other cells.
FUNCTIONS OF MACROPHAGES IN IMMUNE RESPONSE
Macrophages show great heterogeneity and plasticity that it is able to activate and polarize to different phenotypes through the stimulation of multiple signaling molecules in the same or different microenvironment[24-26].Tissue-resident macrophages participate in many pathologies,such as microglia in neurodegeneration,osteoclasts and macrophages in osteoporosis,cardiac or vasculature macrophages in atherosclerosis,Kupffer cells in liver disease,alveolar macrophages in pulmonary disease and so on[27,28].Macrophages can be categorized as classically activated macrophages with microbicidal activity,wound-healing macrophages with tissue repair function,and regulatory macrophages with anti-inflammatory activity[29].Another traditional classification divides macrophages into M1 macrophages and M2 macrophages[25].Notably,reciprocal switch between M1 macrophages to M2 macrophages can be induced[30].Macrophage-targeted therapies were used in clinical trials,based on macrophage functions,such as self-renewal,phagocytosis,chemotaxis,inflammatory response,pro-tumor response,and therapeutic protein secretion[31,32].
INFILTRATION OF MACROPHAGES CONTRIBUTES TO GVHD
Studies about the relationship between macrophages and GVHD in recent years were summarized and presented in Table 1.We found that macrophage infiltration is an important feature in GVHD pathogenesis.
Macrophage infiltration is a biomarker for GVHD occurrence and development.Both free and clustered macrophages are important in GVHD pathogenesis.In the study by Nissenet al[33],an increased number of macrophages was detected in 11 out of 30 patients.Ten of these eleven patients developed GVHD.A remarkable difference was noted between the 10 out of 14 patients who showed the macrophage pattern before bone marrow transplantation,and there was only one patient among the 19 without GVHD.Also,Terakuraet al[34]indicated that heavier macrophage infiltration is correlated with a higher severity of cutaneous GVHD.Piérardet al[35]also illustrated that biopsies from the liver,gut,and skin of patients with lethal GVHD showed a striking preponderance of CD68+ macrophages in the inflammatory infiltration.These findings showed that macrophage infiltration is positively correlated with the occurrence and development of GVHD.Furthermore,macrophages polarize to different populations and infiltrate in different target organs(Table 1),and the dominant macrophage population in acute GVHD differs from that in chronic or refractory GVHD.
Taken together,macrophage regulation in GVHD can be considered from the following directions,including macrophage polarization,regulation of cytokines and interaction with other cells such as T cells,B cells,and mesenchymal stem cells,and fibrosis.
MACROPHAGE POLARIZATION IN GVHD
As mentioned above,macrophage infiltration contributes to GVHD,but macrophage populations vary in different phases,tissues,and conditions of GVHD.Macrophages infiltrating in acute GVHD tend to be pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages,whereas it is M2 macrophages that are predominant in chronic and refractory acute GVHD.Studies demonstrated that the recruitment of macrophages is one of hallmarks in the initiation of acute GVHD,and a higher ratio of M1 macrophage/M2 macrophage(M1/M2)correlates to a higher incidence of grade 2-4 acute GVHD[36,37].
During acute GVHD pathogenesis,except in immune responses,there is a cytostatic effect to inhibit cellular proliferationviareleasing iron from target cells induced by macrophage-producing nitric oxide(NO)[38].Infiltration of inducible NO synthase(iNOS)positive M1 macrophages was found in oral mucosal acute GVHD[39].It means that M1 macrophage polarization can modulate acute GVHD by producing NO.
Although the association between M1 macrophages and acute GVHD have been reported,Holtanet al[40]observed more CD4+ activated memory T cells and M0 macrophages in onset GI acute GVHD,increased M1 macrophages in onset and steroid-refractory acute GVHD but higher M2 macrophages in steroid-refractory GI acute GVHD.For the diversity between macrophage polarization in acute GVHD and refractory GI acute GVHD,it might be due to the phases and complicated mechanism of steroid-refractory GVHD that refractory GVHD was more associated with thrombotic system[41,42].In addition,as a scavenger receptor,CD163 is mostly expressed on M2 macrophages[43].Nishiwakiet al[44]also demonstrated that CD163 macrophage infiltration was the only predictor for refractory acute GVHD when the number of CD163(+)macrophages,CD8(+)T cells,and CD1a(+)dendritic cells was counted.Meanwhile,a higher plasma soluble CD163 concentration at day 80 is related to the incidence ofde novo-onset chronic GVHD[45].Donor-derived M2 macrophage phenotype contributes to chronic GVHD,not only manifesting CD163+ macrophage population,but also CD11b+ monocyte/macrophages and F4/80+CSF-1R+CD206+iNOS- populations[46-50].Therefore,we could conclude that M1 macrophage polarization is predominant in acute GVHD,while M2 macrophage polarization is dominant in refractory acute GVHD and chronic GVHD.
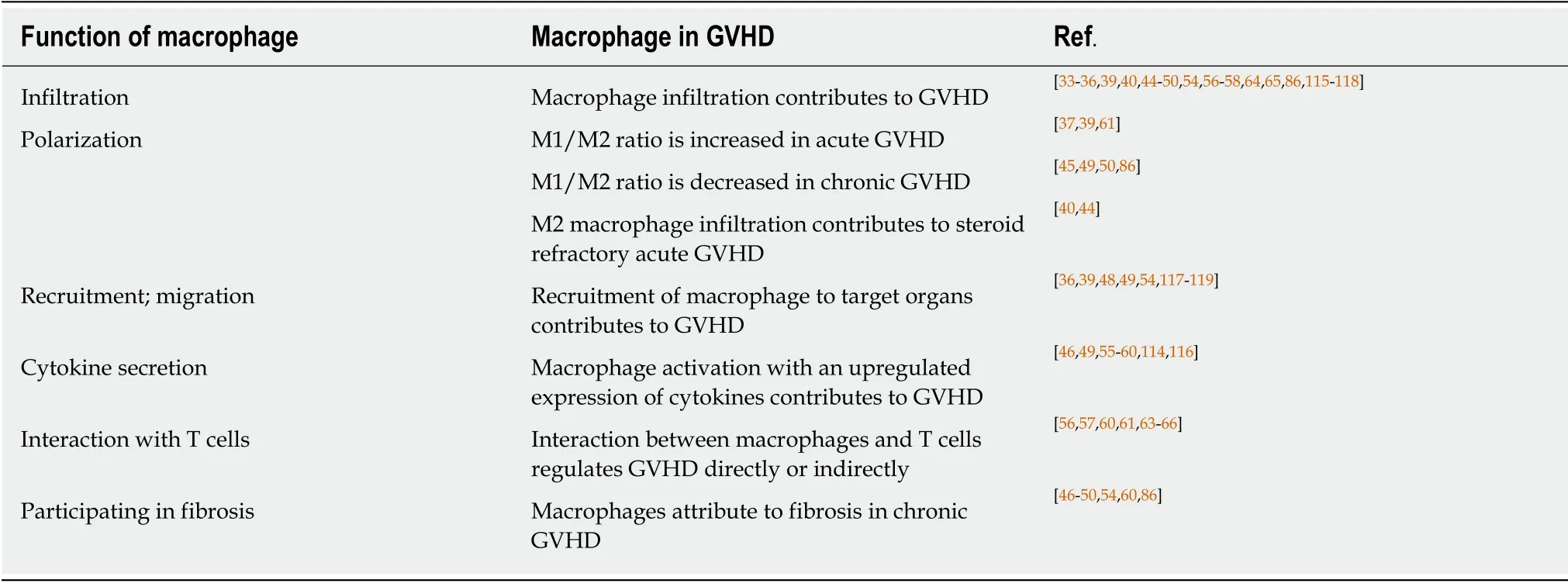
Table 1 Studies about macrophages in graft-vs-host disease
RECRUITMENT OF MACROPHAGES
Chemokines regulate macrophage infiltration in GVHD.On the basis of cysteine residues,four subfamilies of chemokines,including C,CC,CXC,and CX3C are defined,which are able to bind to XCR,CCR,CXCR and CX3CR,respectively,with the ability to regulate recruitment of leukocytes[51,52].CXCL2 is also known as macrophage inflammatory protein-2.CXCL2 played an important role in recruitment of macrophages and T cells to target organs in GVHD,and the severity of GVHD was decreased by blocking CXCL2 and its receptor CXCR2[53].In addition,by binding to CC chemokine receptor 2,monocyte chemoattractant protein(MCP)-1 can also regulate the recruitment of monocytes/macrophages,T cells,and other target cells and engage in the inflammatory response.An accumulation of iNOSpositive M1 macrophages was found in oral mucosal acute GVHDviaboth laminin/CD29 β1 intern and MCP-1/CC chemokine receptor 2 pathways[39].Macrophage migration is mediated by laminin/CD29 β1 intern,meanwhile,macrophage-derived matrix metalloproteinase-2 contributed to basement membrane degradation and activated macrophages interacted with oral epitheliumviathe MCP1/CC chemokine receptor 2 adhesive pathway directly[39].
On the other hand,in chronic GVHD,Duet al[54]indicated that CCL9 showed a biological relevance for chronic GVHD by promoting macrophage infiltration,increasing lung immunoglobulin deposition,and upregulating splenic GC B cells and Tfh cells and the Tfh/T follicular regulatory cells ratio.They also observed that the mouse homolog of human CCL15 was a prognostic and diagnostic biomarker for chronic GVHD in clinical cohorts.In brief,previous studies showed that macrophage recruitment could be regulated by chemokines and results in modulation of GVHD severity.Notably,most chemokines or chemokine inhibitors are not professional,but pleiotropic.
MACROPHAGE-RELATED CYTOKINES IN GVHD
Cytokines secreted by macrophages and receptors play an important role in GVHD.The research of Hyvärinenet al[55]focused on gene expression related to GVHD.They found that genes regulating IL-1β,interferon(IFN)-γ,and IL-6 responses were associated to GVHD;moreover,IL-1,IL-23R,TLR9,TNF,andNOD2genes were associated to the immunological response by monocytes/macrophages that can precede GVHD in intestinal lesions.In other words,macrophages could regulate GVHD by secreting cytokines.Here,we focus on several cytokines.
As shown in Figure 1,TNF-α,IL-12,and IL-6 increased in acute GVHD,whereas TGF-β and IL-6 were upregulated in chronic GVHD[56-58].By analyzing forty-seven consecutive patients,Huesoet al[59]found that IL-10(reflects monocyte-derived macrophage reactivity),citrulline,and myeloablative conditioning are independent factors of acute GVHD development and that IL-10 was increased in acute GVHD.A preponderance of macrophage infiltration with production of TNF-α was observed in acute GVHD[58].Using a human IL-6 transgenic humanized mouse model,Onoet al[60]demonstrated that elevated human IL-12p40,IL-18,M-CSF,and IFN-α2 produced by monocytes/macrophages might facilitate GVHD in chronic GVHD humanized mice.However,most cytokines are not professional but pleiotropic and may present an inverse effect on GVHD in different states.
It is worth noting that macrophages in GVHD can be regulated by cytokines.Th17-production of IL-17 participates in GVHD by modulating the interaction between macrophages and CD4+ T cells.IL-17 can reduce macrophage infiltration,downregulate IL-12 and IFN-γ production,repress Th1 responses,and alleviate acute GVHD[56].Reducing infiltration of macrophages that migrated to MCP-1 and IL-17A and TGF-β production could be therapeutic targets for GVHD[49].Also,M1 macrophage polarization and effector T cell infiltration can be suppressed by expanded Tregs by using IL-33 for acute GVHD[61].IL-33 also has a paradoxical effect because administration of IL-33 after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation aggravated acute GVHD by engaging in the augmentation of donor T cells[62].The opposite effect may be due to the complicated cytokine network,which shows a balance of synergetic and antergic effect.
Notably,viaMHC class II molecules,intestinal epithelium cells could present antigen,activate CD4+ T cells,and initiate lethal gut GVHD,and macrophages could interact with intestinal epithelium cells and regulate MHC class II expression on intestinal epithelium cellsviaIL-12-IFN-γ cytokine axis in addition to the required microbiota[63].Overall,macrophage-produced cytokines participate in interaction between macrophages and other cells,and this role will be described further in the following sections.
INTERACTION BETWEEN MACROPHAGES AND T CELLS
In GVHD pathogenesis,the alloreactive T cell response is essential.It is demonstrated in Table 1 and Figure 1 that infiltration of both T cells and macrophages correlate to GVHD.
T cells,primarily T helper cells,regulate macrophage activation.Using a humanized model andin vitroexperiment,an infiltration of F4/80+ macrophages and human effector memory T helper cells was observed in lymphatic tissues and skin GVHD.Their interaction revealed that macrophages in humanized mice were activated by human T helper 2-type inflammatory cytokines[64].Meanwhile,macrophages influenced the alloreactive T cell response to host antigen.In the study by Haniffaet al[65],persistent recipient dermal CD1a-/CD14+/FXIIIa+ macrophages were detected in GVHD lesions and further showed the ability to influence allogeneic CD8+ T cells on proliferation,secretion of cytokines,and expression of activation antigens.Furthermore,low macrophage infiltration reduced the percentage of Th1 and Tc1 lineages but upregulated the percentages of Th2,Tc2,and Treg lineages that can suppress effector T cell infiltration and eventually alleviate acute GVHD[37,56,60,61].Additionally,chronic lung GVHD is IL-17 and CSF-1/CSF-1R dependent[49].Activated macrophages can induce donor T cells to polarize toward Th17 with an elevation of IL-6,IL-1β,and IL-23.Finally,accumulated IL-17-producing CCR6+/CCR4+ Th17 cells exacerbate lung GVHD[66].This means that macrophages contribute to T cell differentiation and affect the homeostasis of the immune response.Interestingly,host macrophages are opposite to donor macrophage in terms of their interaction with donor T cells(i.e.host macrophages enable the inhibition of donor T cell expansion).Hashimotoet al[67]observed that reduced host macrophage pool can increase donor T cell expansion and aggravate GVHD mortalityviaa CD47-dependent manner,whereas persisting host macrophages can engulf donor allogeneic T cells and inhibit proliferation[67].
Further work to understand the interaction between macrophages and T cells in GVHD models is limited,but complicated interactions between macrophages and T cells have been reported in other models.M1 macrophages can enhance cytolytic and immunomodulatory functions of CD107a+/CD8+ T cells in healthy individuals through a contact-dependent manner with cytokine- and antigen-independent induction[68].In contrast,Liuet al[69]observed that M1 macrophage polarization and macrophage-derived CXCL10 cannot recruit CD4+ and CD8+ T cells,but DCs are recruited,which then promote CD4+ T cells migration.Therefore,macrophages can also regulate T cells indirectly with the help of other immune cells[69].However,macrophage-derived CXCL10 contributed to T cell recruitment.Pettyet al[70]demonstrated that M2 macrophage polarization can mediate immunosuppression through tumor-associated macrophages,which mostly exhibit an M2-like phonotype.These macrophages suppress CD8+ T cell recruitment by inhibiting chemokines of CD8+ T cells produced by macrophages,such as CXCL9 and CXCL10[70].It is noteworthy that cytokine efficacy differs in these two studies may be explained with the different macrophage subsets interacting with T cells.
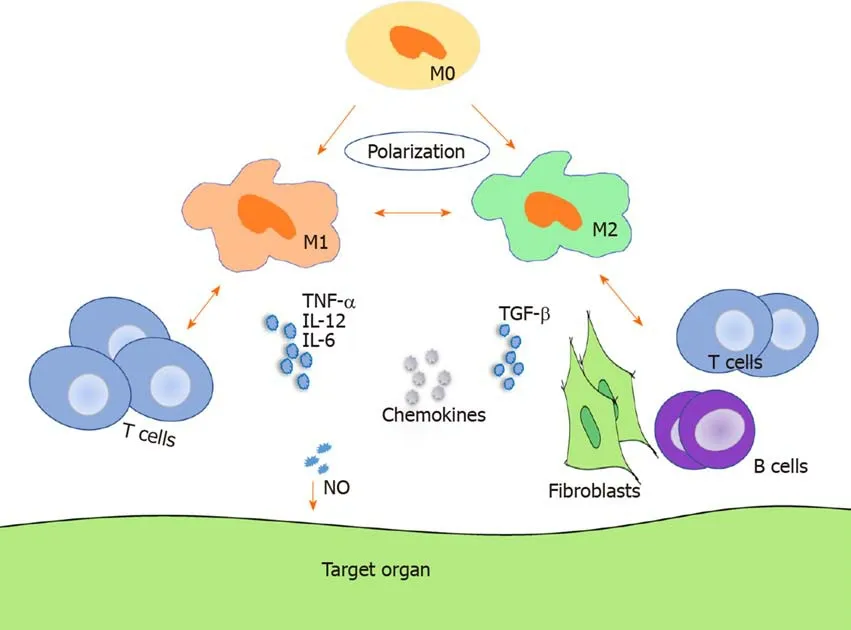
Figure 1 Macrophage regulation of graft-vs-host disease.Macrophages can polarize to M1 macrophages and M2 macrophages and regulate both acute and chronic graft-vs-host disease through migration,cytokine secretion,interaction with T cells in acute graft-vs-host disease,and interaction with T cells,B cells,and fibroblasts in chronic graft-vs-host disease.M0:M0 macrophage;M1:M1 macrophage;M2:M2 macrophage;NO:Nitric oxide.
These results provide a clue that M1 macrophages tend to prime CD8+ T cells in the immune response while M2 macrophages keep the balance by suppressing CD8+ T cells infiltration.Bouchlakaet al[71]also demonstrated that mesenchymal stem celleducated anti-inflammatory immunophenotype macrophages,presenting increased CD206,CD163,IL-6,TGF-β,arginase-1,etcexpression and decreased IL-12 and TNF-α expression,can attenuate GVHD with the help of reduced human T cell proliferation and enhanced fibroblast proliferation[71].Notably,T cells can reciprocally regulate macrophage polarization.T cell Ig mucin-3 on activated T effector cells promotes differentiation of M2 macrophage[72-74].In addition,M2 macrophages may be converted into M1 macrophages and contribute to T cell function.Stimulated by lowdose irradiation,M2-like phonotype macrophages can differentiate towards an iNOS+/M1 phenotype macrophage,produce NO,and promote infiltration of CD3+,CD8+,and CD4+ intratumoral T cells with an increased expression of Th1 cytokines[75,76].But it is still incompletely consistent in the interaction between macrophages and T cells.A study by Woodet al[77]indicated that increased macrophage-derived nitrite production could suppress peritoneal cavity T cells.
Macrophages can interact with T cells and subsequently influence T cell activation and functionviamacrophage polarization,cytokine release,and activating antigen presentation[28,78,79].However,macrophages may promote immunological toleranceviaattenuating effector T cell activation and promoting regulatory T cell differentiation using macrophage-derived complement receptor of immunoglobulin family(an immune checkpoint molecule)[80].Also,granulin derived from macrophages contributes to the exclusion of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells through its resistance to inhibition of immune checkpoints,which may provide new strategies to treat GVHD[81].Notably,binding of the Fcγ-receptor expressed by macrophages to Fc domain glycan of drugs that target alloreactive T cells may be considered for GVHD therapy[82].Other molecules expressed by macrophages can also be alternative targets,such as scavenger receptor MARCO[83].
MACROPHAGES ATTRIBUTE TO FIBROSIS IN CHRONIC GVHD
Autoantibody production,immunoglobulin deposition,and fibrosis are characteristic features of chronic GVHD[84,85].CD4+ T cells,fibroblasts,and B cells interact with macrophages and this interaction plays an important role in chronic GVHD.Reduced infiltration of CD4+ T cells and CD11b+ monocytes/macrophages and suppressed fibroblast proliferation attenuate severity and fibrosis of chronic cutaneous sclerodermatous GVHD[47,48].Duet al[49]also indicated that treatment with pirfenidone can reduce infiltration of macrophages and TGF-β production,impair GC reaction,and inhibit antibody production of B cells and fibrosis,thus attenuating chronic GVHD.In brief,macrophage infiltration,macrophage-production of TGF-β,B cell reactivity,fibroblast proliferation,and CD4+ T cell infiltration contribute to chronic GVHD development.
Another effort to ameliorate fibrosis in chronic GVHD is to use 4-phenylbutyric acid.There are elevated endoplasmic reticulum stress markers in chronic GVHD.Chronic GVHD-elicited endoplasmic reticulum stress in macrophages could be mitigated by administrating 4-phenylbutyric acid,leading to M1 macrophage differentiation and dysfunctional fibroblasts[86].In other words,M2 macrophages and fibroblasts contribute to fibrosis in GVHD.As mentioned before,CCL9 works in chronic GVHD by regulating macrophage infiltration,immunoglobulin deposition,splenic GC B cell reaction,and CD4+ T cell polarization[54].In other words,the alloreactivity and interaction of macrophages,B cells,and T cells are regulated by cytokines.Therefore,we conclude that macrophage infiltration,interactions between macrophages and other cells,and the cytokine network should be considered in chronic GVHD.
Macrophage infiltration has been observed in many fibrotic diseases.Meanwhile,apoptosis and autophagy of macrophages attenuates fibrosis[87-89].Membrane molecules expressed on macrophages and cytokines produced by macrophages participate in this fibrogenesis process.CD14,which is a co-receptor of Toll-like receptor 4 and is expressed on macrophages,may be stimulated by Toll-like receptor exposure and activate macrophages with an induction of TGF-β production,resulting in a profibrotic effectviaa myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent manner in systemic sclerosis[90].Macrophage receptors with collagenous structure containing arginine residues is another scavenger receptor expressed on macrophages,and it can induce the polarization of macrophages to a profibrotic M2 subtype and contribute to fibrosis[91].As for cytokines,increased TGF-β signaling promotes fibrosis[92-94].
Macrophage polarization is another factor that can be modulated to reduce fibrosis.M2 macrophages are infiltrated in fibrosis predominately following TGF-β secretion[95-98].Also,myofibroblasts transited from M2 macrophages could be a source of interstitial fibrosis in chronic allograft rejection[99].Furthermore,macrophages are able to drive fibroblast recruitment and contribute to fibroblast activation,which is also associated with the development of fibrosis[100,101].Macrophage polarization to alternative macrophage subgroups stimulates fibroblasts and attributes to fibrosis.Meanwhile,macrophage polarization to M2 macrophages in fibrosis can be mediated by fibroblasts and cytokines,such as IL-4 and TGF-β1[102,103].Interestingly,the M2c macrophage subset may reduce lung fibrosis by increasing IL-10 levels[104].Regulatory macrophages can inhibit alternative macrophage activation and regulate alternative macrophage-mediated fibrosis[105].Therefore,the balance between M1 macrophages and M2 macrophages and the balance among subgroups of M2 macrophages and regulatory macrophages as well as the dominant effect of the complicated cytokine network should be taken into account in terms of the role of macrophage polarization in fibrosis.
B cell activation regulated by B cell receptor-associated pathways and B cell activating factor plays an important role in the pathology of chronic GVHD[22].Targeting the B cell reaction,especially by blocking some B cell receptor-associated pathways,such as BTK,ITK,and JAK1/2,has been an effective treatment mechanism for chronic GVHD[106].As an important feature of chronic GVHD,the deposition of antibodies from donor B cells augments cutaneous chronic GVHD by damaging the thymus and interacting with CD4+ T cells,especially the pathogenic Th17 and Th2 cells differentiated from Tfh cells[84,107].The deposition of antibodies also plays an important role in fibroblast activity and the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis[108].In chronic GVHD,which is similar to fibrosis disease,macrophages play an important role to regulate B cells.Fantastic reciprocity was found in the relationship between macrophages and B cells.On one hand,CD19-/- donor B cells could augment GVHD severity and fibrosis by increasing splenic IL-6-producing monocyte/macrophage expansion during the early stage of the disease and by increasing TGF-β-producing monocyte/macrophage infiltration in the later stage of chronic sclerodermatous GVHD[46].On the other hand,increased macrophage density is related to antibody mediated rejection[109].Macrophages can modulate antibody production,and macrophage depletion inhibits anti-graft antibody production[110,111].Also,macrophages increase B cell autoantibody production in autoantibody-dependent systemic autoimmune disease[112].Reciprocally,recipient B cells and MHC class II-reactive donor-specific antibodies promote macrophage infiltration[113].Interestingly,macrophage-depletion decreased TGF-β levels and worsened GVHD but increased B cell infiltration,while B cell-depletion led to higher levels of TGF-β and less severe GVHD,especially liver fibrosis[114].A potential explanation is that depleting macrophages can lead to the misbalance of homeostasis in the immune response,whereas the regulation of B cells,which are primary actors,lead to direct and explicit results.
CONCLUSION
Despite advances in GVHD pathogenesis and therapy,GVHD is still a threat to limit administration of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Essentially,it is immune cell responses that contribute to GVHD.Macrophage infiltration correlates to GVHD occurrence and development with a functional regulation of macrophage polarization,production of cytokines,and interaction with other cells.Therapies targeting macrophages to regulate macrophage infiltration have been reported.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年10期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年10期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- French Spine Surgery Society guidelines for management of spinal surgeries during COVID-19 pandemic
- Prophylactic and therapeutic roles of oleanolic acid and its derivatives in several diseases
- Antiphospholipid syndrome and its role in pediatric cerebrovascular diseases:A literature review
- Remotely monitored telerehabilitation for cardiac patients:A review of the current situation
- Keystone design perforator island flap in facial defect reconstruction
- Cross electro-nape-acupuncture ameliorates cerebral hemorrhageinduced brain damage by inhibiting necroptosis
