An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic community structure and biodiversity in the Bohai Sea
ZHU Haoran,YU Yang,LIU Xianbin
Tianjin Marine Environmental Protection and Restoration Technology Engineering Researching Center,Tianjin University of Science&Technology,Tianjin 300457,China
Abstract:Due to the further intense human urbanization and industrialization,the environmental problems and climate changes became global issues that we have to face today.Like increasing environmental pollutants,ocean eutrophication,red-tide and acidification are causing irrevocably damages to the marine ecological environment.As an important part of marine ecosystem,macrobenthos plays an essential role in energy flow and substance circulation in the marine ecosystem.Therefore,the study of macrobenthic community structures and diversities were necessary,meanwhile the protection of macrobenthic diversity was also a tough problem.In recent years,many researches were mainly focus on Jiaozhou Bay of the Yellow Sea,the Yangtze Estuary,the coastal of Zhejiang and Fujian Provinces,while seldom on benthic organisms in the Bohai Sea.In this paper,the community structures and diversities of the common macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea were introduced and the macrobenthic response to environmental changes and environmental pollution caused by the construction of the Bohai Sea were also mentioned.The results showed that the large benthic fauna in th Bohai Sea was relatively simple compared to other China seas.There were about 400 species of large benthic organisms.The dominant species were low temperature and wide salt warm water.In the last five years,the annual average biomass was 23.82 g/m2 and the annual average density was 1 498 ind/m2.The seasonal variation of average habitat density was usually summer autumn spring winter,and the average biomass was usually autumn spring summer winter.Original communities were destroyed and the dominant species appeared to be miniaturized caused by abuse of marine resources.Since the 21st century,the number of crustacean arthropods,bivalve molluscs,and echinoderms have decreased rapidly,but the number of polychaetes and small molluscs increased gradually.With the development of the comprehensive ecological management of the Bohai Sea,the ecological environment and habitat status in the studied area were remedied and improved.Afterwards,the trend of miniaturization was also suppressed.The results of this study presented some existed problems about marine ecological survey and provided some reasonable suggestions for the rational utilization and protection of marine resources.
Keywords:Bohai Sea,macrobenthos,communication,biodiversity,miniaturization
1 Introduction
Bohai Sea is the largest semi-closed inland sea in China[1].It is a typical shallow shelf sea in the temperate waters of the North Pacific Ocean.Located between 37°7′-41°00′N and 117°35′-121°10′E,the area of the Bohai Sea is about 7.7×104km2,with an average water depth of 18 m and a maximum depth of 70 m[2].Surrounded by land on three sides,it is a semi-enclosed warm temperate inner sea.Due to the intrusion of the Liaohe River,the Weihe River,the Haihe River and the Yellow River into the Bohai Sea,the seabed topography is gentle,the water exchange capacity and the self-purification ability of the sea water are weak[3].
Land reclamation is an effective method to solve the contradiction between man and land.The large-scale reclamation project along the Bohai Sea has destroyed the marine environmental resources[4],causing the degradation of ecological environment in the Bohai Sea[5].How to properly and sustainably develop and utilize marine resources has becoming more and more important.So the investigation of the background value of marine resources is required.Marine benthos is the most diverse species of marine life with the most complex ecological relationships.The material circulation and energy flow inside the system play an important role[6].
Marine benthics refer to animals that inhabit in the sediments or on the surface of the sediments.These animals live from the intertidal zone to the oceanic abyss zone with a depth of more than 10 000 meters,including mainly of mollusks,crustaceans,echinoderms,polychaetes and aquatic insects and their larvae[7].The biomass of macrobenthos accounts for more than 90%of benthic animals[8].Because of its special way of life,it is involved in the water environment through burrowing,feeding and exercise.And this way of life affects the stability,migration and transformation of pollutants in the sediment[9,10].
Individuals who will not pass through a 0.5 mm aperture mesh are generally referred to as macrobenthos[11].Because of their large size,large-scale benthic animals are abundant and easy to be collected.Most adults species always inhabit the sediment or move within a limited range of the substrate surface.They are sensitive to pollutants and enriched with some pollutants[12].Their capability to escape the bad changes in the habitat is relatively slow[13],thus the changes of the sea environment can be reflected through the changes in the community structures of benthic animals.Therefore,the biological survey of macrobenthos can be a macroscopic reflection of the ecological environment.
The Bohai Sea is one of the important fishing areas in China,and its fishery resources are abundant[14].As an important food source of many commercial fishery species,benthic animals play an important role in the whole marine ecosystem.Domestic and foreign scholars have conducted monitoring and investigation of the Bohai Sea for a long time,accumulated a large number of animal samples and data,and also published a large number of research results.This paper has collected previous useful data on the diversity and community structure of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea in the past 15 years,and puts forward the existing problems and suggestions for the investigation of macrobenthos in China.At the same time,some suggestions on the comprehensive exploitation and utilization of marine resources and the protection of biodiversity are put forward.
2 Characteristics and diversity of macrobenthos community in Bohai Sea
A large number of studies have shown that there are more than 400 species of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea of China[6].Compared with the Yellow Sea,the East China Sea and the South China Sea,the number of benthic species is relatively small,and the fauna is relatively simple,many mollusks can be used as natural bait for swimming animals.Most mollusks are also commercial fishery resources,and some such asCapitella capitata,sea otters(Thalassodrilidessp.)andNereis virens,can be used as an indicator of certain specific pollutants[15],responding to the ecological environment health status.
Conventional studies of macrobenthos community usually include species composition,habitat density,biomass,biodiversity[16,17].Biodiversity is usually assessed by the Margalef Index,the Shannon-Wiener Index,Pielou Index,and the Dominance Index.Through the community structure and diversity of macrobenthos[18]is a common method to assess environment quality.This paper collects data on macrobenthos surveys in the Bohai Sea from 1998 to 2018,including biomass,habitat density,Margalef Index,Shannon-Wiener Index,and Pielou Index(Fig.1 and Fig.2).The main changes in species composition and dominant species of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea in the past 15 years were showed in Fig.3.Through the comparative analysis,the differences in community structure and diversity of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea and other seas in China(Tab.1).
2.1 Changes in biomass and habitat density
The macrobenthic biomass in the Bohai Sea has changed in the range of 8.30 g/m2to 52.52 g/m2in the past 15 years,with an average of 28.59 g/m2,which gradually decreased from about 44.47 g/m2in 1998 to the lowest level 11.78 g/m2in 2008.The biomass of the Bohai Sea began to rise from 2008 and reached 30.77 g/m2in 2014,and then it has basically recovered to the 1998 level.The biomass change in the Bohai Sea is[1,2]the Laizhou Bay in the Bohai Bay,Liaodong Bay.The biomass of the Bohai Sea is slightly higher than that of the Yellow Sea,while lower than that of the East China Sea and the South China Sea,only 6.59%of the East China Sea and 28.01%of the South China Sea.

Tab.1 Ecological survey data of the Bohai Sea and other areas in China
The habitat density of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea area varied from 228.8 ind/m2to 2 668.1 ind/m2in the past 15 years,with an average of 1 111.91 ind/m2,which fluctuated above the average.The habitat density in the Bohai Sea presents a distribution of Laizhou BayBohai Bay Liaodong Bay.The habitat density of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea is higher than that in other sea areas of China.
2.2 Diversity changes
2.2.1 Margalef index(d)
The Margalef index of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea region varies from 0.91 to 10.84 in recent 15 years,with an average of 4.66.During the past 15 years,the Bohai Sea macrobenthos Margalef Index decreased from 7.49 in 1998 to a minimum of 1.71 in 2007.Since 2007,it has risen year by year.In 2012,it reached the highest value of 10.84 and then stabilized at around 2.5.The Margalef Index in Bohai Sea is relatively flat compared with the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea,and because of the data of the macrobenthic Margalef Index was deficient in the South China Sea,it cannot be compared(Fig.2A).
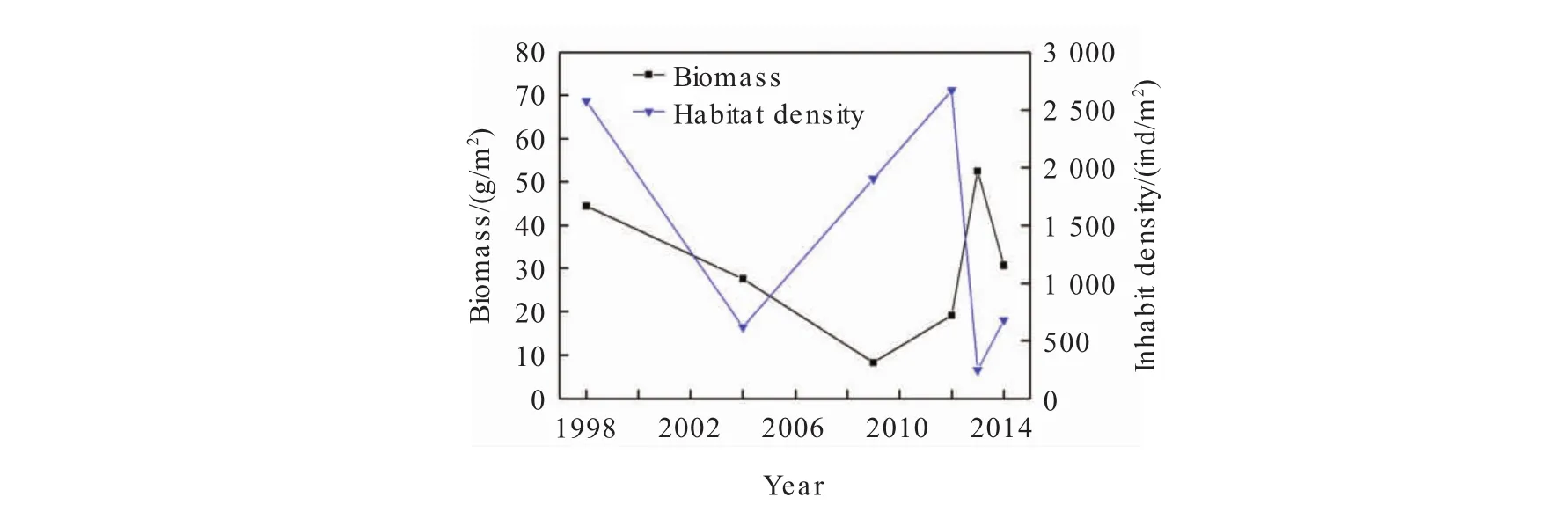
Fig.1 Biomass and habitat density of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea for nearly 15 years
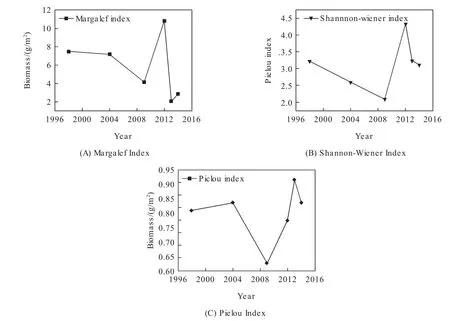
Fig.2 Macrobenthos diversity in the Bohai Sea area for nearly 15 years
2.2.2 Shannon-Wiener Index(H’)
The Shannon-Wiener Diversity Index in the Bohai Sea is range from 1.15 to 4.34 within 15 years,with an average of 2.84.The trend of Shannon-Wiener Index is similar to biomass and Margalef Richness Index during the 15 years,and have been reduced from 1998 to 2007,with the lowest value of 1.15.In 2009,it began to increase to a maximum of 4.34 in 2012.After 2012,it gradually stabilized at around 3.18.The Shannon-Wiener Diversity Index of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea is lower than that in other sea areas in China.In recent years,it has almost reached the level of the East China Sea and the South China Sea,in 2007 and it was slightly lower than the Yellow Sea in 2009(Fig.2B).
2.2.3 Pielou index(J)
The Pielou Evenness Index of the Bohai Sea varies from 0.58 to 0.91 in 15 years,with an average value of 0.80.There was no significant regular change in the past 15 years,and it normally fluctuated around the average of 0.80(Fig.2C).
2.3 Species composition and dominant species changes
Comparing the historical data of macrobenthic surveys in the Bohai Sea,it can be seen that the structure of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea has undergone tremendous changes in the past 15 years.Compared with the 1990s,the larger crustacean arthropods and bivalve mollusks were gradually replaced by smaller polychaetes,crustaceans and mollusks since 21st century,showing a trend of miniaturization in the Bohai Sea(Fig.3).
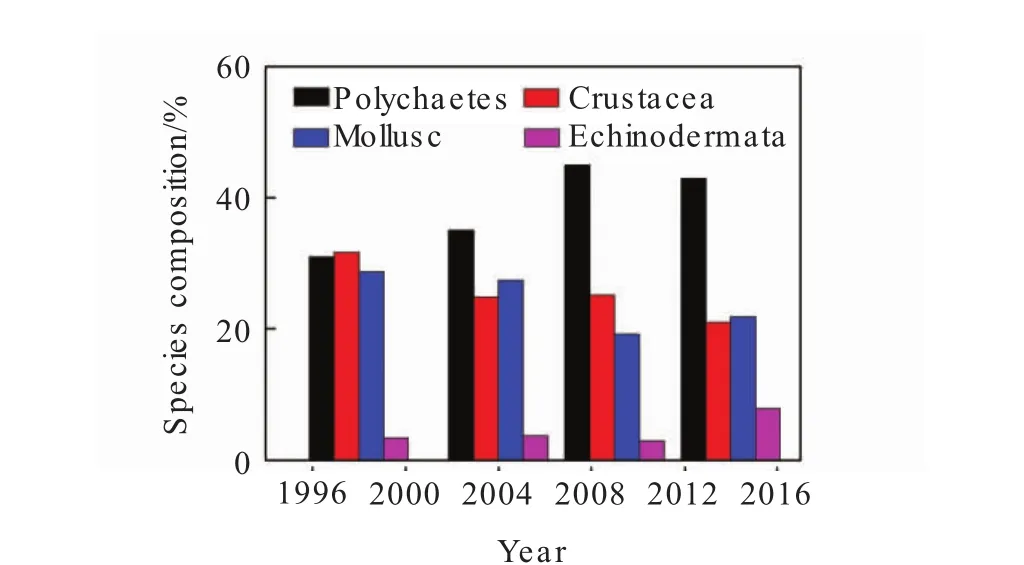
Fig.3 Species composition and dominant species of macrobenthos in Bohai Sea for nearly 15 years.
In the past 15 years from 1998 to 2014,based on the changes in species composition and dominant species in historical data,the number of macrobenthos species in the Bohai Sea remained basically unchanged,but the community structure has undergone tremendous changes.Mcrobenthic animals tend to be miniaturized,and the number of large crustaceans,bivalve molluscs,and echinoderms reduced sharply.The proportion of species with relatively small hairy species is increasing,with a range of 31%to 45%.The proportion of crustacean arthropods and bivalve molluscs with relatively large body species decreased ranging from 31.7%to 21%and 28.8%to 19.2%,respectively.The reason is closely related to coastal land-based pollutants discharged,population surged,reclamation and large-scale aquaculture.The violent external human disturbances caused enormous changes in the macrobenthic habitat,destroyed the homeostasis of the original ecosystem,and changed the original structure.Some bigger macrobenthic animals with higher trophic levels died rapidly before benthic animals begin a new succession process.In the succession process,the small and lower trophic macrobenthic will firstly begin to succeed,so there will be a period of time of miniaturization in the Bohai Sea.
Since the 18thNational Congress of the Communist Party of China,the ecological environment has been raised to the national consciousness,and the comprehensive management of the Bohai Sea aimed at the restoration of the ecological environment has led to the banning of destructive activities in recent years especially reclamation.The marine environment has gradually become steady,and the new community structure succession has been gradually completed.The miniaturization trend of macrobenthos in the whole Bohai Sea area will be controlled.
3 Existing problems and suggestions for the survey of large benthic animals in the Bohai Sea
The relative deficient biological resources e and the simpler macrobenthic fauna are the partial reason that the researches in the Bohai Sea is less than other sea.From the existing data,the current investigation of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea is still short-term,not systematic and comprehensive.Repeated sites may occur in various departments and institutes,while many areas have no survey stations.In the analysis of survey data,different institutes have different purposes;the standards and profundity of data mining are also different.The data can not be shared in domestic institutes.All of them caused the waste of existing data resources.
The existed investigations and studies normally focused on the community structure and diversity of macrobenthos.Therefore,it is possible to establish a public database and data sharing platform by integrating the survey data of various institutions,then predicted the variation regularity and trend of benthic fauna in the Bohai Sea.At the same time,a numerical model can be established by integrating existing data,which can assess the marine ecological environment changes.If all the data is collected into a database for sharing data resources,the limited data can play a greater role and avoid the waste of data resources.After the samples collected and analyzed by the laboratory can be shared the data of different time and voyages in the same sea area on the platform,so that the value of the data resources can be maximized,which can also increase the scientific quality of research.
4 Protection of macrobenthos diversity in the Bohai Sea
As an indicator of the productivity of a region,biodiversity is one of the important characteristics of natural ecosystem.The protection of biodiversity is of great significance to the sustainable development of the region’s economy and society.Macrobenthos directly determine the health and stability of ecosystems,through affecting the energy flow and material circulation.Therefore,in the process of ecological restoration of the Bohai Sea,macrobenthos diversity protection is essential.
Pollution is the direct cause of the rapid death of large benthic animals,therefore,it is necessary to optimize the discharge standards of coastal industrial enterprises and strictly control the total amount of land pollutants discharged into the sea.We should accelerate the construction of marine pastures and ecological protection zones and plant seedlings in specific areas,through manual intervention to accelerate the construction of large benthic community and the restoration of diversity.At the same time,as a result of the specific lifestyle of benthic animals,adding benthic seedlings can speed up the restoration of the ecological environment.In recent years,the coastal provinces in China have generally implemented the policy of resting fishing,scientific and reasonable fishing,actively relieve the pressure of marine ecosystems,and create more conditions for the protection of macrobenthic animal diversity and the restoration of ecological environment.Unreasonable application of antibiotics and nutrients in aquaculture lead to the problems such as water pollution and eutrophication,while the density of culture also affects the diversity of benthic animals.Breeding an economic species that feeds on benthic animals will reduce the number of benthic animals in the cultured area and reduce their diversity[30].
5 Conclusion
Since the 21stcentury,with the rapid development of China's economy and the rapid rise of the Bohai Rim Economic Zone,the coastal ocean environment pressure has increased sharply.A large number of land pollutants have been discharged into the offshore areas,causing a lot of environmental threat such as increasing environmental pollutants,ocean eutrophication,red-tide and acidification.The booming population has also amplified contradiction between people and land,and a large number of reclamation projects have changed the original habitat.The predatory use of marine resources and unscientific aquaculture has also led to the depletion of fisheries resources in the Bohai Sea,and many economic species are almost extinct.The marine environmental problems caused by many factors have changed the community structure of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea,and the biodiversity has decreased sharply.In the past 15 years,the dominant species of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea has become smaller and smaller.However,in recent years,the miniaturization trend has been alleviated thanks to the improvement of the marine environment in the Bohai Sea.
The analysis of the variation of community structure,biodiversity,secondary productivity and other parameters of macrobenthos along with the environment of the Bohai Sea should be more dimensional and comprehensive.Their causes and mechanisms deserve further study.At the same time,it is necessary to coordinate the data of each sampling institutions to establish a data sharing platform,so that the data can be maximized,and the existing data can be used to establish a model to evaluate the ecological environment of the Bohai Sea.Only in this way can we provide a scientific basis for China’s long-term sustainable use of marine resources and the protection of marine biodiversity.
Protect biodiversity is an important part of ecological environment protection.Protect the diversity of macrobenthic in the Bohai Sea by optimizing emissions standards,establishing nature reserves,controlling fishing intensity,and scientific aquaculture is the most effective method.
 Marine Science Bulletin2020年1期
Marine Science Bulletin2020年1期
- Marine Science Bulletin的其它文章
- Research progress of micro(nano)plastics in marine survey in China
- Bibliometric analysis of Ecopath model in different ecosystem in China
- The benthic diatom community of Xiangshan Bay
- Introduction to marine emergency forecasting and early-warning system(MEFES)
- Effect of mangrove forest on coastal hazards reduction
- Estimating shoreline response to sea level rise:the equilibrium model
