标准化早期活动方案减少SICU机械通气危重症患者术后谵妄的意义
刘莹
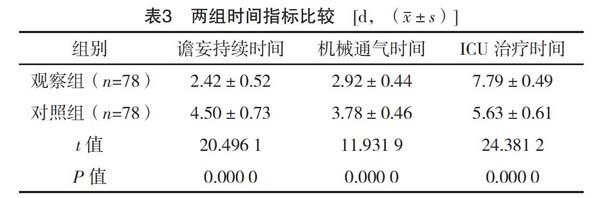
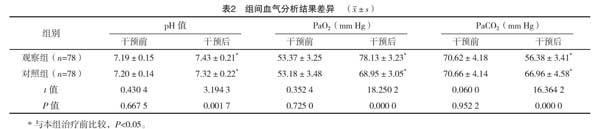
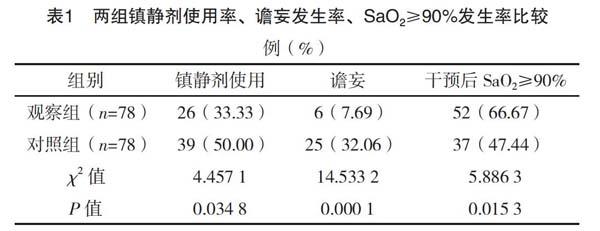
【摘要】 目的:分析标准化早期活动方案减少SICU机械通气危重症患者術后谵妄的意义。方法:择取2017年4月-2019年2月在笔者所在医院就诊的SICU机械通气危重症患者156例,经随机原则分成对照组(78例)及观察组(78例),对照组采取常规护理方案,观察组采用常规护理方案联合标准化早期活动方案,分析组间护理效果差异。结果:干预后,观察组APACHE Ⅱ评分低于对照组,各项时间指标均短于对照组,血气分析指标优于对照组,镇静剂使用率、谵妄发生率均低于对照组,干预后SaO2≥90%发生率高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:在SICU机械通气危重症患者护理方案中加入标准化早期活动方案,能够获得良好的临床效果。
【关键词】 标准化早期活动方案 SICU 机械通气 危重症 术后谵妄
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2020.21.035 文献标识码 B 文章编号 1674-6805(2020)21-00-03
The Significance of Standardized Early Activity Program in Reducing Postoperative Delirium in Critical Patients with SICU Mechanical Ventilation/LIU Ying. //Chinese and Foreign Medical Research, 2020, 18(21): -87
[Abstract] Objective: To analyze the significance of standardized early activity program in reducing postoperative delirium in patients with severe mechanical ventilation of SICU. Method: A total of 156 SICU patients with severe mechanical ventilation from April 2017 to February 2019 in our hospital were selected, and were randomly divided into the control group (78 cases) and the observation group (78 cases). The control group adopted the routine nursing program, and the observation group adopted the routine program combined with the standardized early activity program. The difference of nursing effect between groups was analyzed. Result: After the intervention, the APACHE Ⅱ score in the observation group was lower than that in the control group, all the time indicators were shorter than those in the control group, the blood gas analysis index was better than that in the control group, the sedative utilization rate and incidence of delirium were lower than those in the control group, the incidence of SaO2≥90% after intervention was higher than that in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Adding standardized early activity program into the nursing program of SICU patients with critical mechanical ventilation can obtain good clinical effect.
[Key words] Standardized early activity program SICU Mechanical ventilation Critical illness Postoperative delirium
First-authors address: Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, China
机械通气广泛应用于危重症患者的治疗中,而此类人群多长期处于应急状况,术后谵妄风险较高,而术后谵妄以注意力下降、意识障碍、思维混乱、与病情波动性变化关系密切等有关,故需引起足够的重视[1]。影响接受外科手术治疗的危重症患者术后发生谵妄的因素较多,在治疗过程中采用积极有效的护理方案,有助于提升治疗效果,降低术后谵妄发生风险[2-3]。本次研究以2017年4月-2019年2月在笔者所在医院就诊的SICU机械通气危重症患者156例为研究对象,分析随机分组后分别予以不同护理方案的护理效果差异,现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
参考文献
[1]冯海丽,廖春燕,陈世娟,等.SICU术后谵妄的发生及管理现状[J].护理研究,2018,32(16):2502-2504.
[2]杨富,方芳,陈兰,等.早期渐进式康复方案对SICU机械通气患者术后康复的影响[J].护士进修杂志,2019,34(16):1502-1505.
[3]周利华,张玲,李玉妹.集束化护理对老年术后谵妄的预防作用[J].老年医学与保健,2017,23(2):139-141.
[4]李京连,冯雅笛,姚菲,等.颅脑肿瘤术后ICU患者亚谵妄发生情况及影响因素研究[J].中华现代护理杂志,2019,25(30):3854-3858.
[5] Shaili K P,Samir M K,Dipesh D D.Audit of postoperative surgical intensive care unit admissions[J].Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine,2018,22(1):10-15.
[6]田惠,潘世香,徐向朋,等.ICU患者谵妄发生状况与影响因素分析[J].护理实践与研究,2019,16(20):11-13.
[7]成晶,席明霞,周朝阳,等.eCASH策略预防ICU机械通气患者谵妄效果评价[J].护理学杂志,2019,34(20):27-30.
[8]王爽,惠智艳,袁清霞.预防ICU谵妄的临床研究进展[J].医学综述,2017,23(13):2596-2600.
[9]蓝萍,王辉,周喜良,等.重症监护室患者谵妄评估现状观察及其影响因素分析[J].实用预防医学,2019,26(6):713-714.
[10]陈巧玲,赵慧玲,邱文抒,等.SICU重症患者身体功能和活動能力调查分析[J].护理学杂志,2019,34(7):12-15.
[11]郭慧琦,沈蕴之,蒋红,等.基于最佳证据的危重症患者ICU谵妄三级护理管理[J].护理学杂志,2018,33(18):25-28.
[12]苏丽静,颜艺鹭,黄文娟,等.心脏术后ICU患者谵妄危险因素分析[J].中华危重病急救医学,2019,31(2):165-171.
[13]陈有玺.急诊重症患者谵妄发生的临床因素评估及预防性护理[J].实用临床医药杂志,2018,22(2):22-24.
(收稿日期:2020-03-06) (本文编辑:马竹君)

